Monaural Speech Separation Method Based on Deep Learning Feature Fusion and Joint Constraints
-
摘要: 为了提高单通道语音分离性能,该文提出基于深度学习特征融合和联合约束的单通道语音分离方法。传统基于深度学习的分离算法的损失函数只考虑了预测值和真实值的误差,这使得分离后的语音与纯净语音之间误差较大。该文提出一种新的联合约束损失函数,该损失函数不仅约束了理想比值掩蔽的预测值和真实值的误差,还惩罚了相应幅度谱的误差。另外,为了充分利用多种特征的互补性,提出一种含特征融合层的卷积神经网络(CNN)结构。利用该CNN提取多通道输入特征的深度特征,并在融合层中将深度特征与声学特征融合用来训练分离模型。由于融合构成的特征含有丰富的语音信息,具有强的语音信号表征能力,使得分离模型预测的掩蔽更加准确。实验结果表明,从信号失真比(SDR) 、主观语音质量评估( PESQ)和短时客观可懂度(STOI)3个方面评价,相比其他优秀的基于深度学习的语音分离方法,该方法能够更有效地分离目标语音。Abstract: To improve the performance of monaural speech separation, a monaural speech separation method based on deep learning feature fusion and joint constraints is proposed. The loss function of the traditional separation algorithm based on deep learning only considers the error between the predicted value and the true one, which makes the error between the separated speech and the pure speech larger. To combat it, a new joint constrained loss function is proposed, which not only constrains the error between the predicted value and the true one of ideal ratio mask, but also penalizes the error of the corresponding amplitude spectrum. In addition, to make full use of the complementarity of multiple features, a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) structure with feature fusion layer is proposed, which extracts the depth feature of the multi-channel input feature, and then fuses the depth feature and the acoustic feature in the fusion layer to train the separation model. The fused separation feature contains abundant acoustic information and has a strong acoustic representative ability, which makes the mask predicted by the separation model more accurate. The experimental results show that from Signal Distortion Ratio (SDR), Perceptual Evaluation of Speech Quality (PESQ) and Short-Time Objective Intelligibility (STOI), compared with other excellent speech separation methods based on deep learning, the proposed method can separate the mixed speech more effectively.
-
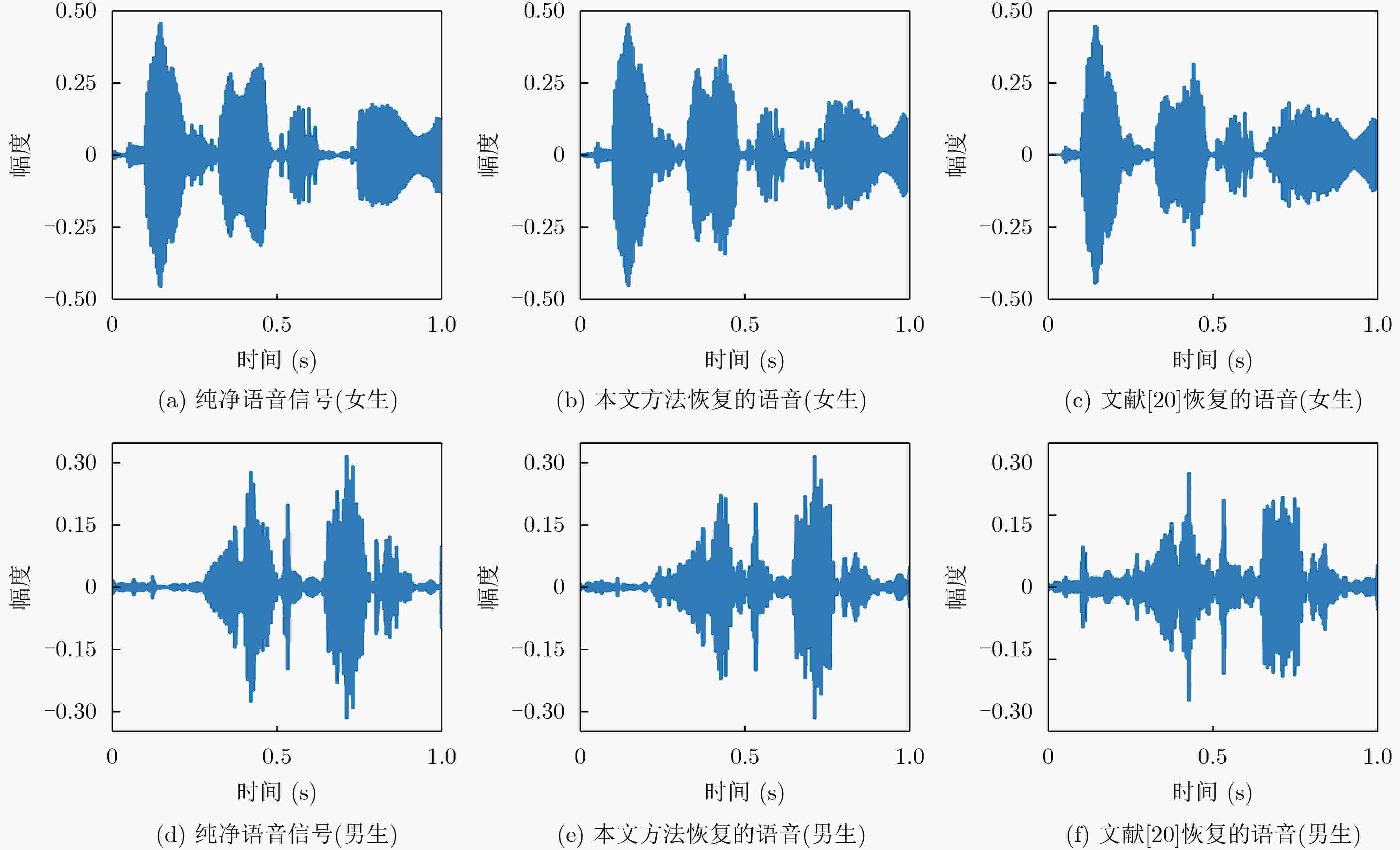
图 8 本文方法和文献[20]时域波形对比
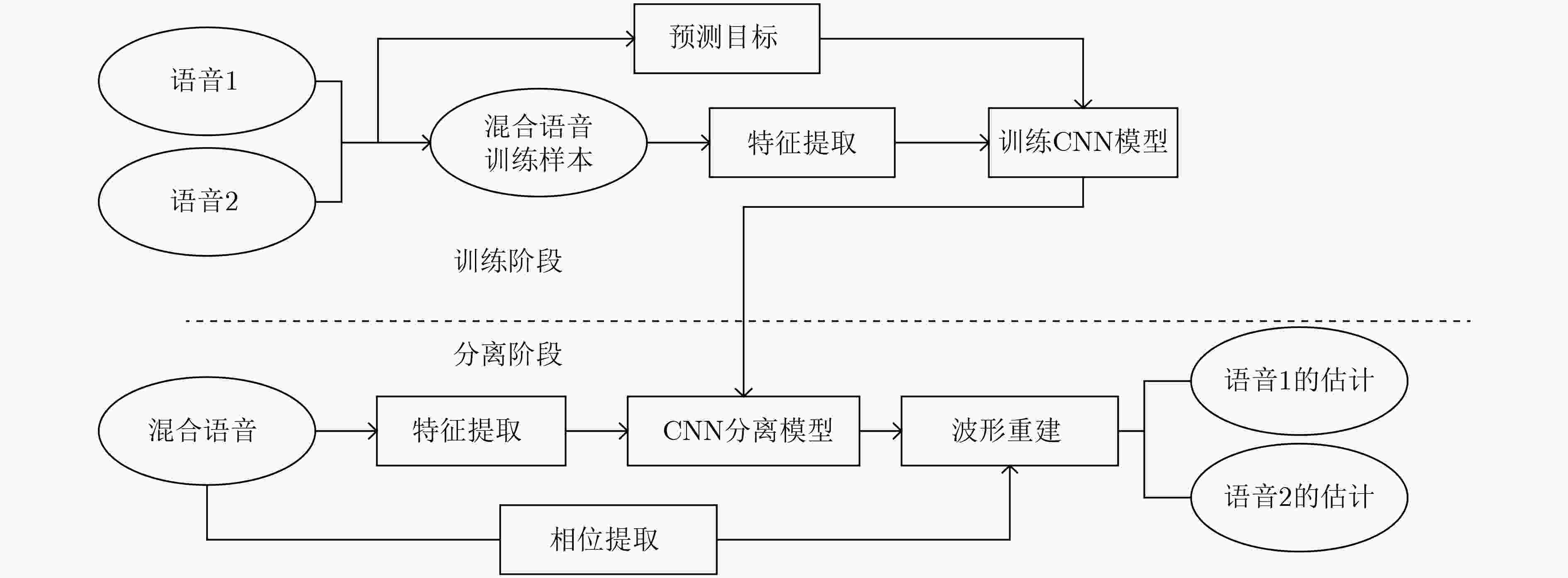
表 1 基于CNN特征融合的单通道语音分离联合约束算法流程
(1) 训练阶段: 输入:混合语音信号的${{\boldsymbol{s}}_{{\rm{train}}} }$、目标语音信号${{\boldsymbol{s}}_{1{\rm{train}}} }$和其他源语音信号。 输出:训练好的分离模型。 步骤1 首先对目标源语音和混合语音做分帧处理后进行STFT, 归一化后的混合信号幅度谱${\boldsymbol{Y} }_{\mathrm{t}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n} }$,目标信号的幅度谱${{\boldsymbol{Y}}_{1{\rm{train} } } }$和
其他源语音信号的幅度谱,还有功率谱${\left\| { {{\boldsymbol{Y}}_{ {\rm{train} } } } } \right\|^2}$以及对数功率谱$\lg {\left\| { {{\boldsymbol{Y}}_{{\rm{train}}} } } \right\|^2}$。步骤2 通过式(10)计算得到目标信号的理想比值掩蔽。
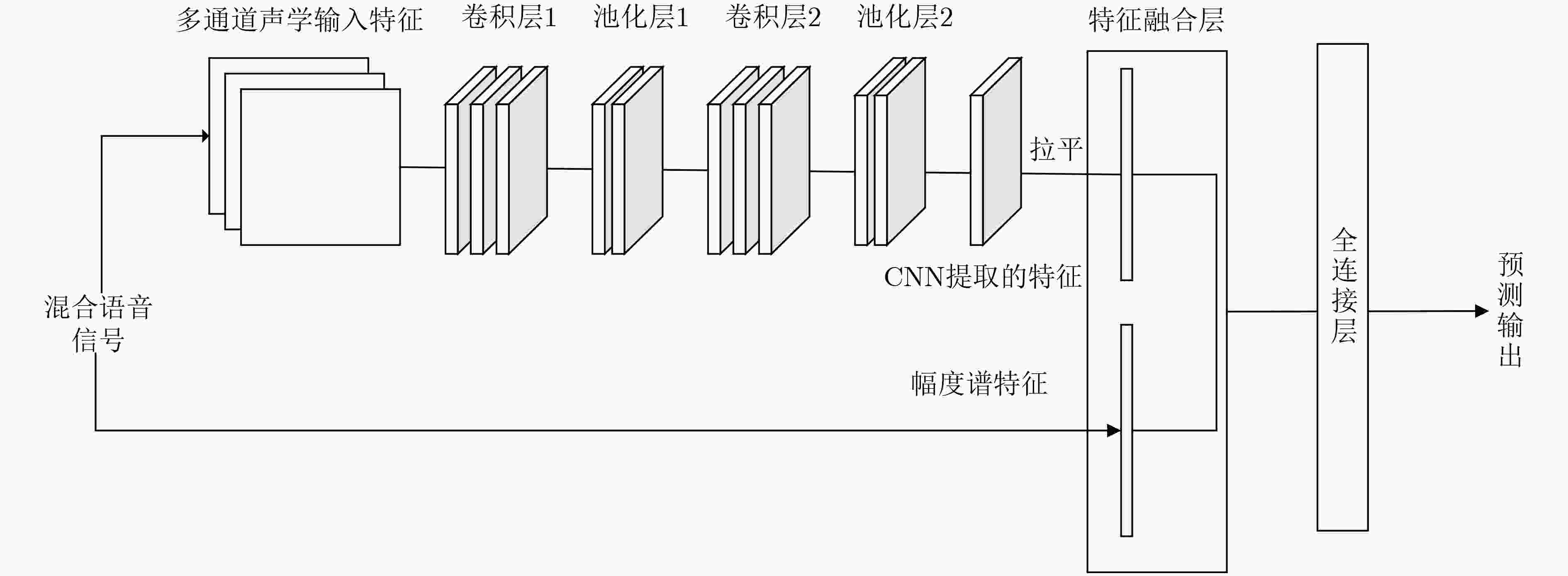
步骤3 $\left[ { {{\boldsymbol{Y}}_{{\rm{train}}} },{ {\left\| { {{\boldsymbol{Y}}_{{\rm{train}}} } } \right\|}^2},\lg { {\left\| { {{\boldsymbol{Y}}_{{\rm{train}}} } } \right\|}^2} } \right]$作为CNN输入特征和${{\boldsymbol{M}}_{1{\rm{train}}} }$作为分离模型的输出目标。步骤4 在前向传播阶段,随机初始化每层神经元的权重和偏置。将CNN的输出特征和${{\boldsymbol{Y}}_{{\rm{train}}} }$进行拼接融合作为全连层的输入,估计
比值掩蔽${\hat {\boldsymbol{M}}_{1{\rm{train}}} }$。步骤5 在反向传播阶段,通过整合优化器寻优使得联合损失函数式(3)最小,迭代调整每层神经元的权重和偏置。 步骤6 得到训练完好的用于分离的深度神经网络。 (2) 分离阶段: 输入:测试信号${{\boldsymbol{s}}_{ {\rm{test} } } }$和训练好的分离模型。 输出:估计的目标值${\hat {\boldsymbol{M}}_{1{\rm{test}}} }$。 步骤1 首先对测试的混合语音做预处理之后进行STFT, 归一化后得到混合信号幅度谱 ${{\boldsymbol{Y}}_{{\rm{test}}} }$,还有功率谱${\left\| { {{\boldsymbol{Y}}_{{\rm{test}}} } } \right\|^2}$以及对数功率谱
$\lg {\left\| { {{\boldsymbol{Y}}_{{\rm{test}}} } } \right\|^2}$和混合语音相位谱${{\boldsymbol{P}}_{{\rm{test}}} }$。步骤2 获得分离模型输出估计的目标值${\hat {\boldsymbol{M}}_{1{\rm{test}}} }$。 (3) 语音重构阶段: 步骤1 利用${\hat {\boldsymbol{M}}_{1{\rm{test}}} }$和混合语音幅度谱通过式(11)可以得到估计的目标语音帧幅度谱${\hat {\boldsymbol{S}}_{1{\rm{test}}} }$。 步骤2 利用估计的幅度谱和提取的混合语音相位谱得到估计语音的频谱。 步骤3 通过ISTFT得到目标语音信号帧的时域信号,所有帧连接得到目标语音信号。 表 2 本文方法与基于DNN方法性能对比
方法比较 性别组合 SDR(dB) PESQ STOI
本文方法F-F 8.4626 2.567 0.76 F-M 10.6765 2.887 0.88 M-M 7.7658 2.335 0.65
文献[20]方法F-F 7.3623 2.306 0.68 F-M 8.9548 2.632 0.80 M-M 6.9021 2.061 0.59 -
[1] 田元荣, 王星, 周一鹏. 一种新的基于稀疏表示的单通道盲源分离算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(6): 1371–1378. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160888TIAN Yuanrong, WANG Xing, and ZHOU Yipeng. Novel single channel blind source separation algorithm based on sparse representation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(6): 1371–1378. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160888 [2] 付卫红, 张琮. 基于步长自适应的独立向量分析卷积盲分离算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(9): 2158–2164. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171156FU Weihong and ZHANG Cong. Independent vector analysis convolutive blind separation algorithm based on step-size adaptive[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(9): 2158–2164. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171156 [3] 李红光, 郭英, 张东伟, 等. 基于欠定盲源分离的同步跳频信号网台分选[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(2): 319–328. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190920LI Hongguang, GUO Ying, ZHANG Dongwei, et al. Synchronous frequency hopping signal network station sorting based on underdetermined blind source separation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(2): 319–328. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190920 [4] UDREA R M, CIOCHINA S, and VIZIREANU D N. Multi-band bark scale spectral over-subtraction for colored noise reduction[C]. International Symposium on Signals, Circuits and Systems, Iasi, Romania, 2005: 311–314. [5] CHEN Jingdong, BENESTY J, HUANG Yiteng, et al. New insights into the noise reduction wiener filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2006, 14(4): 1218–1234. doi: 10.1109/TSA.2005.860851 [6] WIEM B, ANOUAR B M M, and AICHA B. Monaural speech separation based on linear regression optimized using gradient descent[C]. 2020 5th International Conference on Advanced Technologies for Signal and Image Processing, Sousse, Tunisia, 2020: 1–6. [7] WANG Chunpeng and ZHU Jie. Neural network based phase compensation methods on monaural speech separation[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Shanghai, China, 2019: 1384–1389. [8] SUN Yang, WANG Wenwu, CHAMBERS J, et al. Two-stage monaural source separation in reverberant room environments using deep neural networks[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2019, 27(1): 125–139. doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2018.2874708 [9] XIAN Yang, SUN Yang, WANG Wenwu, et al. Two stage audio-video speech separation using multimodal convolutional neural networks[C]. 2019 Sensor Signal Processing for Defence Conference (SSPD), Brighton, UK, 2019: 1–5. [10] LIU Yuzhou, DELFARAH M, and WANG Deliang. Deep casa for talker-independent monaural speech separation[C]. ICASSP 2020 - 2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 2020: 6354–6358. [11] WANG Deliang. On ideal binary mask as the computational goal of auditory scene analysis[M]. DIVENYI P. Speech Separation by Humans and Machines. New York: Springer, 2005, 60: 63–64. [12] KIM G, LU Yang, HU Yi, et al. An algorithm that improves speech intelligibility in noise for normal-hearing listeners[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2009, 126(3): 1486–1494. doi: 10.1121/1.3184603 [13] HAN Kun and WANG Deliang. A classification based approach to speech segregation[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2012, 132(5): 3475–3483. doi: 10.1121/1.4754541 [14] SRINIVASAN S, ROMAN N, and WANG Deliang. Binary and ratio time-frequency masks for robust speech recognition[J]. Speech Communication, 2006, 48(11): 1486–1501. doi: 10.1016/j.specom.2006.09.003 [15] ZHANG Xiaolei and WANG Deliang. A deep ensemble learning method for monaural speech separation[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2016, 24(5): 967–977. doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2016.2536478 [16] HUANG Posen, KIM N, HASEGAWA-JOHNSON M, et al. Joint optimization of masks and deep recurrent neural networks for monaural source separation[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2015, 23(12): 2136–2147. doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2015.2468583 [17] DU Jun, TU Yanhui, DAI Lirong, et al. A regression approach to single-channel speech separation via high-resolution deep neural networks[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2016, 24(8): 1424–1437. doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2016.2558822 [18] WANG Yannan, DU Jun, DAI Lirong, et al. A gender mixture detection approach to unsupervised single-channel speech separation based on deep neural networks[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2017, 25(7): 1535–1546. doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2017.2700540 [19] LI Xiang, WU Xihong, and CHEN Jing. A spectral-change-aware loss function for DNN-based speech separation[C]. ICASSP 2019 - 2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 2019: 6870–6874. [20] SUN Linhui, ZHU Ge, and LI Ping’an. Joint constraint algorithm based on deep neural network with dual outputs for single-channel speech separation[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2020, 14(7): 1387–1395. doi: 10.1007/s11760-020-01676-6 [21] COOKE M, BARKER J, CUNNINGHAM S, et al. An audio-visual corpus for speech perception and automatic speech recognition[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2006, 120(5): 2421–2424. doi: 10.1121/1.2229005 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
