Secrecy Performance Optimization of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle -aided Physical Layer Security
-
摘要: 信息安全是影响物联网(IoT)应用的关键因素之一,物理层安全是解决物联网信息通信安全问题的有效技术。该文针对物联网中带有主动攻击的全双工窃听者,利用无人机(UAV)辅助发射人工噪声的方法,提升系统物理层安全性能。为了跟踪窃听者位置移动,首先采用贝叶斯测距和最小二乘法迭代估计窃听者位置,然后提出基于Q-learning的无人机轨迹优化算法,以达到在窃听者移动情况下系统保密性能最优。仿真结果表明,该算法能快速收敛,并且无人机能够跟踪窃听者移动来确定自身最佳位置,对窃听信道实施有效干扰,从而保证系统可达安全速率最大。
-
关键词:
- 物理层安全 /
- 人工噪声 /
- Q-learning /
- 可达安全速率 /
- 无人机轨迹优化
Abstract: Physical layer security is effective to solve the problem of communication security of Internet of Things (IoT). As a full duplex eavesdropper with active attack and passive eavesdropping exists in the IoT, Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) transmits artificial noise to the eavesdropper for improving secrecy performance in this paper. Based on estimating eavesdropper position, a trajectory optimization algorithm based on Q-learning is proposed to track the eavesdropper mobility and obtain the optimal secrecy performance. The results show that the proposed algorithm converges quickly. UAV can track the eavesdropper mobility to determine the best position of jamming the eavesdropping channel, which guarantees maximum achievable secrecy rate. -
表 1 基于Q-learning的无人机动态轨迹优化算法
输入 以Bob为圆心的圆环内,根据随机移动模型产生Eve位置。 While ${E_{ {\text{J\_remain} } } }(t) \ge {E_{ {\text{J\_min} } } }$ do 采用贝叶斯测距和最小二乘法迭代估计Eve位置坐标;初始化$Q(s,a)$, $s \in S$,$a \in A$,初始化无人机位置状态${s_t}$。 重复(每个回合) 在当前状态${s_t}$下,根据$\varepsilon - {\text{greedy}}$策略从动作空间$A$中选择动作${a_t}$; 执行动作${a_t}$,获得奖励值${R_t}$,状态${s_t}$转移为下一个状态${s_{t + 1}}$,根据式(17)更新$ Q({s_t},{a_t}) $; $ {s_t} \leftarrow {s_{t + 1}} $; 更新无人机当前能量$ {E_{{\text{J\_remain}}}}(t) $;if $ {E_{{\text{J\_remain}}}}(t) < {E_{{\text{J\_min}}}} $, break; until ${s_t}$为终止状态(含边界和超出边界)或 Eve位置移动 无人机获得当前Eve位置下的最优位置。 输出 无人机跟踪Eve移动的动态运动轨迹。 说明:实际中算法程序实时检测无人机空间位置坐标,当发现无人机当前位置等于或超出边界坐标,程序发一个指令给无人机控制系统,
使控制系统控制飞机飞回到算法给定的初始位置,进而避免无人机在边界之外。 -
[1] BHAYO J, HAMEED S, and SHAH S A. An efficient counter-based DDoS attack detection framework leveraging software defined IoT (SD-IoT)[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 221612–221631. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3043082 [2] WANG Ning, WANG Pu, ALIPOUR-FANID A, et al. Physical-Layer security of 5G wireless networks for IoT: Challenges and opportunities[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(5): 8169–8181. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2927379 [3] 张波, 黄开枝, 林胜斌, 等. MIMO异构网络中一种基于人工噪声的抗主动窃听者的鲁棒安全传输方案[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(9): 2186–2193. doi: 10.11999/5EIT190649ZHANG Bo, HUANG Kaizhi, LIN Shengbin, et al. A robust secure transmission scheme based on artificial noise for resisting active eavesdropper in MIMO heterogeneous networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(9): 2186–2193. doi: 10.11999/5EIT190649 [4] LIU Chenxi, LEE J, and QUEK T Q S. Safeguarding UAV communications against full-duplex active eavesdropper[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(6): 2919–2931. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2906177 [5] HUO Yan, TIAN Yuqi, HU Chunqiang, et al. A location prediction-based helper selection scheme for suspicious eavesdroppers[J]. Wireless Communication and Mobile Computing, 2017, 2017: 1832051. [6] LIU Chenxi, YANG Nan, MALANEY R, et al. Artificial-Noise-Aided transmission in multi-antenna relay wiretap channels with spatially random eavesdroppers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2016, 15(11): 7444–7456. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2016.2602337 [7] CAO Kunrui, WANG Buhong, DING Haiyang, et al. Improving physical layer security of uplink NOMA via energy harvesting jammers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2021, 16: 786–799. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2020.3023277 [8] WANG Huiming, ZHANG Xu, and JIANG Jiacheng. UAV-Involved wireless physical-layer secure communications: overview and research directions[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2019, 26(5): 32–39. doi: 10.1109/MWC.001.1900045 [9] ZHOU Xiaobo, WU Qingqing, YAN Shihao, et al. UAV-Enabled secure communications: Joint trajectory and transmit power optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(4): 4069–4073. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2900157 [10] LI An, WU Qingqing, and ZHANG Rui. UAV-Enabled cooperative jamming for improving secrecy of ground wiretap channel[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2019, 8(1): 181–184. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2018.2865774 [11] CUI Jingjing, LIU Yuanwei, and NALLANATHAN A. Multi-Agent reinforcement learning-based resource allocation for UAV networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(2): 729–743. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2935201 [12] DING Ruijin, GAO Feifei, and SHEN X S. 3D UAV trajectory design and frequency band allocation for energy-efficient and fair communication: A deep reinforcement learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(12): 7796–7809. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3016024 [13] ZHANG Yu, MOU Zhiyu, GAO Feifei, et al. UAV-Enabled secure communications by multi-agent deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(10): 11599–11611. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3014788 [14] CHEN Mingzhe, MOZAFFARI M, SAAD W, et al. Caching in the sky: Proactive deployment of cache-enabled unmanned aerial vehicles for optimized quality-of-experience[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2017, 35(5): 1046–1061. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2017.2680898 [15] TANG Jinchuan, CHEN Gaojie, and COON J P. Secrecy performance analysis of wireless communications in the presence of UAV jammer and randomly located UAV eavesdroppers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2019, 14(11): 3026–3041. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2019.2912074 [16] LIU Xiao, LIU Yuanwei, and CHEN Yue. Reinforcement learning in multiple-UAV networks: deployment and movement design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(8): 8036–8049. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2922849 [17] WANG Qian, CHEN Zhi, LI Hang, et al. Joint power and trajectory design for physical-layer secrecy in the UAV-aided mobile relaying system[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 62849–62855. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2877210 [18] COLUCCIA A and RICCIATO F. RSS-Based localization via Bayesian ranging and iterative least squares positioning[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2014, 18(5): 873–876. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2014.040214.132781 [19] LIU Xiao, LIU Yuanwei, CHEN Yue, et al. Trajectory design and power control for multi-UAV assisted wireless networks: A machine learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(8): 7957–7969. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2920284 -





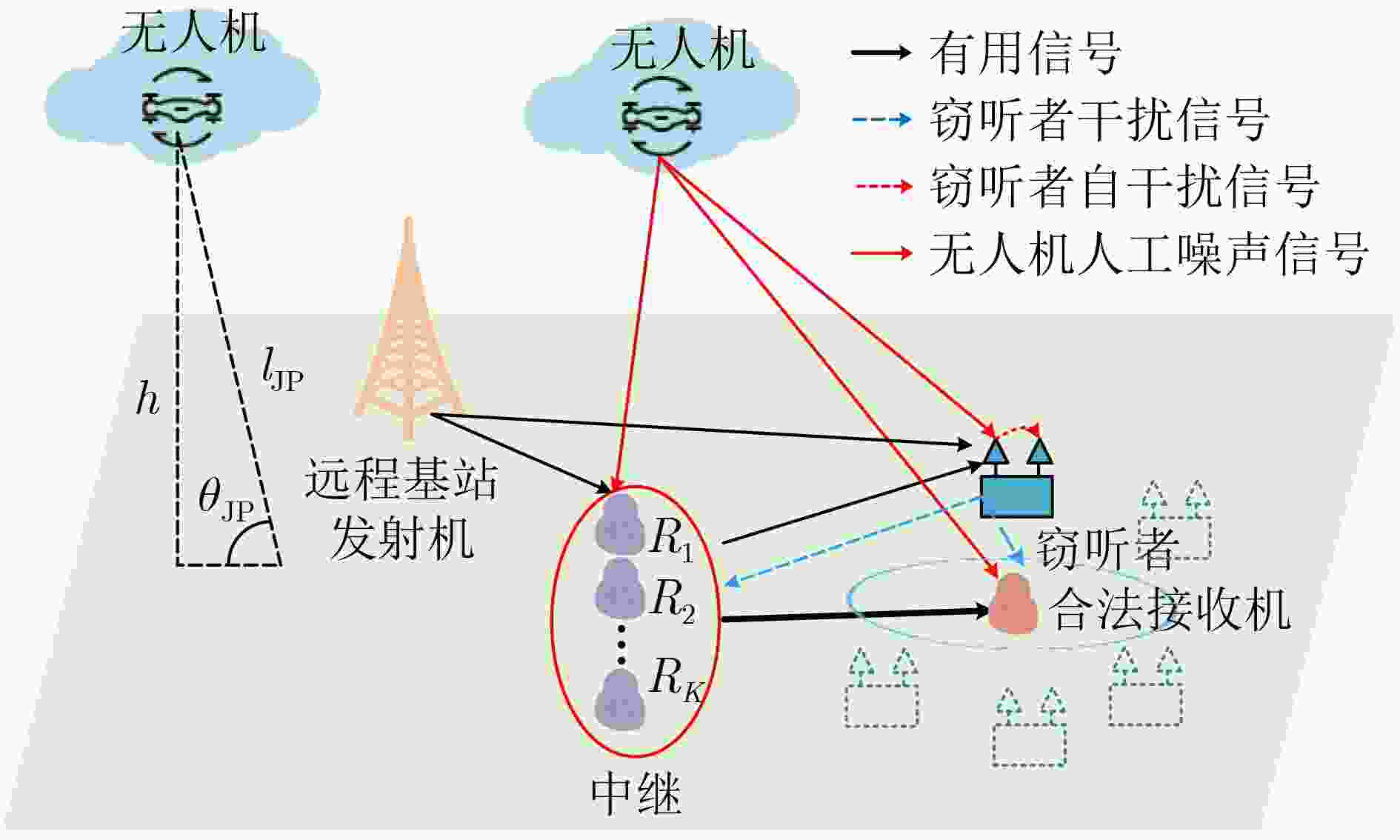
 下载:
下载:
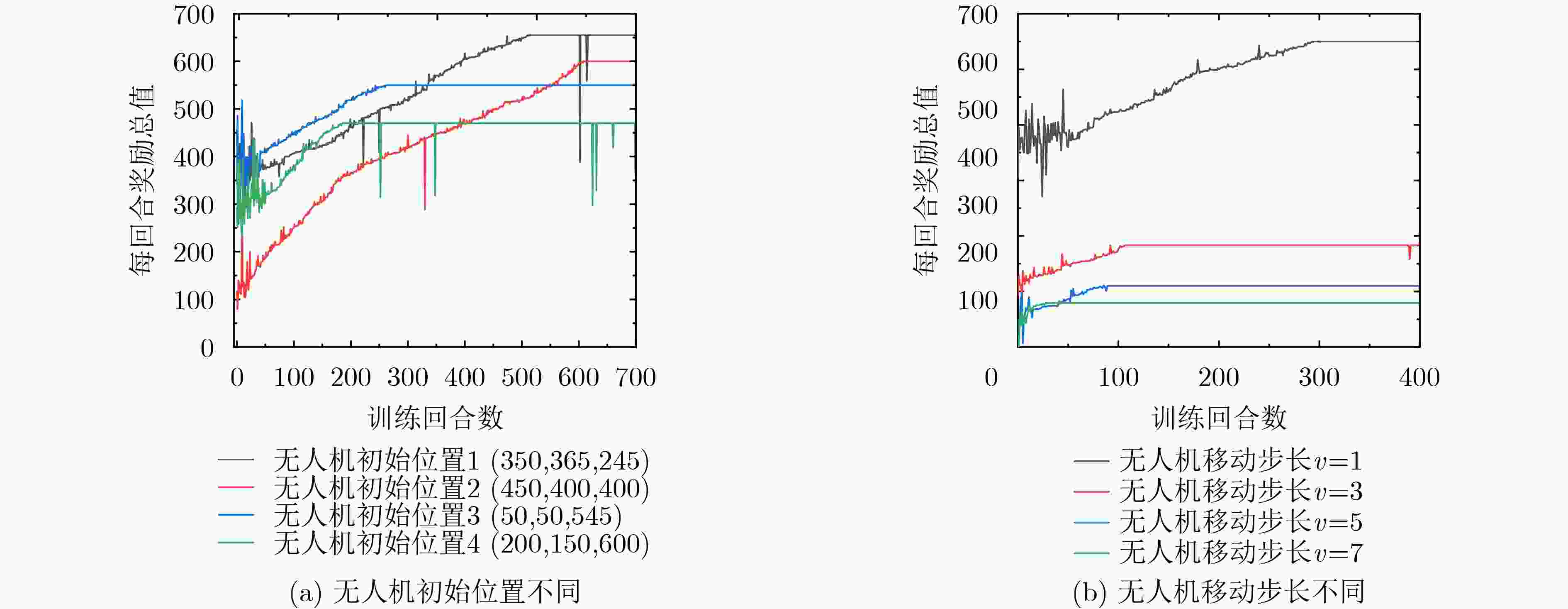
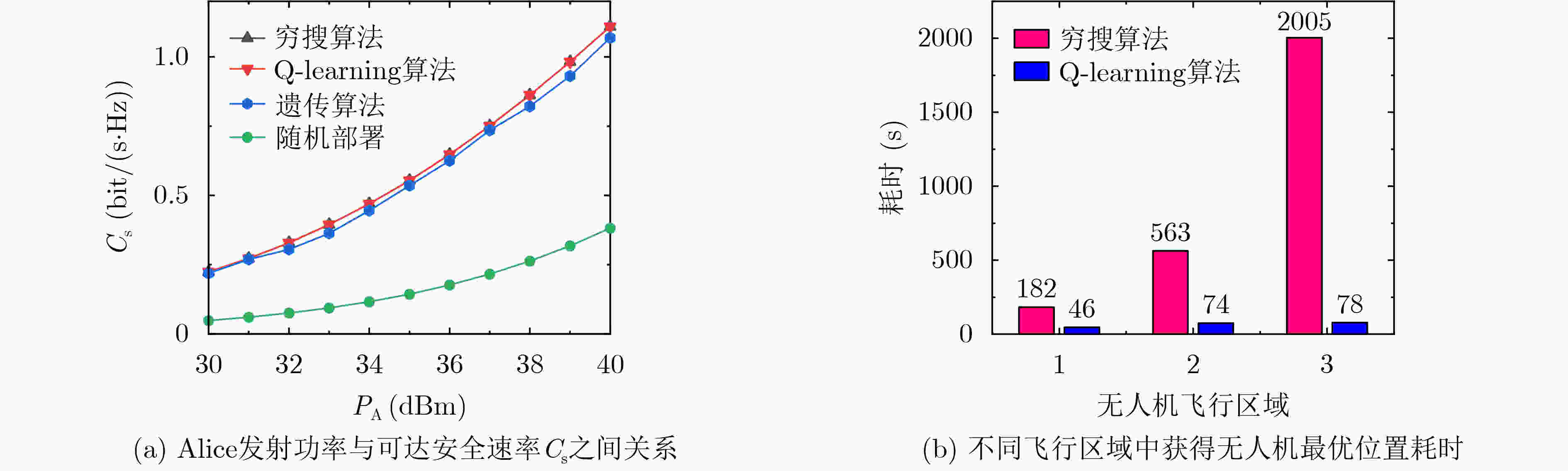
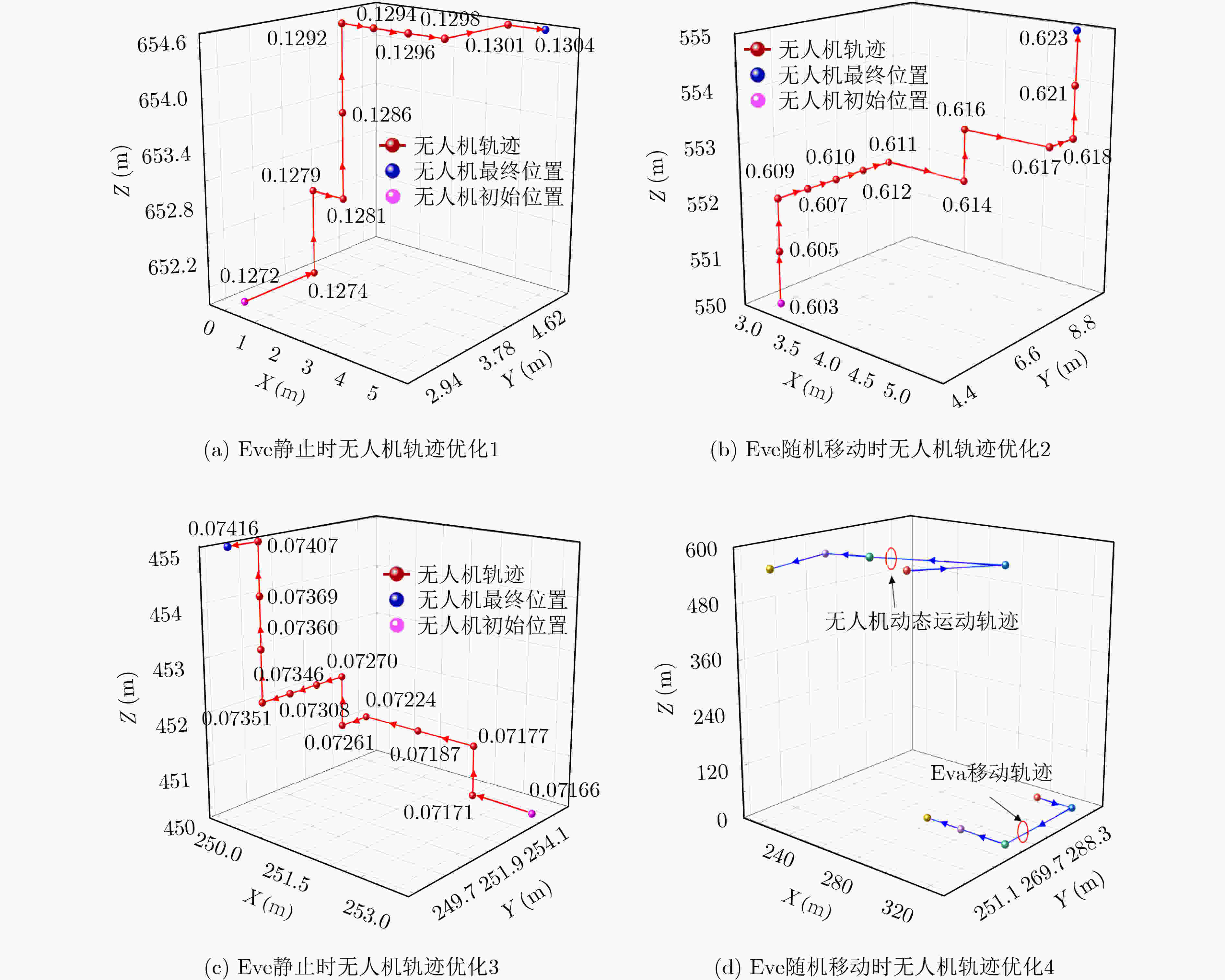
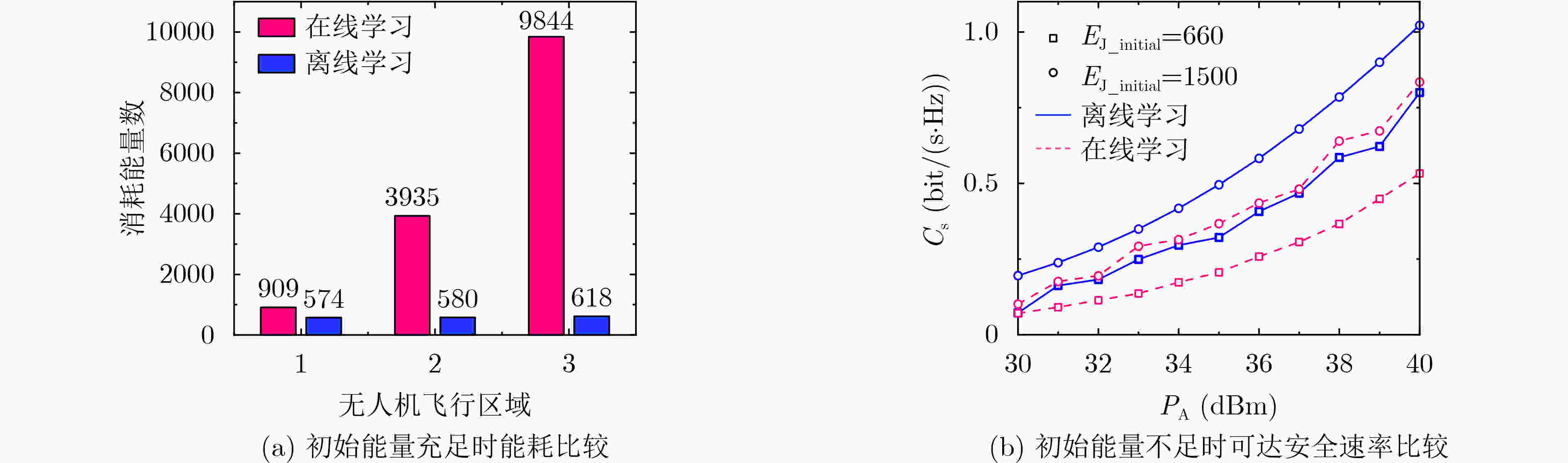
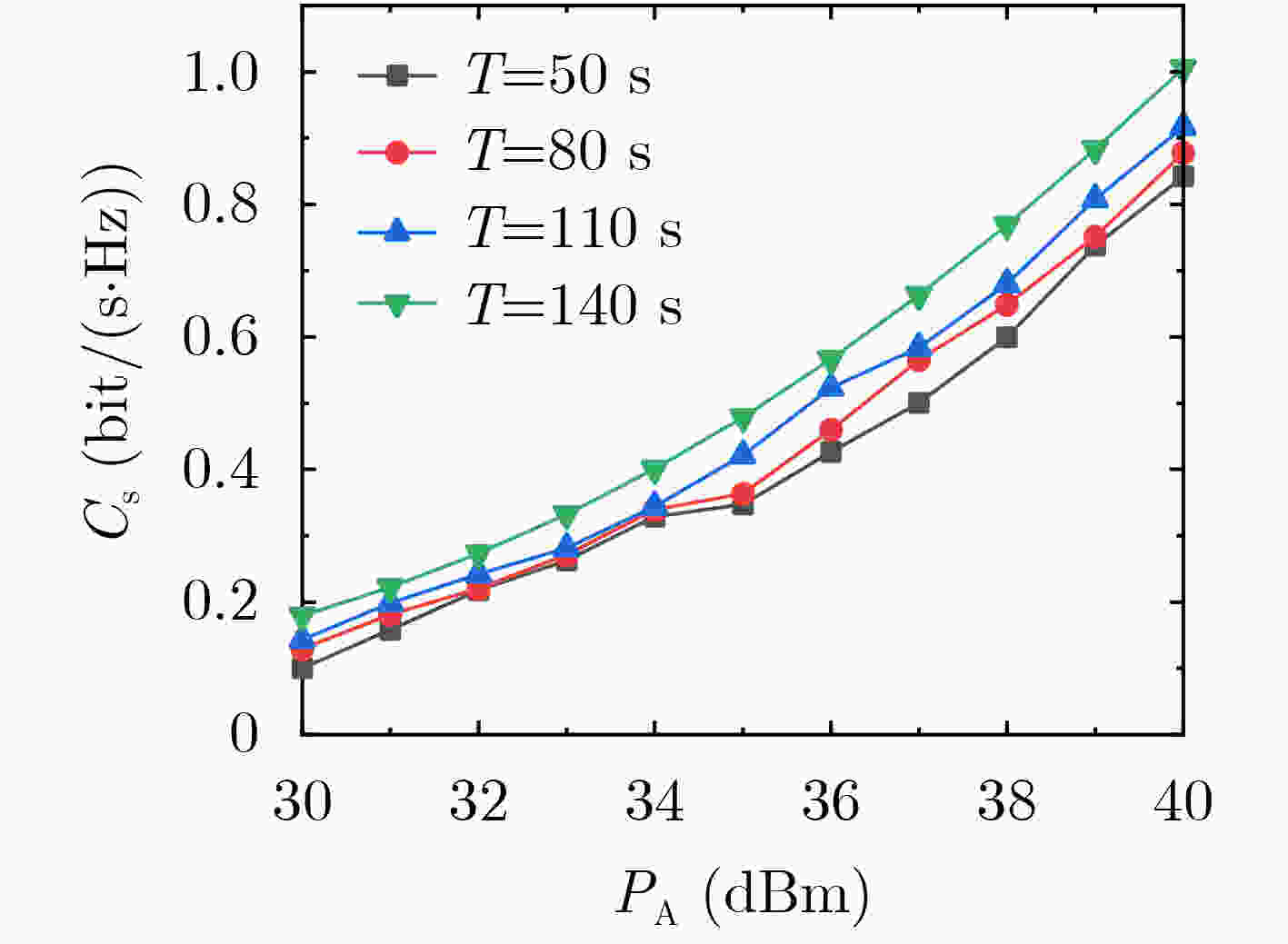


 下载:
下载:
