Research on Non-Line-Of-Sight Recognition Method Based on Weighted K-Nearest Neighbor Classification
-
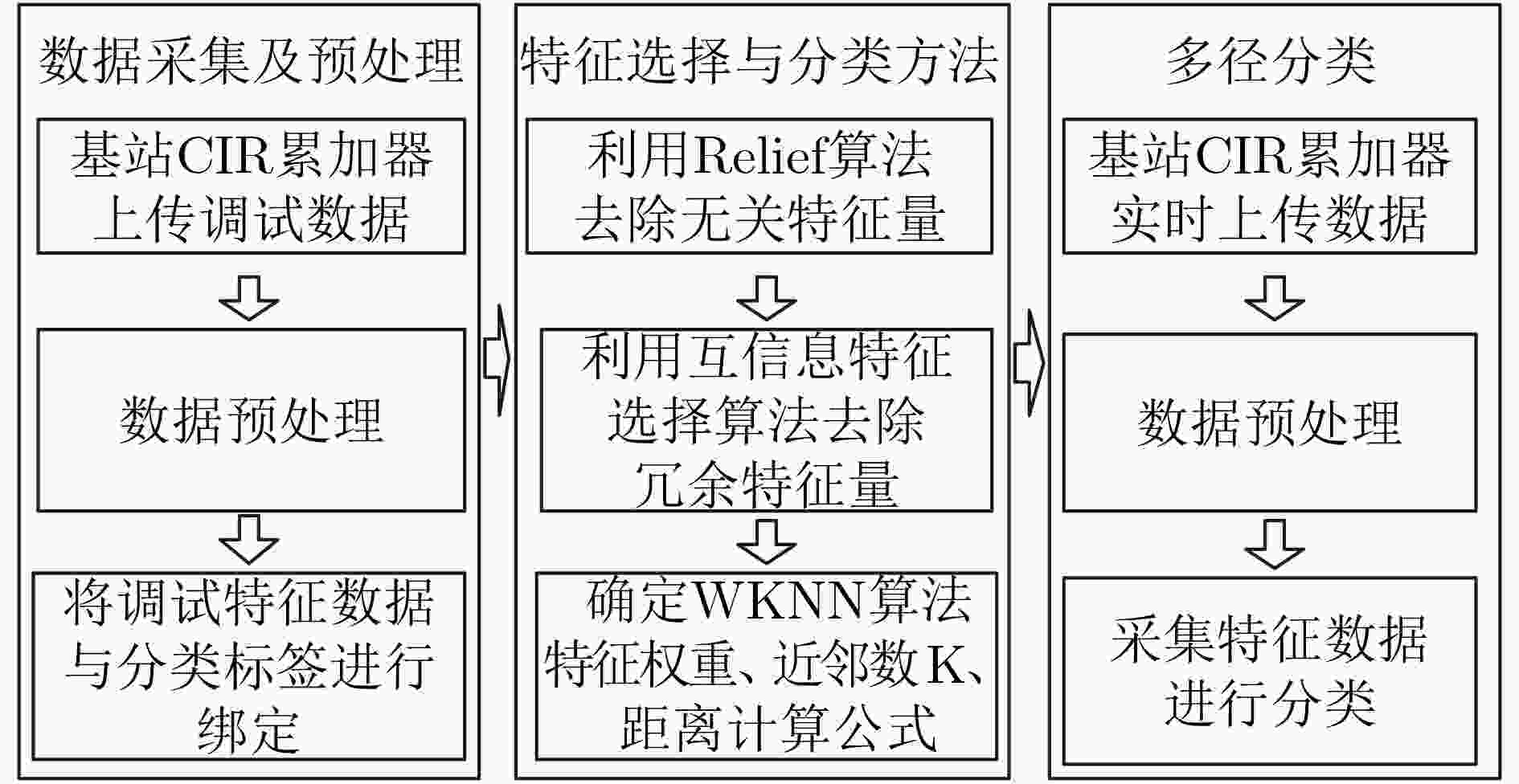
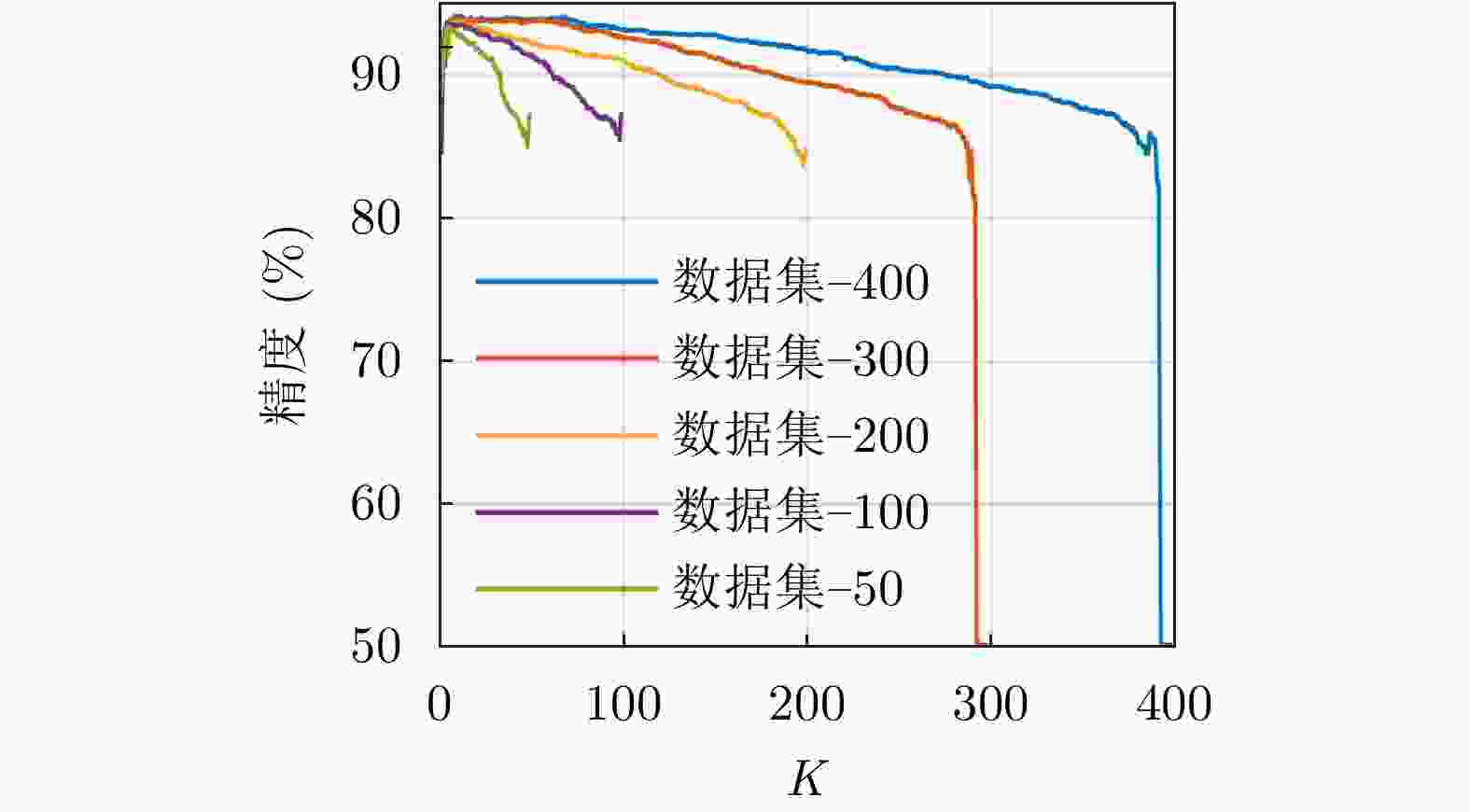
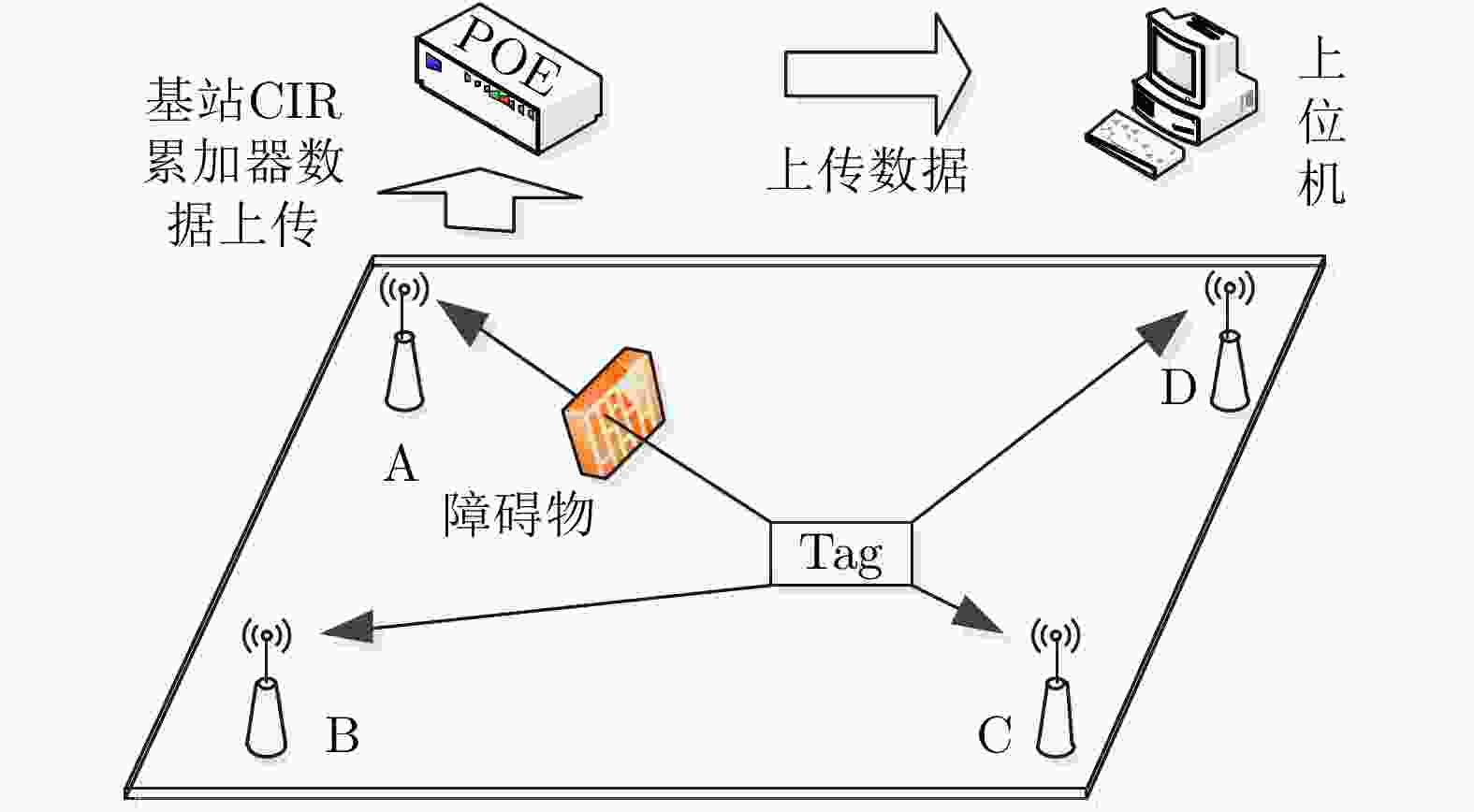
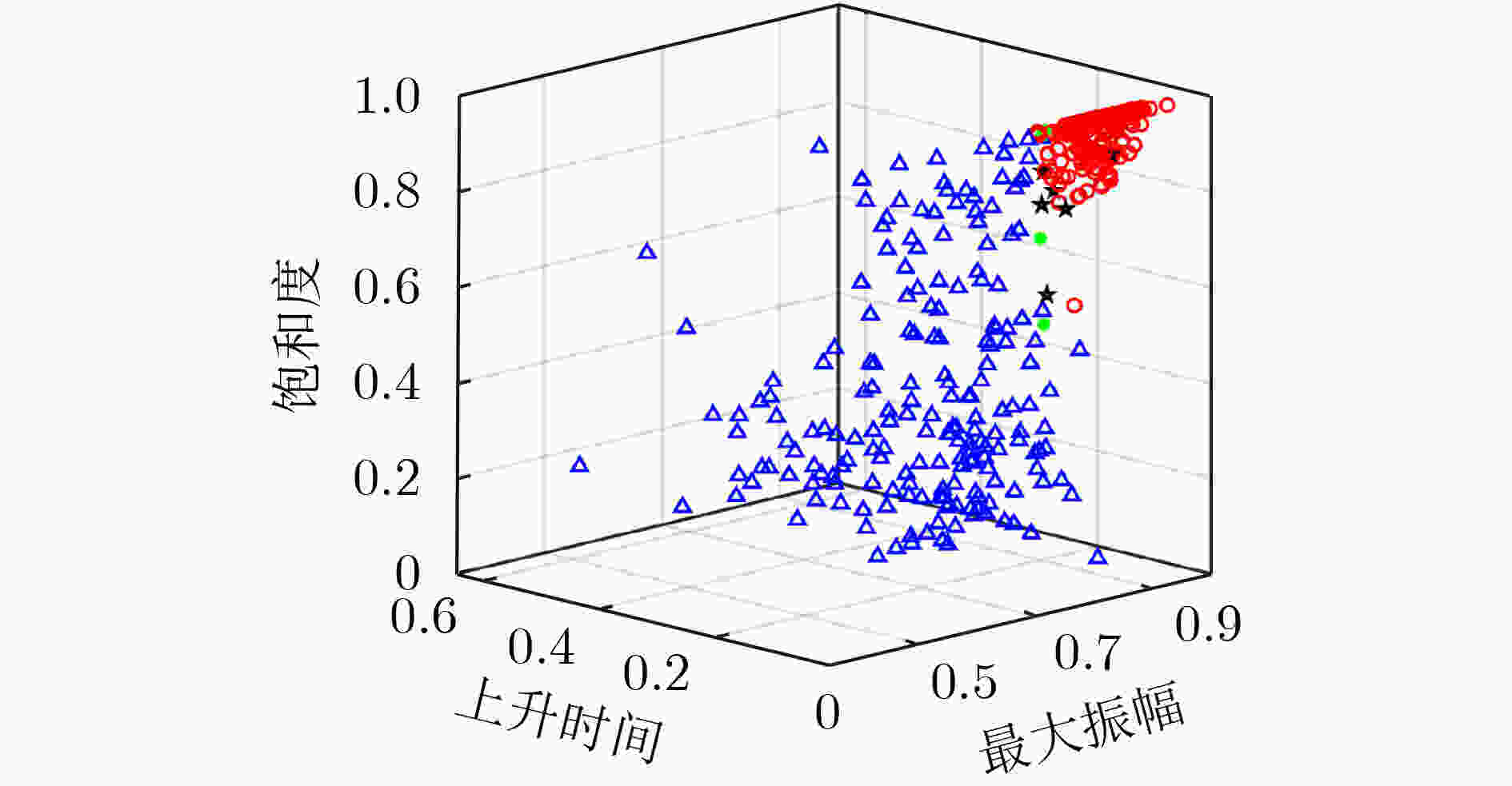
摘要: 超宽带(UWB)定位系统中,针对复杂的环境下,信号的遮挡、直达信号的错误判断严重影响定位精度问题,该文基于信道冲激响应(CIR)提出一种新型特征参量——饱和度(S),结合前人提出的特征参量利用Relief算法和互信息特征选择(MIFS)算法进行特征选择,在相关性的基础上赋予特征相应的权重,选择最优的特征子集进行加权K-近邻(WKNN)分类,提高了非视距(NLOS)识别系统准确度。并且分析了WKNN算法中的训练数据集数量与近邻数K对算法的影响,确定优选方案,减小了算法计算量,提高了NLOS识别系统实时性。在不同环境下进行实验验证,结果表明,该方法具备较高的识别准确度和环境适用性,识别精度达到95%。Abstract: In the Ultra-WideBand (UWB) positioning system, the signal occlusion and the misjudgment of the direct signal affect seriously the positioning accuracy in complex environment. To solve this problem, Saturation (S) is proposed, which is a new characteristic parameter based on Channel Impulse Response (CIR). In this study, the Relief algorithm and the Mutual Information Feature Selection (MIFS) algorithm are used for feature selection combined with feature parameters proposed by researchers. Based on the correlation of the parameters, the optimal feature subset with corresponding weights is used for weighted K-nearest neighbor classification, which improves the accuracy of the Non-Line-Of-Sight (NLOS) recognition system. The influence of the number of training dataset and the value of K on the Weighted K-Nearest Neighbor (WKNN) algorithm is analyzed. An optimization scheme is proposed to reduce the amount of calculation and improve the real-time performance of the NLOS recognition system. The experimental results in different environments show that the method has high recognition accuracy and wide applicability, and the recognition accuracy reaches 95%.
-
表 1 各特征参量的数学模型
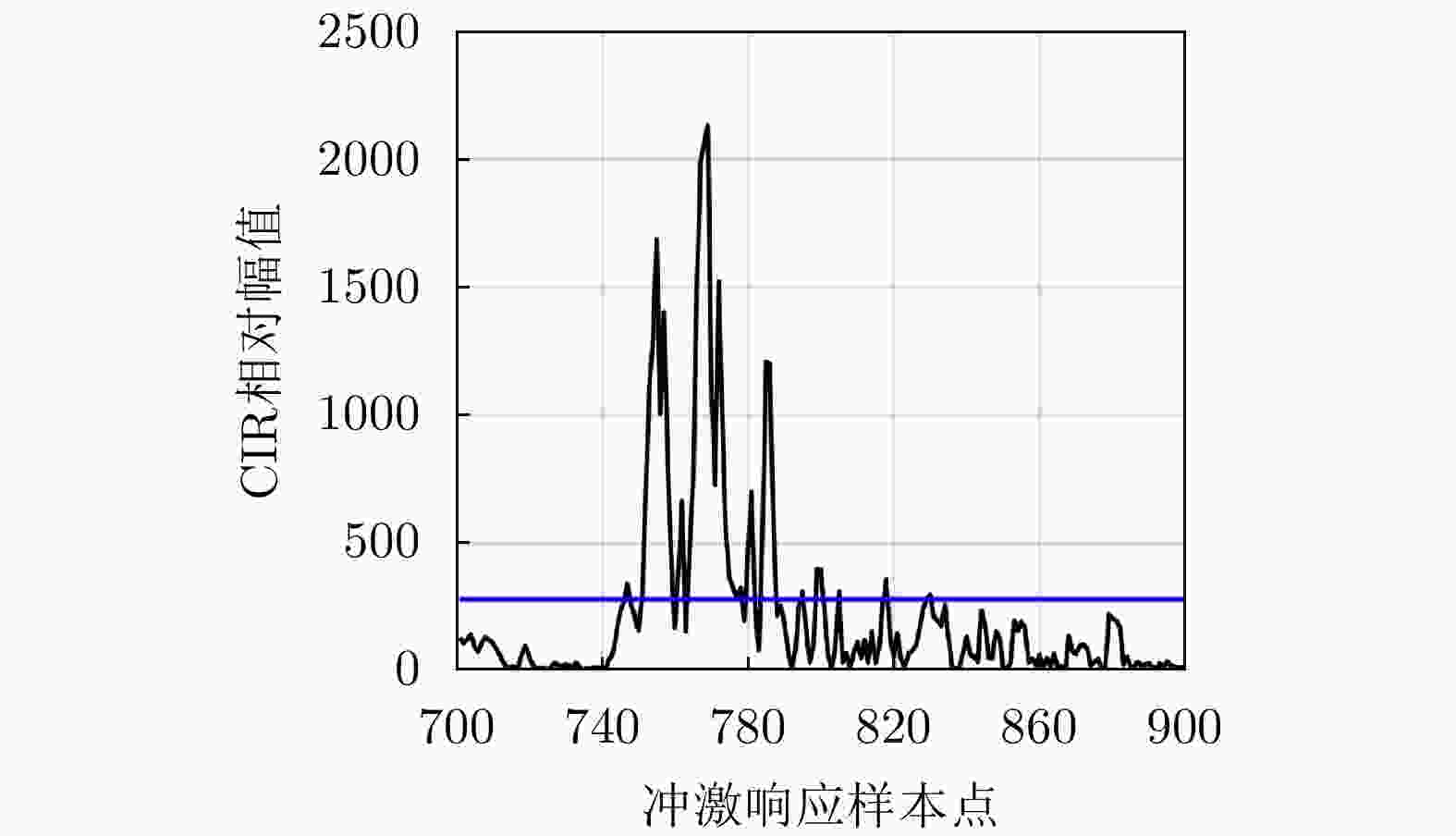
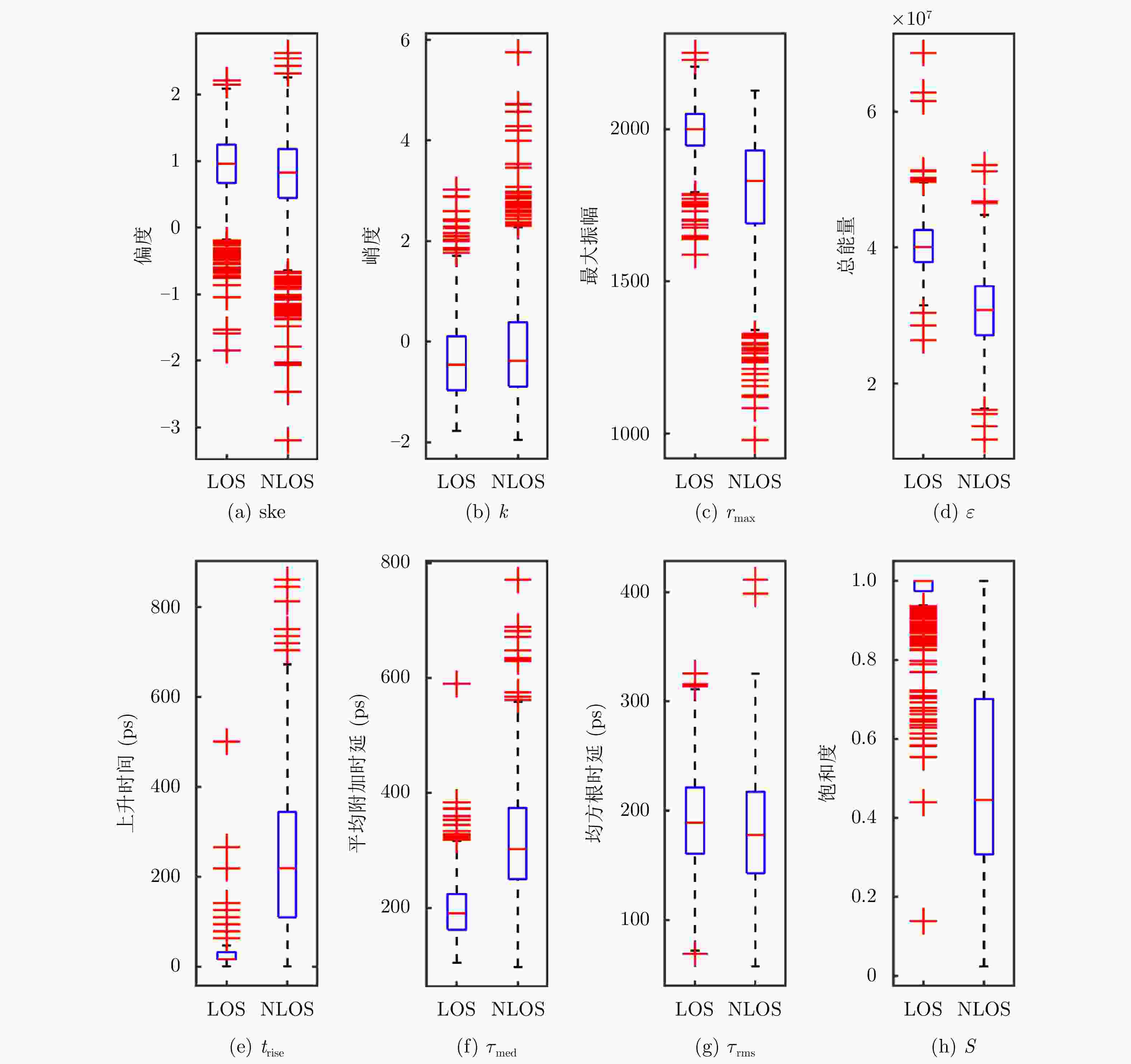
特征参量 数学模型 峭度 (kurtosis, $ k $) $k = \dfrac{ {{\rm{E}}\left\{ { { {\left[ {\left| {h\left( t \right)} \right| - {\mu _{\left| h \right|} } } \right]}^4} } \right\} } }{ {{\rm{E}}{ {\left\{ { { {\left[ {\left| {h\left( t \right)} \right| - {\mu _{\left| h \right|} } } \right]}^2} } \right\} }^2} } } = \dfrac{ {{\rm{E}}\left\{ { { {\left[ {\left| {h\left( t \right)} \right| - {\mu _{\left| h \right|} } } \right]}^4} } \right\} } }{ {\sigma _{\left| h \right|}^4} }$ 偏度 (skewness, $ {\text{ske}} $) ${\text{ske = } }\dfrac{ {{\rm{E}}\left[ { { {\left( {\left| {h\left( t \right)} \right| - {\mu _{\left| h \right|} } } \right)}^3} } \right]} }{ {\sigma _{\left| h \right|}^3} }$ 最大振幅 (maximum amplitude, $ {r_{\max }} $) $ {r_{{\text{max}}}} = \max \left\{ {\left| {r\left( {{t_i}} \right)} \right|} \right\} $ 总能量 (total energy, $ \varepsilon $) $ \varepsilon = {\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^N {\left| {r\left( {{t_i}} \right)} \right|} ^2} $ 上升时间 (rise time, $ {t_{\rm{rise}}} $) $\begin{gathered}{t_{ {\text{rise} } } } = {t_{ {\text{stop} } } } - {t_{ {\text{start} } } } \\ \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c} }{ {t_{ {\text{start} } } } = \min \left\{ { {t_i}:\left| {r\left( { {t_i} } \right)} \right| \ge 0.1{r_{\max } } } \right\} } \\ { {t_{ {\text{stop} } } } = \min \left\{ { {t_i}:\left| {r\left( { {t_i} } \right)} \right| \ge 0.9{r_{\max } } } \right\} } \end{array} } \right. \\ \end{gathered}$ 平均附加时延 (mean excess delay, $ {\tau _{{\text{med}}}} $) $ {\tau _{{\text{med}}}} = \dfrac{1}{\varepsilon }\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^N {\left( {{t_i}{{\left| {r\left( {{t_i}} \right)} \right|}^2}} \right)} $ 均方根延迟传播 (root-mean-squre delay spread, $ {\tau _{{\text{rms}}}} $) $ {\tau _{{\text{rms}}}} = \dfrac{1}{\varepsilon }\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^N {\left[ {{{\left( {{t_i} - {\tau _{{\text{med}}}}} \right)}^2}{{\left| {r\left( {{t_i}} \right)} \right|}^2}} \right]} $ 表 2 各参量与分类标签的相关性
特征参量 $ {\text{ske}} $ $ k $ $ {r_{\max }} $ $ \varepsilon $ 权值 0.1607 0.2537 17.2957 1.9692 特征参量 $ {t_{{\text{rise}}}} $ $ {\tau _{{\text{med}}}} $ $ {\tau _{{\text{rms}}}} $ $ S $ 权值 26.3062 13.0316 1.8136 34.2643 表 3 两特征参量之间的冗余度
$ {t_{{\text{rise}}}} $ $ {\tau _{{\text{med}}}} $ $ {r_{\max }} $ $ S $ $ {t_{{\text{rise}}}} $ 1 $ {\tau _{{\text{med}}}} $ 0.4932 1 $ {r_{\max }} $ 0.4774 0.8345 1 $ S $ 0.6050 0.7305 0.7223 1 表 4 混淆矩阵
混淆矩阵 预测值 传播信道为LOS 传播信道NLOS 真实值 传播信道为LOS TP FN 传播信道NLOS FP TN 表 5 单一参量在不同信道(CM)下的识别精度
CM1 CM2 CM3 CM4 CM5 CM6 $ k $ 0.5717 0.8917 0.8567 0.8750 0.5950 0.6417 $ {\text{ske}} $ 0.5450 0.5983 0.6900 0.6867 0.5517 0.5400 $ {r_{\max }} $ 0.8083 0.8583 0.9583 0.8150 0.9733 0.9450 $ \varepsilon $ 0.8983 0.8167 0.9550 0.8167 0.9967 0.8867 $ {t_{{\text{rise}}}} $ 0.9267 0.9217 0.9067 0.6933 0.6617 0.7333 $ {\tau _{{\text{med}}}} $ 0.8817 0.9250 0.9800 0.7983 0.9000 0.8967 $ {\tau _{\rm{rms} }} $ 0.5667 0.9083 0.5900 0.7867 0.7200 0.8167 $ S $ 0.9133 0.9267 0.9067 0.6967 0.6827 0.7467 表 6 多参量对不同信道(CM)的识别精度
CM1 CM2 CM3 CM4 CM5 CM6 $ {r_{{\text{max}}}} + {t_{{\text{rise}}}} $ 0.9675 0.9225 0.9825 0.9825 0.9550 0.9500 $ {t_{{\text{rise}}}} + S $ 0.9125 0.9250 0.9000 0.9325 0.6475 0.6875 $ k + {\tau _{{\text{rms}}}} $ 0.4925 0.7750 0.7925 0.7625 0.7550 0.7975 $ {\tau _{{\text{med}}}} + {\tau _{{\text{rms}}}} $ 0.8775 0.9125 0.9525 0.9475 0.9100 0.7500 $ {\text{ske}} + k + {\tau _{{\text{med}}}} $ 0.6775 0.7575 0.7800 0.7750 0.9225 0.8200 $ {\text{ske}} + k + {t_{{\text{rise}}}} $ 0.8900 0.8600 0.8750 0.4925 0.8025 0.7900 $ k + {\tau _{{\text{med}}}} + {\tau _{{\text{rms}}}} $ 0.8450 0.8875 0.9300 0.9325 0.8500 0.7375 $ {r_{{\text{max}}}} + {t_{{\text{rise}}}} + {\tau _{{\text{med}}}} $ 0.9400 0.9375 0.9775 0.9775 0.9575 0.9525 $ {{\boldsymbol{r}}_{{\bf{max}}}} + {{\boldsymbol{t}}_{{\bf{rise}}}} + {\boldsymbol{S}} $ 0.9725 0.9525 0.9875 0.9825 0.9675 0.9600 $ {r_{{\text{max}}}} + {t_{{\text{rise}}}} + k $ 0.7950 0.8525 0.8050 0.9750 0.8025 0.7600 $ {t_{{\text{rise}}}} + {\tau _{{\text{med}}}} + S $ 0.9275 0.9575 0.9700 0.9725 0.8825 0.7625 $ {t_{{\text{rise}}}} + \varepsilon + {\tau _{{\text{med}}}} $ 0.9300 0.9325 0.9825 0.9725 0.9625 0.9525 $ \varepsilon + {\tau _{{\text{rms}}}} + {\tau _{{\text{med}}}} $ 0.9025 0.9200 0.9725 0.9675 0.9800 0.8925 -
[1] 王振朝, 曹永青, 韦子辉. 基于WSN的射频定位技术[J]. 河北大学学报: 自然科学版, 2013, 33(5): 554–560. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1565.2013.05.020WANG Zhenchao, CAO Yongqing, and WEI Zihui. Radiofrequency positioning technology based on WSN[J]. Journal of Hebei University:Natural Science Edition, 2013, 33(5): 554–560. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1565.2013.05.020 [2] 肖竹, 王勇超, 田斌, 等. 超宽带定位研究与应用: 回顾和展望[J]. 电子学报, 2011, 39(1): 133–141.XIAO Zhu, WANG Yongchao, TIAN Bin, et al. Development and prospect of ultra-wideband localization research and application[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2011, 39(1): 133–141. [3] SCHROEDER J, GALLER S, KYAMAKYA K, et al. NLOS detection algorithms for Ultra-Wideband localization[C]. The 4th Workshop on Positioning, Navigation and Communication, Hannover, Germany, 2007: 159–166. doi: 10.1109/WPNC.2007.353628. [4] YAN Leibing, LU Yin, and ZHANG Yerong. An improved NLOS identification and mitigation approach for target tracking in wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 2798–2807. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2677480 [5] 王长强, 徐爱功, 隋心. UWB测距的NLOS误差削弱方法[J]. 导航定位学报, 2017, 5(3): 24–27, 32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4999.2017.03.006WANG Changqiang, XU Aigong, and SUI Xin. A method of NLOS error inhibition for UWB ranging[J]. Journal of Navigation and Positioning, 2017, 5(3): 24–27, 32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4999.2017.03.006 [6] CASAS R, MARCO A, GUERRERO J J, et al. Robust estimator for non-line-of-sight error mitigation in indoor localization[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2006, 2006(1): 043429. doi: 10.1155/ASP/2006/43429 [7] GUSTAFSON D E, ELWELL J M, and SOLTZ J A. Innovative indoor geolocation using RF multipath diversity[C]. 2006 IEEE/ION Position, Location, and Navigation Symposium, Coronado, USA, 2006: 904–912. doi: 10.1109/PLANS.2006.1650690. [8] 孙希延, 刘健, 纪元法, 等. 基于似然比检验的超宽带信道检测与定位算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(3): 590–597. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160484SUN Xiyan, LIU Jian, JI Yuanfa, et al. UWB channel detection and location algorithm based on likelihood ratio test[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(3): 590–597. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160484 [9] MARANÒ S, GIFFORD W M, WYMEERSCH H, et al. NLOS identification and mitigation for localization based on UWB experimental data[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2010, 28(7): 1026–1035. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2010.100907 [10] MIAO Zhimin, ZHAO Luwen, YUAN Weiwei, et al. Application of one-class classification in NLOS identification of UWB positioning[C]. 2016 International Conference on Information System and Artificial Intelligence, Hong Kong, China, 2016: 318–322. doi: 10.1109/ISAI.2016.0074. [11] YANG Xiaofeng, ZHAO Feng, and CHEN Tiejun. NLOS identification for UWB localization based on import vector machine[J]. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 2018, 87: 128–133. doi: 10.1016/j.aeue.2018.02.003 [12] HUANG An, TIAN Lei, JIANG Tao, et al. NLOS identification for wideband mmWave systems at 28 GHz[C]. The 89th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2019-Spring), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2019: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/VTCSpring.2019.8746362. [13] MUCCHI L and MARCOCCI P. A new parameter for UWB indoor channel profile identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2009, 8(4): 1597–1602. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2009.070318 [14] 张浩, 梁晓林, 吕婷婷, 等. 一种新颖的基于偏度的非视距区分算法[J]. 电讯技术, 2015, 55(5): 484–490. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2015.05.004ZHANG Hao, LIANG Xiaolin, LYU Tingting, et al. A novel non-line-of-sight identification algorithm based on skewness[J]. Telecommunication Engineering, 2015, 55(5): 484–490. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2015.05.004 [15] 纪元法, 杨政权, 孙希延, 等. 基于信道特征的超宽带非视距鉴别及定位算法[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2018, 18(19): 66–71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2018.19.011JI Yuanfa, YANG Zhengquan, SUN Xiyan, et al. UWB non-line-of-sight identification and location algorithm based on channel features[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2018, 18(19): 66–71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2018.19.011 [16] GUVENC I, CHONG C C, and WATANABE F. NLOS identification and mitigation for UWB localization systems[C]. 2007 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Hong Kong, China, 2007: 1571–1576. doi: 10.1109/WCNC.2007.296. [17] 范学满, 胡生亮, 贺静波. 对海雷达目标识别中全极化HRRP的特征提取与选择[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(12): 3261–3268. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160722FAN Xueman, HU Shengliang, and HE Jingbo. Feature extraction and selection of full polarization HRRP in target recognition process of maritime surveillance radar[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(12): 3261–3268. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160722 [18] JIN Cheng, KONG Xianguang, CHANG Jiantao, et al. Internal crack detection of castings: A study based on relief algorithm and Adaboost-SVM[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2020, 108(9/10): 3313–3322. doi: 10.1007/s00170-020-05368-w [19] HUANG Wanwei, ZHANG Jianwei, SUN Haiyan, et al. An anomaly detection method based on normalized mutual information feature selection and quantum wavelet neural network[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2017, 96(2): 2693–2713. doi: 10.1007/s11277-017-4320-2 [20] ZHENG Jianyang, ZHU Hexing, CHANG Fangfang, et al. An improved relief feature selection algorithm based on Monte-Carlo tree search[J]. Systems Science & Control Engineering, 2019, 7(1): 304–310. doi: 10.1080/21642583.2019.1661312 [21] 姚英彪, 毛伟勇, 姚瑞丽, 等. 基于改进支持向量回归的室内定位算法[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2017, 38(9): 2112–2119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2017.09.003YAO Yingbiao, MAO Weiyong, YAO Ruili, et al. Indoor positioning algorithm based on improved support vector regression[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2017, 38(9): 2112–2119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2017.09.003 [22] NARAYAN Y. Comparative analysis of SVM and Naive Bayes classifier for the SEMG signal classification[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2021, 37: 3241–3245. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2020.09.093 [23] YANG Haifeng, ZHANG Yongbo, HUANG Yuliang, et al. WKNN indoor location algorithm based on zone partition by spatial features and restriction of former location[J]. Pervasive and Mobile Computing, 2019, 60: 101085. doi: 10.1016/j.pmcj.2019.101085 [24] 李炜, 李全龙, 刘政怡. 基于加权的K近邻线性混合显著性目标检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(10): 2442–2449. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190093LI Wei, LI Quanlong, and LIU Zhengyi. Salient object detection using weighted K-nearest neighbor linear blending[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(10): 2442–2449. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190093 [25] 孔英会, 景美丽. 基于混淆矩阵和集成学习的分类方法研究[J]. 计算机工程与科学, 2012, 34(6): 111–117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-130X.2012.06.022KONG Yinghui and JING Meili. Research of the classification method based on confusion matrixes and ensemble learning[J]. Computer Engineering &Science, 2012, 34(6): 111–117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-130X.2012.06.022 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
