Associative Memory Circuit Based on Memristor with The Ebbinghaus Forgetting Rule
-
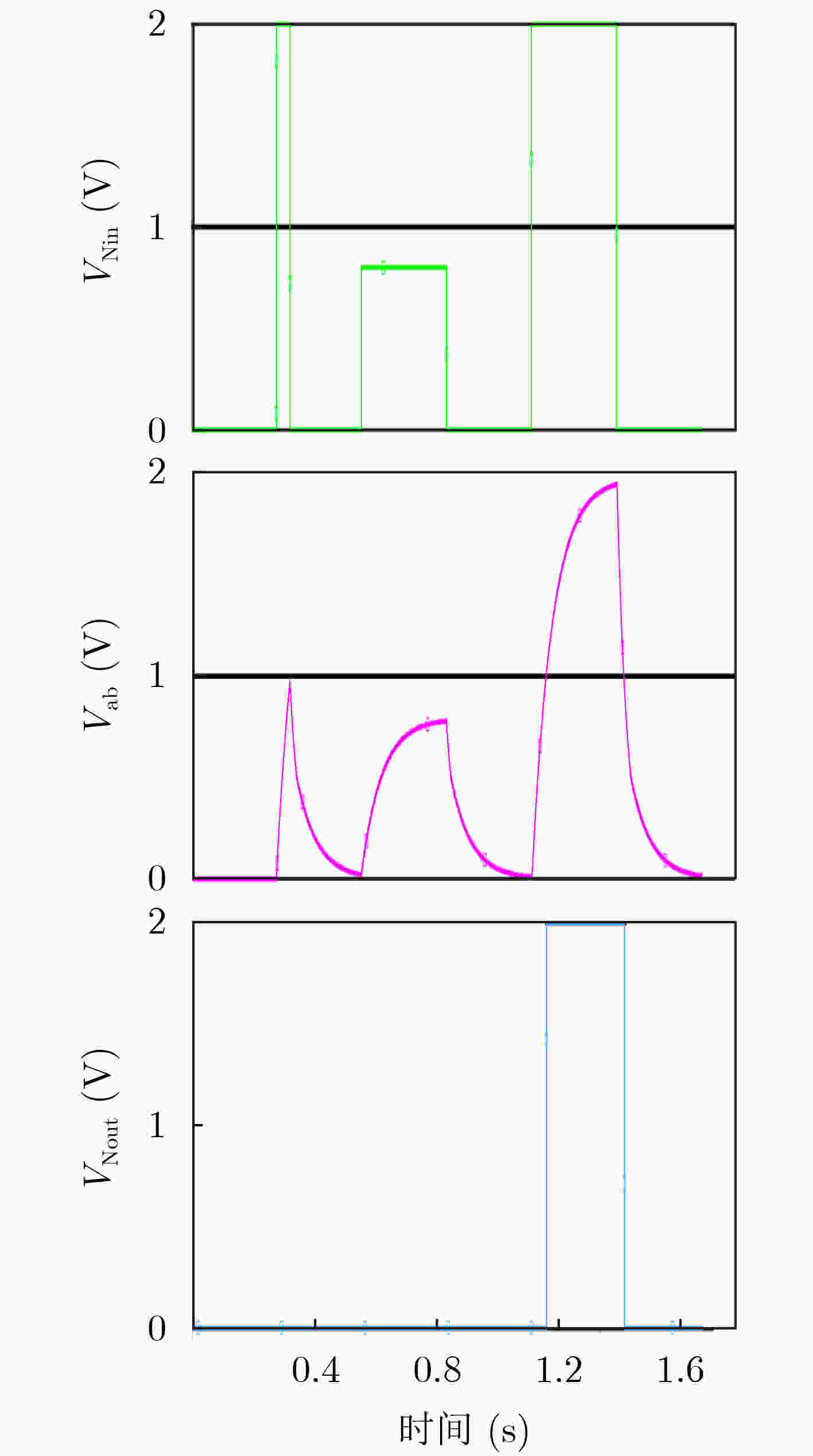
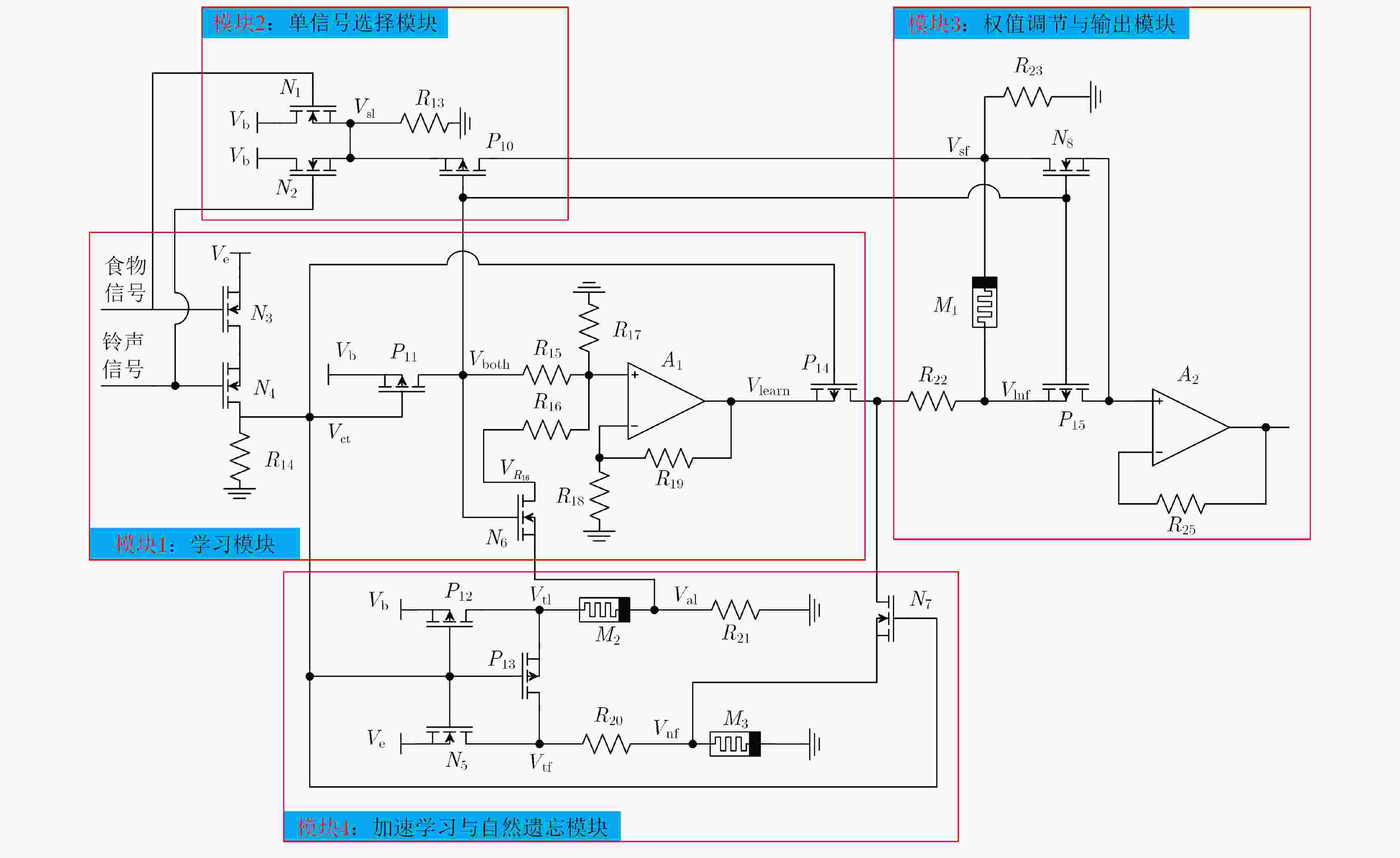
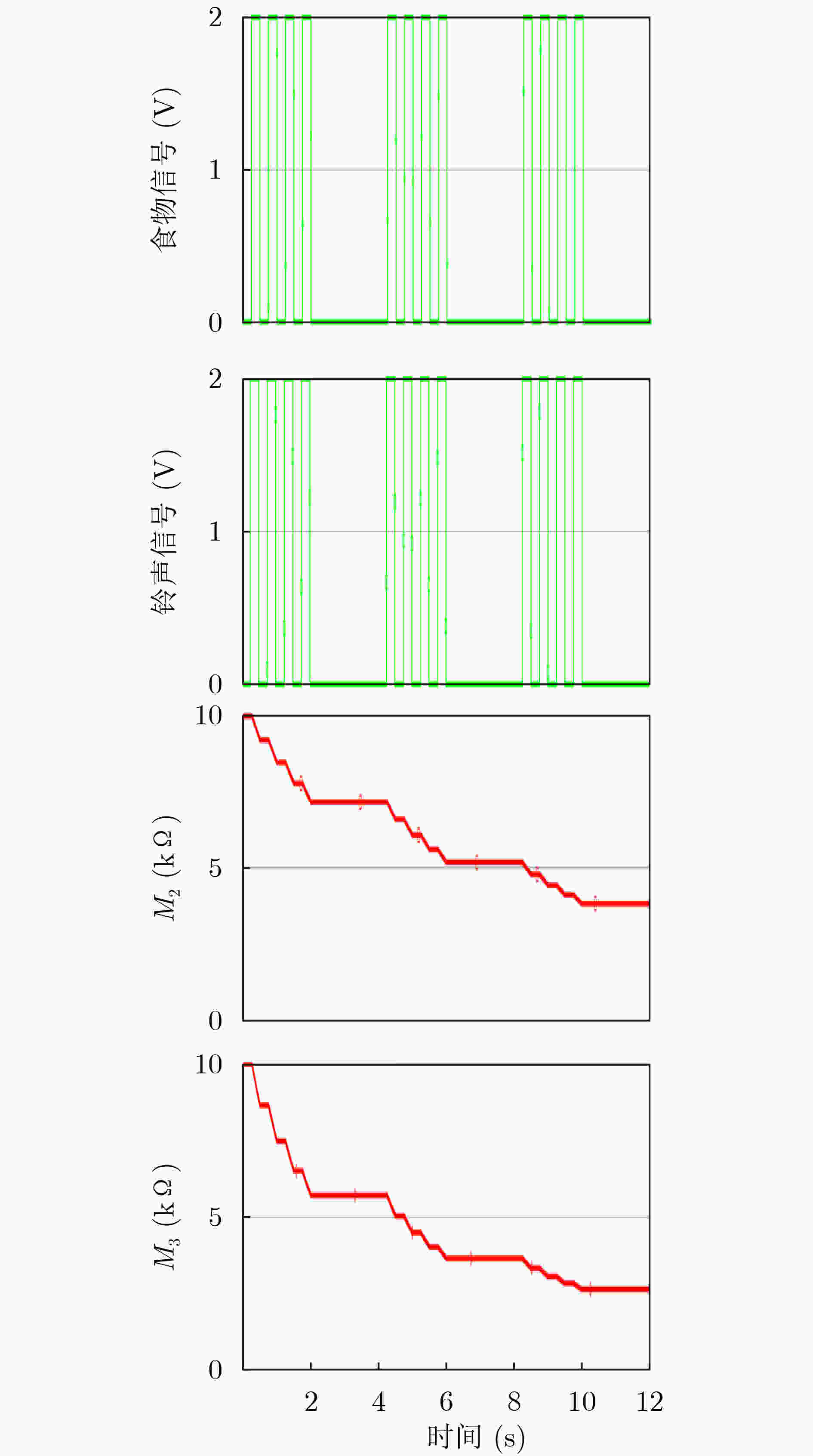
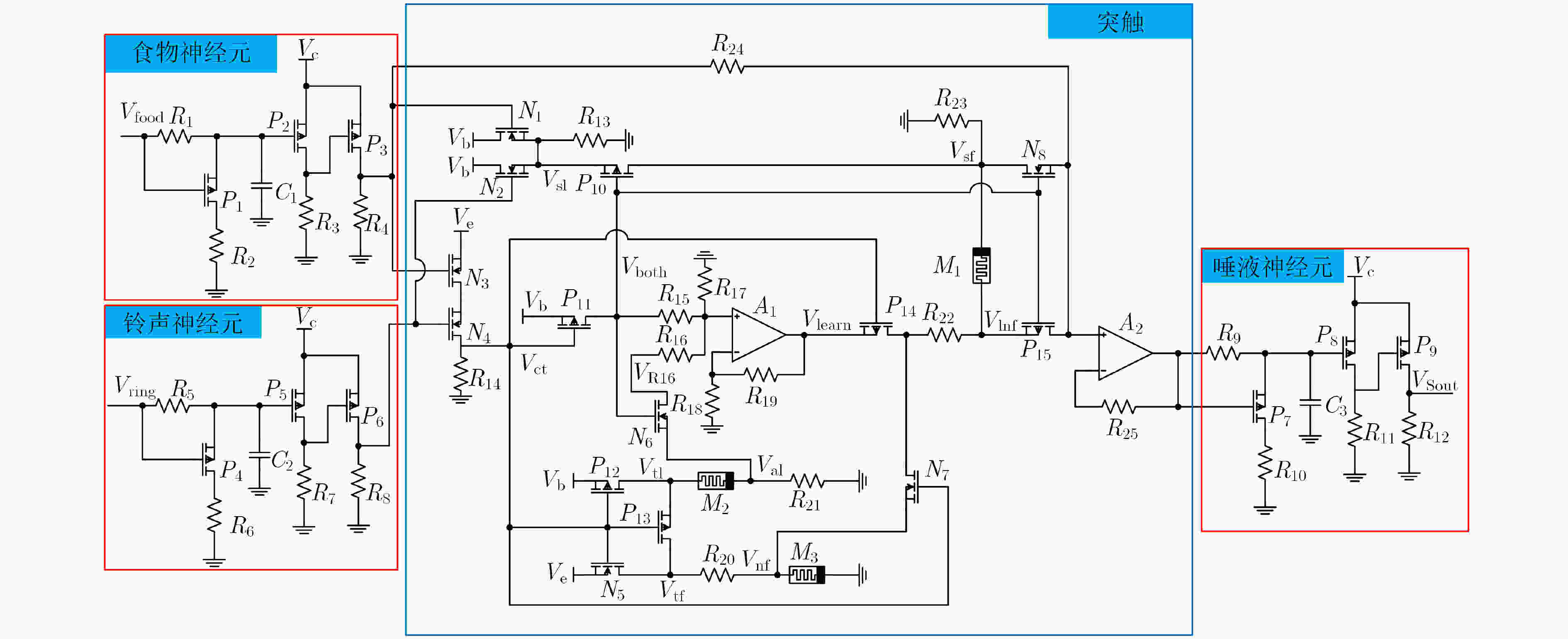
摘要: 忆阻器由于具有低功耗、记忆能力和纳米尺寸等特点,是实现人工神经突触的理想器件。为构建简洁、高效、功能全面地联想记忆电路,该文首先提出一种简单的神经元电路和基于压控阈值忆阻器的突触电路。然后根据巴甫洛夫联想记忆模型,设计了相应的联想记忆电路。电路结构简单,仅包含3个神经元电路和突触电路,可有效降低网络复杂度和功耗。尤为重要的是该电路可以模拟全功能的联想记忆行为,不但实现了学习、遗忘、加速学习、减速遗忘以及减速自然遗忘等功能,而且学习速率和自然遗忘速率能够根据学习的次数自动调整,使电路更具仿生性。此外,该电路与艾宾浩斯遗忘曲线相吻合,扩大了电路的适用范围。Abstract: Memristor is an ideal device to realize artificial synapses due to its low power consumption, memory ability and nanometer size. In order to construct a simple, efficient and comprehensive associative memory circuit, a simple neuron circuit and a synaptic circuit based on the voltage-controlled threshold memristor is proposed. Then according to Pavlov’s associative memory model, the corresponding associative memory circuit is designed. This circuit has a simple structure and only contains three neurons and a memristive synapse, which can effectively reduce the network complexity and power consumption. what’s more, the circuit can simulate the full function of associative memory behavior. It not only realizes functions of learning, forgetting, accelerated-learning, deceleration-forgetting and deceleration-nature-forgetting, but also the learning rate and natural forgetting rate can be automatically adjusted according to the number of learning, so that the circuit is more bionic. In addition, the designed circuit agrees well with the Ebbinghaus forgetting curve, which enlarges the scope of application of the circuit.
-
表 1 联想记忆电路中各忆阻器参数
参数 M1 M2 M3 RON (Ω) 1×103 1×103 1×103 ROFF (Ω) 6×104 1×104 1×104 VT+ (V) 0.5 0.5 0.5 VT– (V) –0.2 –0.5 –0.5 -
[1] WANG Rubin and ZHANG Zhikang. Energy coding in biological neural networks[J]. Cognitive Neurodynamics, 2007, 1(3): 203–212. doi: 10.1007/s11571-007-9015-z [2] DOSSET P, RASSAM P, FERNANDEZ L, et al. Automatic detection of diffusion modes within biological membranes using back-propagation neural network[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2016, 17(1): 197. doi: 10.1186/s12859-016-1064-z [3] MEROLLA P, ARTHUR J, AKOPYAN F, et al. A digital neurosynaptic core using embedded crossbar memory with 45 pJ per spike in 45 nm[C]. 2011 IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC), San Jose, USA, 2011: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/CICC.2011.6055294. [4] LINDSEY C S, LINDBLAD T, SEKHNIAIDZE G, et al. Experience with the IBM ZISC036 neural network chip[J]. International Journal of Modern Physics C, 1995, 6(4): 579–584. doi: 10.1142/S0129183195000460 [5] WANG Zilu, HONG Qinghui, and WANG Xiaoping. Memristive circuit design of emotional generation and evolution based on skin-like sensory processor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, 2019, 13(4): 631–644. doi: 10.1109/TBCAS.2019.2923055 [6] ANDERSON J R. Language, Memory, and Thought[M]. New York: Psychology Press, 1976: 39–40. [7] ZHAO Liang, HONG Qinghui, and WANG Xiaoping. Novel designs of spiking neuron circuit and STDP learning circuit based on memristor[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018, 314: 207–214. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.06.062 [8] CHUA L. Memristor-the missing circuit element[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuit Theory, 1971, 18(5): 507–519. doi: 10.1109/tct.1971.1083337 [9] STRUKOV D B, SNIDER G S, STEWART D R, et al. The missing memristor found[J]. Nature, 2008, 453(7191): 80–83. doi: 10.1038/nature06932 [10] XIE Wenli, WANG Chunhua, and LIN Hairong. A fractional-order multistable locally active memristor and its chaotic system with transient transition, state jump[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2021, 104(4): 4523–4541. doi: 10.1007/s11071-021-06476-2 [11] LIANG Yan, WANG Guangyi, CHEN Guanrong, et al. S-type locally active memristor-based periodic and chaotic oscillators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2020, 67(12): 5139–5152. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2020.3017286 [12] DONG Yujiao, WANG Guangyi, CHEN Guanrong, et al. A bistable nonvolatile locally-active memristor and its complex dynamics[J]. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2020, 84: 105203. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2020.105203 [13] HONG Qinghui, LI Ya, and WANG Xiaoping. Memristive continuous hopfield neural network circuit for image restoration[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2020, 32(12): 8175–8185. doi: 10.1007/s00521-019-04305-7 [14] YANG Linmao and WANG Chunhua. Emotion model of associative memory possessing variable learning rates with time delay[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 460: 117–125. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.07.011 [15] WANG Leimin and ZOU Huayu. A new emotion model of associative memory neural network based on memristor[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 410: 83–92. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.05.002 [16] YANG Jiu, WANG Lidan, WANG Yan, et al. A novel memristive Hopfield neural network with application in associative memory[J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 227: 142–148. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2016.07.065 [17] ALIBART F, ZAMANIDOOST E, and STRUKOV D B. Pattern classification by memristive crossbar circuits using ex situ and in situ training[J]. Nature Communications, 2013, 4(1): 2072. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3072 [18] TRUONG S N and MIN K S. New memristor-based crossbar array architecture with 50-% area reduction and 48-% power saving for matrix-vector multiplication of analog neuromorphic computing[J]. Journal of Semiconductor Technology and Science, 2014, 14(3): 356–363. doi: 10.5573/jsts.2014.14.3.356 [19] PERSHIN Y V and DI VENTRA M. Experimental demonstration of associative memory with memristive neural networks[J]. Neural Networks, 2010, 23(7): 881–886. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2010.05.001 [20] CHEN Ling, LI Chuandong, WANG Xin, et al. Associate learning and correcting in a memristive neural network[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2013, 22(6): 1071–1076. doi: 10.1007/s00521-012-0868-7 [21] WANG Lidan, LI Huifang, DUAN Shukai, et al. Pavlov associative memory in a memristive neural network and its circuit implementation[J]. Neurocomputing, 2016, 171: 23–29. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.05.078 [22] YANG Le, ZENG Zhigang, and WEN Shiping. A full-function pavlov associative memory implementation with memristance changing circuit[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018, 272: 513–519. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.07.020 [23] HU Xiaofang, DUAN Shukai, CHEN Guanrong, et al. Modeling affections with memristor-based associative memory neural networks[J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 223: 129–137. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2016.10.028 [24] SUN Junwei, HAN Gaoyong, ZENG Zhigang, et al. Memristor-based neural network circuit of full-function pavlov associative memory with time delay and variable learning rate[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(7): 2935–2945. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2019.2951520 [25] LI Yi, ZHONG Yingpeng, ZHANG Jinjian, et al. Activity-dependent synaptic plasticity of a chalcogenide electronic synapse for neuromorphic systems[J]. Scientific Reports, 2014, 4(1): 4906. doi: 10.1038/srep04906 [26] LIU Xiaoyang, ZENG Zhigang, and WEN Shiping. Implementation of memristive neural network with full-function pavlov associative memory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2016, 63(9): 1454–1463. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2016.2570819 [27] EBBINGHAUS H. Memory: A contribution to experimental psychology[J]. Annals of Neurosciences, 2013, 20(4): 155–156. doi: 10.5214/ans.0972.7531.200408 [28] ROE D G, KIM S, CHOI Y Y, et al. Biologically plausible artificial synaptic array: Replicating ebbinghaus’ memory curve with selective attention[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(14): 2007782. doi: 10.1002/adma.202007782 [29] WANG Yabo, WANG Guangyi, SHEN Yiran, et al. A memristor neural network using synaptic plasticity and its associative memory[J]. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 2020, 39(7): 3496–3511. doi: 10.1007/s00034-019-01330-8 [30] SHANG Meijia and WANG Xiaoping. A memristor-based circuit design for generalization and differentiation on Pavlov associative memory[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 389: 18–26. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.12.106 [31] MA Deming, WANG Guangyi, HAN Chunyan, et al. A memristive neural network model with associative memory for modeling affections[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 61614–61622. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2875433 -





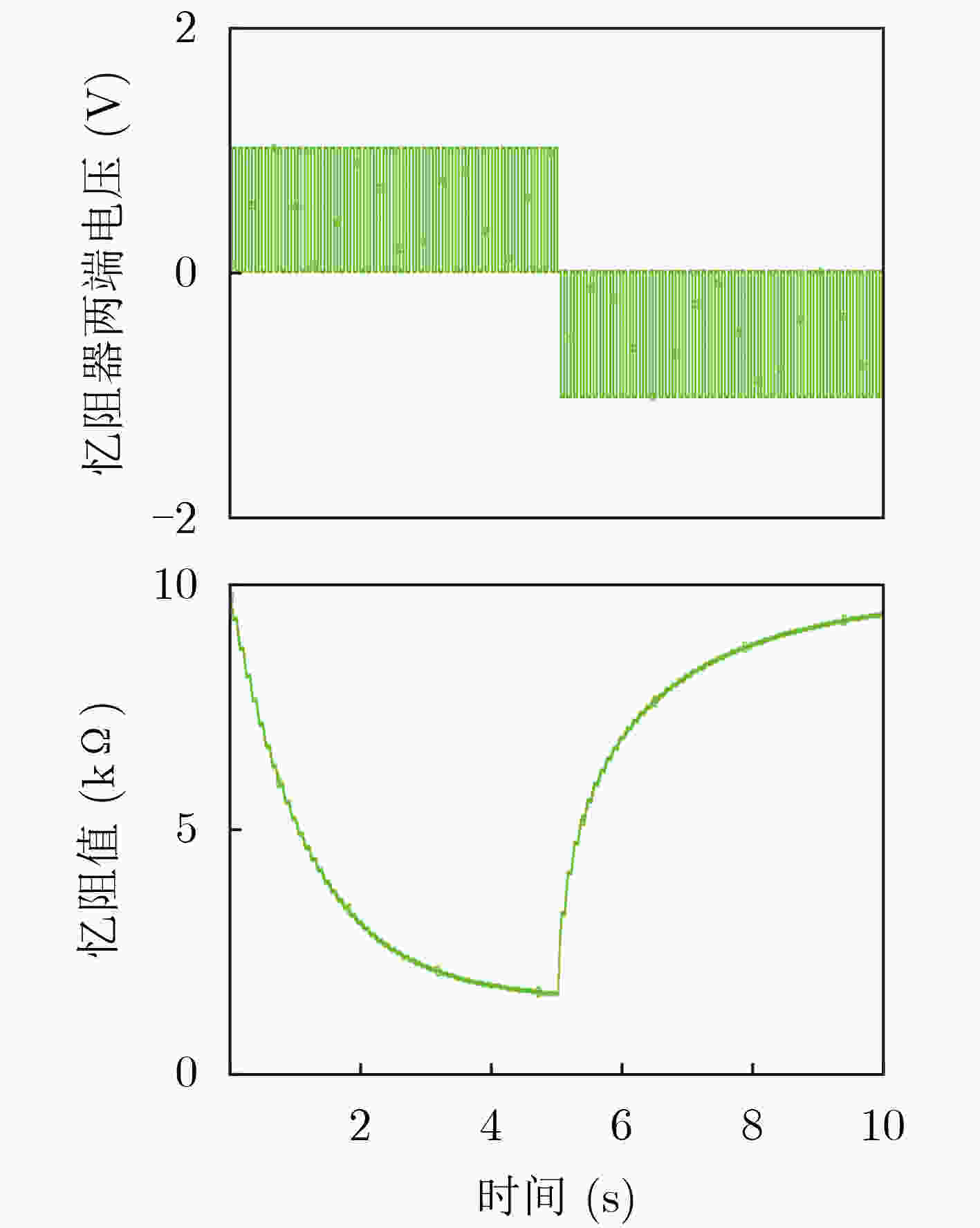
 下载:
下载:
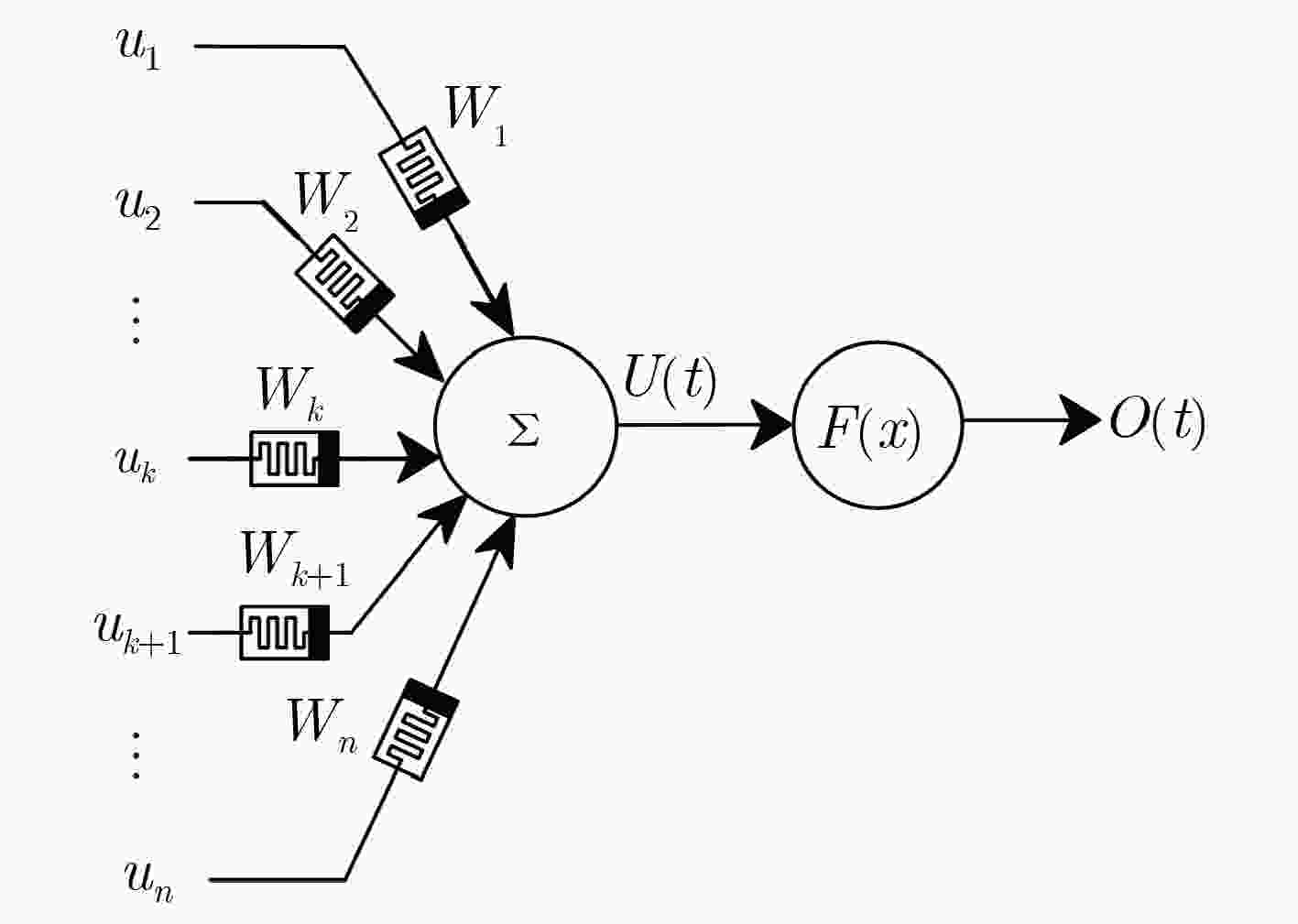
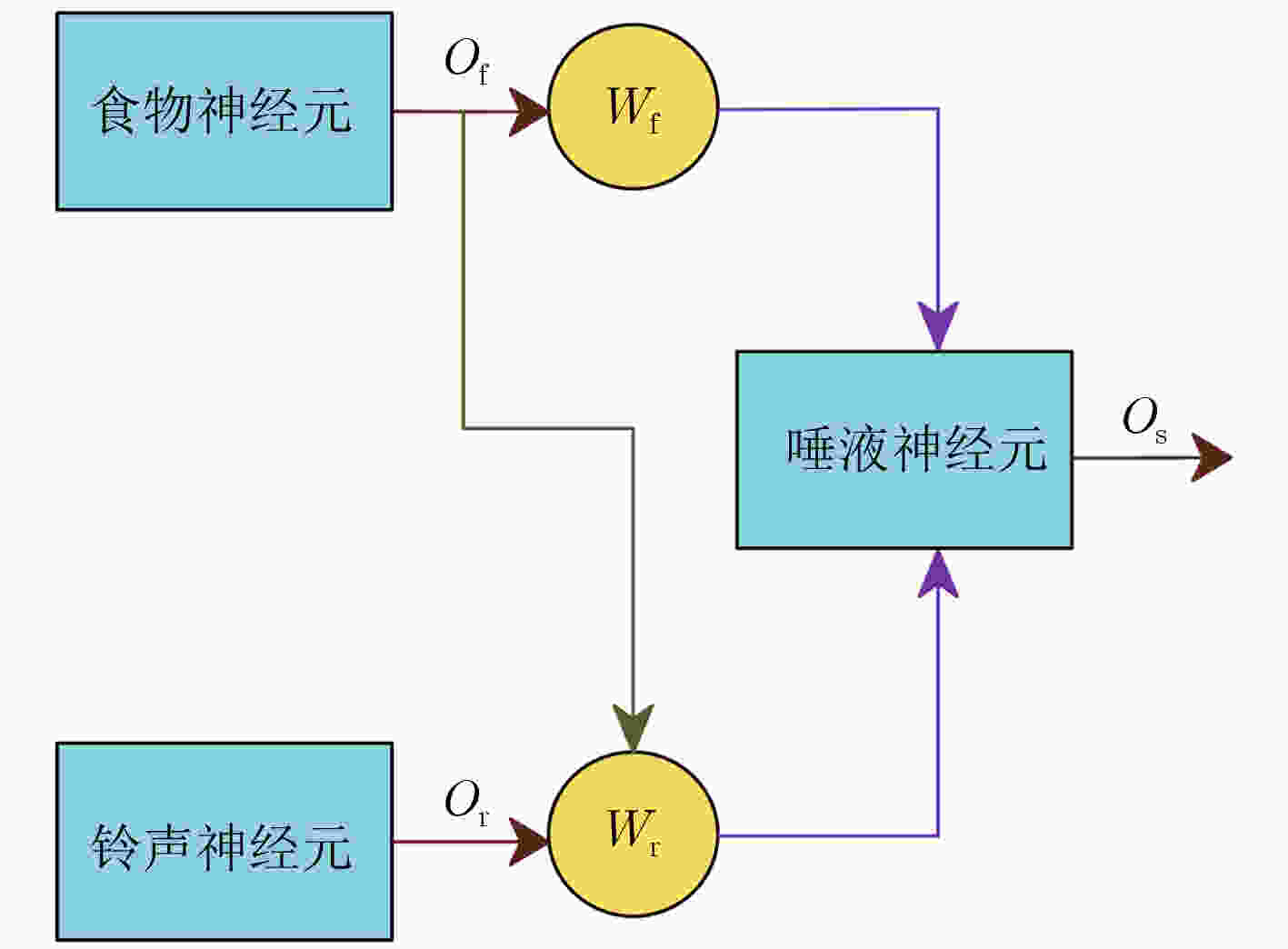
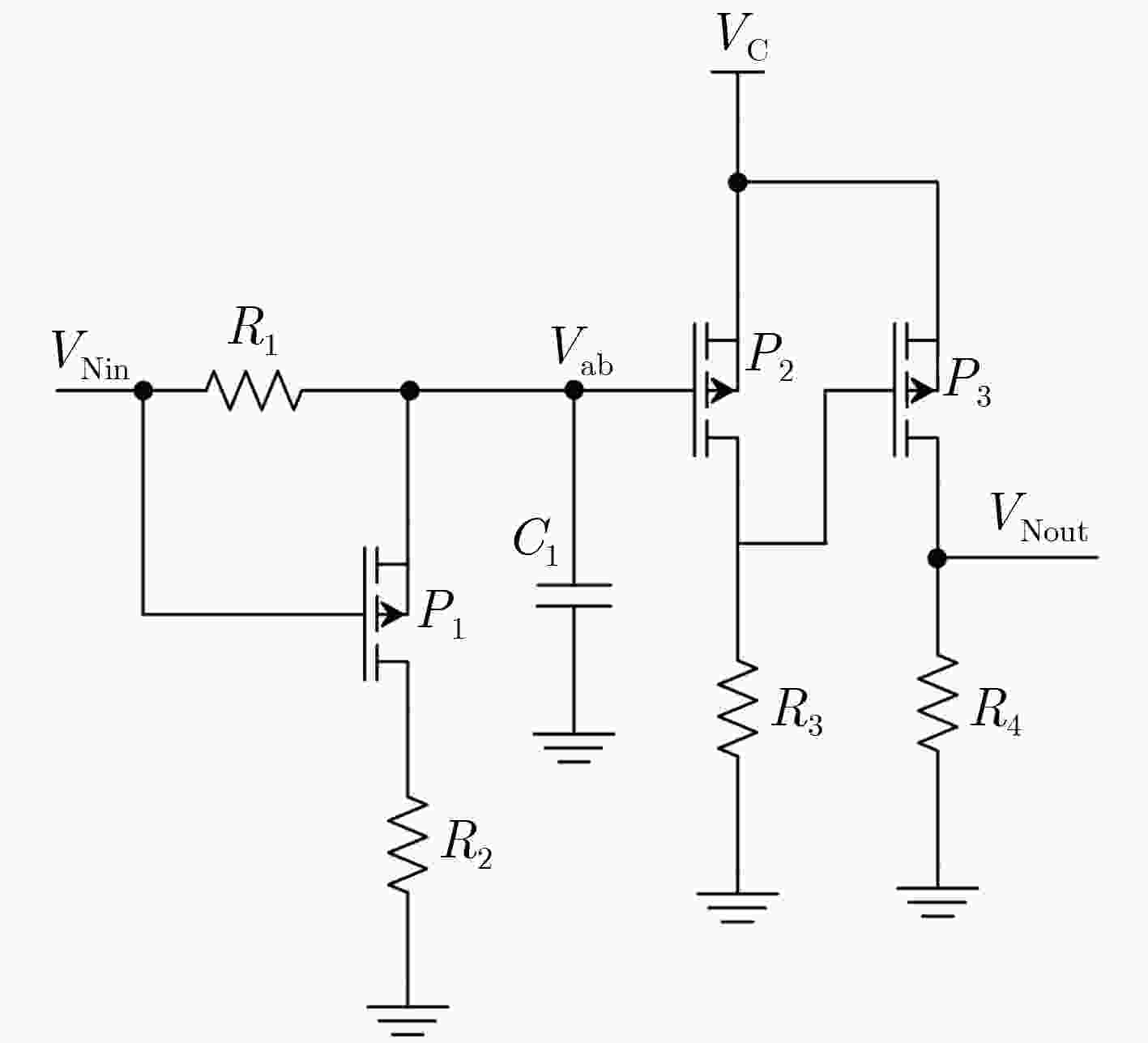
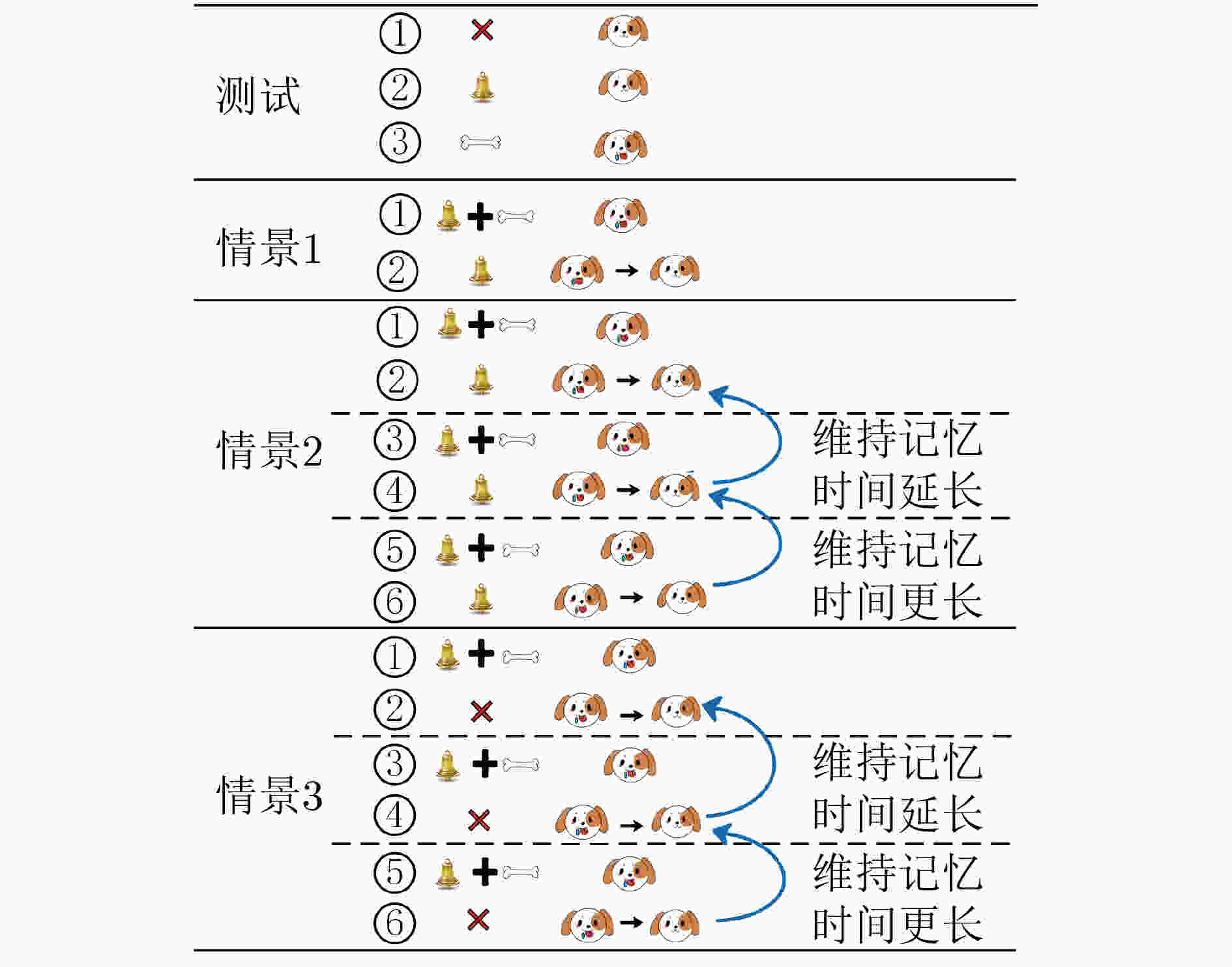
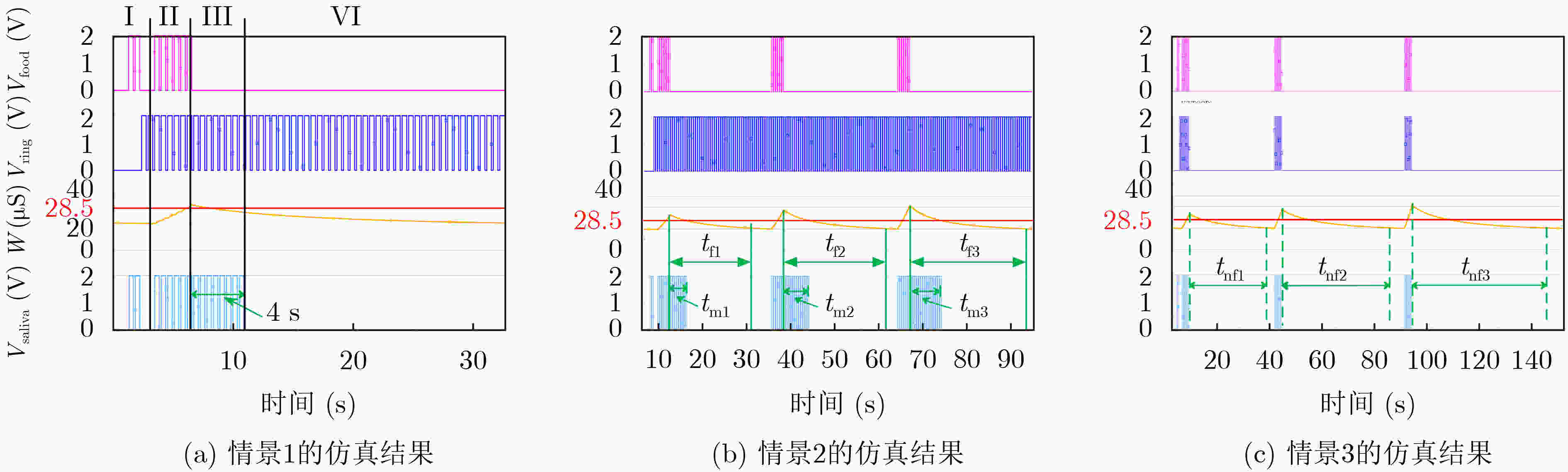
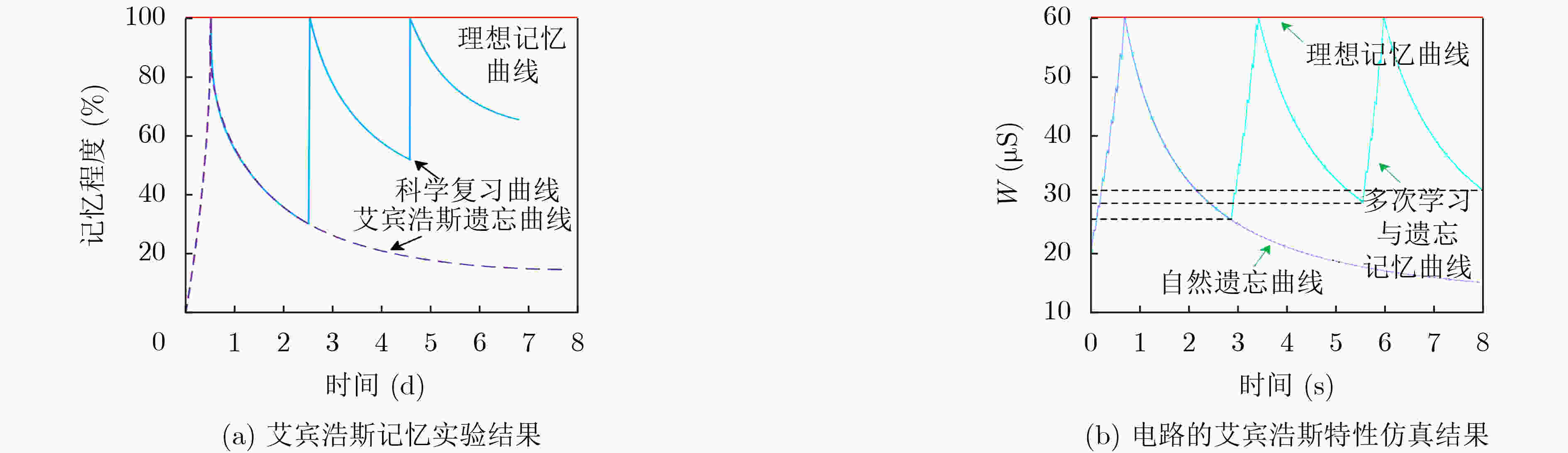


 下载:
下载:
