Intelligent Anti-jamming Decision Algorithm for Frequency Hopping Network Based on Multi-agent Fuzzy Deep Reinforcemnet Learning
-
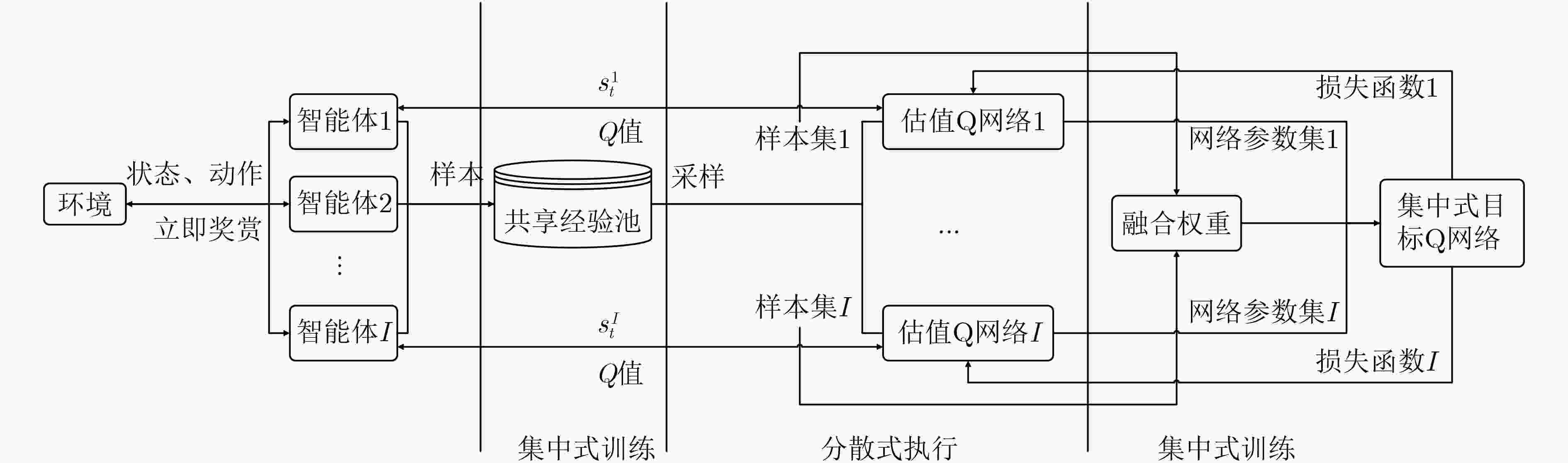
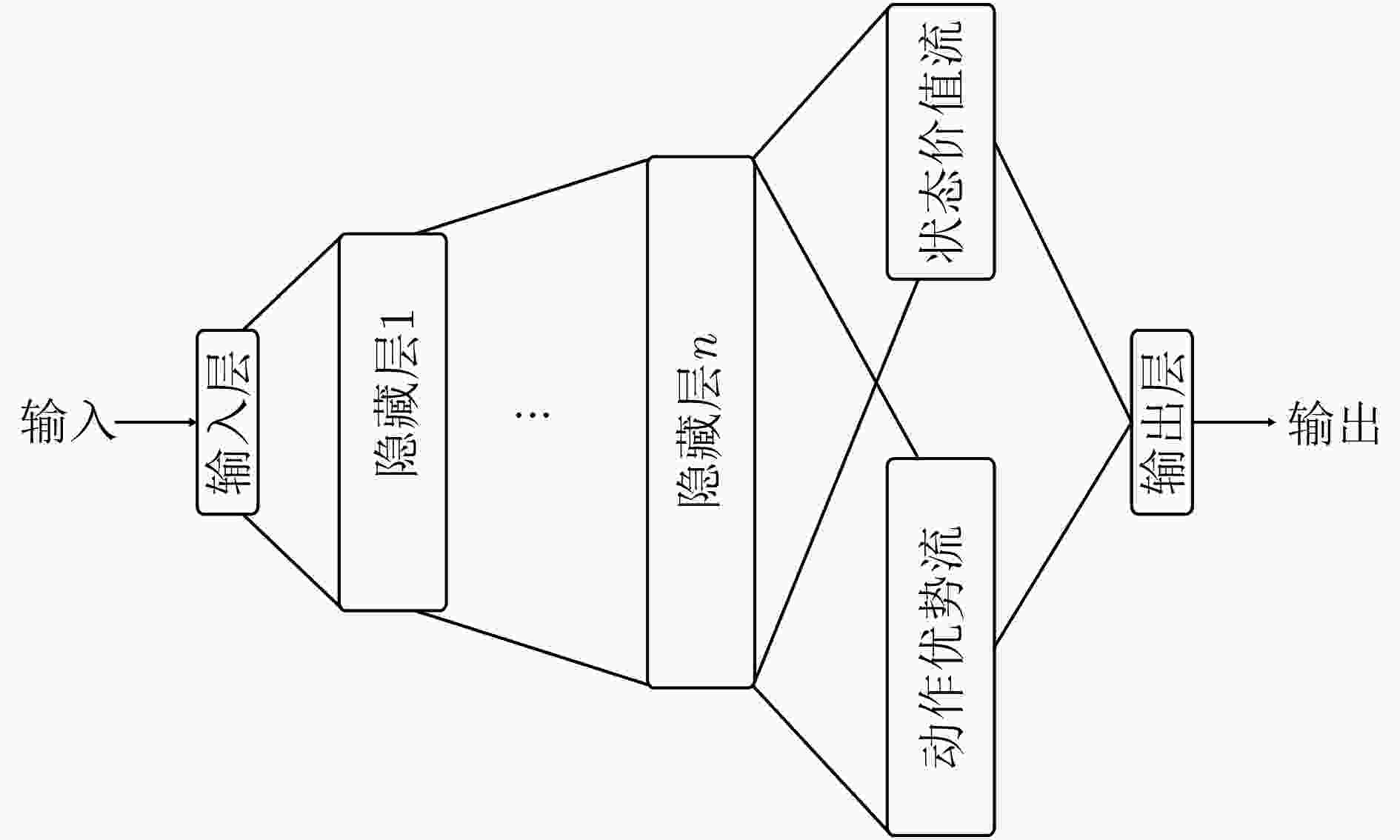
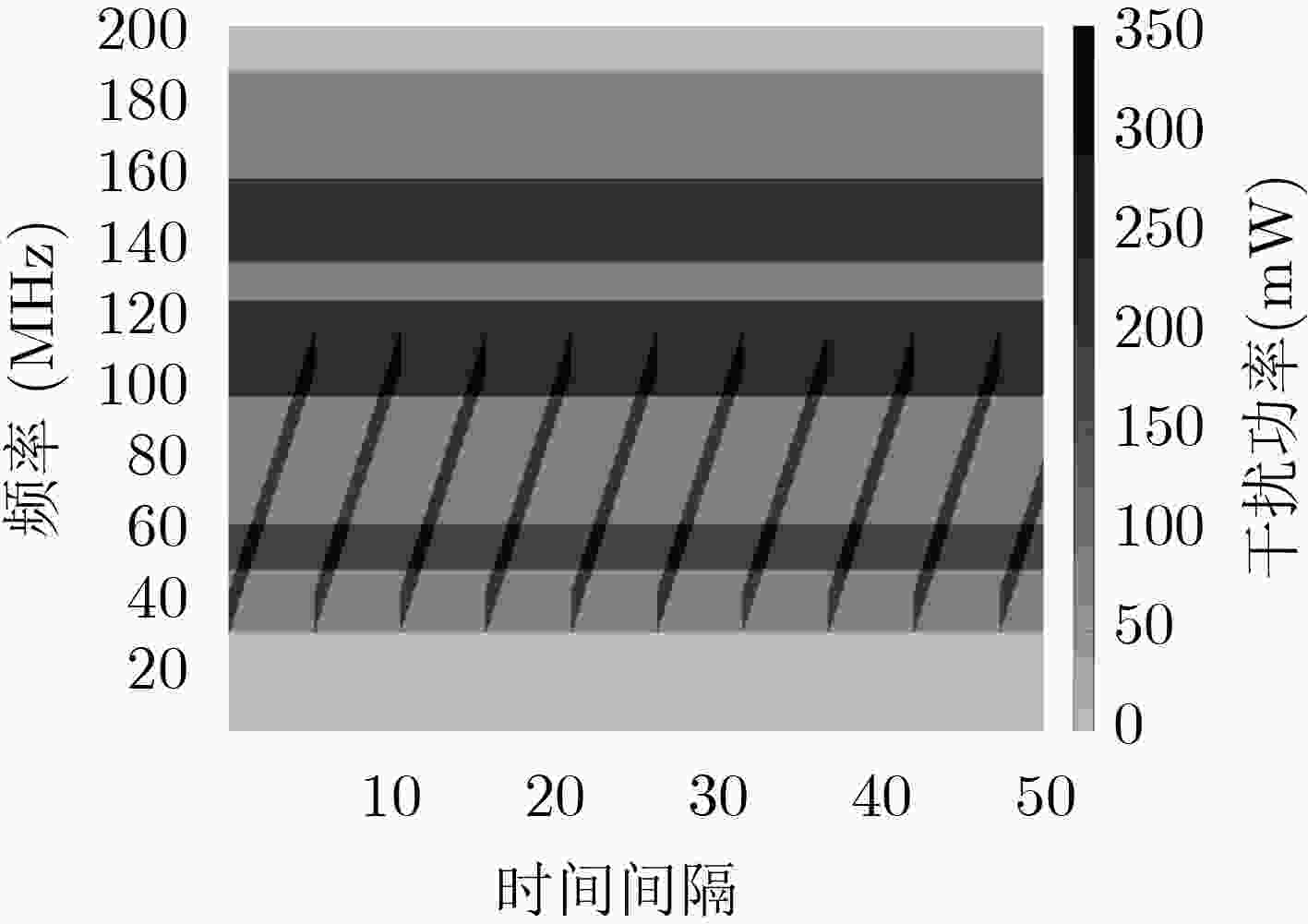
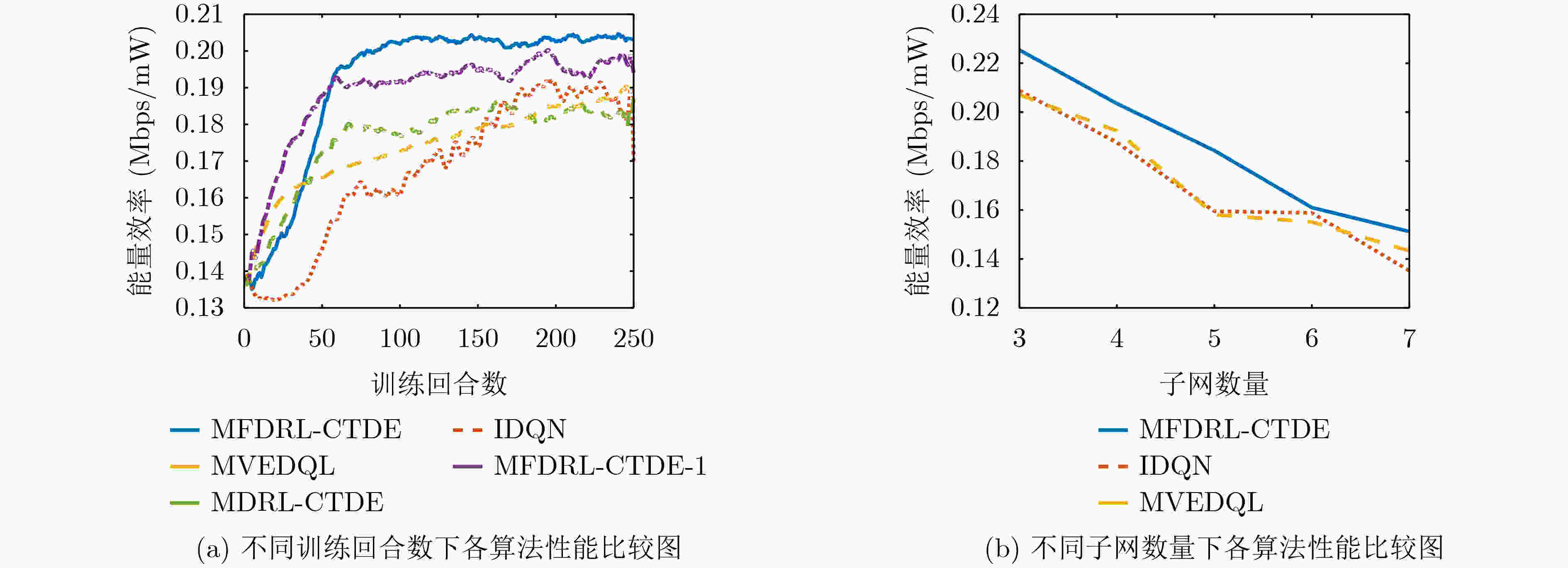
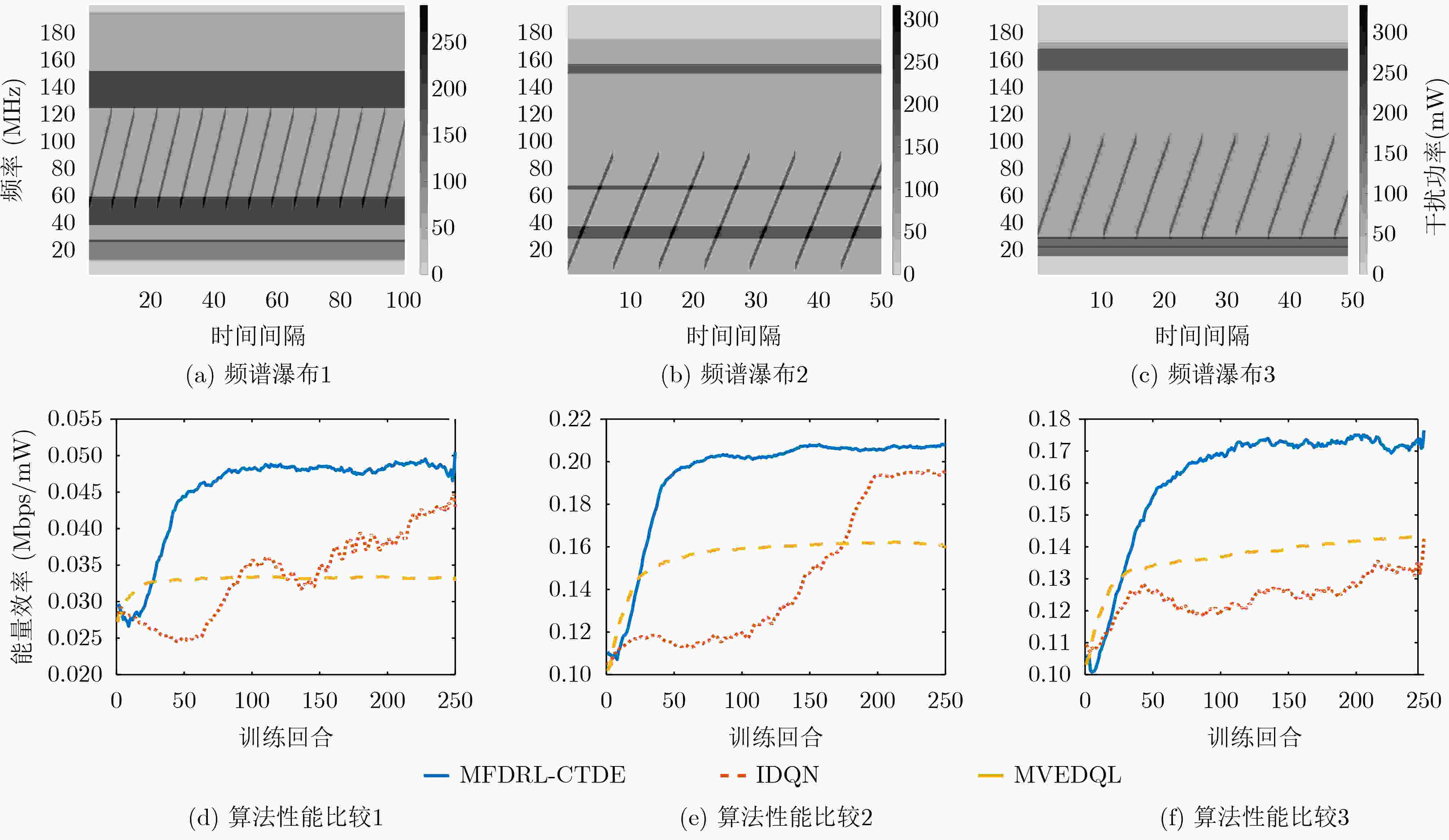
摘要: 为提高复杂电磁环境下跳频异步组网的抗干扰性能,该文提出一种基于集中式训练和分散式执行框架的多智能体模糊深度强化学习(MFDRL-CTDE)算法。针对多种干扰并存的复杂电磁环境和异步组网结构,设计了相应的状态-动作空间和奖赏函数。为应对智能体之间的相互影响和动态的环境,引入集中式训练和分散式执行(CTDE)框架。该文提出基于模糊推理系统的融合权重分配策略,用于解决网络融合过程中各智能体的权重分配问题。采用竞争性深度Q网络算法和优先经验回放技术以提高算法的效率。仿真结果表明,该算法在收敛速度和最佳性能方面都具有较大优势,且对多变复杂电磁环境具有较好的适应性。
-
关键词:
- 异步组网 /
- 多智能体 /
- 深度强化学习 /
- 集中式学习和分散式执行 /
- 模糊推理系统
Abstract: In order to improve the anti-jamming performance of frequency hopping asynchronous network in complex electromagnetic environment, a Multi-agent Fuzzy Deep Reinforcement Learning algorithm based on Centralized Training and Decentralized Execution (MFDRL-CTDE) is proposed. Considering the complex electromagnetic environment with multiple interferences and the asynchronous network structure, the corresponding state-action space and reward function are designed. For dealing with the interaction between agents and the dynamic environment, the framework of Centralized Training and Decentralized Execution (CTDE) is introduced. Then, a fusion weight allocation strategy based on fuzzy inference system is proposed to solve the weight allocation problem in the process of network fusion. And the Dueling DQN algorithm and the prioritized experience replay technology are used to improve the efficiency of the algorithm. The simulation results show that the algorithm has a great advantage in convergence speed and best performance, and has good adaptability to the changeable complex electromagnetic environment. -
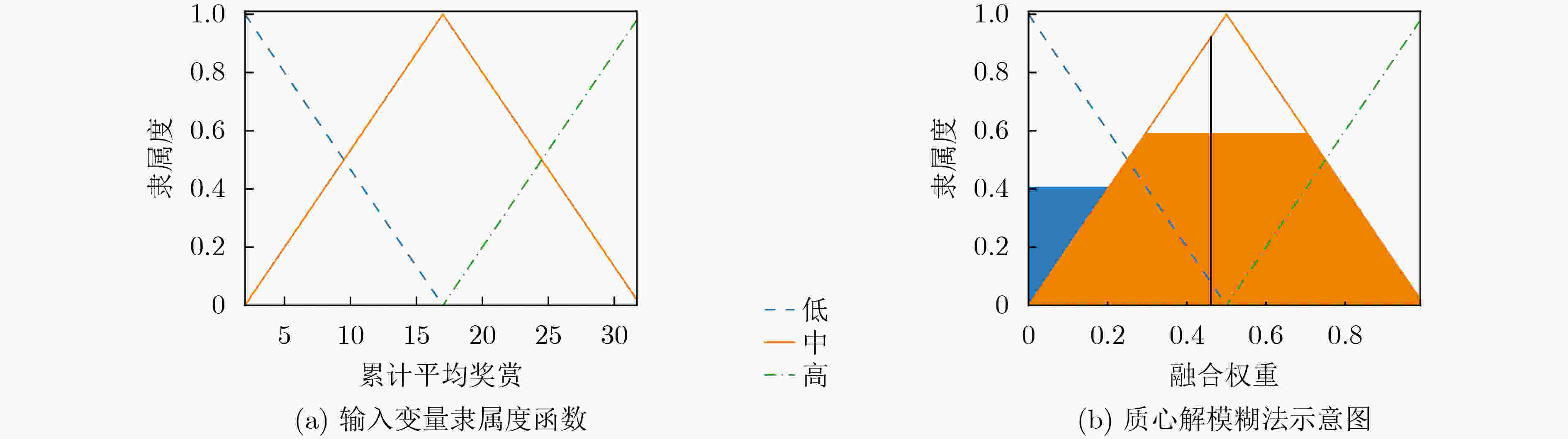
表 1 模糊规则定义
融合权重$ {w_{{F_i}}} $ 累计平均奖赏$ r{'_i} $ 低 中 高 累计平均样本
优先度$ g{'_i} $低 中 高 高 中 低 中 高 高 低 低 中 区间 累计平均奖赏$ r{'_i} $ $ \left[ {r{'_{\min }},r{'_{\max }}} \right] $ 累计平均样本优先度$ g{'_i} $ $ \left[ {g{'_{\min }},g{'_{\max }}} \right] $ 融合权重$ {w_{{F_i}}} $ [0, 1] -
[1] WANG Qian, ZHANG Feng, ZHAO Jing, et al. Application of HBM2 data storage in time and frequency hopping network communication system[C]. The 2020 IEEE 6th International Conference on Computer and Communications, Chengdu, China, 2020: 1799–1803. [2] 孙杜娟, 马迁, 王睿. 海上大型编队短波跳频组网问题研究[J]. 指挥控制与仿真, 2020, 42(1): 25–28.SUN Dujuan, MA Qian, and WANG Rui. Research on the large warship fleet HF frequency hopping network[J]. Command Control &Simulation, 2020, 42(1): 25–28. [3] 王泽. 同步组网跳频电台网络系统的研究与实现[D]. [硕士论文], 北京化工大学, 2015.WANG Ze. Research and implementation of frequency-hopping radio network system with synchronous networking[D]. [Master dissertation], Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2015. [4] 古稀林, 王超, 冯志先, 等. 移动Ad-hoc网络中无线跳频频率资源分配机制研究[J]. 通信技术, 2019, 52(3): 646–652.GU Xilin, WANG Chao, FENG Zhixian, et al. Wireless hopping-frequency planning algorithm in mobile ad-hoc network[J]. Communications Technology, 2019, 52(3): 646–652. [5] 崔佩璋, 全厚德, 张世杰. 跳频组网同频干扰消除方法研究[J]. 中国测试, 2014, 40(5): 115–118. doi: 10.11857/j.issn.1674-5124.2014.05.030CUI Peizhang, QUAN Houde, and ZHANG Shijie. Research on eliminating co-channel interference of frequency-hopping communication network[J]. China Measurement &Test, 2014, 40(5): 115–118. doi: 10.11857/j.issn.1674-5124.2014.05.030 [6] YOO S J, WON J M, SEO M, et al. Dynamic frequency hopping channel management in cognitive radio ad-hoc networks[C]. The 2015 21st Asia-Pacific Conference on Communications, Kyoto, Japan, 2015: 422–426. [7] 罗明刚. 无线通信抗干扰技术分析[J]. 中国新通信, 2020, 22(12): 10–11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4866.2020.12.009LUO Minggang. Analysis of wireless communication anti-jamming technology[J]. China New Telecommunications, 2020, 22(12): 10–11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4866.2020.12.009 [8] 陈前斌, 谭颀, 贺兰钦, 等. 云雾混合网络下基于多智能体架构的资源分配及卸载决策研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(9): 2654–2662. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200256CHEN Qianbin, TAN Qi, HE Lanqin, et al. Research on resource allocation and offloading decision based on multi-agent architecture in cloud-fog hybrid network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(9): 2654–2662. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200256 [9] NAEEM F, SRIVASTAVA G, and TARIP M. A software defined network based fuzzy normalized neural adaptive multipath congestion control for the internet of things[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2020, 7(4): 2155–2164. doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2020.2991106 [10] 徐琳, 赵知劲. 基于CBR与合作Q学习的分布式CRN资源分配算法[J]. 电信科学, 2019, 35(2): 35–42.XU Lin and ZHAO Zhijin. A distributed CRN resource allocation algorithm based on CBR and cooperative Q-learning[J]. Telecommunications Science, 2019, 35(2): 35–42. [11] YANG Ning, ZHANG Haijun, and BERRY R. Partially observable multi-agent deep reinforcement learning for cognitive resource management[C]. 2020 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Taipei, China, 2020: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/GLOBECOM42002.2020.9322150. [12] MAJUMDAR A, BENAVIDEZ P, and JAMSHIDI M. Multi-agent exploration for faster and reliable deep Q-learning convergence in reinforcement learning[C]. 2018 World Automation Congress, Stevenson, USA, 2018: 1–6. doi: 10.23919/WAC.2018.8430409. [13] KONG Weiren, ZHOU Deyun, and YANG Zhen. Air combat strategies generation of CGF based on MADDPG and reward shaping[C]. 2020 International Conference on Computer Vision, Image and Deep Learning, Chongqing, China, 2020: 651–655. doi: 10.1109/CVIDL51233.2020.000-7. [14] 李红光, 郭英, 张东伟, 等. 基于欠定盲源分离的同步跳频信号网台分选[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(2): 319–328. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190920LI Hongguang, GUO Ying, ZHANG Dongwei, et al. Synchronous frequency hopping signal network station sorting based on underdetermined blind source separation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(2): 319–328. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190920 [15] MAN Jiaxi, LI Wei, WANG Hong, et al. On the technology of frequency hopping communication network-station selection[C]. 2021 International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Information Engineering, Zhengzhou, China, 2021: 35–41. doi: 10.1109/ECIE52353.2021.00015. [16] JIANG Fu, ZHENG Chuyu, GAO Dianzhu, et al. A novel multi-agent cooperative reinforcement learning method for home energy management under a peak power-limiting[C]. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Toronto, Canada, 2020: 350–355. doi: 10.1109/SMC42975.2020.9282976. [17] 严季, 梁涛, 祈竹. 变跳速、变间隔跳频通信技术研究[J]. 无线通信技术, 2012, 21(4): 25–29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8329.2012.04.006YAN Ji, LIANG Tao, and QI Zhu. Research on the frequenct hopping communication technology of variable hopping rate and variable interval[J]. Wireless Communication Technology, 2012, 21(4): 25–29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8329.2012.04.006 [18] LI Menglin, CHEN Shaofei, and CHEN Jing. Adaptive learning: A new decentralized reinforcement learning approach for cooperative multiagent systems[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 99404–99421. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2997899 [19] 叶梓峰, 王永华, 万频, 等. 基于优先记忆库结合竞争深度Q网络的动态功率控制[J]. 电讯技术, 2019, 59(10): 1132–1139. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2019.10.004YE Zifeng, WANG Yonghua, WAN Pin, et al. A dynamic power control strategy based on dueling deep Q network with prioritized experience replay[J]. Telecommunication Engineering, 2019, 59(10): 1132–1139. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2019.10.004 [20] HUANG Chong, ZHONG Jie, GONG Yu, et al. Novel deep reinforcement learning-based delay-constrained buffer-aided relay selection in cognitive cooperative networks[J]. Electronics Letters, 2020, 56(21): 1148–1150. doi: 10.1049/el.2020.1495 [21] 王雪, 金涛, 钱志鸿, 等. D2D中继辅助通信的能效优化算法研究[J]. 通信学报, 2020, 41(3): 71–79. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2020048WANG Xue, JIN Tao, QIAN Zhihong, et al. Research on maximizing energy efficiency for relay-aided D2D communication[J]. Journal on Communications, 2020, 41(3): 71–79. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2020048 [22] LIU Xin, XU Yuhua, JIA Luliang, et al. Anti-jamming communications using spectrum waterfall: A deep reinforcement learning approach[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2018, 22(5): 998–1001. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2018.2815018 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
