CAEFI: Channel State Information Fingerprint Indoor Location Method Using Convolutional Autoencoder for Dimension Reduction
-
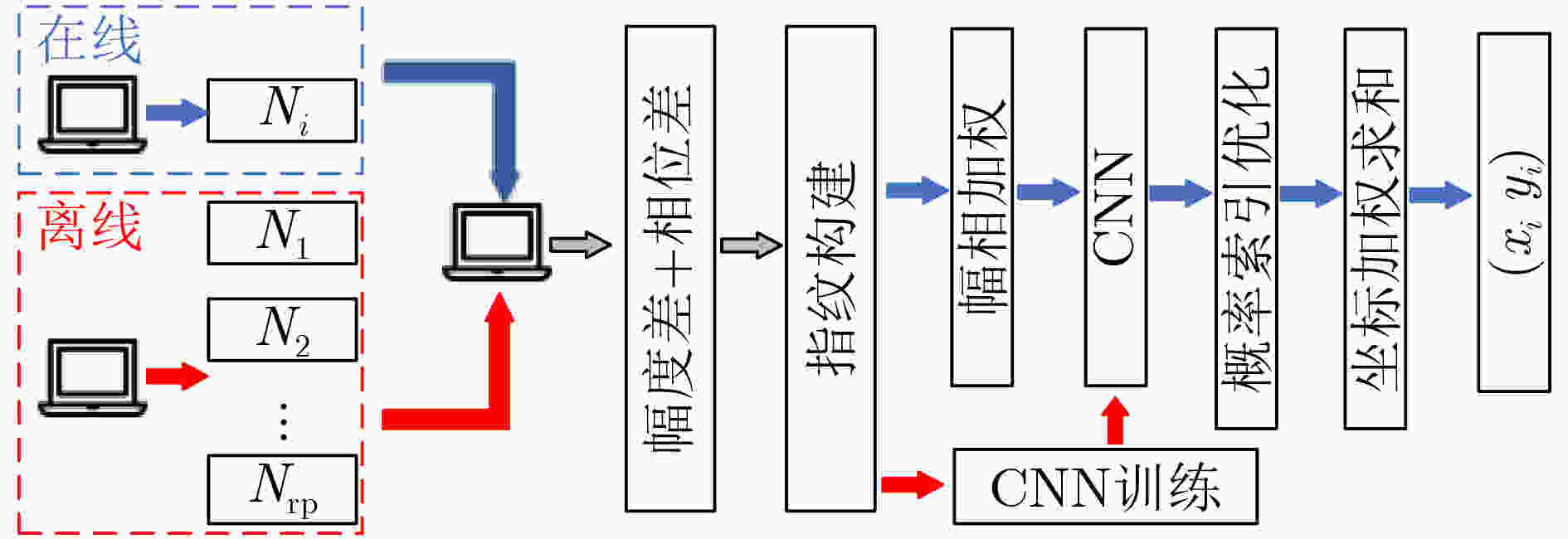
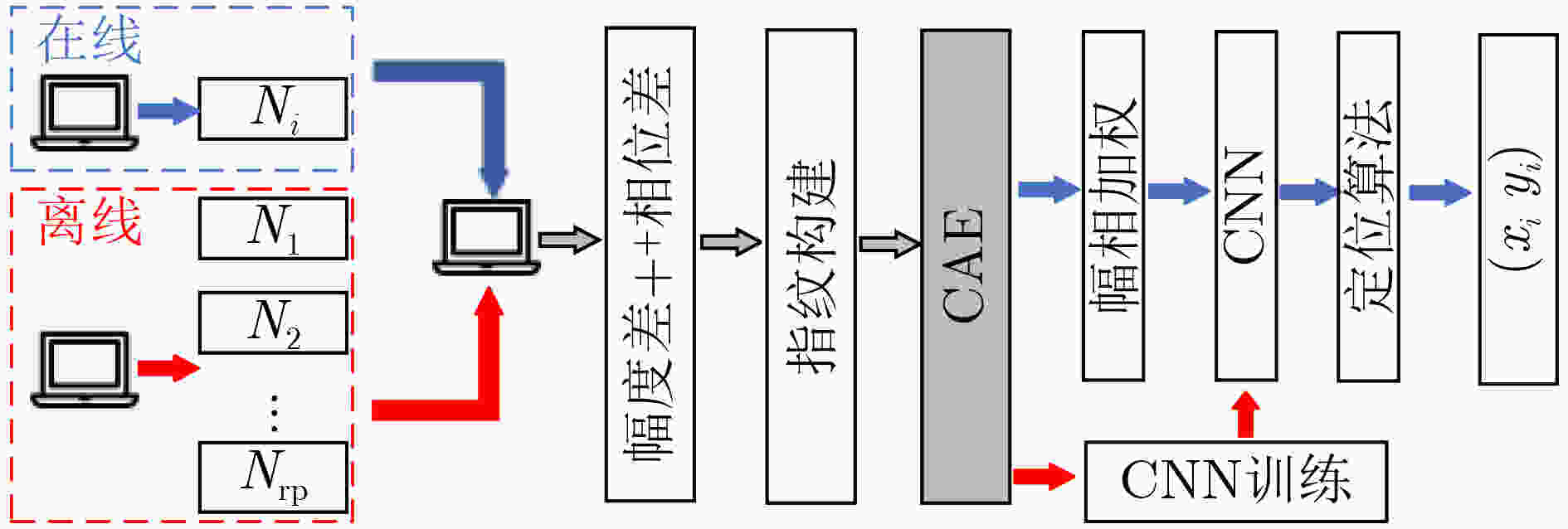
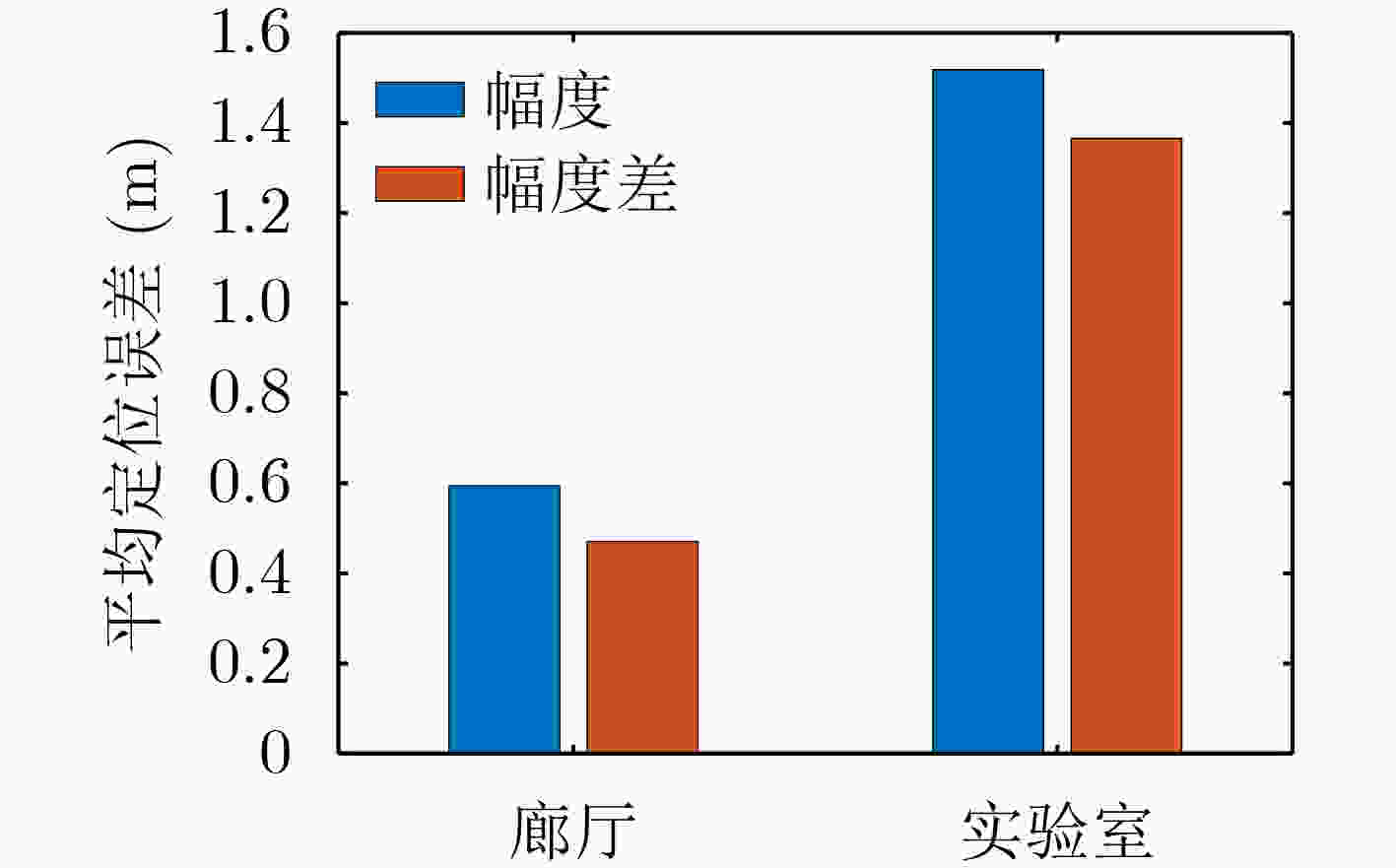
摘要: 针对提高Wi-Fi指纹室内定位技术性能,该文首先提出一种基于卷积神经网络(CNN)的信道状态信息(CSI)指纹室内定位方法。该方法在离线阶段联合CSI幅度差和相位差信息对CNN模型进行训练。在廊厅和实验室两种不同室内定位场景进行了定位实验,分别获得了25 cm和48 cm的平均定位误差;然后,在此基础上重点针对提高基于CNN的CSI室内定位时效性,引入卷积自编码器(CAE)实现CSI的降维处理,在保证原始定位方法精度的前提下,定位时间提高了40%,同时将内存消耗降低到原算法的1/15,实验结果验证了所提算法的有效性。Abstract: In order to improve the performance of Wi-Fi fingerprint indoor positioning technology, a method based on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) for Channel State Information (CSI) fingerprint indoor positioning is first proposed. This method combines the CSI amplitude difference and phase difference information to train the CNN model in the offline stage. Positioning experiments are carried out in two different indoor positioning scenarios in the gallery and the laboratory, and the average positioning errors of 25 cm and 48 cm are obtained respectively; Then, on this basis, the focus is on improving the timeliness of CNN-based CSI indoor positioning. The Convolutional AutoEncoder (CAE) is introduced to realize the dimensionality reduction processing of CSI. Under the premise of ensuring the accuracy of the original positioning method, the positioning time is increased by 40% and the memory consumption is reduced to 1/15 of the original algorithm. The experimental results verify the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.
-
表 1 CNN网络参数
网络层 参数 输出维度 输入层 训练数据 (30,30,3,m) 2维卷积层1 Conv 2D,fs=5,s=1,padding=same (30,30,16,m) 2维卷积层2 Conv 2D,fs=5,s=1,padding=same (30,30,16,m) 2维卷积层3 Conv 2D,fs=2,s=2,padding=valid (15,15,32,m) 2维卷积层4 Conv 2D,fs=5,s=1,padding=same (15,15,32,m) 平坦层 K=7200 (7200,m) 全连接层1 K=1024 (1024,m) 全连接层2 K=512 (512,m) 输出层 K=Nrp (Nrp,m) 表 2 CAE网络参数
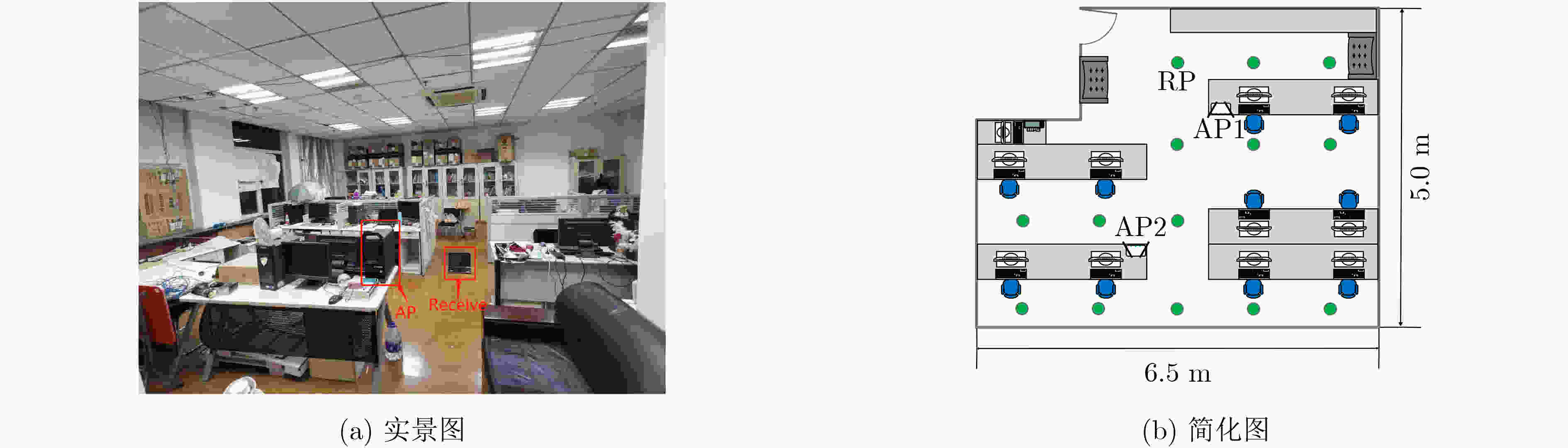
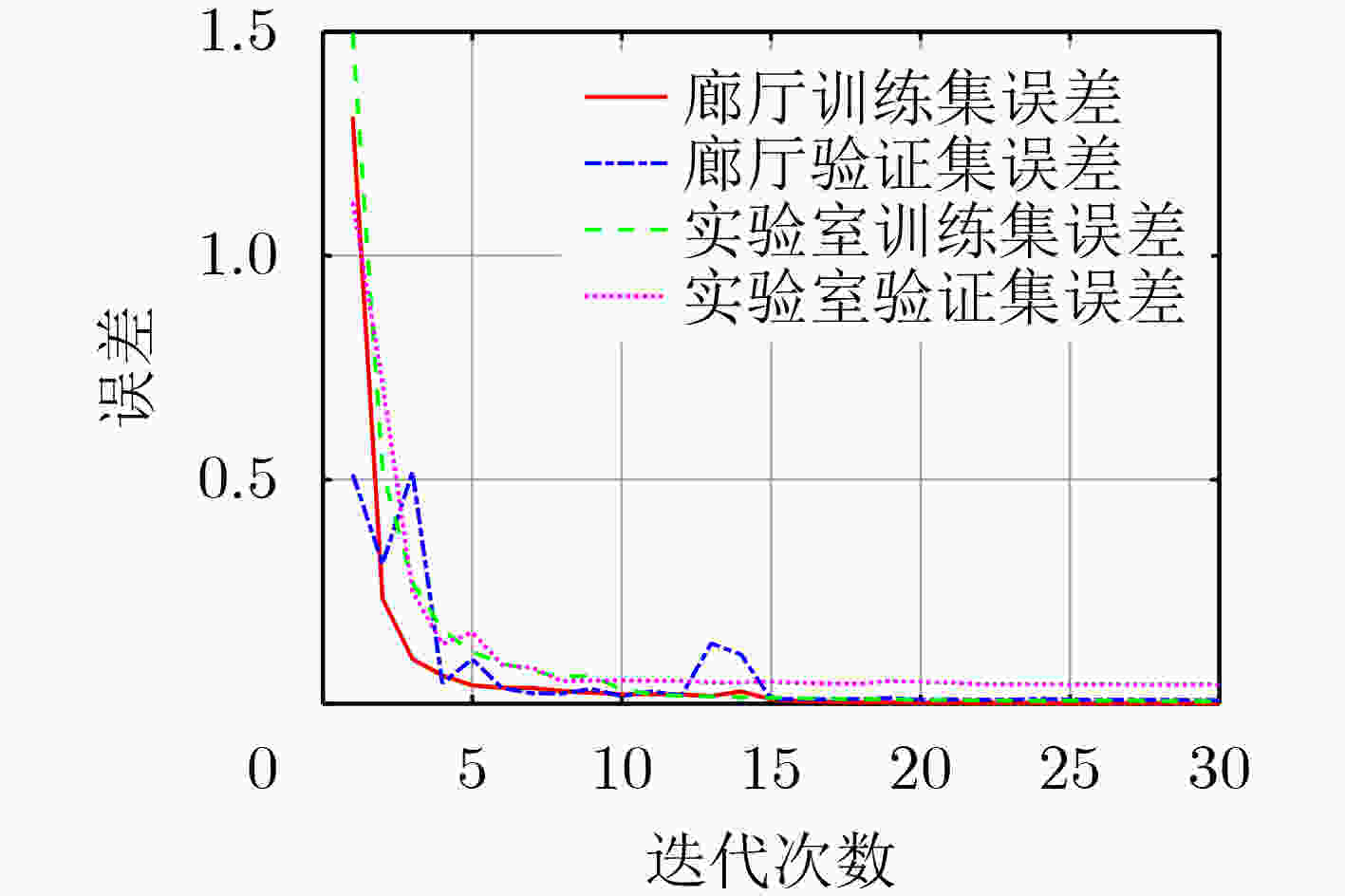
网络层 参数 输出维度 输入层 训练数据 (90,1,m) 1维卷积层1 Conv 1D,fs=5,s=1,padding=same (90,64,m) 1维池化层1 Maxpool 1D,s=2,padding=same (45,64,m) 1维卷积层2 Conv 1D,fs=5,s=1,padding=same (45,32,m) 1维池化层2 Maxpool 1D,s=2,padding=same (23,32,m) 1维卷积层3 Conv 1D,fs=5,s=1,padding=same (23,32,m) 1维池化层3 Maxpool 1D,s=2,padding=same (12,32,m) 1维卷积层4 Conv 1D,fs=5,s=1,padding=same (12,12,m) 1维卷积层5 Conv 1D,fs=3,s=1,padding=valid (10,10,m) 1维上采样层1 Upsampool 1D,size=2 (20,10,m) 1维卷积层6 Conv 1D,fs=9,s=1,padding=valid (12,12,m) 1维上采样层2 Upsampool 1D,size=2 (24,12,m) 1维卷积层7 Conv 1D,fs=2,s=1,padding=valid (23,23,m) 1维上采样层3 Upsampool 1D,size=2 (46,23,m) 1维卷积层8 Conv 1D,fs=2,s=1,padding=valid (45,32,m) 1维上采样层4 Upsampool 1D,size=2 (90,32,m) 1维卷积层9 Conv 1D,fs=5s=1,padding=same (90,64,m) 输出层 Conv 1D,fs=5,s=1,padding=same (90,1,m) 表 3 廊厅定位误差
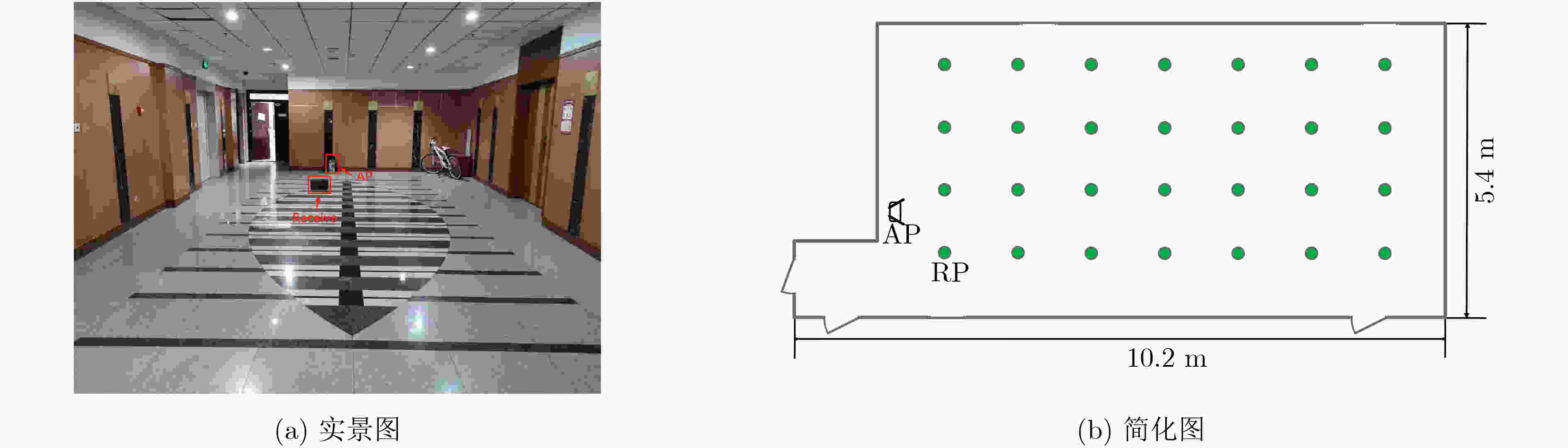
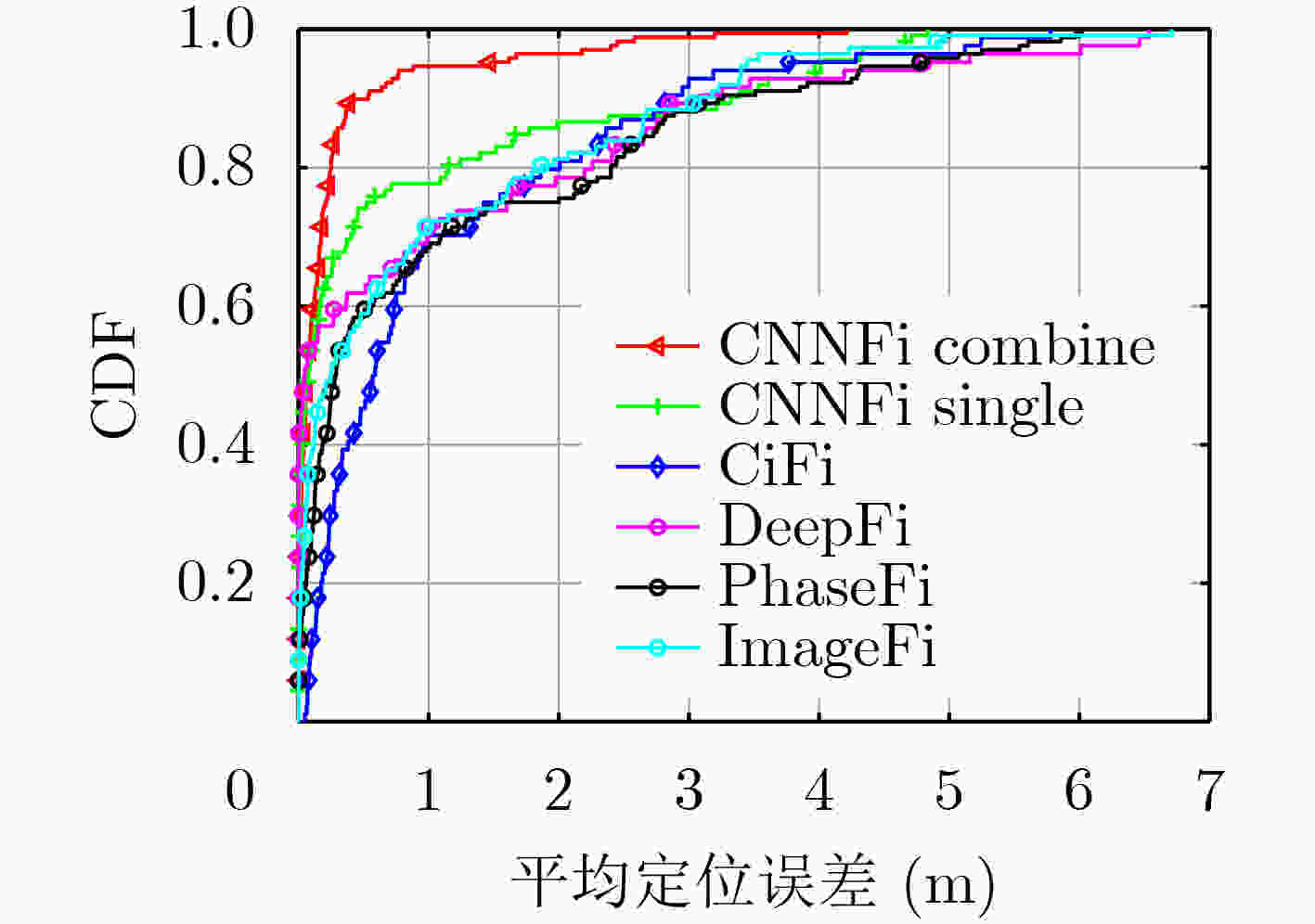
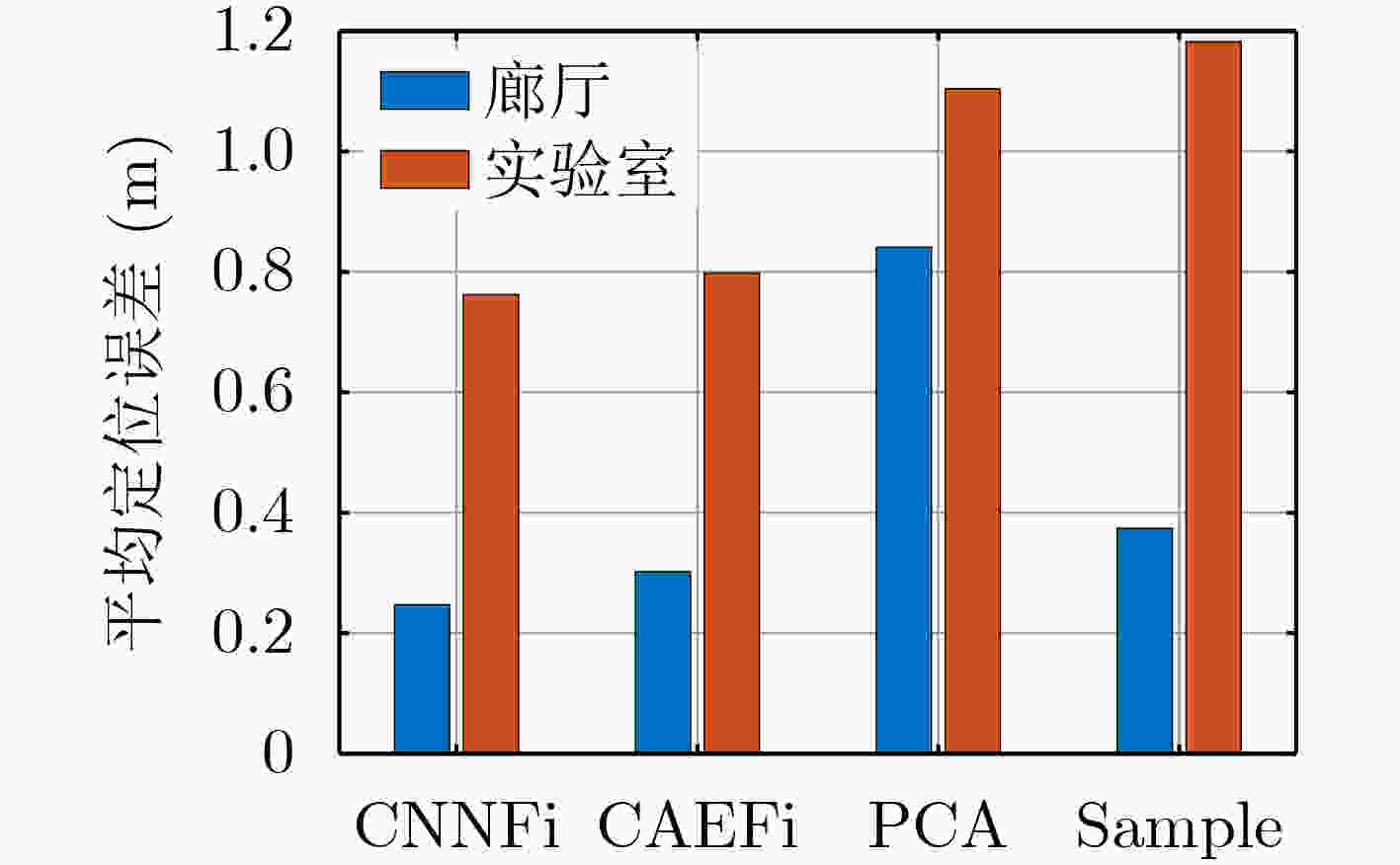
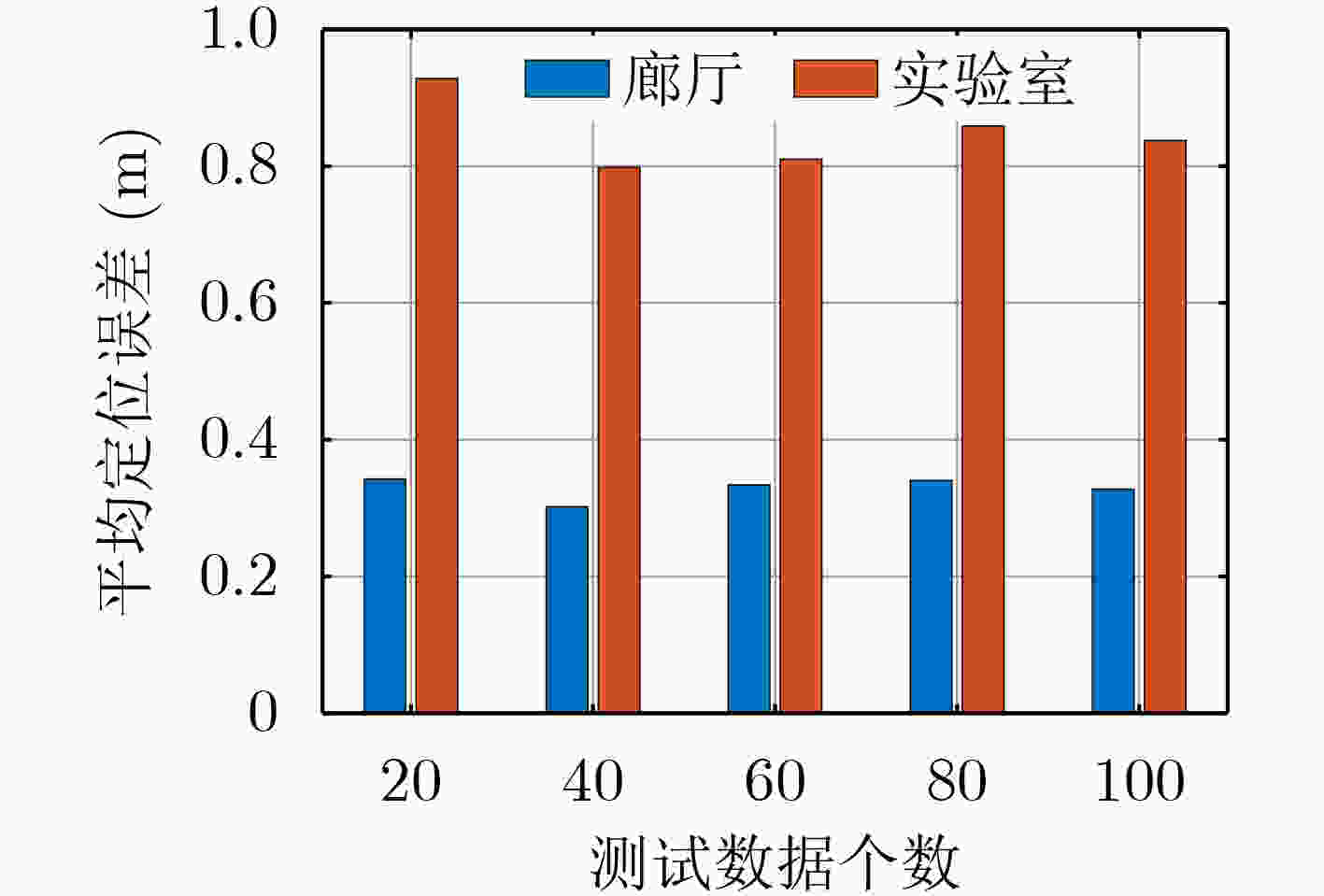
定位算法 平均误差(m) 标准差(m) CNNFi combine 0.25 0.58 CNNFi single 0.73 1.24 CiFi 1.09 1.28 DeepFi 0.99 1.62 PhaseFi 1.10 1.53 ImageFi 0.93 1.34 表 4 实验室定位误差
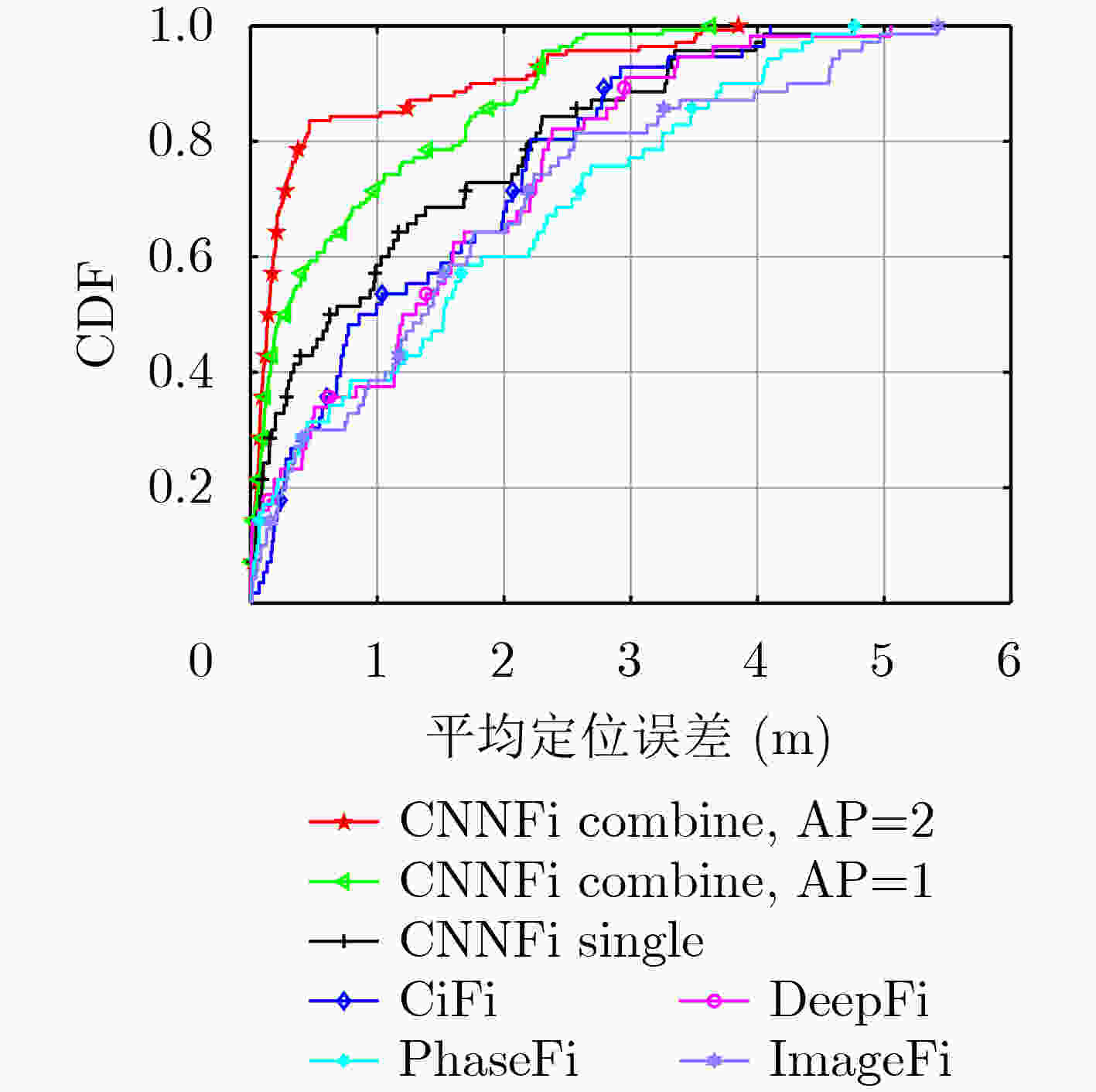
定位算法 平均误差(m) 标准差(m) CNNFi combine AP=2 0.48 0.86 CNNFi combine AP=1 0.72 0.86 CNNFi single 1.15 1.22 CiFi 1.36 1.14 DeepFi 1.45 1.21 PhaseFi 1.71 1.43 ImageFi 1.67 1.47 表 5 3种神经网络的训练参数
神经网络 可训练参数 非训练参数 总参数 CNNFi 7944414 3264 7947678 Auto Encoder 16121 0 16121 CAE-CNN 490494 1344 491838 表 6 两种定位方法的在线定位时间与内存大小
定位方法 Matlab运行
时间(s)Python运行
时间(s)总运行
时间(s)内存大小
(MB)CNNFi 0.1269 0.1399 0.2668 91 CAEFi 0.0062 0.1598 0.1660 5.7898 -
[1] ALI M U, HUR S, and PARK Y. Poster abstract: IoT enabled Wi-Fi indoor positioning system using raster maps[C]. The 18th ACM/IEEE International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks, Montreal, Canada, 2019: 327–328. [2] REZAZADEH J, SUBRAMANIAN R, SANDRASEGARAN K, et al. Novel iBeacon placement for indoor positioning in IoT[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(24): 10240–10247. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2875037 [3] TORRES-SOSPEDRA J, JIMÉNEZ A R, MOREIRA A, et al. Off-line evaluation of mobile-centric indoor positioning systems: The experiences from the 2017 IPIN competition[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(2): 487. doi: 10.3390/s18020487 [4] ZHANG Daqiang, ZHAO Shengjie, YANG L T, et al. NextMe: Localization using cellular traces in internet of things[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2015, 11(2): 302–312. doi: 10.1109/TII.2015.2389656 [5] PAK J M, AHN C K, SHMALIY Y S, et al. Improving reliability of particle filter-based localization in wireless sensor networks via hybrid particle/FIR filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2015, 11(5): 1089–1098. doi: 10.1109/TII.2015.2462771 [6] ZHU Yuke, MOTTAGHI R, KOLVE E, et al. Target-driven visual navigation in indoor scenes using deep reinforcement learning[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 2017: 3357–3364. [7] DARDARI D, CLOSAS P, and, DJURIĆ P M. Indoor tracking: Theory, methods, and technologies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2015, 64(4): 1263–1278. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2015.2403868 [8] WISANMONGKOL J, KLINKUSOOM L, SANPECHUDA T, et al. Multipath mitigation for RSSI-based Bluetooth low energy localization[C]. The 19th International Symposium on Communications and Information Technologies (ISCIT), Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 2019: 47–51. [9] ABBAS M, ELHAMSHARY M, RIZK H, et al. WiDeep: WiFi-based accurate and robust indoor localization system using deep learning[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications, Kyoto, Japan, 2019: 1–10. [10] FENG Daquan, WANG Chunqi, HE Chunlong, et al. Kalman-filter-based integration of IMU and UWB for high-accuracy indoor positioning and navigation[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(4): 3133–3146. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.2965115 [11] PEREKADAN V, MUKHERJEE T, BANERJEE C, et al. RF-MSiP: Radio frequency multi-source indoor positioning[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Los Angeles, USA, 2019: 5259–5268. [12] 许浩, 王旭东, 吴楠. 基于卷积神经网络的室内可见光指纹定位方法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2021, 58(17): 1706008.XU Hao, WANG Xudong, and WU Nan. Indoor visible light fingerprint positioning scheme based on convolution neural network[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2021, 58(17): 1706008. [13] SINGH V, AGGARWAL G, and UJWAL B V S. Ensemble based real-time indoor localization using stray WiFi signal[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics (ICCE), Las Vegas, USA, 2018: 1–5. [14] KHALAJMEHRABADI A, GATSIS N, and AKOPIAN D. Modern WLAN fingerprinting indoor positioning methods and deployment challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2017, 19(3): 1974–2002. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2017.2671454 [15] ACHROUFENE A, AMIRAT Y, and CHIBANI A. RSS-based indoor localization using belief function theory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2019, 16(3): 1163–1180. doi: 10.1109/TASE.2018.2873800 [16] SOHAN A A, ALI M, FAIROOZ F, et al. Indoor positioning techniques using RSSI from wireless devices[C]. The 22nd International Conference on Computer and Information Technology (ICCIT), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2019: 1–6. [17] BAHL P and PADMANABHAN V N. RADAR: An in-building RF-based user location and tracking system[C]. IEEE INFOCOM 2000. Conference on Computer Communications. Nineteenth Annual Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications Societies, Tel Aviv, Israel, 2000: 775–784. [18] YOUSSEF M and ASHOK A. The Horus location determination system[J]. Wireless Networks, 2008, 14(3): 357–374. doi: 10.1007/s11276-006-0725-7 [19] HOANG M T, YUEN B, DONG Xiaodai, et al. Recurrent neural networks for accurate RSSI indoor localization[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(6): 10639–10651. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2940368 [20] WANG Xuyu, GAO Lingjun, and MAO Shiwen. CSI phase fingerprinting for indoor localization with a deep learning approach[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2016, 3(6): 1113–1123. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2016.2558659 [21] HALPERIN D, HU Wenjun, SHETH A, et al. Predictable 802.11 packet delivery from wireless channel measurements[J]. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 2010, 40(4): 159–170. doi: 10.1145/1851275.1851203 [22] XIE Yaxiong, LI Zhenjiang, and LI Mo. Precise power delay profiling with commodity Wi-Fi[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2019, 18(6): 1342–1355. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2018.2860991 [23] WU Kaishun, XIAO Jiang, YI Youwen, et al. CSI-based indoor localization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2013, 24(7): 1300–1309. doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2012.214 [24] WANG Xuyu, GAO Lingjun, MAO Shiwen, et al. DeepFi: Deep learning for indoor fingerprinting using channel state information[C]. 2015 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, New Orleans, USA, 2015: 1666–1671. [25] WANG Xuyu, WANG Xiangyu, and MAO Shiwen. CiFi: Deep convolutional neural networks for indoor localization with 5 GHz Wi-Fi[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Paris, France, 2017: 1–6. [26] 江小平, 王妙羽, 丁昊, 等. 基于信道状态信息幅值-相位的被动式室内指纹定位[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(5): 1165–1171. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180871JIANG Xiaoping, WANG Miaoyu, DING Hao, et al. Passive fingerprint indoor positioning based on CSI amplitude-phase[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(5): 1165–1171. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180871 [27] LI Haihan, ZENG Xiangsheng, LI Yunzhou, et al. Convolutional neural networks based indoor Wi-Fi localization with a novel kind of CSI images[J]. China Communications, 2019, 16(9): 250–260. doi: 10.23919/JCC.2019.09.019 [28] SHI Shuyu, SIGG S, CHEN Lin, et al. Accurate location tracking from CSI-based passive device-free probabilistic fingerprinting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(6): 5217–5230. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2810307 -





 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:
