Design of Hardware IP Core Security Protection Based on Multi-Level Co-obfuscation
-
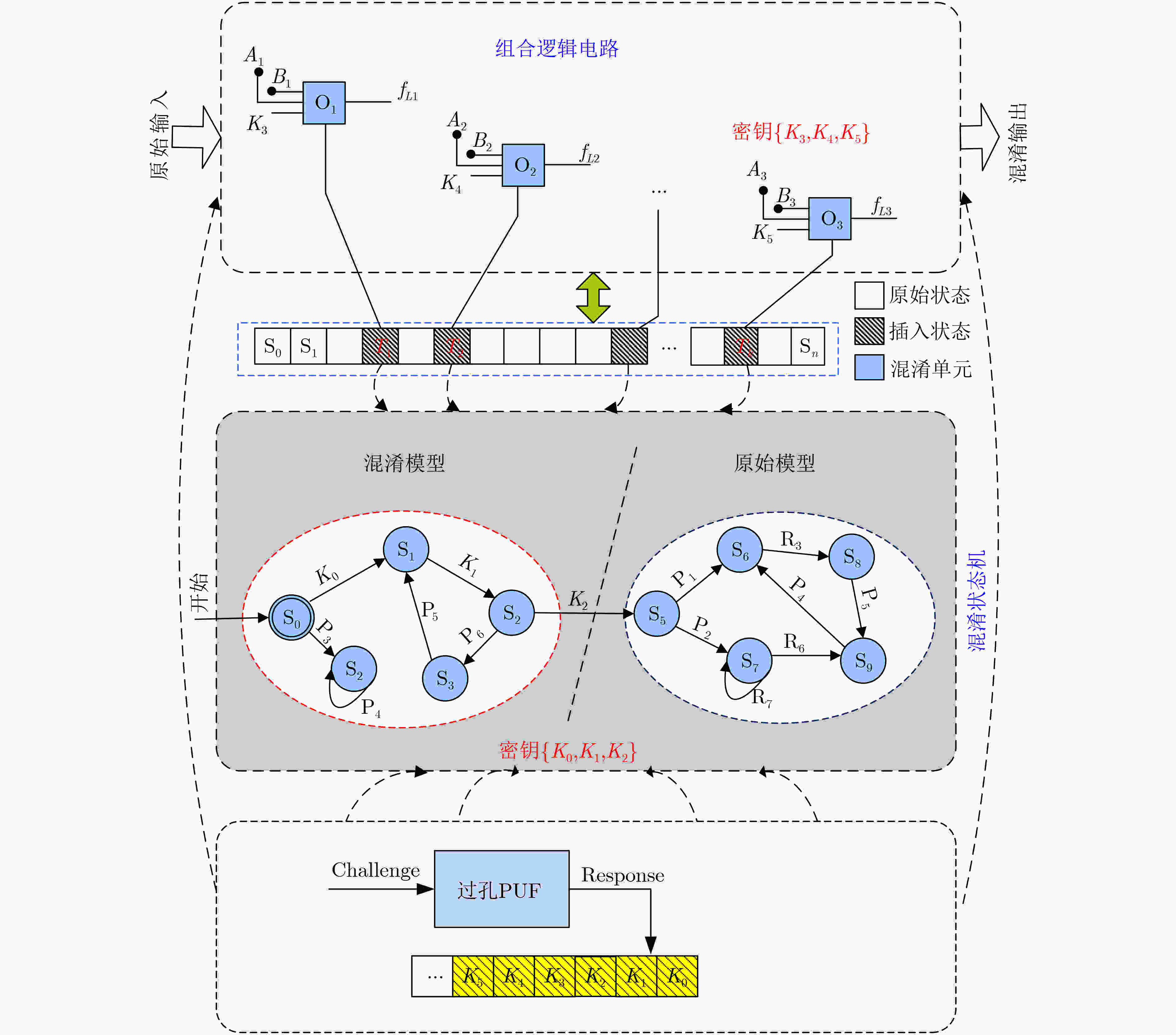
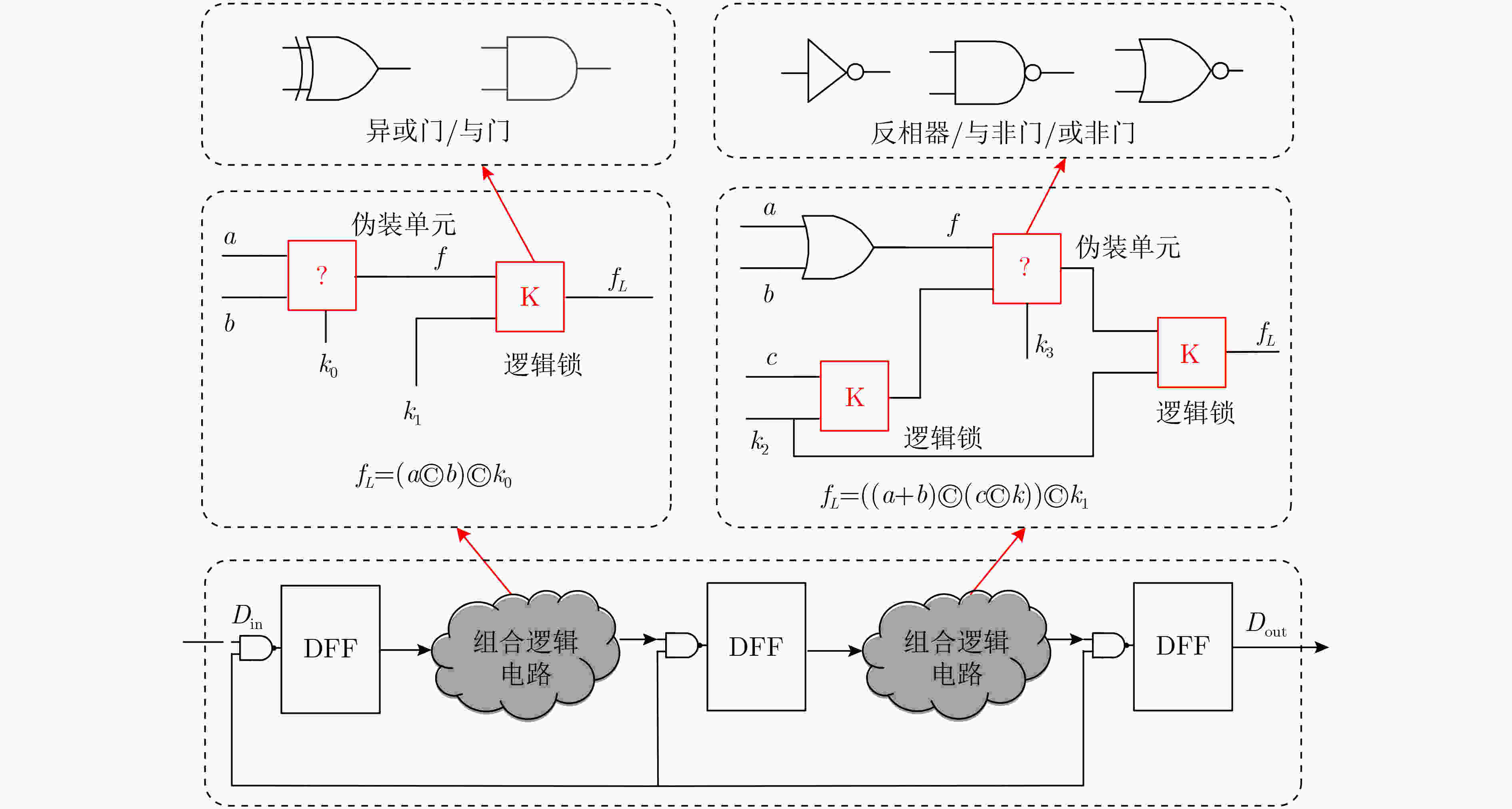
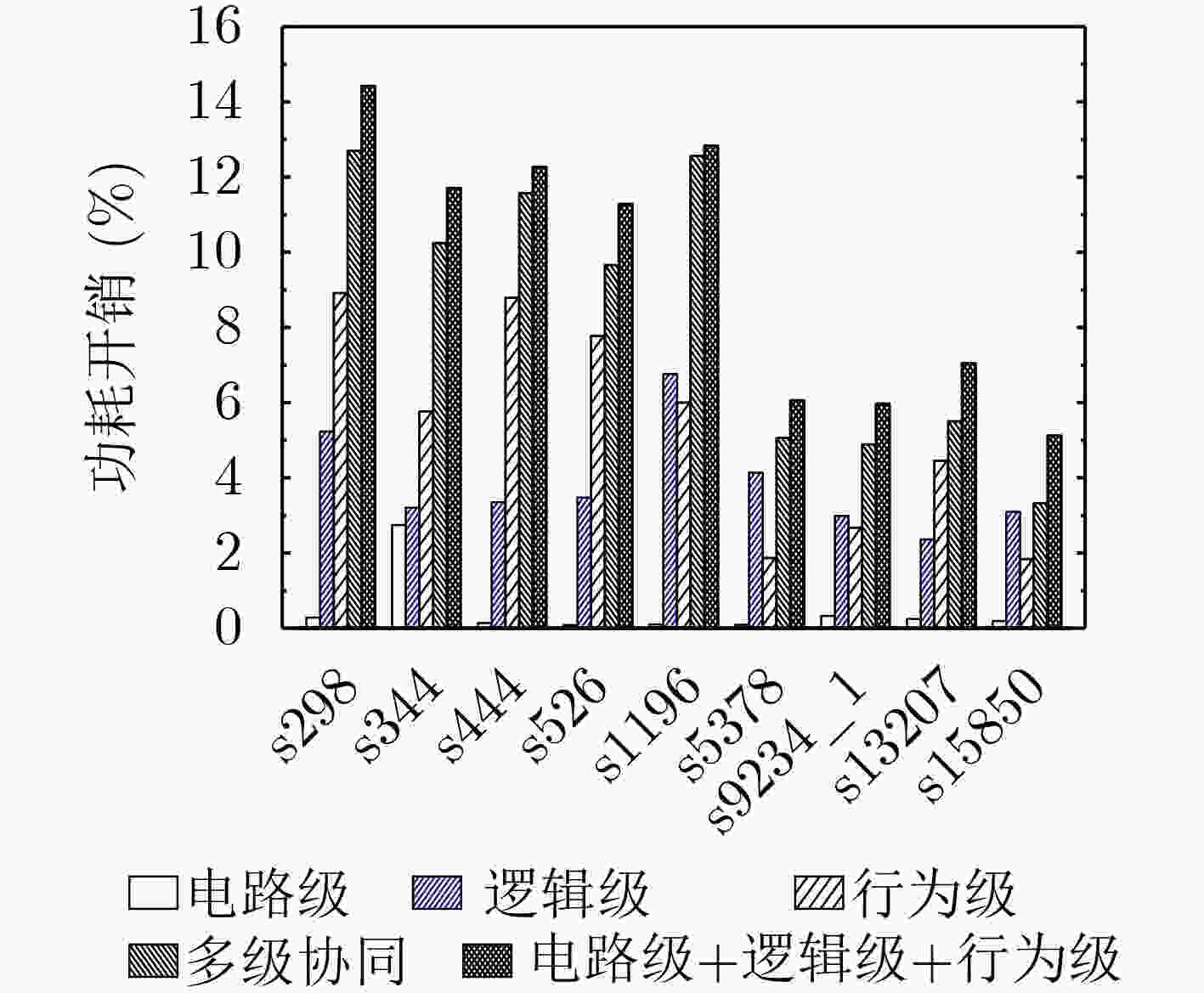
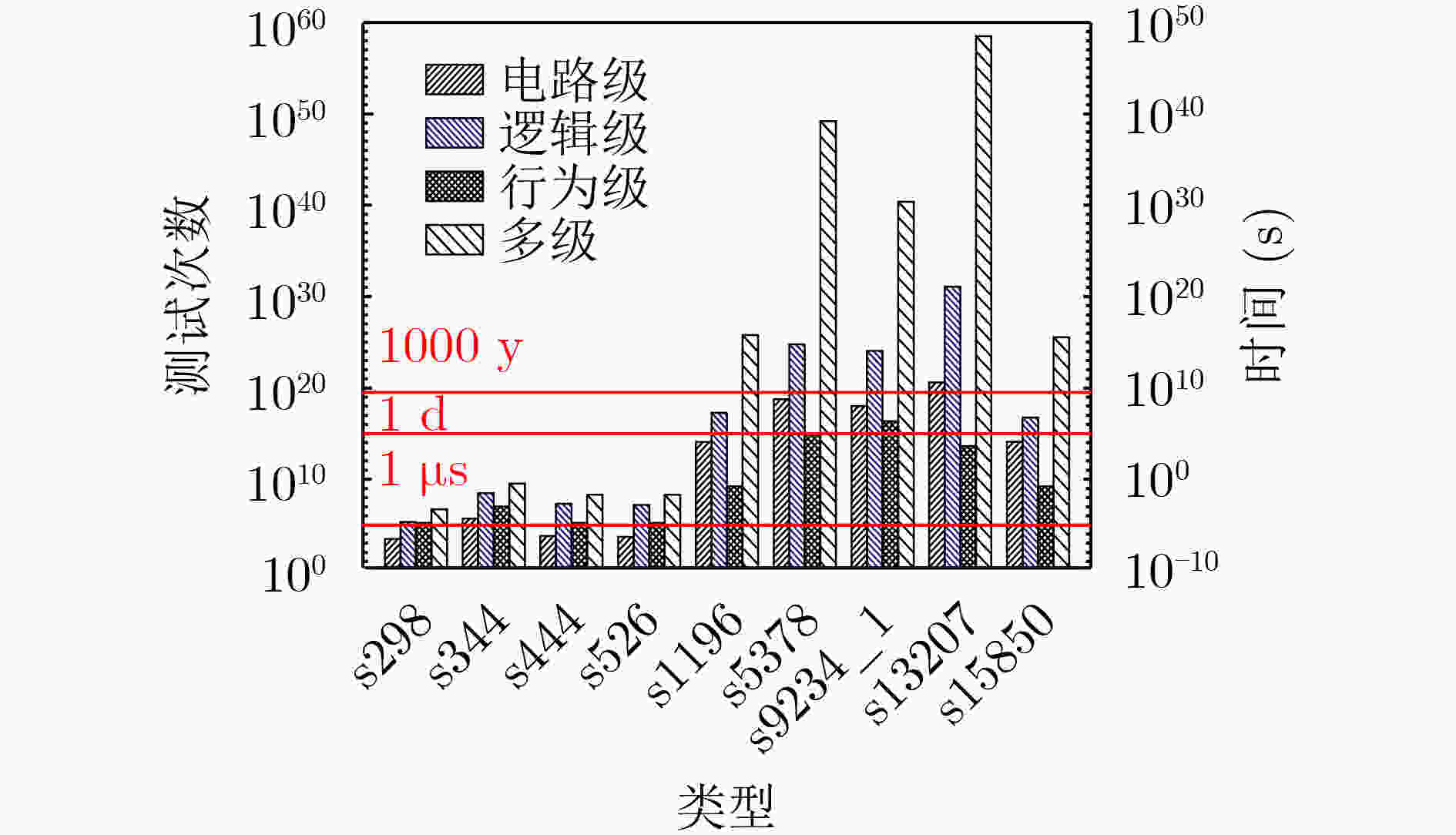
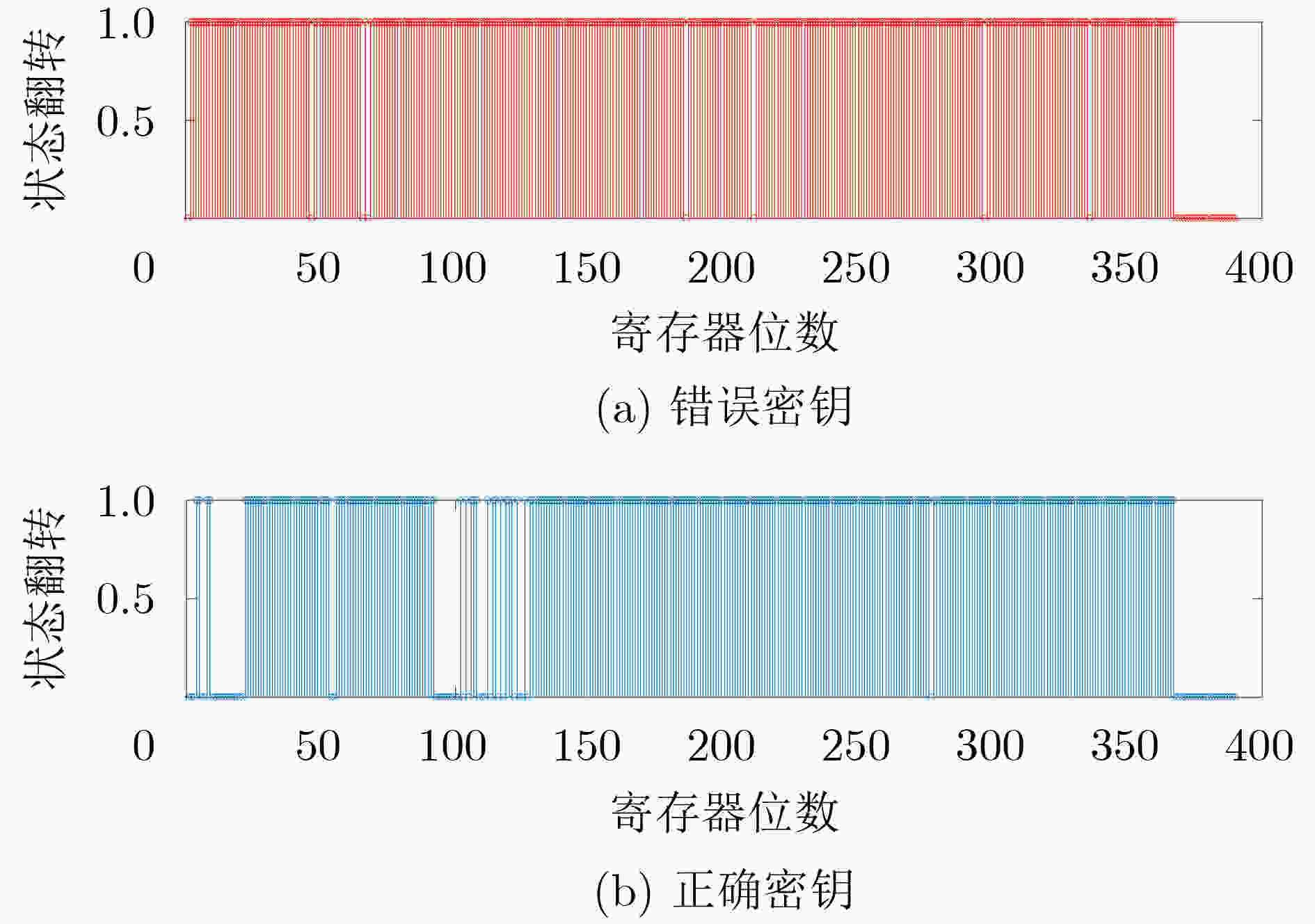
摘要: 传统硬件混淆从物理级、逻辑级、行为级等进行单层次混淆,没有发挥多级协同优势,存在安全隐患。该文通过对物理版图、电路逻辑和状态跳变行为的关系研究,提出多级协同混淆的硬件IP核防护方法。该方案首先在自下而上协同混淆中,采用虚拟孔设计版图级伪装门的方式进行物理-逻辑级混淆,采用过孔型物理不可克隆函数(PUF)控制状态跳变的方式实现物理-行为级混淆;然后,在自上而下协同混淆中,利用密钥控制密钥门进行行为-逻辑级混淆,利用并行-支路混淆线的方法完成行为-物理级混淆;最后提出混淆电路在网表的替换机制,设计物理-逻辑-行为的3级协同混淆,实现多级协同混淆的IP核安全防护。ISCAS-89基准电路测试结果表明,在TSMC 65 nm工艺下,多级协同混淆IP核在较大规模测试电路中的面积开销占比平均为11.7%,功耗开销占比平均为5.1%,正确密钥和错误密钥下的寄存器翻转差异低于10%,所提混淆方案可有效抵御暴力攻击、逆向工程、SAT等攻击。Abstract: Most of the reported hardware obfuscations are single-level ones focusing on physical level, logical level or behavior level, in which the lack of synergy among different levels commonly results in limited security performance. Based on study of the relationships among circuit layout, logic and states transition, a multi-level co-obfuscation scheme is proposed to protect hardware IP cores. In bottom-up collaborative confusion design, dummy vias are introduced into camouflage gates layout to perform physical-logic obfuscation, and via-PUF (Physical Unclonable Fuction) are utilized in state transition control to realize physical-behavior obfuscation. Then, in top-down collaborative obfuscation design, logic locks are used to perform behavior-logic obfuscation, and parallel-branch obfuscation wire technique is designed to complete the behavior-physical confusion. Finally, a substitution algorithm of the obfuscation gates into the circuit’s netlist is proposed, and the three-level cooperative obfuscation is realized to achieve IP core security protection. ISCAS-89 Benchmarks and a typical cryptogram algorithm are used to verify the correctness and efficiency of the proposed IP core protection scheme. The test results show that under TSMC 65nm process, the average area cost percentage of the proposed co-obfuscation in large-scale circuits is 11.7%, the average power consumption accounts for 5.1%, The difference of register toggle between correct and wrong keys is less than 10%, and the proposed scheme can effectively resist violence attack, reverse engineering, boolean SATisfiability (SAT) attack.
-
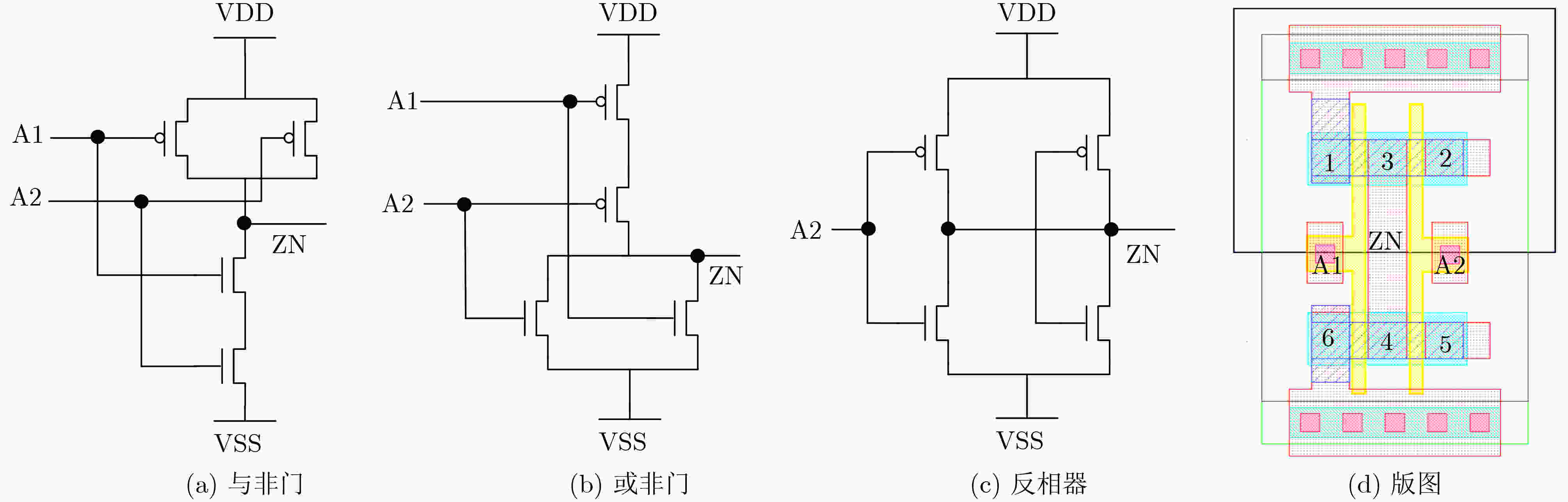
表 1 与非、或非、反相器伪装门的接触孔配置
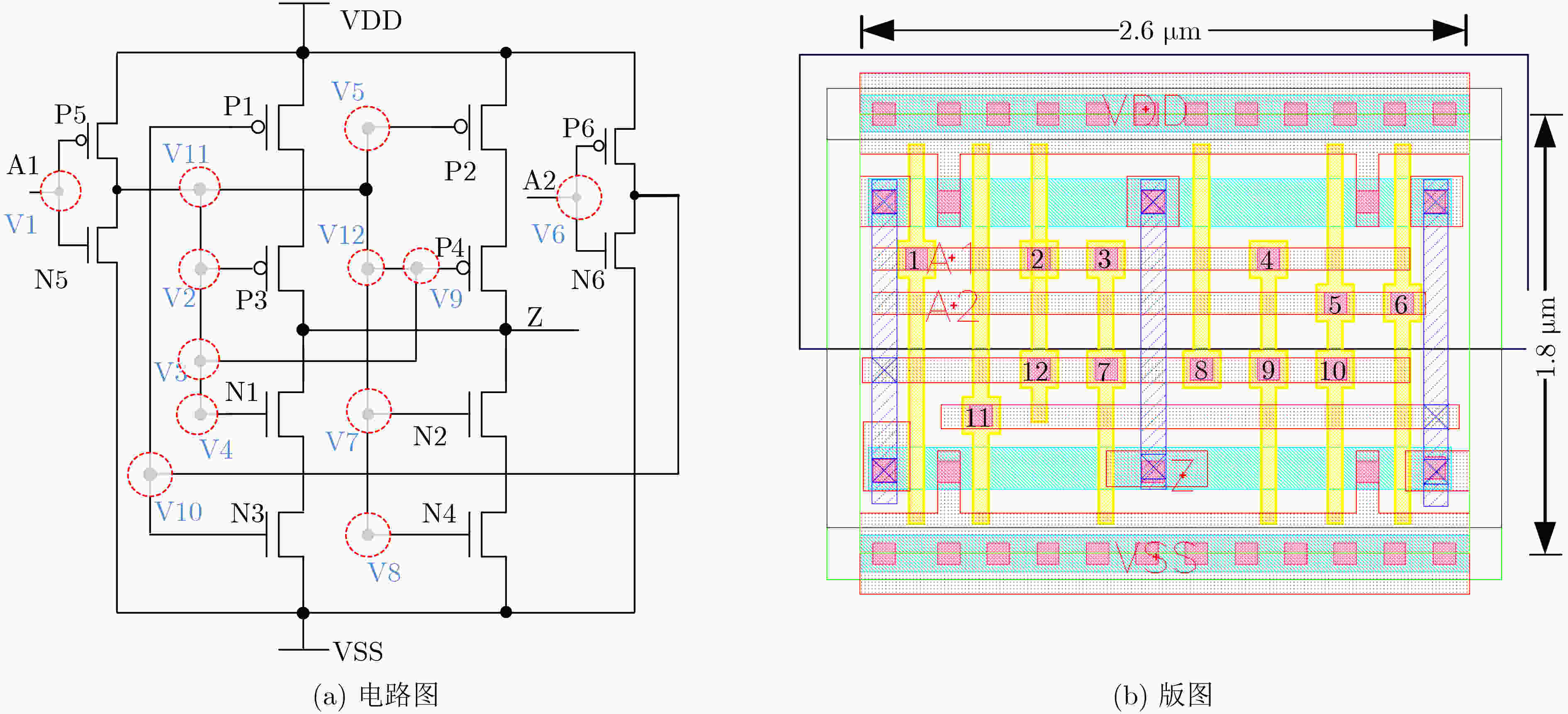
逻辑门 接触孔 过孔 Dummy True Dummy True NAND 4 1 2 3 5 6 3 6 1 2 4 5 NOR 2 4 5 1 2 4 5 6 1 4 2 3 5 6 INV / 1 2 3 4 5 6 3 4 1 2 5 6 表 2 异或门和与门密钥门接触孔配置
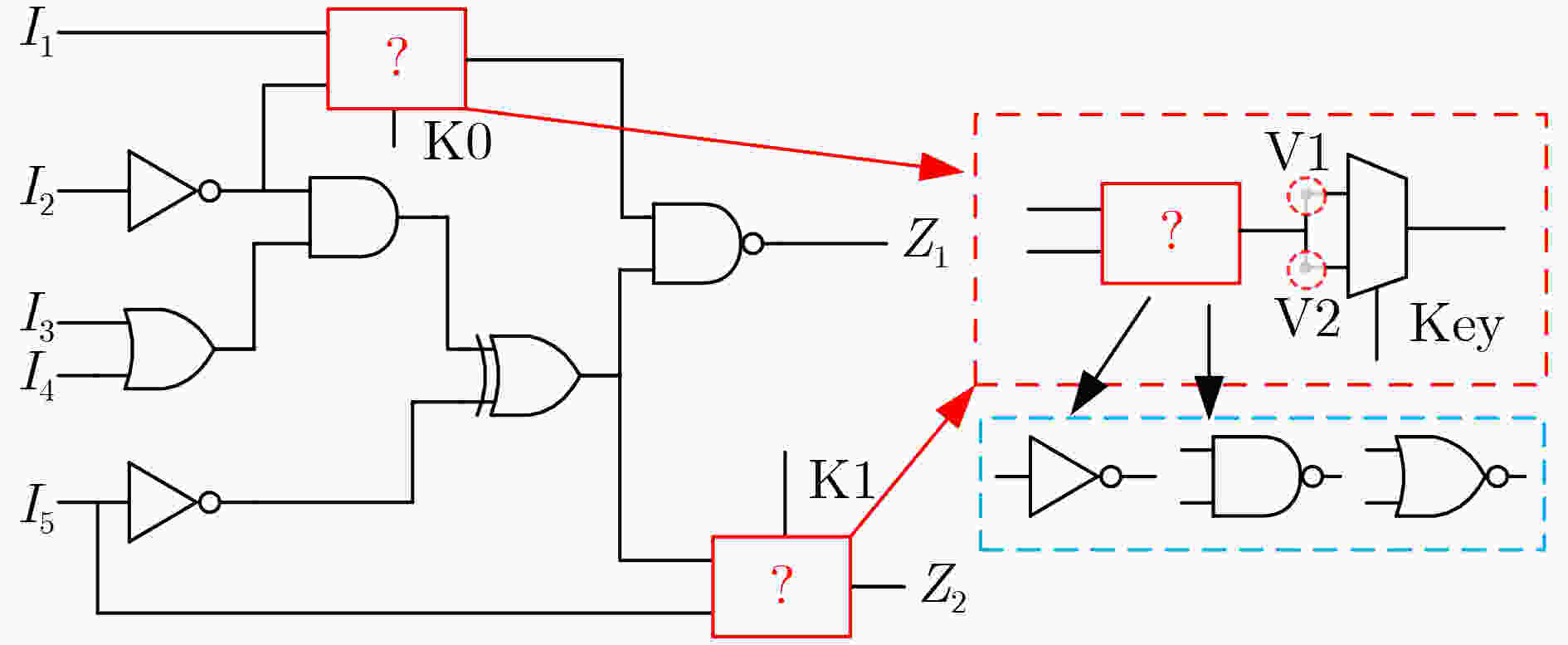
逻辑门 接触孔 True Dummy XOR 1 2 4 5 6 7 8 11 3 9 10 12 AND 1 3 6 8 9 10 11 12 2 4 5 7 表 3 混淆单元插入/替换算法伪代码
输入:原始网表,密钥数据,时序报告 输出:混淆网表 (1) Key Gatelocation={}; (2)将关键路径上的门单元存放到Key Gatelocation; (3) For i←2 to Key size do (4) 搜索原始网表中第i个符合条件的门 Gatei (5) 如果 Gatei不在CriticalPath_ Gate中, (6) 则把其地址存入数组Key Gatelocation; (7) end (8) 替换混淆单元门; (9) 在输出选择门中插入密钥门; (10) 插入新的输入端口和互连线; (11) 更新电路网表; (12) 结束 表 4 所提混淆与已有方案的相关性能
文献 类型 硬件开销 安全性 基准 面积(%) 功耗(%) 时延 SAT RE BFA RA [2] Practical Logic Obfuscation s9234 0.56 4.57 0.94 GB – √ – – [10] Dynamic State-Deflection s9234 11.00 5.30 0.94 GB – – – – [11] DUP s9234 42.70 34.10 0.98 GB √ – √ – [12] ISO s9234 25.80 3.80 0.94 GB √ – – – [13] SARLock s9234 6.80 13.30 0.89 GB √ – – – [14] Camouflage gate s9234 7.20 28.10 0.73 GB – √ – – 本文 Multi-level Obfuscation s9234 29.30 3.40 0.47 GB √ √ √ √ -
[1] 杨亚君, 陈章. 分块制造下硬件木马攻击方法及安全性分析[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 2019, 46(4): 167–175.YANG Yajun and CHEN Zhang. Hardware trojan attack methods and security analysis under split manufacturing[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2019, 46(4): 167–175. [2] GUIN U, HUANG K, DIMASE D, et al. Counterfeit integrated circuits: A rising threat in the global semiconductor supply chain[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2014, 102(8): 1207–1228. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2014.2332291 [3] 张跃军, 王佳伟, 潘钊, 等. 基于正交混淆的多硬件IP核安全防护设计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(8): 1847–1854. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180898ZHANG Yuejun, WANG Jiawei, PAN Zhao, et al. Hardware security for multi IPs protection based on orthogonal obfuscation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(8): 1847–1854. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180898 [4] DE A and GHOSH S. Preventing reverse engineering using threshold voltage defined multi-input camouflaged gates[C]. 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Technologies for Homeland Security, Waltham, USA, 2017: 1–6. [5] RAJENDRAN J, SAM M, SINANOGLU O, et al. Security analysis of integrated circuit camouflaging[C]. 2013 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer & Communications Security, Berlin, Germany, 2013: 709–720. [6] 徐金甫, 吴缙, 李军伟, 等. 基于敏感度混淆机制的控制型物理不可克隆函数研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(7): 1601–1609. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180775XU Jinfu, WU Jin, LI Junwei, et al. Controlled Physical unclonable function research based on sensitivity confusion mechanism[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(7): 1601–1609. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180775 [7] 孙子文, 叶乔. 利用震荡环频率特性提取多位可靠信息熵的物理不可克隆函数研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(1): 234–241. doi: 10.11999/JEIT191013SUN Ziwen and YE Qiao. Study on the physical unclonable function of the reliable information entropy extracted by the frequency characteristic of oscillating ring[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(1): 234–241. doi: 10.11999/JEIT191013 [8] ZHANG Jiliang, LIN Yaping, LYU Yongqiang, et al. A PUF-FSM binding scheme for FPGA IP protection and pay-per-device licensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2015, 10(6): 1137–1150. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2015.2400413 [9] ZHANG Jiliang and SHEN Chaoqun. Set-based obfuscation for strong PUFs against machine learning attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2021, 68(1): 288–300. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2020.3028508 [10] DOFE J and YU Qiaoyan. Novel dynamic state-deflection method for gate-level design obfuscation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2018, 37(2): 273–285. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2017.2697960 [11] KOUSHANFAR F. Provably secure active IC metering techniques for piracy avoidance and digital rights management[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2012, 7(1): 51–63. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2011.2163307 [12] CHAKRABORTY R S and BHUNIA S. RTL hardware IP protection using key-based control and data flow obfuscation[C]. The 23rd International Conference on VLSI Design, Bangalore, India, 2010: 405–410. [13] YASIN M, MAZUMDAR B, RAJENDRAN J J V, et al. SARLock: SAT attack resistant logic locking[C]. 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Hardware Oriented Security and Trust, McLean, USA, 2016: 236–241. [14] LI Liwei, WANG Pengjun, and ZHANG Yuejun. Design of anti-key leakage camouflage gate circuit for reverse engineering based on dummy vias[J]. Microelectronics Journal, 2019, 90: 163–168. doi: 10.1016/j.mejo.2019.06.006 -





 下载:
下载:
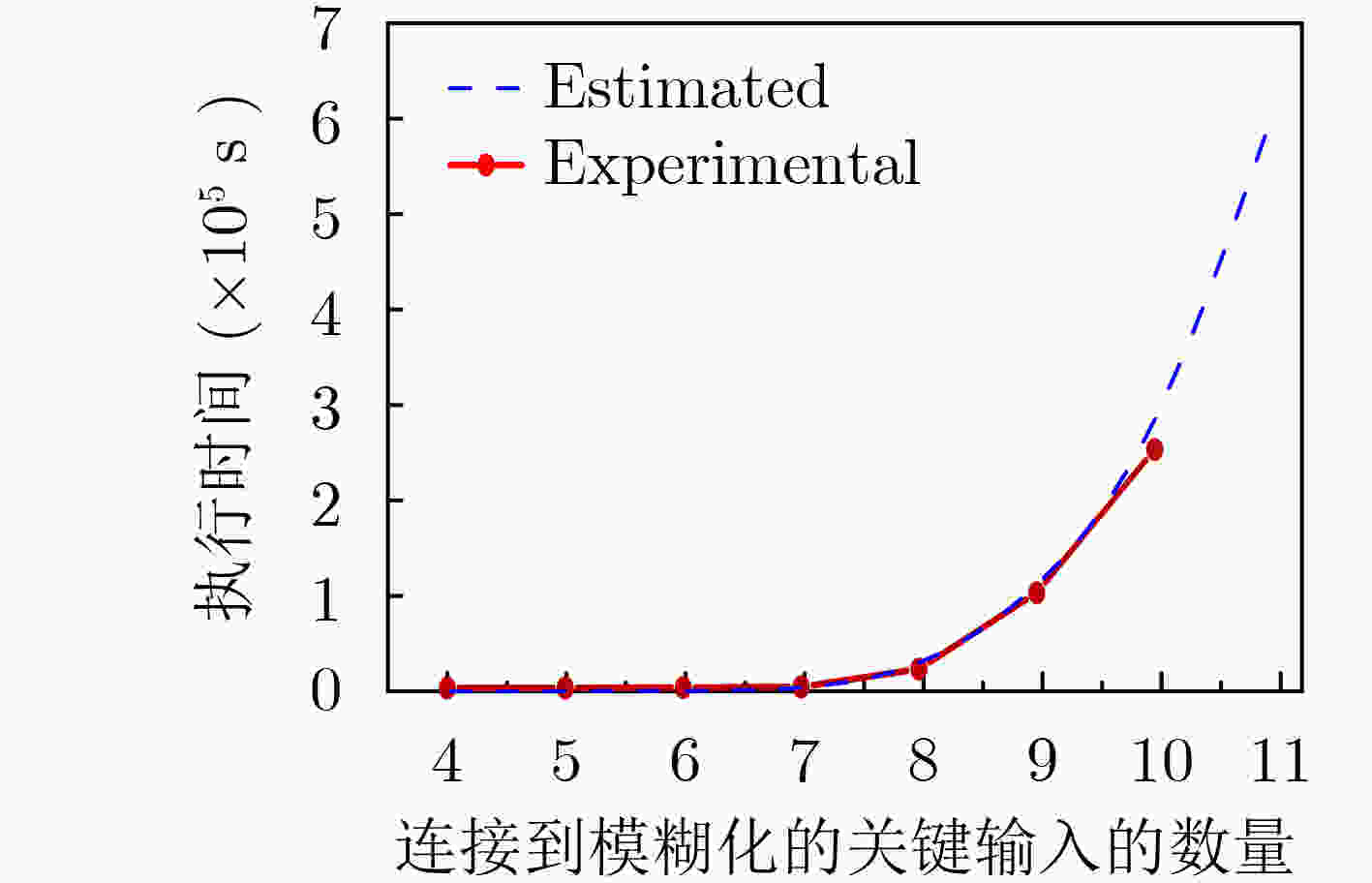


 下载:
下载:
