A Parameter Estimation Method of Non-instantaneous Diffusion Point Source Based on Finite Rate of Innovation
-
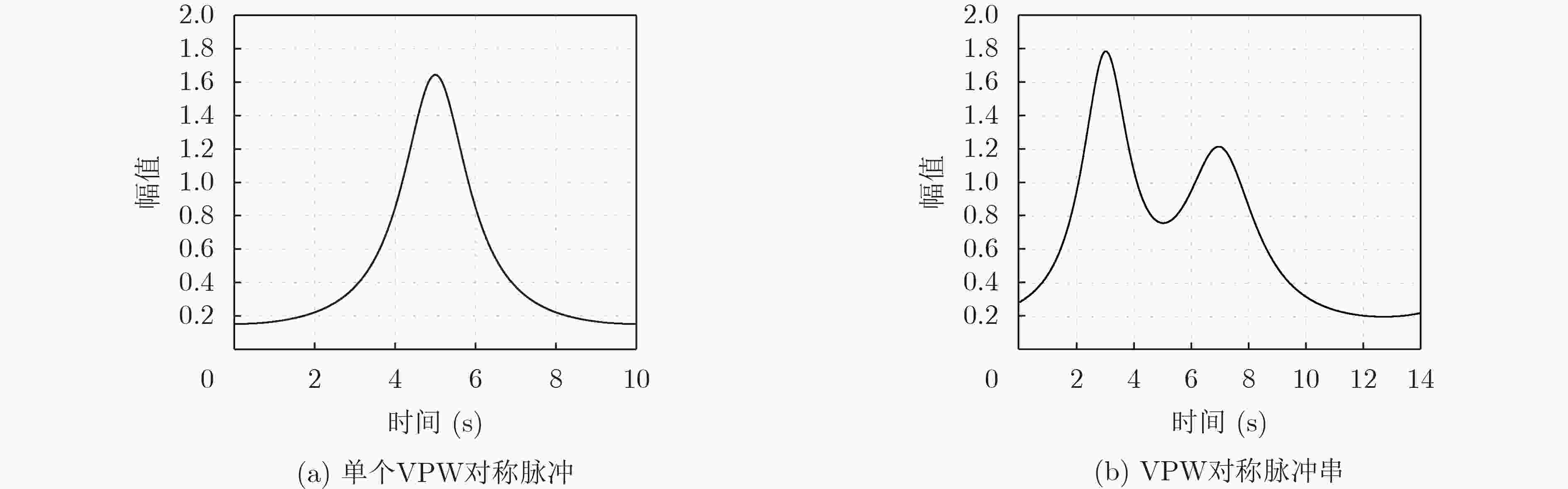
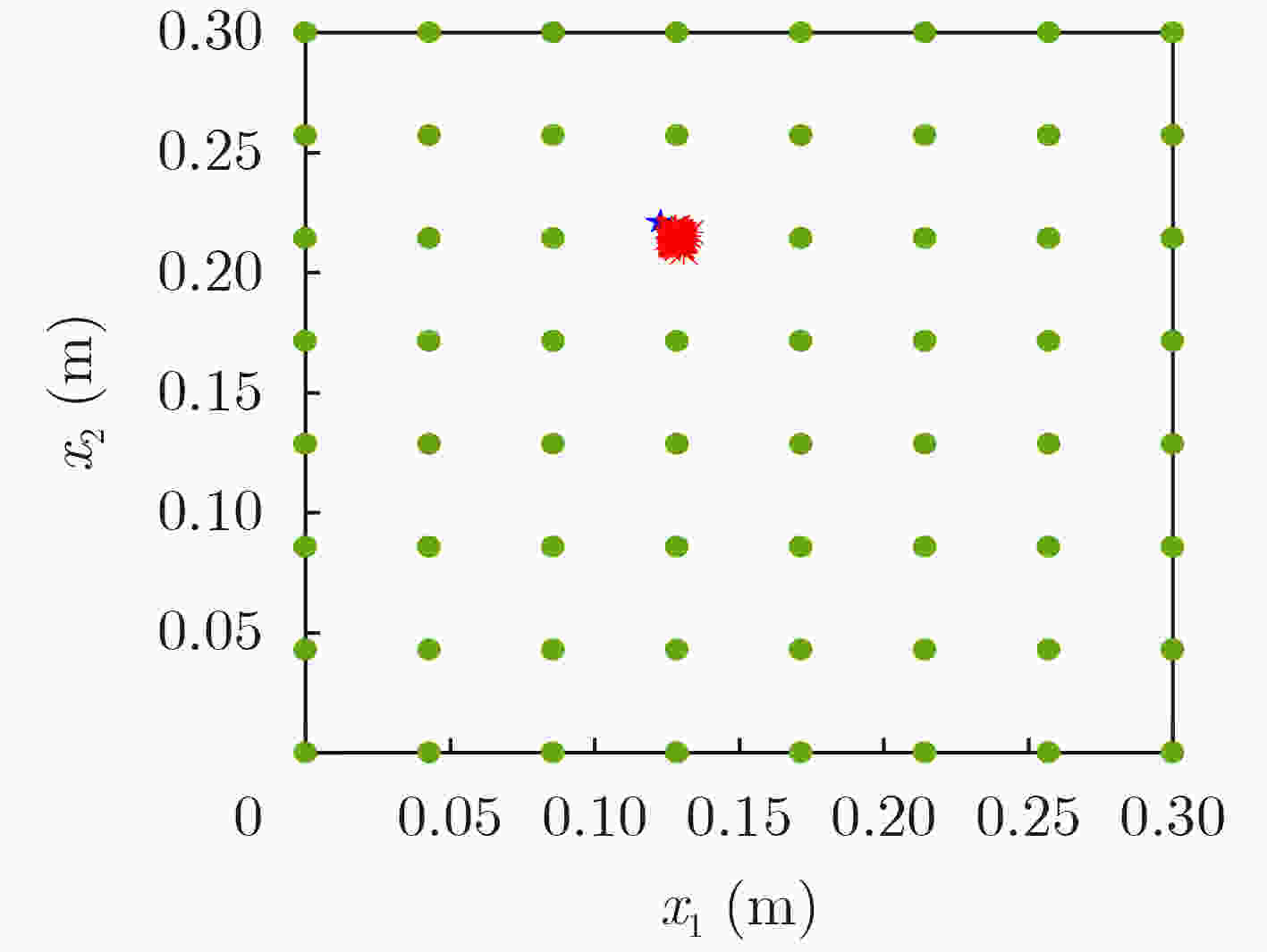
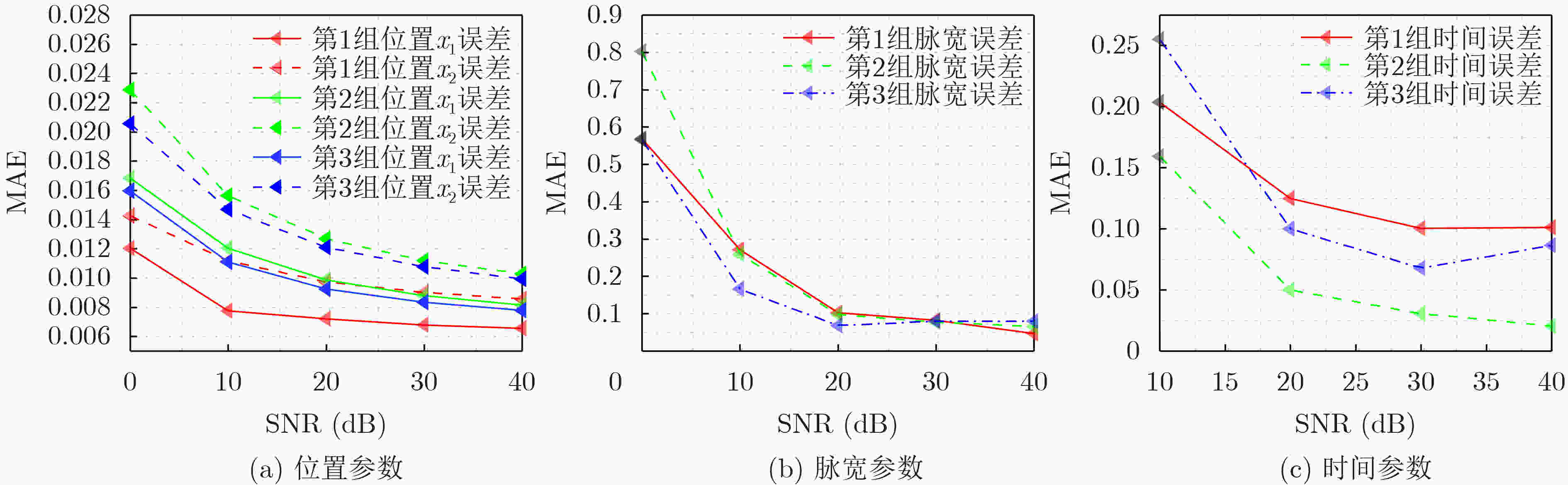
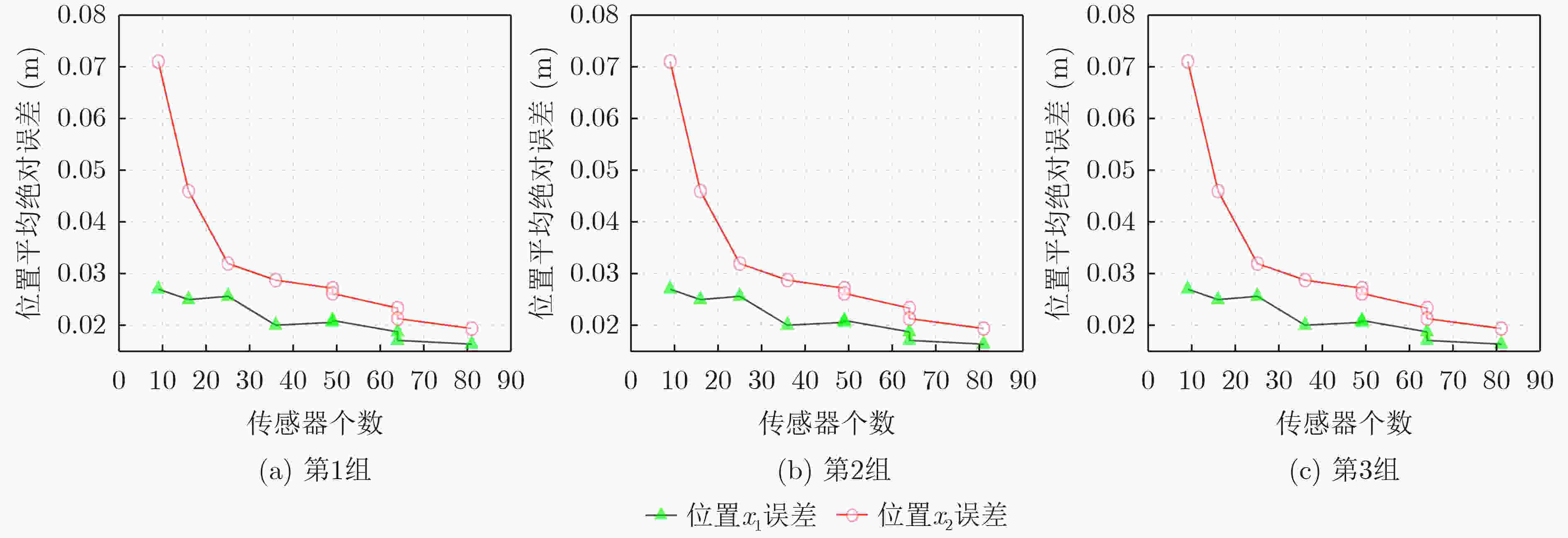
摘要: 扩散现象在农业真菌传播、大气污染等现实场景广泛存在,扩散源参数估计也因此在农业、工业等实际应用中具有重要意义。目前针对扩散源参数估计提出的方法大多针对理想的瞬时点源信号,对于非瞬时的实际扩散过程存在模型失配问题,极大地限制了算法的实际应用场景。为了解决模型不匹配的问题,同时有效估计扩散源持续时间参数,该文将扩散源信号模型拓展为脉宽可变信号,并提出相应的非瞬时点源模型的参数估计算法。该算法中,利用无线传感网络采样得到实际测量值,找到一个组合系数将实际测量值线性组合为指数函数,再根据有限新息率(FRI)采样理论对组合后的数据用零化滤波器方法求解扩散源参数。仿真结果表明,在信噪比20 dB,位置参数重构MAE能够达到0.008左右,脉宽参数能够达到0.1左右,持续时间参数能够达到0.05左右,这验证了非瞬时点源参数估计的准确性。同时我们分析了传感器个数等因素对参数恢复性能的影响。Abstract: Many physical phenomena can be described by the diffusion equations, such as the emission of chimney pollutants, chemical substance leakage, etc. Therefore, the estimation of diffusion source parameters is of great significance in practical applications. Currently, most of the proposed methods for estimating parameters of diffusion sources are aimed at instantaneous point source signals. For non-instantaneous actual diffusion processes, there is a problem of model mismatch. In this paper, the diffusion source model is extended to variable pulse-width signals, and the parameter estimation algorithm of corresponding non-instantaneous point sources are proposed. In this algorithm, the actual measurement value is obtained by sampling with the wireless sensor network, a combination coefficient is found to combine linearly the actual measurement value into an exponential function, and then the combined data is analyzed according to the Finite Rate of Innovation (FRI) sampling theory by using the annihilation filter method to solve the diffusion source parameters. The simulation results analyze the performance factors that affect parameter recovery, including noise, the number of sensors, etc., and the accuracy of the non-instantaneous diffusion point source parameter estimation method is validated.
-
表 1 非理想时间脉冲扩散点源参数估计过程
输入:传感器位置${{\boldsymbol{x}}_n}$,采样时刻${t_l}$,传感器采样值$ {\varphi _n}({t_l}) $,扩散
系数$\mu $,脉冲个数K,采样时长T输出:位置参数${\boldsymbol{\xi}}$,时延参数,脉宽参数,幅度参数。 (1) 根据式(40)计算当$ r = 0 $时的组合加权系数
$\{ {w_{{\boldsymbol{n}},l} }({\boldsymbol{k} },0)\} _{ {\boldsymbol{k} } = (0,0)}^{({K_1},{K_2})}$。(2) 根据式(28)对采样值进行组合,得到$\hat Q({\boldsymbol{k}},0)$。 (3) 利用2维谱估计算法得到($ {\xi _1},{\xi _2} $)。 (4) 根据式(40)计算当$ {k_1} = 0 $, $ {k_2} = 1 $时的加权系数
$\{ {w_{{\boldsymbol{n}},l} }(k,r)\} _{r = 0}^{2K + 1}$。(5) 根据式(28)对采样值进行组合,得到$\hat Q({\boldsymbol{k}},r)$。 (6) 根据式(26)与式(27)获取傅里叶系数$ H(r) $。 (7) 利用改进的零化滤波器恢复时延,脉宽和幅度参数。 表 2 参数设置及恢复结果
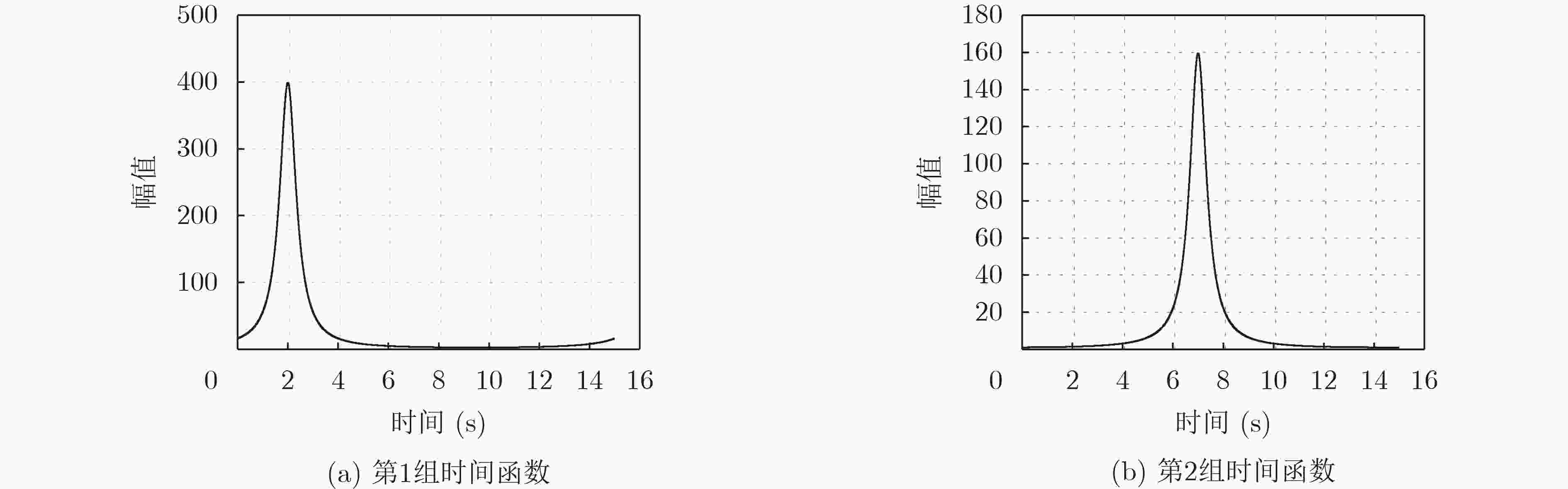
实验组 参数 真实值 估计均值 估计值方差 脉宽$ {r_k} $ (1.0000, 1.0000) (0.9171, 1.0102) (0.0018, 0.0028) 第1组 时延$ {t_k} $ (3.0000, 7.0000) (2.9996, 7.1626) (5.9602$ \times $10–4, 9.7505$ \times $10–4) 幅度$ {c_k} $ (5.0000, 5.0000) (6.4175, 4.6885) (0.7995, 0.8620) 脉宽$ {r_k} $ (0.8000, 0.8000) (0.7122, 0.7689) (7.4302$ \times $10–4, 7.1916$ \times $10–4) 第2组 时延$ {t_k} $ (4.0000, 7.0000) (4.0159, 7.0212) (2.8550$ \times $10–4, 3.3058$ \times $10–4) 幅度$ {c_k} $ (4.0000, 4.0000) (4.6386, 4.0244) (0.1670, 0.1475) 脉宽$ {r_k} $ (0.9000, 0.9000) (0.7965, 0.8395) (8.3376$ \times $10–4, 0.0011) 第3组 时延$ {t_k} $ (2.0000, 7.0000) (1.9525, 7.1132) (8.0755$ \times $10–4, 5.3718$ \times $10–4) 幅度$ {c_k} $ (5.0000, 5.0000) (5.2004, 4.7983) (0.0901, 0.1080) 表 3 参数估计结果
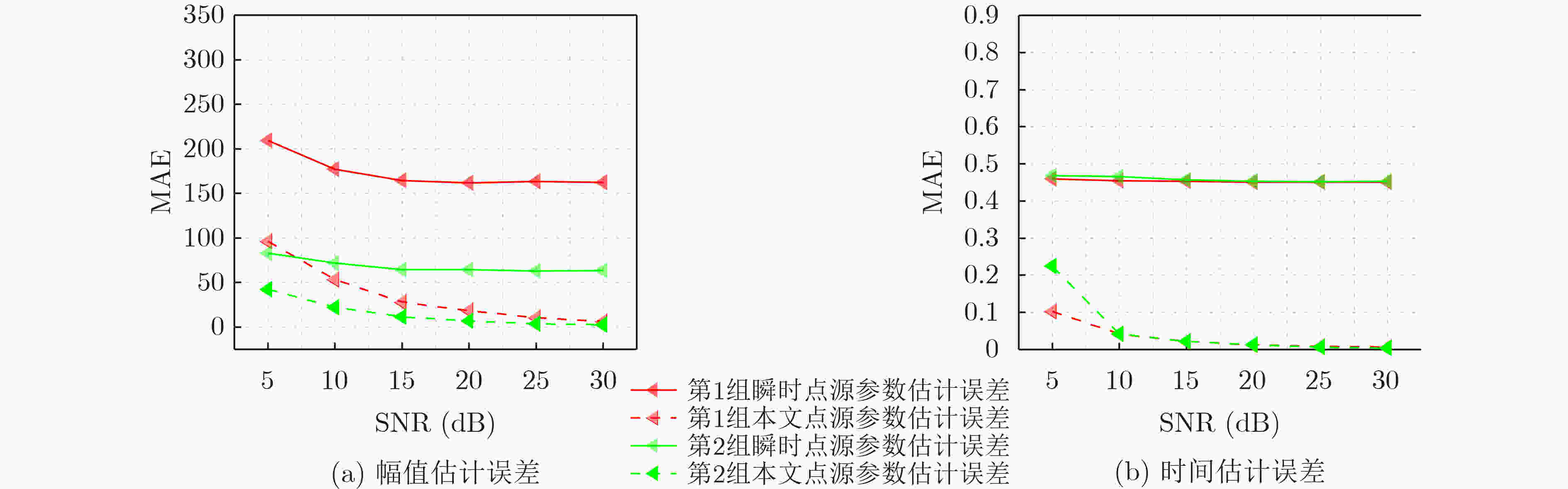
实验组 参数 真实值 瞬时点源模型估计值 瞬时点源估计方差 本文点源模型估计值 本文点源估计方差 第1组 时延 2.0000 1.5497 6.5657$ \times $10–7 2.0055 2.6604$ \times $10–5 幅值 398.8178 560.8293 84.2846 405.4113 31.8795 第2组 时延 7.0000 6.5475 1.7676$ \times $10–6 6.9988 1.5820$ \times $10–5 幅值 159.5271 222.7944 11.8788 158.6228 6.1016 -
[1] BENSALEH M S, SAIDA R, KACEM Y H, et al. Wireless Sensor Network Design Methodologies: A Survey[J]. Journal of Sensors, 2020,, 2020(1): 1–13. doi: 10.1155/2020/9592836 [2] 蒋俊正, 李杨剑, 赵海兵, 等. 一种大规模传感器网络节点分布式定位算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(12): 3022–3028. doi: 10.11999/JEIT181101JIANG Junzheng, LI Yangjian, ZHAO Haibing, et al. A distributed node localization algorithm for large scale sensor networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(12): 3022–3028. doi: 10.11999/JEIT181101 [3] VAN WATERSCHOOT T and LEUS G. Static field estimation using a wireless sensor network based on the finite element method[C]. The 4th IEEE International Workshop on Computational Advances in Multi-sensor Adaptive Processing, San Juan, USA, 2011: 369–372. [4] ZHANG Yong, WANG Tong, SHI Yu, et al. Joint variational Bayesian based localization estimation algorithm on distributed gas source sensor network[J]. Computer Communications, 2020, 154: 262–268. doi: 10.1016/j.comcom.2020.02.060 [5] RANIERI J, CHEBIRA A, LU Y M, et al. Sampling and reconstructing diffusion fields with localized sources[C]. 2011 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Prague, Czech Republic, 2011: 4016–4019. [6] ROSTAMI M, CHEUNG N M, and QUEK T Q S. Compressed sensing of diffusion fields under heat equation constraint[C]. 2013 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Vancouver, Canada, 2013: 4271–4274. [7] ZHANG Yuexin and ZHANG Jianjun. K-coverage: A monitor node selection algorithm for diffusion source localizations[J]. Research Briefs on Information & Communication Technology Evolution, 2020, 6(8): 1–12. doi: 10.22667/ReBiCTE.2020.12.01.008 [8] ALEXANDRU R, BLU T, and DRAGOTTI P L. D-SLAM: Diffusion source localization and trajectory mapping[C]. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 2020: 5600–5604. [9] WANG Zhixiao, SUN Chengcheng, RUI Xiaobin, et al. Localization of multiple diffusion sources based on overlapping community detection[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2021, 226: 106613. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2020.106613 [10] FLEGG M B, MUÑOZ M A, SMITH-MILES K, et al. Parameter estimation for a point-source diffusion-decay morphogen model[J]. Journal of Mathematical Biology, 2020, 80(7): 2227–2255. doi: 10.1007/s00285-020-01494-x [11] VETTERLI M, MARZILIANO P, and BLU T. Sampling signals with finite rate of innovation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2002, 50(6): 1417–1428. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2002.1003065 [12] DOKMANIć I, RANIERI J, CHEBIRA A, et al. Sensor networks for diffusion fields: Detection of sources in space and time[C]. The 49th Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing, Monticello, USA, 2011: 1552–1558. [13] LU Y M, DRAGOTTI P L, and VETTERLI M. Localizing point sources in diffusion fields from spatiotemporal samples[C]. The 9th International Conference on Sampling Theory and Applications, Singapore, 2011. [14] RANIERI J, DOKMANIć I, CHEBIRA A, et al. Sampling and reconstruction of time-varying atmospheric emissions[C]. 2012 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Kyoto, Japan, 2012: 3673–3676. [15] MURRAY-BRUCE J and DRAGOTTI P L. Spatio-temporal sampling and reconstruction of diffusion fields induced by point sources[C]. 2014 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Florence, Italy, 2014: 31–35. [16] MURRAY-BRUCE J and DRAGOTTI P L. Estimating localized sources of diffusion fields using spatiotemporal sensor measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(12): 3018–3031. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2419187 [17] MURRAY-BRUCE J and DRAGOTTI P L. A Sampling framework for solving physics-driven inverse source problems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(24): 6365–6380. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2742983 [18] BAECHLER G, SCHOLEFIELD A, BABOULAZ L, et al. Sampling and exact reconstruction of pulses with variable width[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(10): 2629–2644. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2669900 [19] 王亚军, 李明, 刘高峰. 基于改进指数再生采样核的有限新息率采样系统[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2013, 35(9): 2088–2093. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00059WANG Yajun, LI Ming, and LIU Gaofeng. Finite rate of innovation sampling system based on modified exponential reproducing sampling kernel[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2013, 35(9): 2088–2093. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00059 [20] 王亚军, 李明, 刘高峰. 复杂脉冲序列的有限新息率采样方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2013, 35(7): 1606–1611. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01329WANG Yajun, LI Ming, and LIU Gaofeng. Sampling complex pulse streams with finite rate of innovation methods[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2013, 35(7): 1606–1611. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01329 [21] URIGÜEN J A, BLU T, and DRAGOTTI P L. FRI sampling with arbitrary kernels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(21): 5310–5323. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2278152 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
