An Accelerated Back-Projection Algorithm Based on Large Swath for Geosynchronous-Earch-Orbit SAR Imaging
-
摘要: 在高轨(GEO)合成孔径雷达(SAR)成像中,超大的成像幅宽导致成像区域不满足平面近似,使得基于平面网格的快速BP算法失效。该文提出一种基于地表网格的快速BP算法来精确高效地处理高轨SAR信号。首先针对轨道弯曲和地表弯曲所带来的信号复杂空变问题,采用一种基于实际地表的曲面网格布置方法。针对子孔径BP图像的频谱混叠问题,提出基于曲面网格的两步频谱压缩函数,将子孔径图像在合成之前实现频谱解混叠。同时采用多级子孔径图像合成的方法提高成像效率。最后,通过对比仿真,证明了该文所提算法的精确性以及高效性。Abstract: In the Geosynchronous-Earth-Orbit (GEO) SAR imaging, the extremely large swath width causes the imaging plane to no longer satisfy the flat plane approximation, which makes the accelerated BP algorithms based on the flat plane grid invalid. In this paper, an accelerated BP algorithm based on ground grid is proposed to process accurately and efficiently the GEO SAR signals. The imaging grids are arranged on the ground surface to correct the complex space variance of the signal caused by orbit and ground surface curvature. To solve the spectrum aliasing of sub-aperture images, a two-step spectrum compressing method is proposed to achieve the sub-aperture spectrum de-aliasing before fusion. And a multi-stage sub-aperture image fusion method is adopted to improve the imaging efficiency. Finally, simulation results are shown to verify the accuracy and efficiency of the proposed focusing approaches.
-
表 1 仿真参数
类型 名称 值 轨道参数 轨道高度(km) 35786 偏心率 0 倾角(°) 16 近地点幅角(°) 0 雷达参数 载频(GHz) 1.25 带宽(MHz) 13 PRF (Hz) 150 斜视角(°) 0 合成孔径时间(s) 450 地面距离/多普勒分辨率(m) 20/20 场景参数 距离子场景宽度(km) 20 场景宽度(距离/方位)(km) 400/400 表 2 本文算法和对比算法成像质量评估
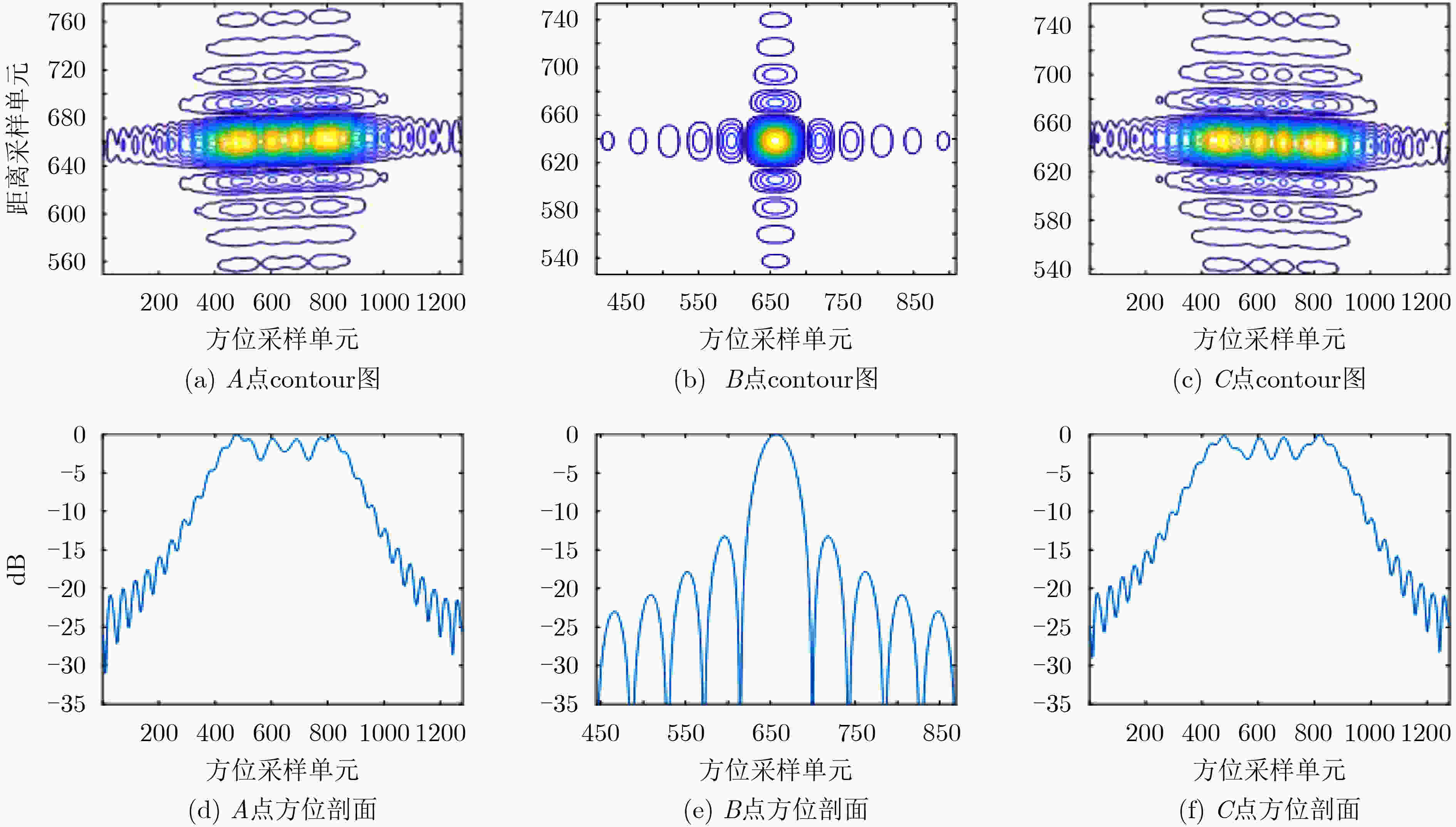
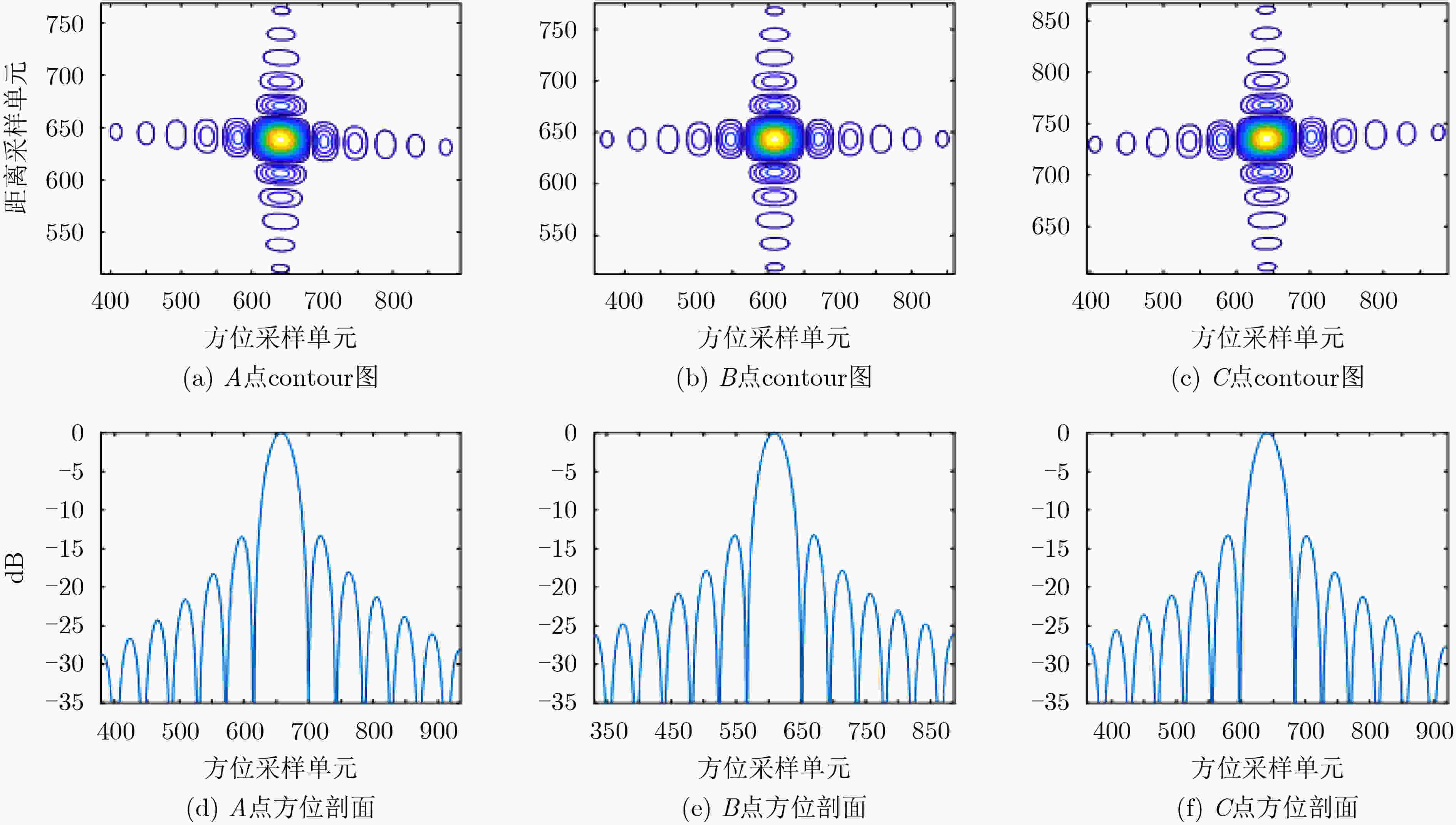
点目标 PSLR(dB) ISLR(dB) 分辨率(m) 展宽比(方位) 距离向 方位向 距离向 方位向 距离向 方位向 距离向 方位向 本文方法 A –13.24 –13.27 –10.02 –10.05 20.13 20.06 1.011 1.012 B –13.31 –13.28 –10.02 –10.00 20.05 20.05 1.003 1.002 C –13.30 –13.23 –10.05 –10.04 20.11 20.07 1.012 1.014 对比方法 A –13.26 –0.35 –10.02 –2.13 21.03 – – – B –13.27 –13.29 –10.01 –9.73 21.10 20.05 1.004 1.002 C –13.25 –0.23 –10.13 –2.75 21.07 – – – -
[1] MADSEN S N, CHEN C, and EDELSTEIN W. Radar options for global earthquake monitoring[C]. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toronto, Canada, 2002: 1483–1485. [2] TOMIYASU K. Conceptual performance of a satellite borne, wide swath synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1981, GE-19(2): 108–116. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.1981.350361 [3] TOMIYASU K. Synthetic aperture radar in geosynchronous orbit[C]. 1978 Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, Washington, USA, 1978: 42–45. [4] BRUNO D, HOBBS S E, and OTTAVIANELLI G. Geosynchronous synthetic aperture radar: Concept design, properties and possible applications[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2006, 59(1-5): 149–156. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2006.02.005 [5] 刘文康, 景国彬, 孙光才, 等. 基于两步方位重采样的中轨SAR聚焦方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(1): 136–142.LIU Wenkang, JING Guobin, SUN Guangcai, et al. Medium-earth-orbit SAR data focusing method based on two-step azimuth resampling[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(1): 136–142. [6] CHEN Jianlai, SUN Guangcai, WANG Yong, et al. A TSVD-NCS algorithm in range-Doppler domain for geosynchronous synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(11): 1631–1635. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2599224 [7] 陈权, 孙光才, 刘文康, 等. 基于时频联合尺度变换的中轨SAR斜视成像方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2020, 42(2): 309–314. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2020.02.08CHEN Quan, SUN Guangcai, LIU Wenkang, et al. Highly-squinted MEO SAR focusing based on joint time and Doppler scaling[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronic, 2020, 42(2): 309–314. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2020.02.08 [8] GUARNIERI A M, LEANZA A, RECCHIA A, et al. Atmospheric phase screen in GEO-SAR: Estimation and compensation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(3): 1668–1679. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2766084 [9] LIU Wenkang, SUN Guangcai, XING Mengdao, et al. Focusing of MEO SAR data based on principle of optimal imaging coordinate system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(8): 5477–5489. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2966581 [10] 陈杰, 杨威, 王鹏波, 等. 多方位角观测星载SAR技术研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(2): 205–220. doi: 10.12000/JR20015CHEN Jie, YANG Wei, WANG Pengbo, et al. Review of novel azimuthal multi-angle observation spaceborne SAR technique[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(2): 205–220. doi: 10.12000/JR20015 [11] 李航, 刘文康, 孙光才, 等. 基于成像坐标系优化的中轨星载SAR成像方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(5): 856–864. doi: 10.12000/JR20098LI Hang, LIU Wenkang, SUN Guangcai, et al. Medium orbit spaceborne SAR imaging method based on Optimization of imaging coordinate system[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(5): 856–864. doi: 10.12000/JR20098 [12] SUN Guangcai, XING Mengdao, WANG Yong, et al. A 2-D space-variant chirp scaling algorithm based on the RCM equalization and subband synthesis to process geosynchronous SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(8): 4868–4880. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2285721 [13] LI Zhuo, LI Chunsheng, YU Ze, et al. Back projection algorithm for high resolution GEO-SAR image formation[C]. 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, Canada, 2011: 336–339. [14] ULANDER L M H, HELLSTEN H, and STENSTROM G. Synthetic-aperture radar processing using fast factorized back-projection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2003, 39(3): 760–776. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2003.1238734 [15] BIE Bowen, XING Mengdao, SUN Guangcai, et al. A frequency domain backprojection algorithm based on local Cartesian coordinate and subregion range migration correction for high-squint SAR mounted on maneuvering platforms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(12): 7086–7101. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2848249 [16] CHEN Juan, XIONG Jintao, HUANG Yulin, et al. Research on a novel fast backprojection algorithm for stripmap bistatic SAR imaging[C]. The 2007 1st Asian and Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Huangshan, China, 2007: 622–625. [17] DONG Qi, SUN Guangcai, YANG Zemin, et al. Cartesian factorized backprojection algorithm for high-resolution spotlight SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(3): 1160–1168. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2017.2780164 [18] CHEN Xiaoxiang, SUN Guangcai, XING Mengdao, et al. Ground Cartesian back-projection algorithm for high squint diving TOPS SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(7): 5812–5827. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3011589 -





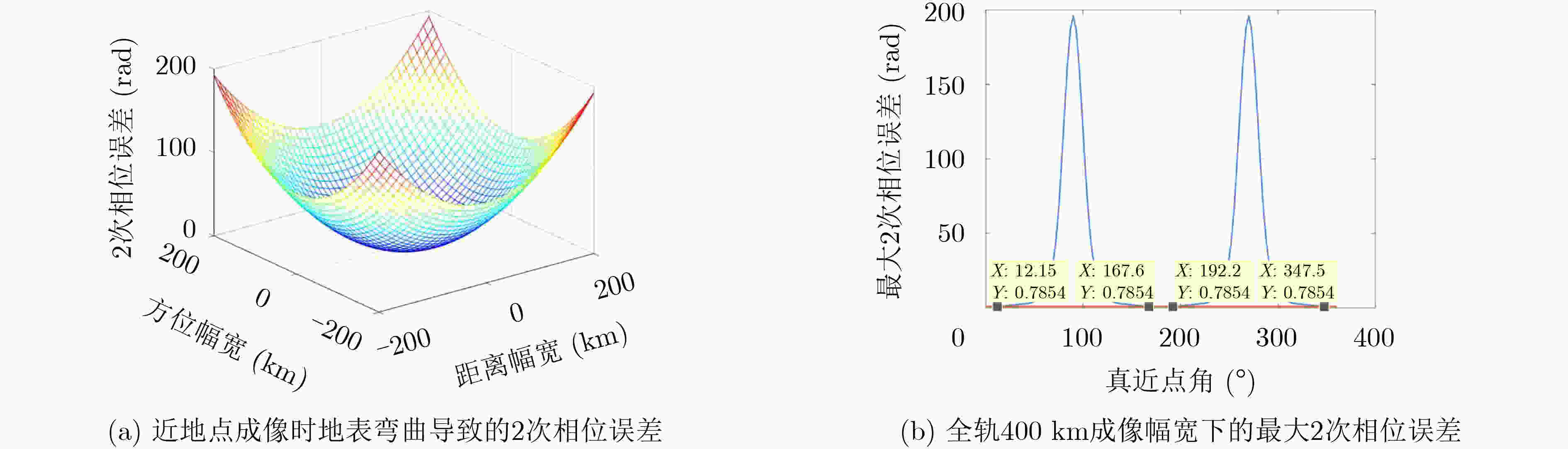
 下载:
下载:
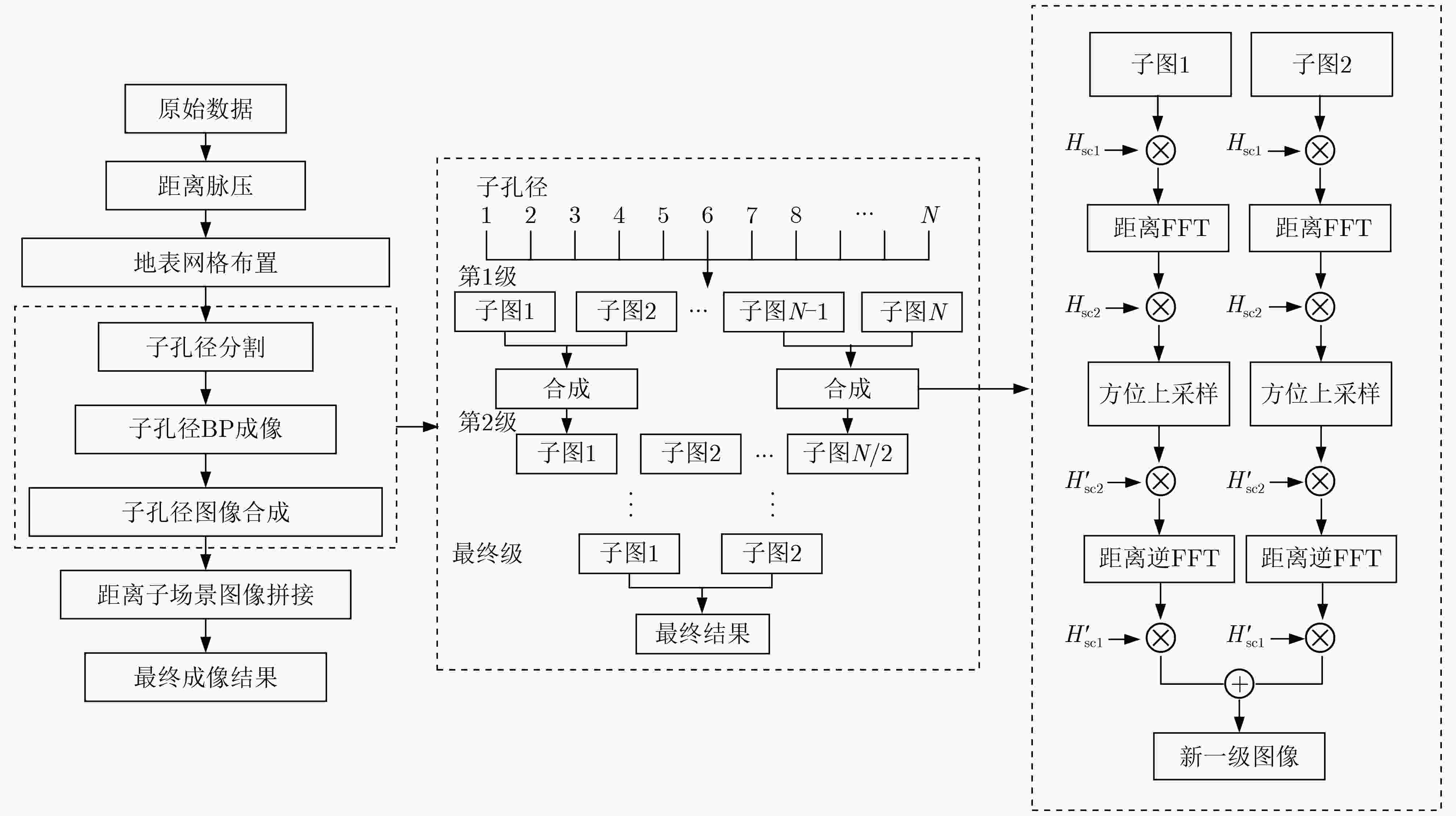
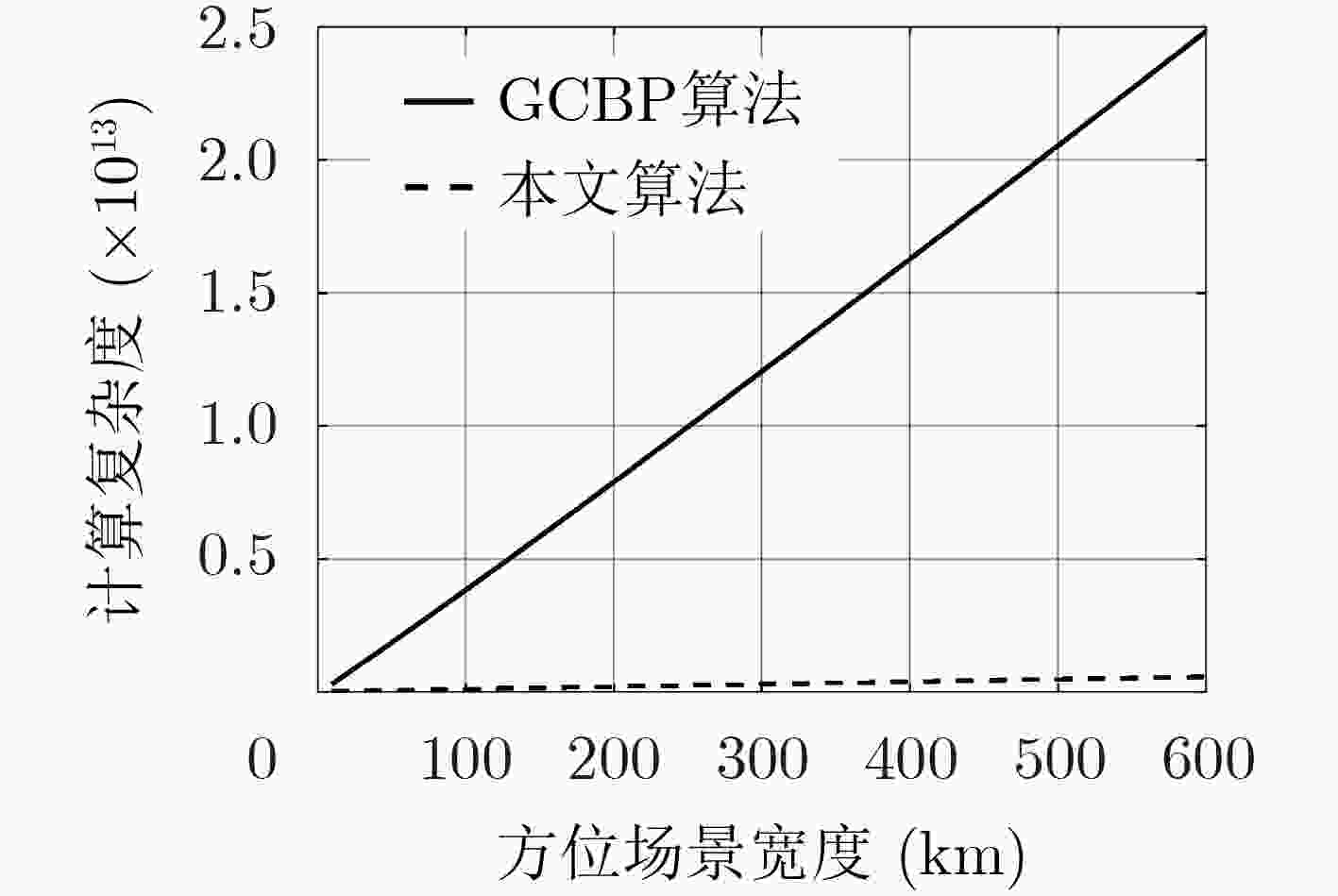
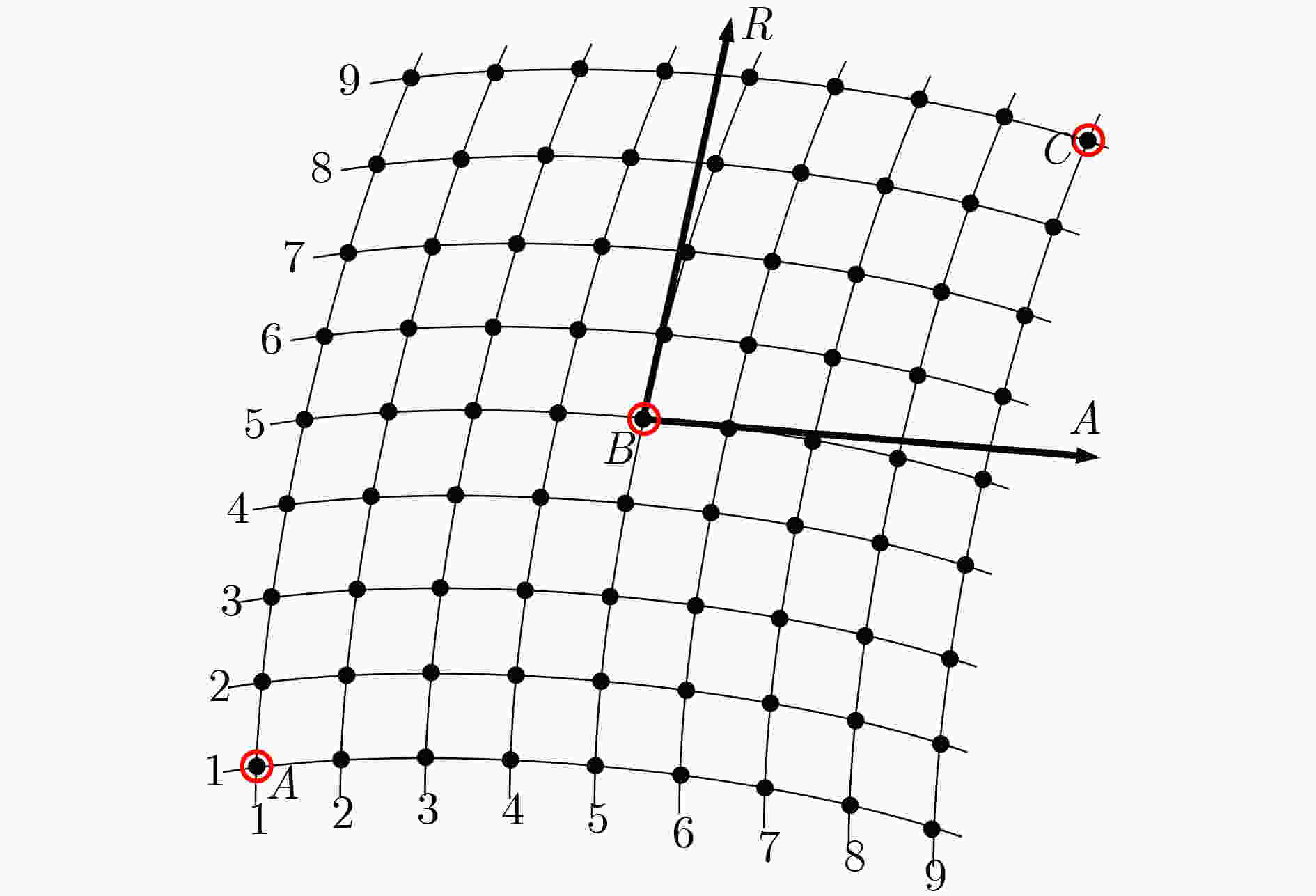


 下载:
下载:
