Unreferenced Low-lighting Image Enhancement Based on Deep Convolutional Neural Network
-
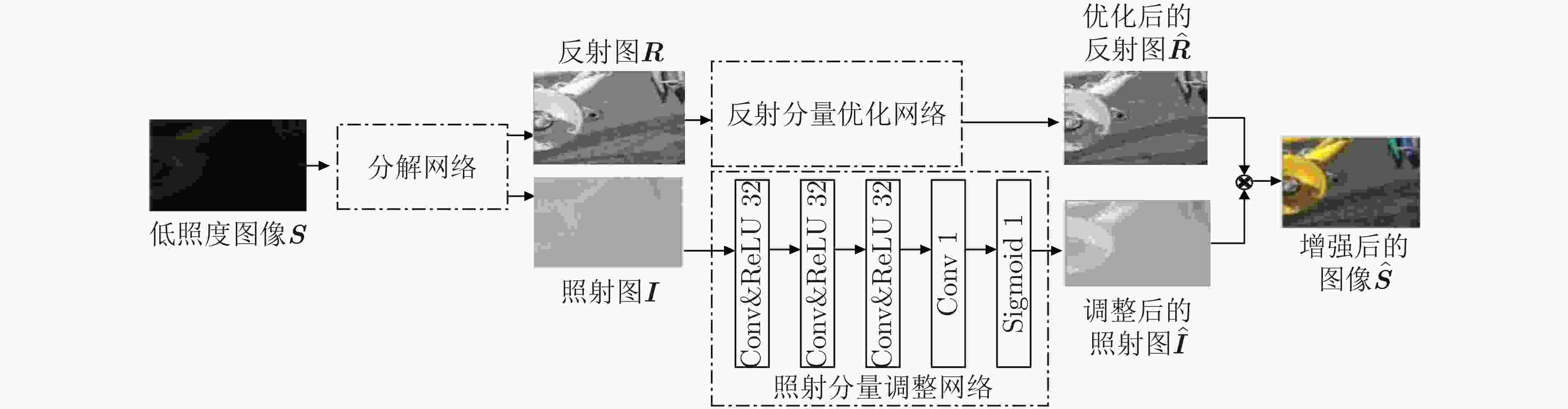
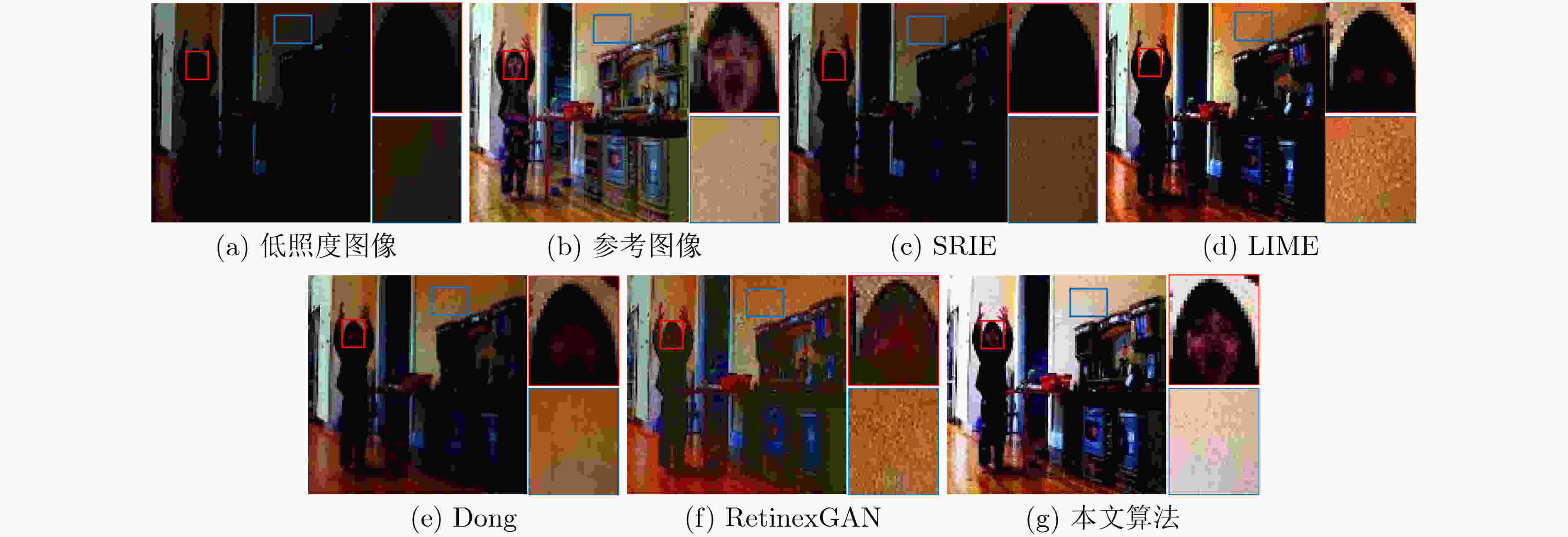
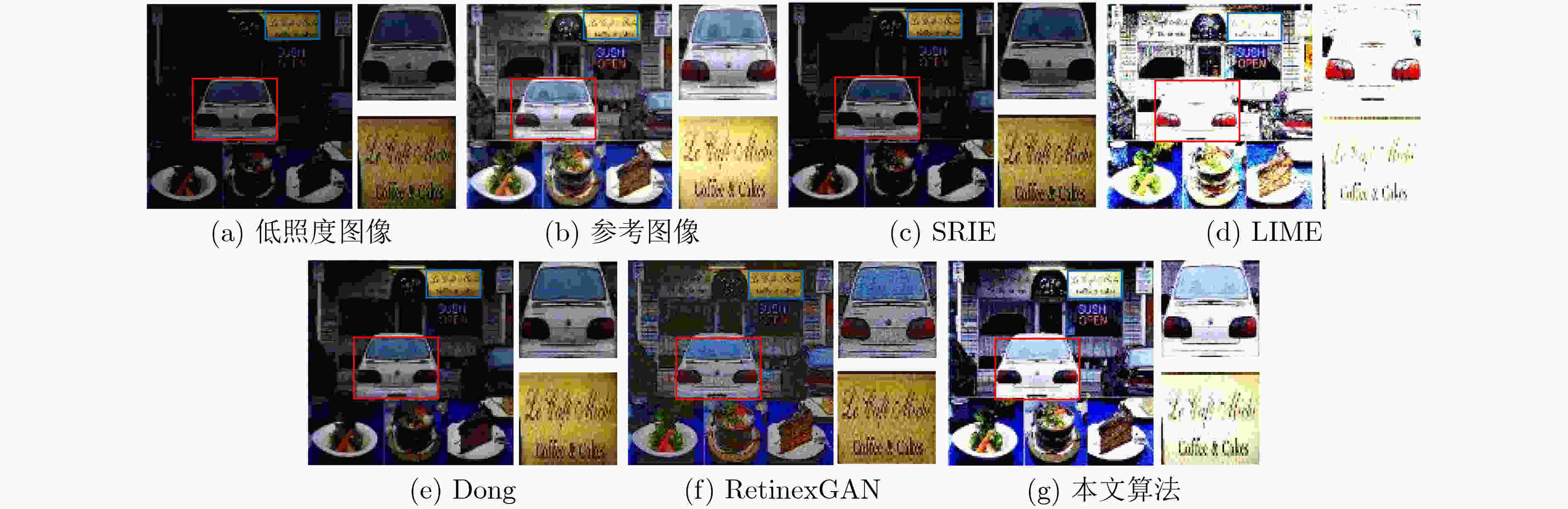
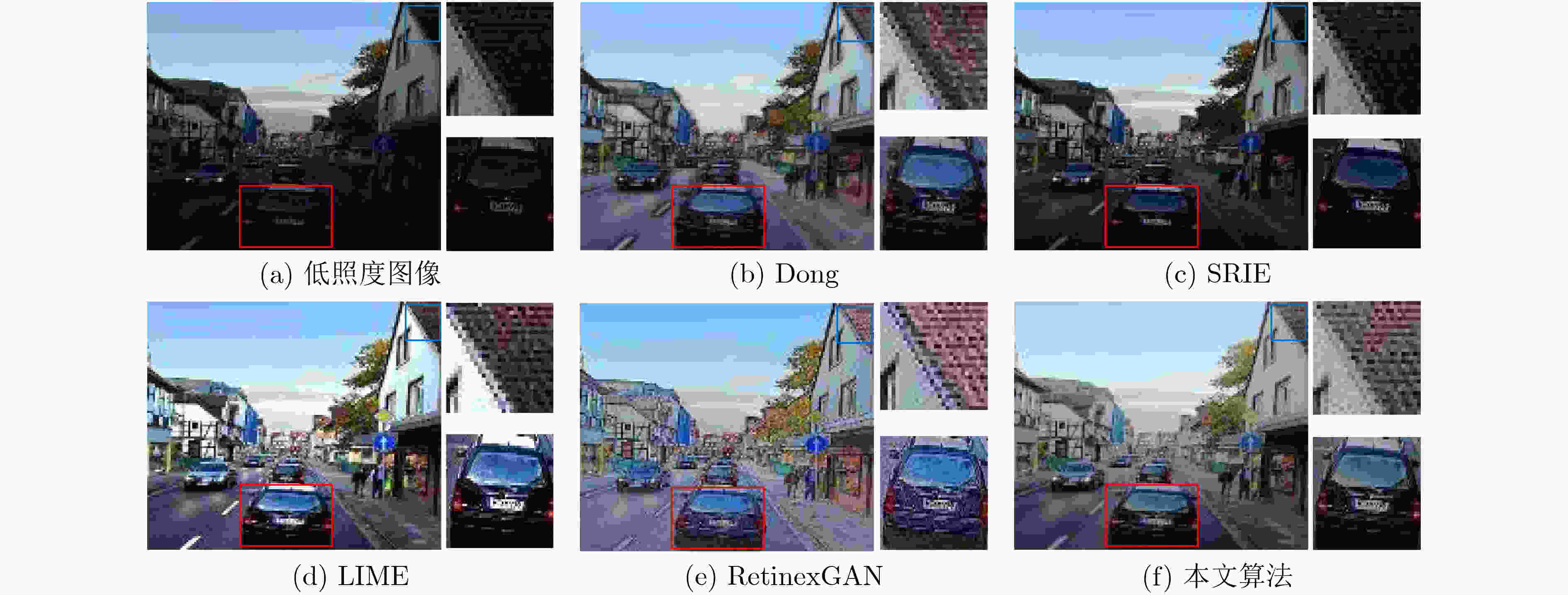
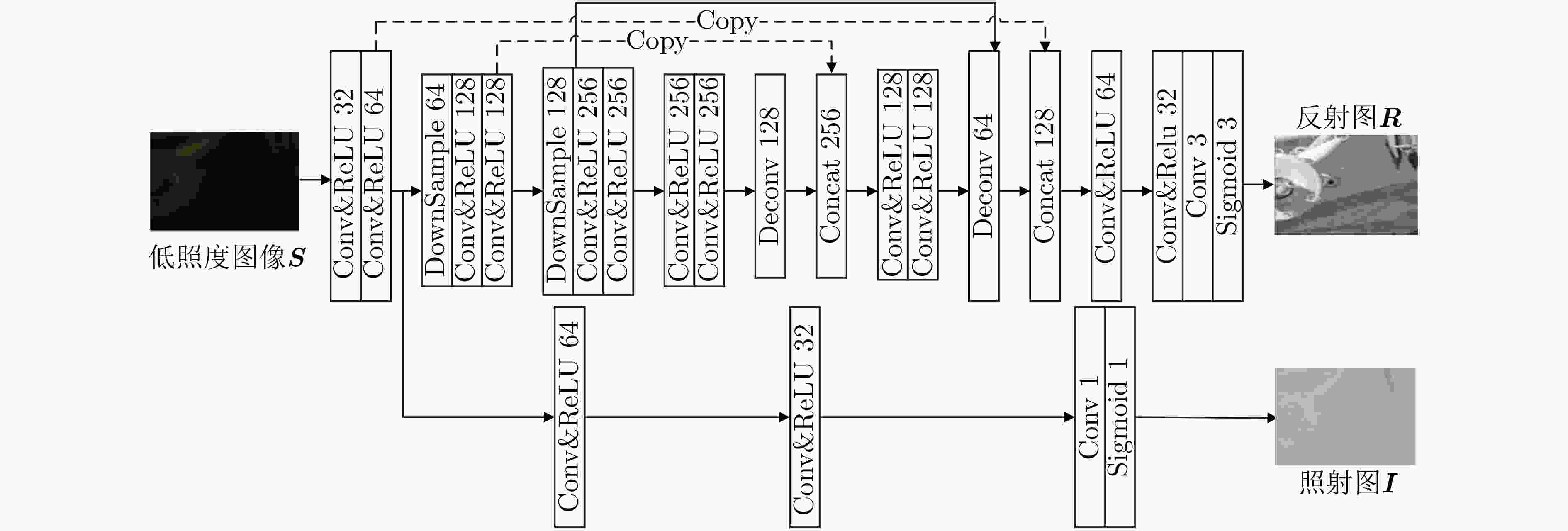
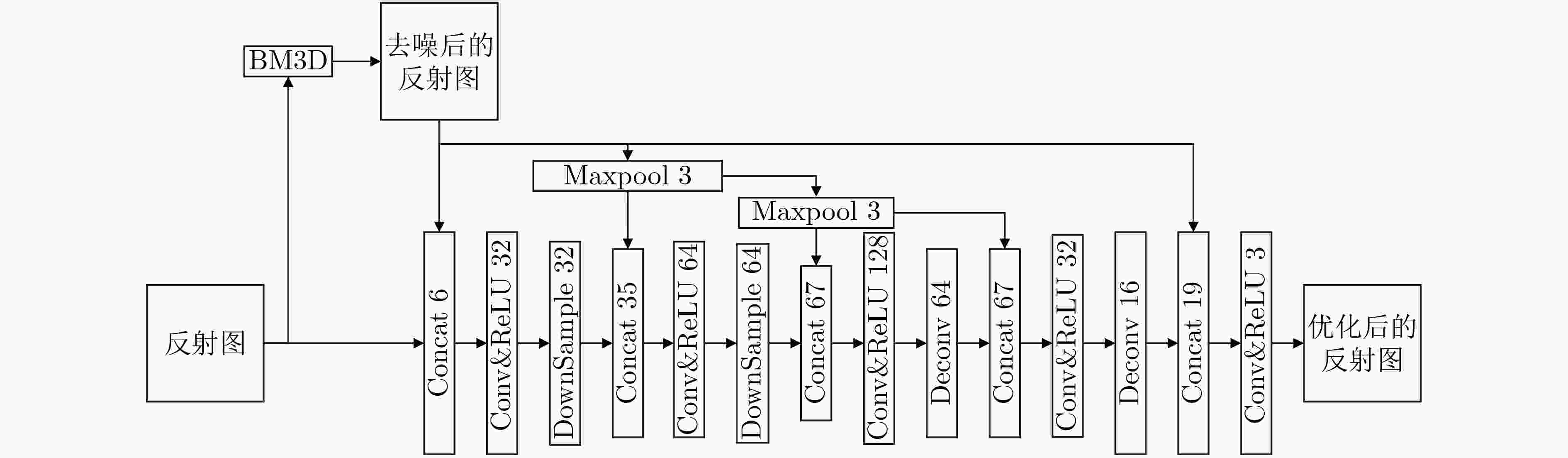
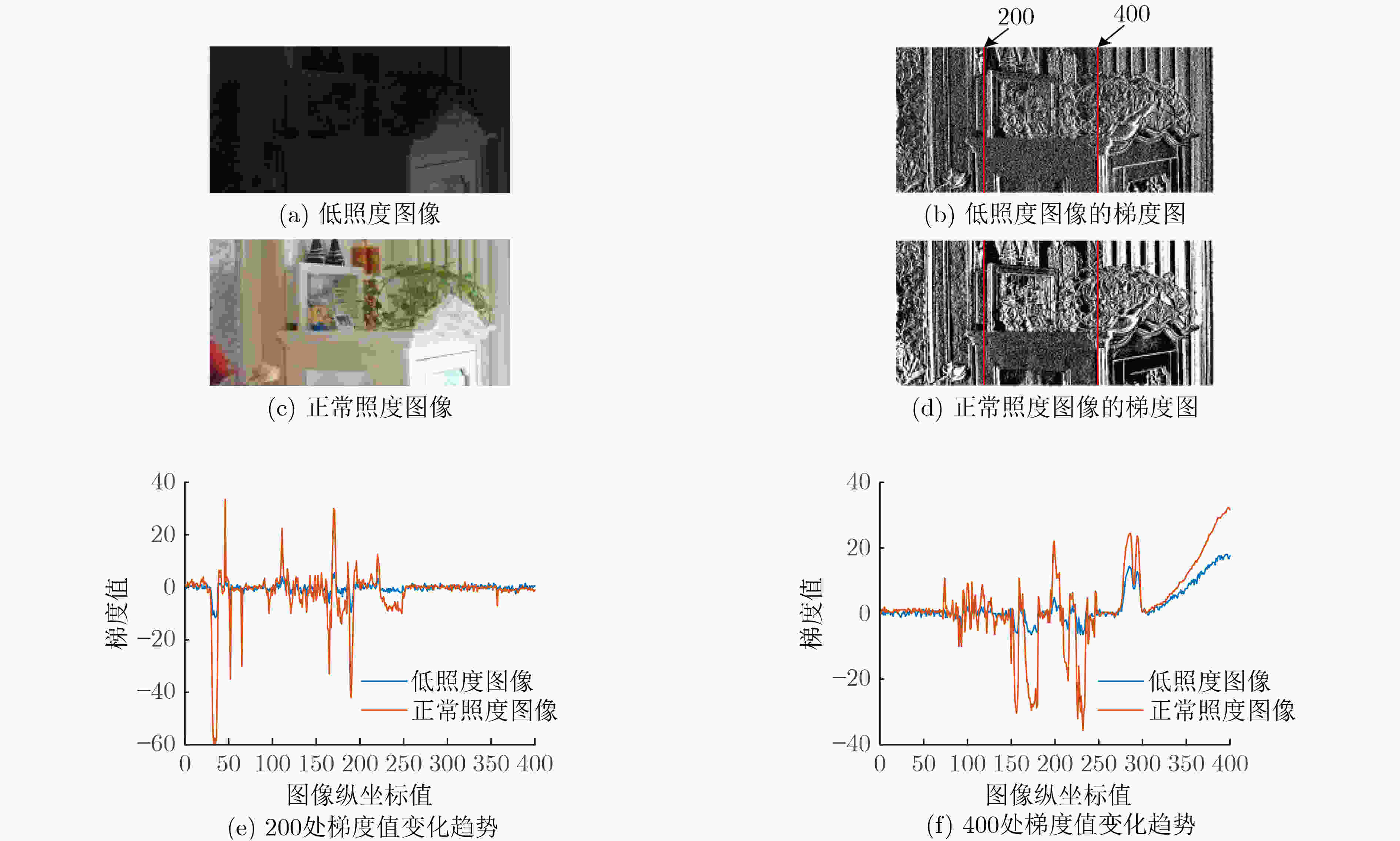
摘要: 针对低照度图像增强算法在实现细节增强的同时对噪声抑制考虑的不足问题,该文提出一种基于深度卷积神经网络的无参考低照度图像增强方法。首先,基于Retinex理论从输入的低照度图像中提取照射分量和反射分量,并分别对二者进行优化,随后将优化后的照射分量和反射分量相乘得到增强后的图像;同时,将3D块匹配(BM3D)的去噪效果融合进反射分量的优化过程中;最后,采用无参考图像训练的方式,并配合改进后的趋势一致性损失对网络参数进行更新。实验结果表明,该文算法相较于现有的主流算法,可有效地提升低照度图像的对比度和亮度,同时保持图像的自然性。Abstract: To address the shortcomings of existing low illumination image enhancement algorithms in achieving detail enhancement while considering noise suppression, a reference-free low-illumination image enhancement method based on deep convolutional neural networks is proposed in the paper. First, the illumination and reflection components are extracted from the input low-illumination image based on Retinex theory and optimised separately, after which the optimised illumination and reflection components are multiplied to obtain the enhanced image. loss to update the network parameters, meanwhile, the denoising effect of Block Matching 3D (BM3D ) is integrated into the optimization process of reflection components. The experimental results show that the algorithm in this paper can effectively enhance the contrast and brightness of low-illumination images compared to existing mainstream algorithms, while maintaining the naturalness of the images.
-
Key words:
- Image enhancement /
- Low light /
- Retinex /
- Convolutional Neural Network(CNN) /
- Consistent trend
-
表 1 不同算法处理结果的客观评价指标得分
表 2 算法处理时间对比(s)
-
[1] 张敏辉, 杨剑. 评价SAR图像去噪效果的无参考图像质量指标[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报:自然科学版, 2018, 30(4): 530–536. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2018.04.014ZHANG Minhui and YANG Jian. A new referenceless image quality index to evaluate denoising performance of SAR images[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications:Natural Science Edition, 2018, 30(4): 530–536. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2018.04.014 [2] 徐弦秋, 刘宏清, 黎勇, 等. 基于RGB通道下模糊核估计的图像去模糊[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报:自然科学版, 2018, 30(2): 216–221. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2018.02.009XU Xianqiu, LIU Hongqing, LI Yong, et al. Image deblurring with blur kernel estimation in RGB channels[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications:Natural Science Edition, 2018, 30(2): 216–221. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2018.02.009 [3] 张功国, 吴建, 易亿, 等. 基于集成卷积神经网络的交通标志识别[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报:自然科学版, 2019, 31(4): 571–577. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2019.04.019ZHANG Gongguo, WU Jian, YI Yi, et al. Traffic sign recognition based on ensemble convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications:Natural Science Edition, 2019, 31(4): 571–577. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2019.04.019 [4] LAND E H and MCCANN J J. Lightness and retinex theory[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1971, 61(1): 1–11. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.61.000001 [5] 胡正平, 刘博, 王成儒. 基于极大灰度频数抑制结合动态直方图均衡的图像增强算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2009, 31(6): 1327–1331. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2008.00580HU Zhengping, LIU Bo, and WANG Chengru. Image enhancement algorithm combines maximum gray frequency restrict with dynamic histogram equalization[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2009, 31(6): 1327–1331. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2008.00580 [6] FU Xueyang, ZENG Delu, HUANG Yue, et al. A weighted variational model for simultaneous reflectance and illumination estimation[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2782–2790. [7] GUO Xiaojie, LI Yu, and LING Haibin. LIME: Low-light image enhancement via illumination map estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(2): 982–993. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2639450 [8] DABOV K, FOI A, KATKOVNIK V, et al. Image denoising by sparse 3-D transform-domain collaborative filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2007, 16(8): 2080–2095. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2007.901238 [9] LORE K G, AKINTAYO A, and SARKAR S. LLNet: A deep autoencoder approach to natural low-light image enhancement[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2017, 61: 650–662. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.06.008 [10] CHEN Chen, CHEN Qifeng, XU Jia, et al. Learning to see in the dark[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 3291–3300. [11] WEI Chen, WANG Wenjing, YANG Wenhan, et al. Deep retinex decomposition for low-light enhancement[C]. British Machine Vision Conference 2018, Newcastle, UK, 2018. [12] MA Tian, GUO Ming, YU Zhenhua, et al. RetinexGAN: Unsupervised low-light enhancement with two-layer convolutional decomposition networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 56539–56550. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3072331 [13] GUO Chunle, LI Chongyi, GUO Jichang, et al. Zero-reference deep curve estimation for low-light image enhancement[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 1777–1786. [14] 陈勇, 詹帝, 刘焕淋. 基于物理模型与边界约束的低照度图像增强算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(12): 2962–2969. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170267CHEN Yong, ZHAN Di, and LIU Huanlin. Enhancement algorithm for low-lighting images based on physical model and boundary constraint[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(12): 2962–2969. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170267 [15] DONG Xuan, WANG Guan, PANG Yi, et al. Fast efficient algorithm for enhancement of low lighting video[C]. 2011 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, Barcelona, Spain, 2011: 1–6. [16] WANG Liqian, XIAO Liang, LIU Hongyi, et al. Variational Bayesian method for retinex[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2014, 23(8): 3381–3396. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2014.2324813 [17] REN Xutong, YANG Wenhan, CHENG Wenhuang, et al. LR3M: Robust low-light enhancement via low-rank regularized retinex model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 5862–5876. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.2984098 [18] WANG Yang, CAO Yang, ZHA Zhengjun, et al. Progressive retinex: Mutually reinforced illumination-noise perception network for low-light image enhancement[C]. The 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Nice, France, 2019: 2015–2023. [19] ZHANG Yonghua, ZHANG Jiawan, and GUO Xiaojie. Kindling the darkness: A practical low-light image enhancer[C]. The 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Nice, France, 2019: 1632–1640. [20] LV Feifan and LU Feng. Attention-guided low-light image enhancement[J]. arXiv: 1908.00682, 2019. [21] WANG Zhou, BOVIK A C, SHEIKH H R, et al. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(4): 600–612. doi: 10.1109/tip.2003.819861 [22] MITTAL A, SOUNDARARAJAN R, and BOVIK A C. Making a “completely blind” image quality analyzer[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2013, 20(3): 209–212. -





 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:
