Accuracy of Precise Timing Based on Uncombined Precise Point Positioning Algorithm in BeiDou Navigation Satellite System
-
摘要: 全球导航卫星系统(GNSS)精密单点定位(PPP)技术具有操作简单、成本低廉、定位精度高等优点,在精密授时领域得到了广泛应用。针对现有研究中消电离层PPP模型的组合噪声大、卫星系统多采用全球定位系统(GPS)及实时动态场景少等问题,该文采用非组合PPP模型对北斗卫星导航系统(BDS)精密授时精度开展了研究,并利用Kalman滤波静态模型和动态加速模型进行参数估计。给出了静态和实时动态场景PPP处理策略,并利用超快速预报星历保证动态实时性。结果表明:在静态和实时动态条件下,非组合PPP模型精密授时精度均优于消电离层组合PPP模型;在静态条件下,考虑到BDS和GPS定位精度相当,且亚太地区BDS定位精度更高,BDS授时精度略高于GPS;在实时动态条件下,BDS和GPS精密授时精度在2 ns以内,但BDS授时精度略低于GPS,这是由于空间位置精度因子(PDOP)、载体速度突变和环境因素等的影响,而当完成收敛后,两种系统的授时精度相当,其钟差项中误差均在0.3 m以内。Abstract: Precise Point Positioning (PPP) of Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) has the advantages of simple operation, low cost, and high positioning accuracy, and has been widely used in precise timing. Considering the problems of high combined noise of ionosphere-free PPP model, major navigation satellite system being Global Positioning System (GPS), and fewer real-time dynamic scenes in the existing research, the uncombined PPP model is used to study the accuracy of timing in BeiDou navigation Satellite system (BDS). Static and dynamic models of Kalman filter is used in parameter estimation. PPP processing strategies for static and real-time dynamic scenarios are proposed, and ultra-fast forecast ephemeris is used to ensure real time. The results show that: Under static and real-time dynamic conditions, the accuracy of precise timing with the uncombined PPP model is better than that of the ionosphere-free PPP model; Under static condition, considering that the positioning accuracy of BDS and GPS is equivalent, and the positioning accuracy of BDS in the Asia Pacific Region is even higher, the timing accuracy of BDS is slightly higher than that of GPS; Under real-time dynamic condition, the precise timing accuracy of BDS and GPS is both within 2 ns. But owing to Position Dilution Of Precision (PDOP), sudden changes of carrier speed, and environmental factors, the timing accuracy of BDS is slightly lower. And when the convergence is completed, the timing accuracy of the two systems is equivalent, and the clock biases are all within 0.3 m.
-
表 1 静态实验所用IGS监测站的基本信息
监测站 位置 接收机类型 天线类型 GMSD 日本 TRIMBLE NETR9 TRM59800.00 KARR 澳大利亚 TRIMBLE NETR9 TRM59800.00 KZN2 俄罗斯 TRIMBLE ALLOY TRM59800.00 MAYG 法国 TRIMBLE NETR9 TRM59800.00 URUM 中国 JAVAD TRE_3 JAVRINGANT WUH2 中国 JAVAD TRE_3 JAVRINGANT 表 2 静态消电离层组合PPP模型处理策略
误差项 处理策略 卫星星历 IGS提供的精密星历 卫星钟差 IGS提供的精密钟差 对流层延迟 Saastamoinen模型改正干分量,
估计湿分量电离层延迟 消电离层组合 卫星天线相位中心改正 IGS提供的PCO, PCV产品 接收机天线相位中心改正 IGS提供的PCV产品 相位缠绕 模型改正 相对论效应 模型改正 地球自转 模型改正 参数估计与质量控制 处理策略 参数估计 (1)接收机坐标,SPP结果作为初始值,初始标准差为1000 m
(2)接收机钟差,SPP结果作为初始值,初始标准差为1000 m
(3)天顶对流层湿分量,初始值0.5 m,初始标准差0.01 m
(4)模糊度初始值为$\phi _{{\rm{IF}}}^s - P_{{\rm{IF}}}^s$,
标准差为1000 m数据质量控制 标准卡尔曼滤波 观测值随机模型 高度角定权 表 3 BDS/GPS各测站E, N, U方向RMS值(m)
监测站 BDS GPS E N U E N U GMSD 0.008 0.006 0.021 0.007 0.008 0.040 KARR 0.021 0.003 0.016 0.032 0.007 0.011 KZN2 0.016 0.004 0.043 0.008 0.006 0.021 MAYG 0.012 0.019 0.053 0.007 0.004 0.035 URUM 0.016 0.019 0.015 0.014 0.005 0.027 WUH2 0.017 0.009 0.049 0.015 0.011 0.045 表 4 BDS/GPS各测站E, N, U方向的STD(m)
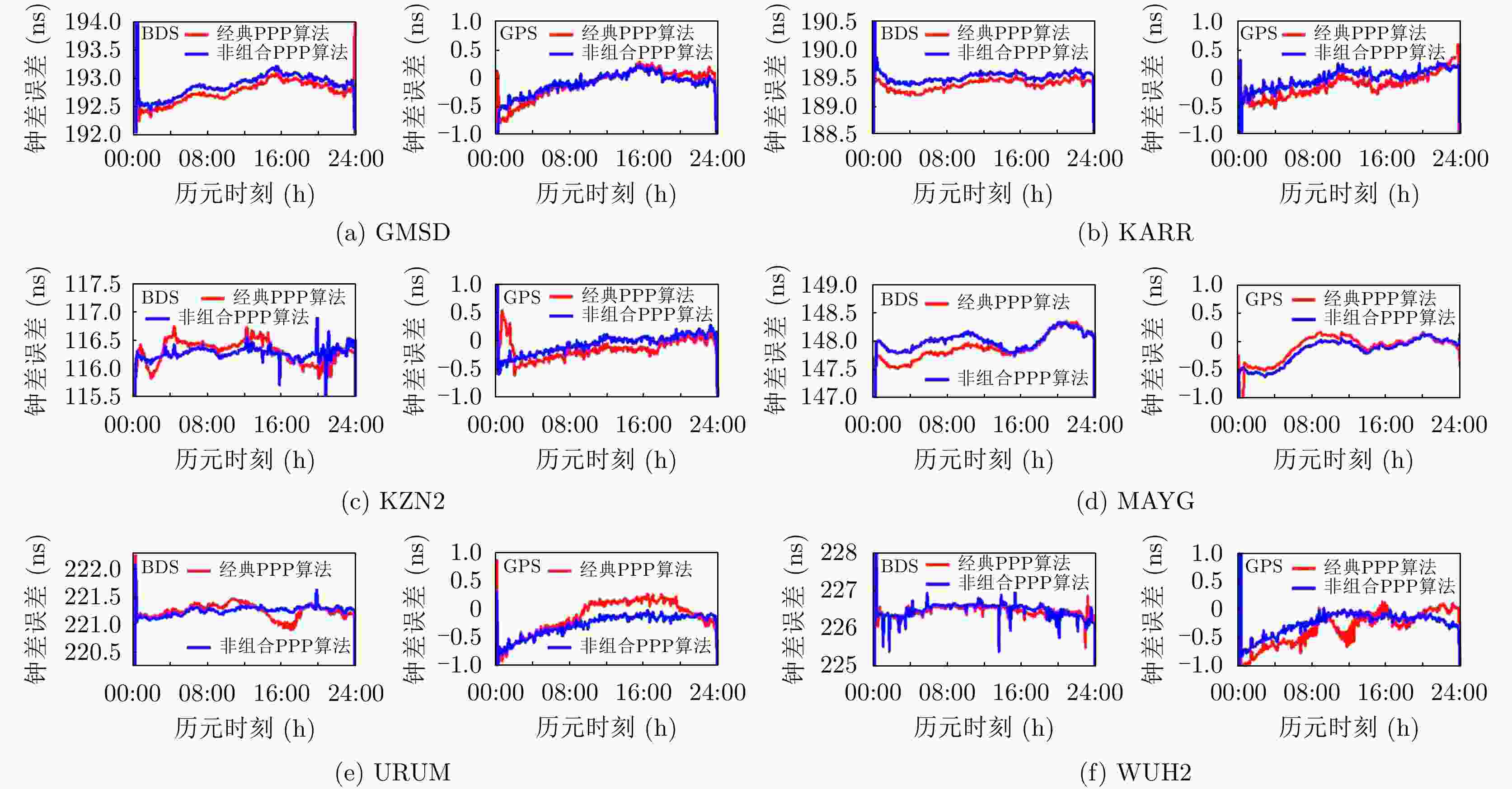
监测站 BDS GPS E N U E N U GMSD 0.006 0.005 0.015 0.004 0.004 0.001 KARR 0.010 0003 0.009 0.013 0.003 0.015 KZN2 0.003 0.002 0.006 0.008 0.003 0.004 MAYG 0.007 0.003 0.037 0.006 0.003 0.018 URUM 0.003 0.005 0.012 0.011 0.002 0.012 WUH2 0.009 0.003 0.041 0.009 0.002 0.016 表 5 GPS静态PPP钟差误差的RMS值(ns)
监测站 GPS 消电离层组合PPP 非组合PPP GMSD 0.257 0.187 KARR 0.245 0.147 KZN2 0.231 0.161 MAYG 0.323 0.258 URUM 0.186 0.222 WUH2 0.278 0.187 表 6 BDS/GPS静态PPP钟差解误差的STD(ns)
监测站 BDS GPS 消电离层组合 非组合 消电离层组合 非组合 GMSD 0.181 0.183 0.246 0.174 KARR 0.089 0.070 0.197 0.147 KZN2 0.203 0.131 0.167 0.150 MAYG 0.217 0.150 0.318 0.171 URUM 0.124 0.075 0.198 0.112 WUH2 0.103 0.148 0.205 0.103 表 7 动态PPP中参数估计处理策略
参数估计 处理策略 接收机坐标 SPP结果作为初始值,初始标准差为100 m 接收机速度 原始多普勒解为初始值,初始标准差5 m/s,
动态噪声为10 m/s接收机加速度 初始值为1×10–6 m/s2,初始标准差为5 m/s2,
动态噪声为1×10–2 m/s2接收机钟差 SPP结果作为初始值,初始标准差为1000 m 天顶对流层湿分量 初始值0.5 m,初始标准差为0.01 m 模糊度 初始值为$\phi _{{\rm{IF}}}^s - P_{{\rm{IF}}}^s$,标准差为1000 m 表 8 动态PPP钟差误差RMS, STD和均值(ns)
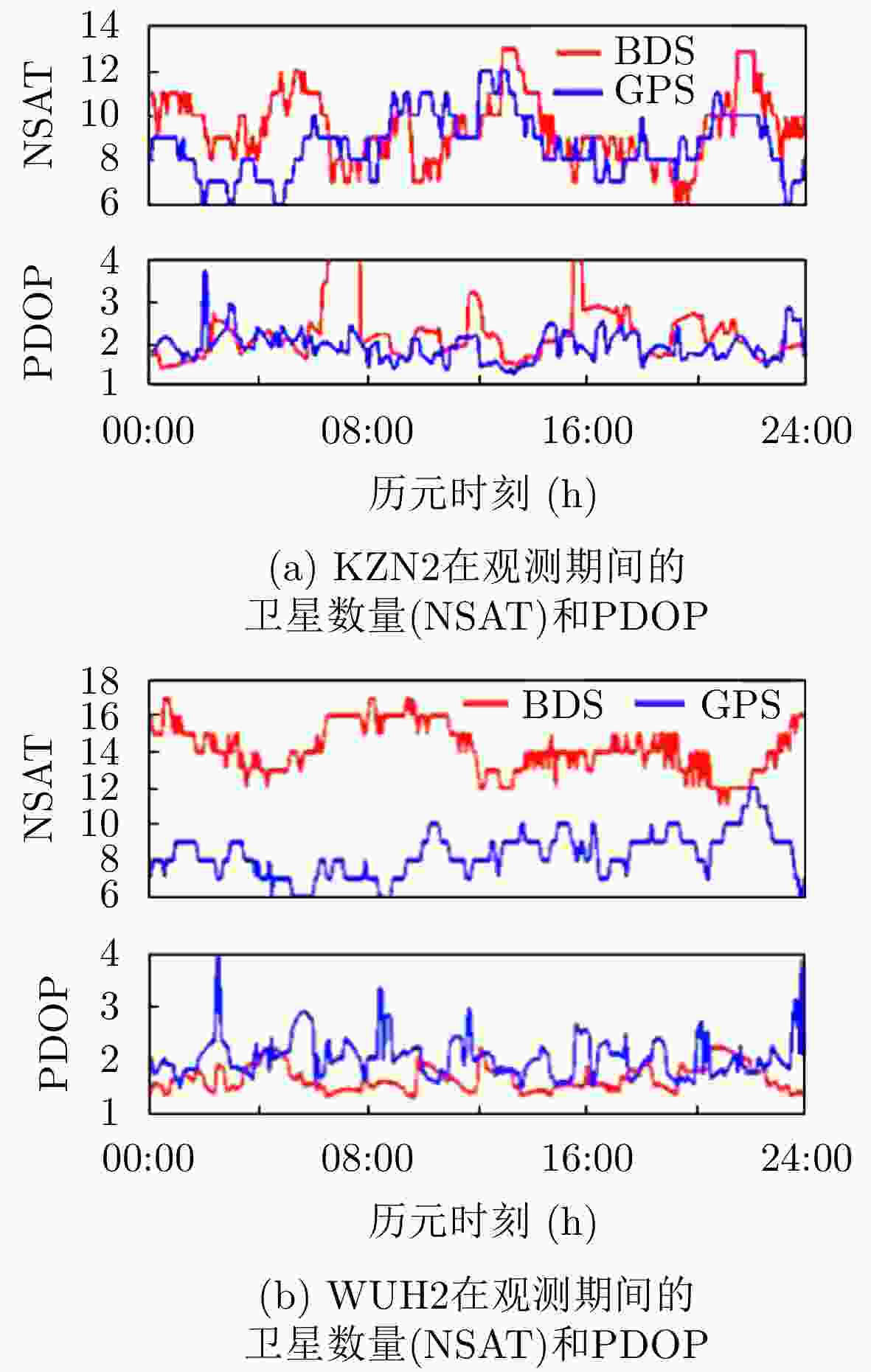
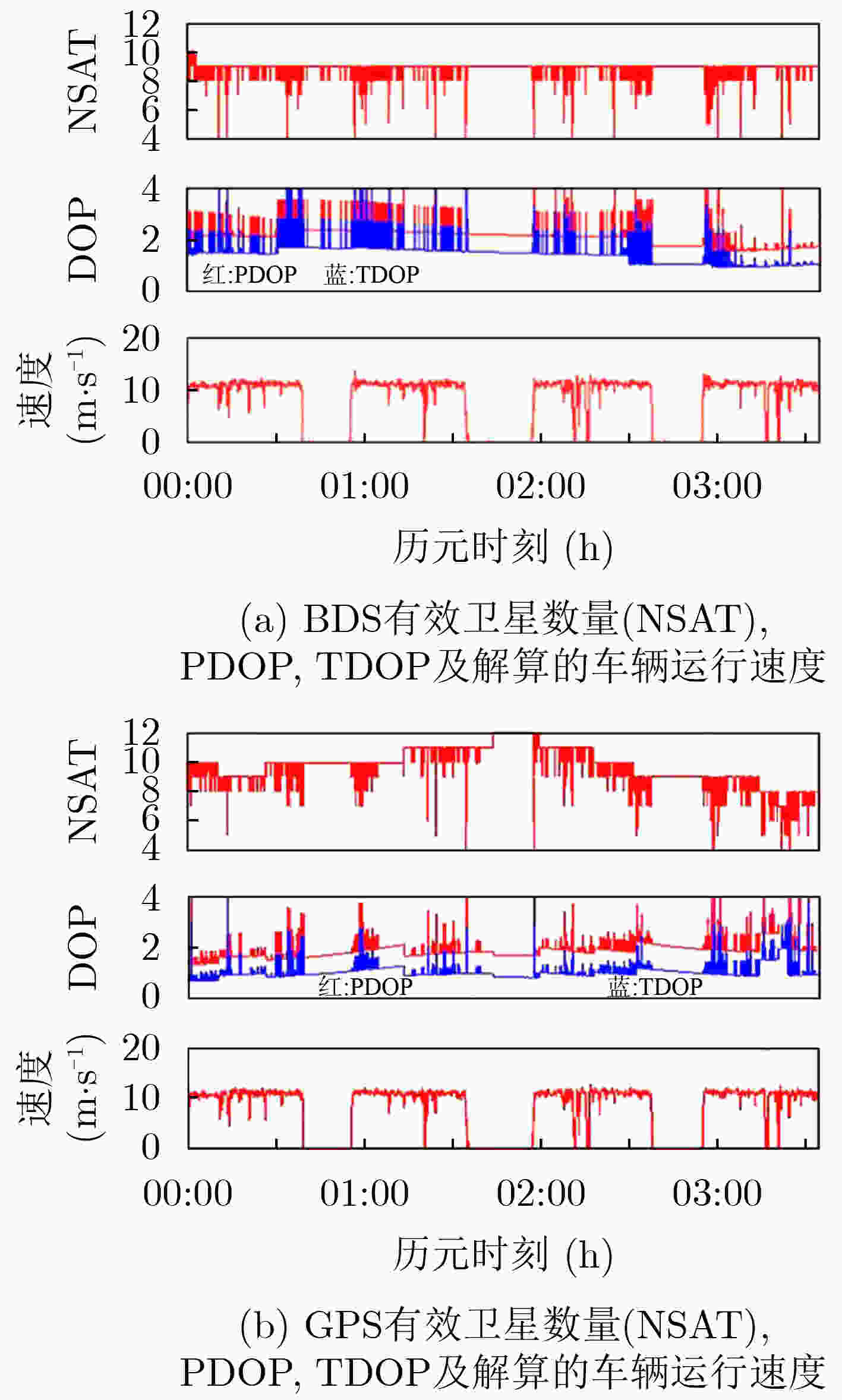
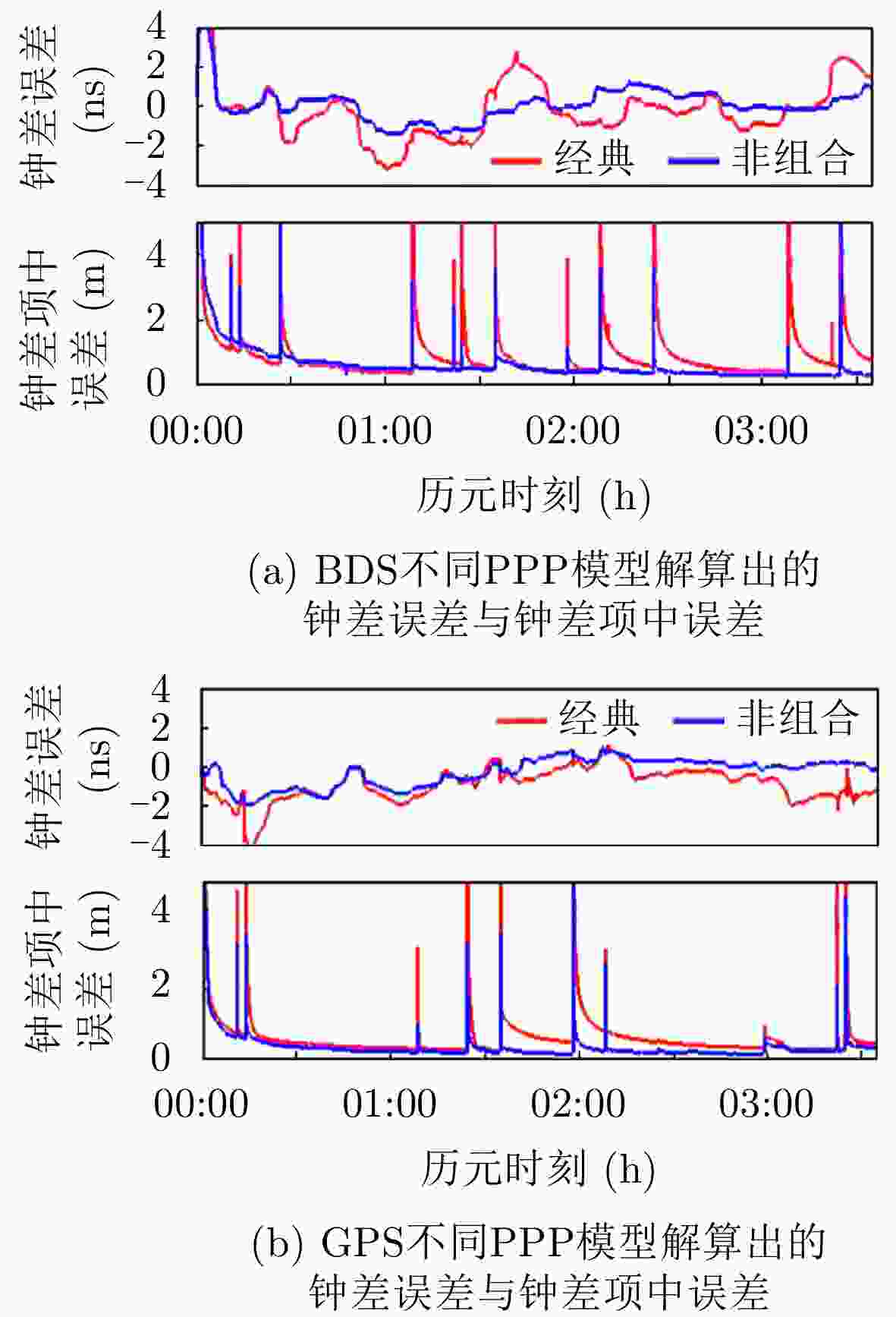
评估指标 GPS BDS 非组合 消电离层组合 非组合 消电离层组合 RMS 1.154 1.880 1.244 2.088 STD 1.079 1.309 1.237 2.079 均值 –0.409 –1.349 0.135 –0.193 -
[1] 杨元喜. 综合PNT体系及其关键技术[J]. 测绘学报, 2016, 45(5): 505–510. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2016.20160127YANG Yuanxi. Concepts of comprehensive PNT and related key technologies[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2016, 45(5): 505–510. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2016.20160127 [2] WANG Rong, XIONG Zhi, LIU Jianye, et al. Resilient fusion navigation based on failure influence level evaluation[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2019, 13(5): 721–729. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2018.5161 [3] DEFRAIGNE P, PINAT E, and BERTRAND B. Impact of Galileo-to-GPS-Time-Offset accuracy on multi-GNSS positioning and timing[J]. GPS Solutions, 2021, 25(2): 45. doi: 10.1007/s10291-021-01090-6 [4] 蔡洪亮, 孟轶男, 耿长江, 等. 北斗三号全球导航卫星系统服务性能评估: 定位导航授时、星基增强、精密单点定位、短报文通信与国际搜救[J]. 测绘学报, 2021, 50(4): 427–435. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2021.20200549CAI Hongliang, MENG Yinan, GENG Changjiang, et al. BDS-3 performance assessment: PNT, SBAS, PPP, SMC and SAR[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2021, 50(4): 427–435. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2021.20200549 [5] 丁硕. 基于北斗GEO卫星的精密共视时间频率传递方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院大学(中国科学院国家授时中心), 2020.DING Shuo. Study of the method of precise common-view time and frequency transfer via BDS GEO satellites[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National Time Service Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020. [6] PETIT G and DEFRAIGNE P. The performance of GPS time and frequency transfer: Comment on ‘A detailed comparison of two continuous GPS carrier-phase time transfer techniques’[J]. Metrologia, 2016, 53(3): 1003–1008. doi: 10.1088/0026-1394/53/3/1003 [7] 张小红, 蔡诗响, 李星星, 等. 利用GPS精密单点定位进行时间传递精度分析[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2010, 35(3): 274–278. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis2010.03.002ZHANG Xiaohong, CAI Shixiang, LI Xingxing, et al. Accuracy analysis of time and frequency transfer based on precise point positioning[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2010, 35(3): 274–278. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis2010.03.002 [8] 朱荷欢, 吴向阳, 高成发, 等. GPS系统精密单点定位模型与精密授时研究[J]. 东南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2013, 43(S2): 423–427. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0505.2013.S2.044ZHU Hehuan, WU Xiangyang, GAO Chengfa, et al. Research of model and precise timing based on precise point positioning in GPS system[J]. Journal of Southeast University:Natural Science Edition, 2013, 43(S2): 423–427. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0505.2013.S2.044 [9] 葛玉龙. 多频多系统精密单点定位时间传递方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院大学(中国科学院国家授时中心), 2020.GE Yulong. Research on methodology of multi-frequency and multi-GNSS precise point positioning time transfer[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National Time Service Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020. [10] HARMEGNIES A, DEFRAIGNE P, and PETIT G. Combining GPS and GLONASS in all-in-view for time transfer[J]. Metrologia, 2013, 50(3): 277–287. doi: 10.1088/0026-1394/50/3/277 [11] GE Yulong, ZHOU Feng, DAI Peipei, et al. Precise point positioning time transfer with multi-GNSS single-frequency observations[J]. Measurement, 2019, 146: 628–642. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2019.07.009 [12] 闫伟, 袁运斌, 欧吉坤, 等. 非组合精密单点定位算法精密授时的可行性研究[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2011, 36(6): 648–651. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis2011.06.015YAN Wei, YUAN Yunbin, OU Jikun, et al. Feasibility of precise timing with uncombined PPP[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2011, 36(6): 648–651. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis2011.06.015 [13] CAO Yu, HUANG Guanwen, XIE Wei, et al. Assessment and comparison of satellite clock offset between BeiDou-3 and other GNSSs[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Geophysica, 2021, 56(2): 303–319. doi: 10.1007/s40328-021-00334-8 [14] 宿晨庚, 郭树人, 刘旭楠, 等. 北斗三号基本系统空间信号质量评估[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(11): 2689–2697. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190683SU Chengeng, GUO Shuren, LIU Xunan, et al. Signal quality assessment of BDS-3 preliminary system[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(11): 2689–2697. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190683 [15] YANG Yuanxi, GAO Weiguang, GUO Shuren, et al. Introduction to Beidou-3 navigation satellite system[J]. Navigation, 2019, 66(1): 7–18. doi: 10.1002/navi.291 [16] 董孝松, 孙保琪, 杨海彦, 等. GNSS实时动态授时精度分析[J/OL]. 中国空间科学技术, http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1859.V.20210402.1825.002.html, 2021.DONG Xiaosong, SUN Baoqi, YANG Haiyan, et al. Accuracy analysis of GNSS real-time kinematic timing[J/OL]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1859.V.20210402.1825.002.html, 2021. [17] 赵兴旺, 王胜利, 刘超. GNSS精密单点定位理论与方法[M]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社, 2015: 92–93. [18] LI Juan and TANG Gongyou. Fault diagnosis for networked control systems with delayed measurements and inputs[J]. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2010, 4(6): 1047–1054. doi: 10.1049/iet-cta.2009.0062. [19] 贺成艳, 郭际, 卢晓春, 等. 北斗卫星导航系统B1信号伪距偏差问题研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(11): 2698–2704. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180074HE Chengyan, GUO Ji, LU Xiaochun, et al. Researches on pseudo-range biases of BeiDou navigation satellite system B1 signals[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(11): 2698–2704. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180074 [20] 刘丹, 王剑, 姜维, 等. 列车组合定位系统定位精度评估方法研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2019, 41(11): 79–87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2019.11.011LIU Dan, WANG Jian, JIANG Wei, et al. Research on positioning accuracy evaluation method for integrated train positioning system[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2019, 41(11): 79–87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2019.11.011 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
