Pedestrian Re-IDentification Algorithm Based on Dual-domain Filtering and Triple Metric Learning
-
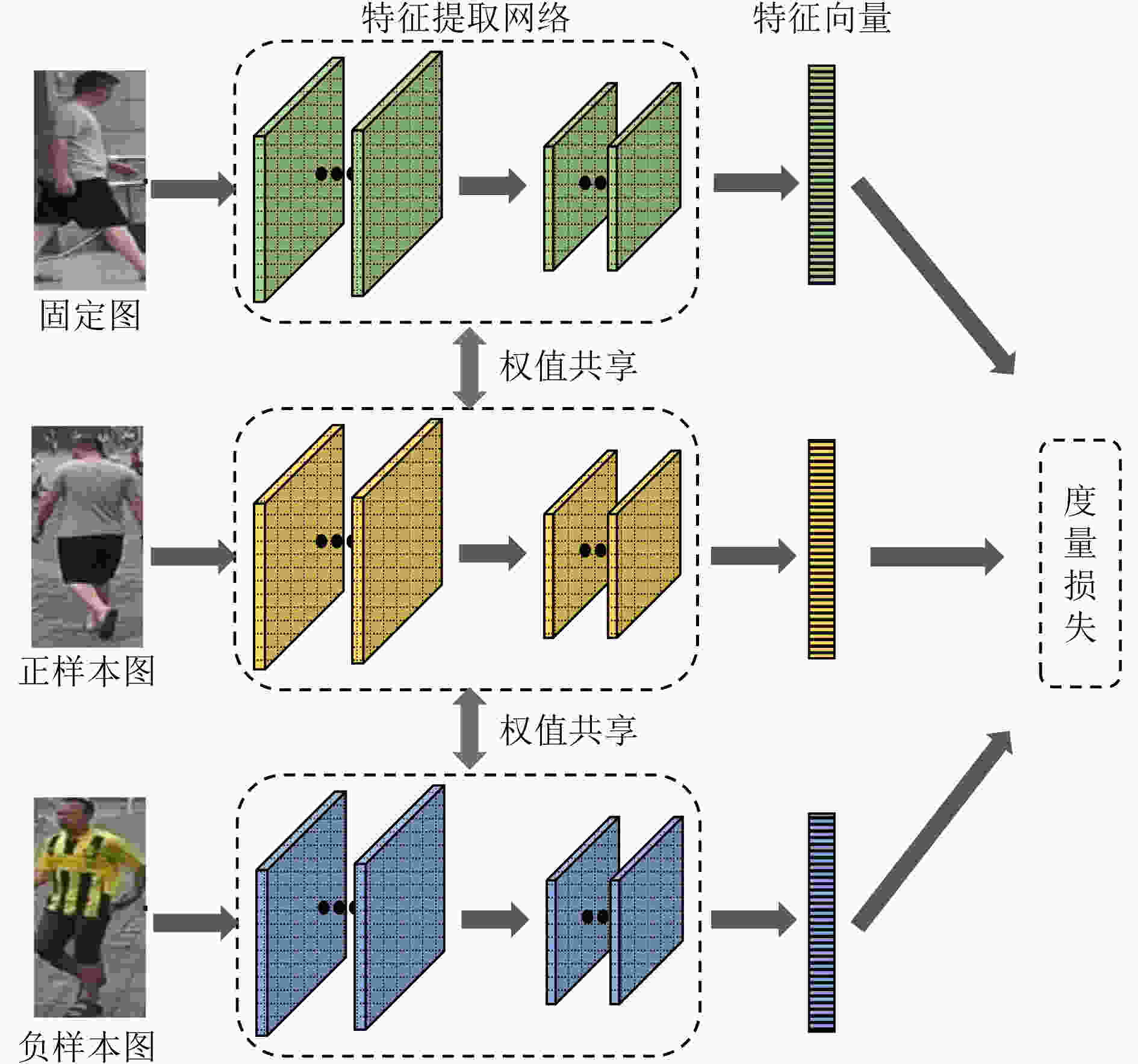
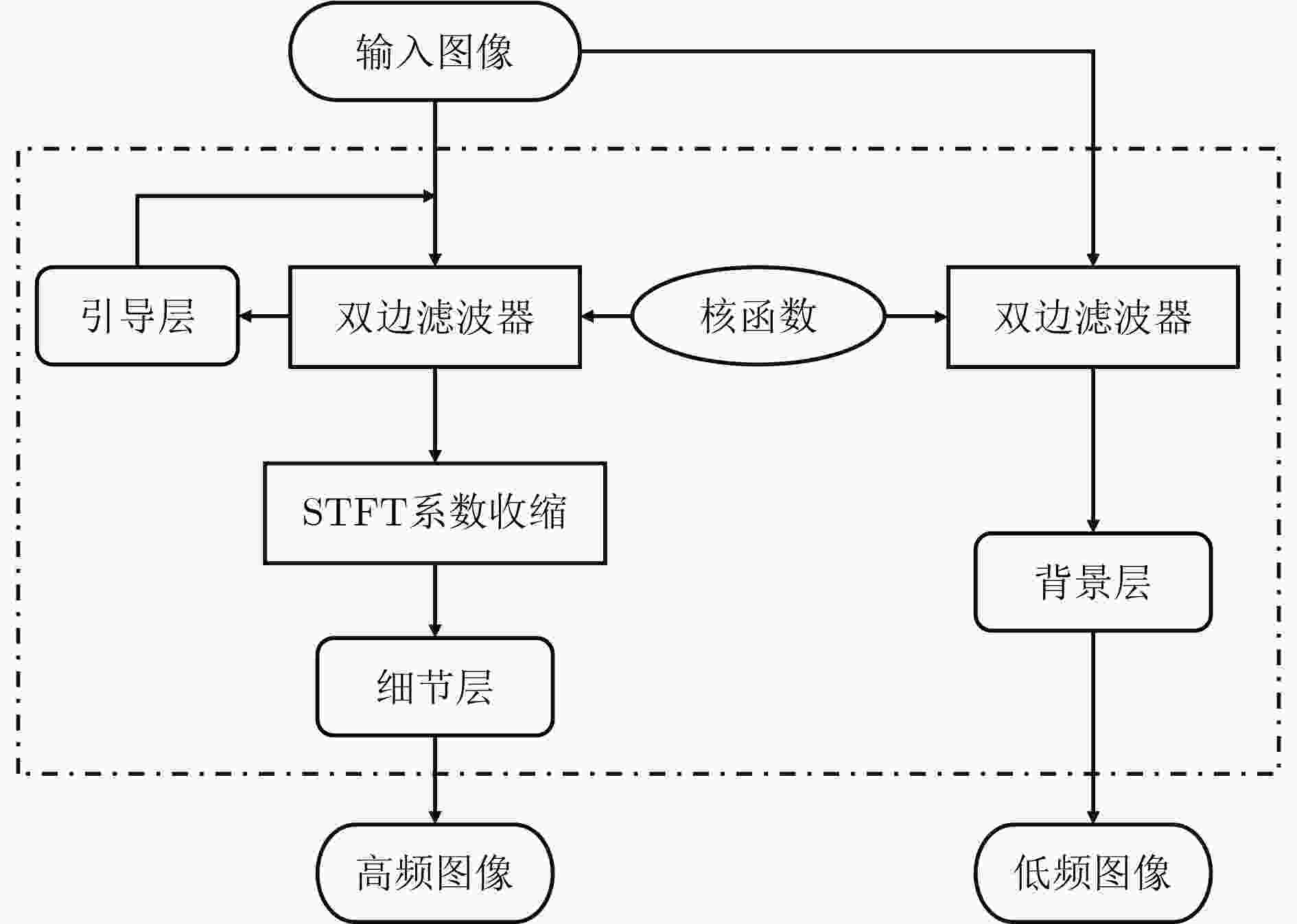
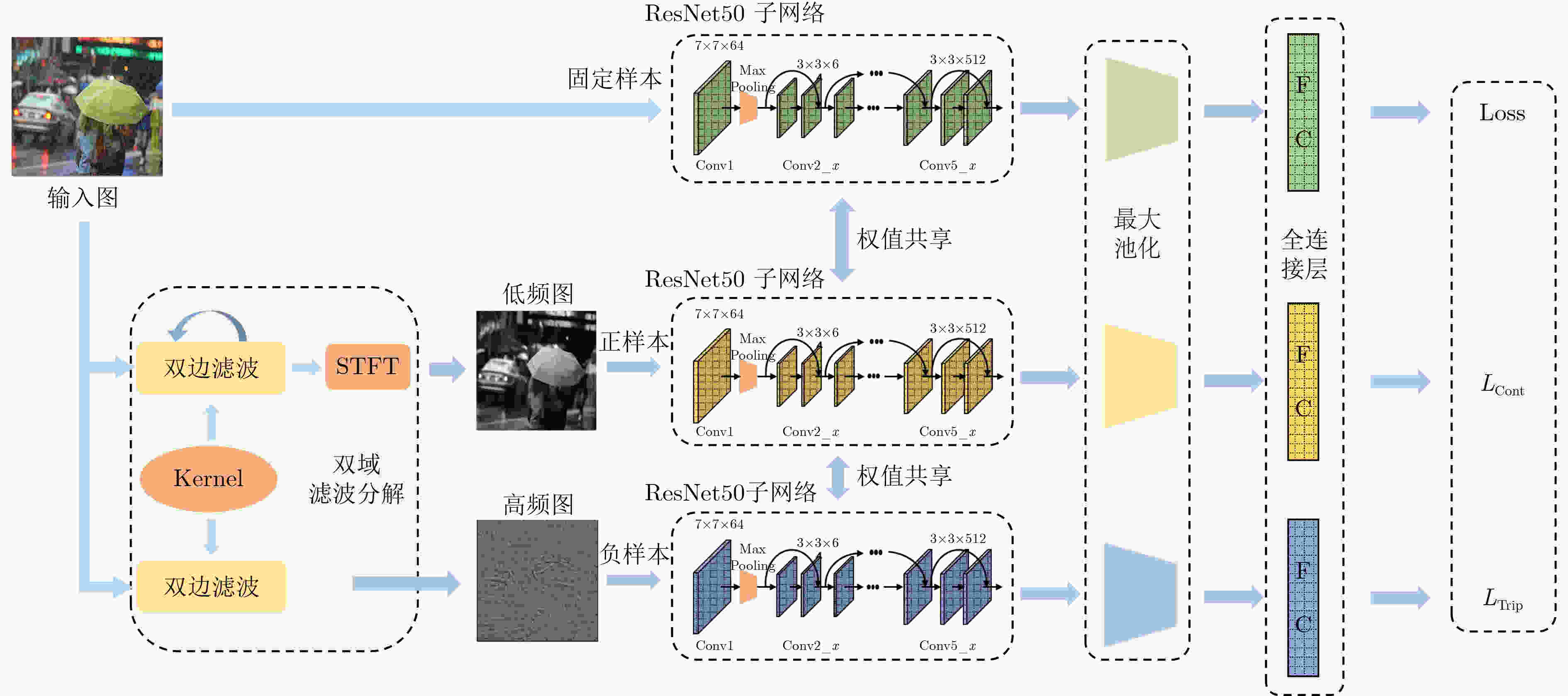
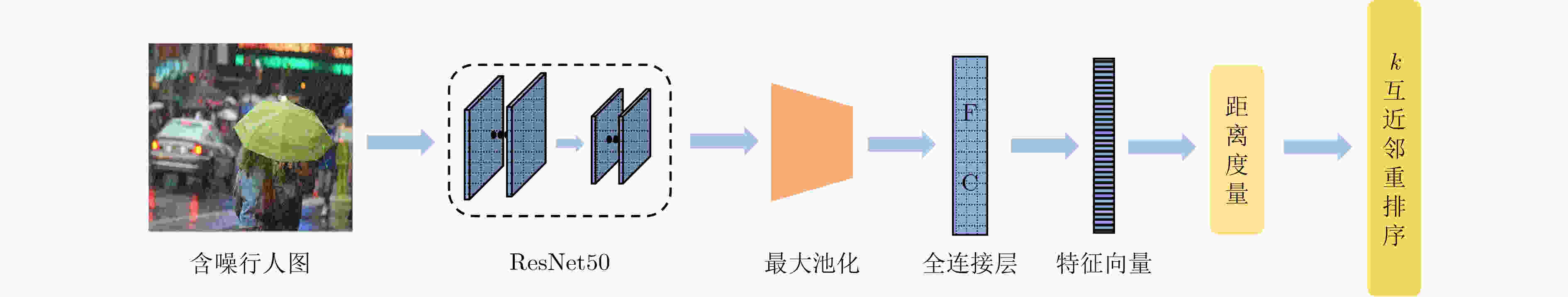
摘要: 在图像的捕获、传输或者处理过程中都有可能产生噪声,当图像被大量噪声影响时,许多行人再识别(ReID)方法将很难提取具有足够表达能力的行人特征,表现出较差的鲁棒性。该文主要针对低质图像的行人再识别问题,提出双域滤波分解构建3元组,用于训练度量学习模型。所提方法主要分为两个部分,首先分析了监控视频中不同图像噪声的分布特性,通过双域滤波进行图像增强。然后基于双域滤波分解对图像噪声具有很好的分离作用,该文提出一种新的3元组构建方式。在训练阶段,将双域滤波生成的低频原始图像和高频噪声图像,与原图一起作为输入3元组,网络可以进一步抑制噪声分量。同时优化了损失函数,将3元组损失和对比损失组合使用。最后利用re-ranking扩充排序表,提高识别的准确率。在加噪Market-1501和CUHK03数据集上的平均Rank-1为78.3%和21.7%,平均准确率均值(mAP)为66.9%和20.5%。加噪前后的Rank-1精度损失只有1.9%和7.8%,表明该文模型在含噪情况表现出较强的鲁棒性。Abstract: Noise may be generated in the process of image capture, transmission or processing. When the image is affected by a large amount of noise, it is difficult for many pedestrian Re-IDentification(ReID) methods to extract pedestrian features with sufficient expressive ability, which shows poor robustness. This paper focuses on the pedestrian re-identification with low quality image. The dual-domain filtering decomposition is proposed to construct triplet, which is used to train metric learning model. The proposed method mainly consists of two parts. Firstly, the distribution characteristics of different image noise in surveillance videos is analyzed and images are enhanced by dual-domain filtering. Secondly, based on the separation effect of dual-domain filtering, a new triplet is proposed. In the training stage, the original image with the low-frequency component, the noise with high-frequency component generated by the dual-domain filtering and the original image are used as the input triplet. So the noise component can be further suppressed by the network. At the same time, the loss function is optimized, and the triple loss and contrast loss are used in combination. Finally, re-ranking is used to expand the sorting table to improve the accuracy of identification. The average Rank-1 on the noisy Market-1501 and CUHK03 datasets are 78.3% and 21.7%, and the mean Average Precision(mAP) is 66.9% and 20.5%. The accuracy loss of Rank-1 before and after adding noise is only 1.9% and 7.8%, which indicates that the model in this paper shows strong robustness in the case of noise.
-
表 1 不同图像增强方法在Market-1501和CUHK03数据集上的性能对比(%)
指标 无处理[12] K-SVD[13] Huang等人[14] Kang等人[15] Luo等人[16] Son等人[17] 双域滤波[11] 高斯噪声 Rank-1 74.0/18.4 72.3/19.3 75.3/20.1 73.5/19.7 75.0/20.2 74.8/19.9 75.5/20.5 mAP 49.2/17.2 46.7/18.1 51.4/18.8 47.8/18.6 51.2/19.1 51.0/18.7 51.9/19.2 椒盐噪声 Rank-1 64.8/18.5 65.6/19.1 66.6/20.9 66.3/19.6 66.4/20.1 66.2/19.6 66.4/20.3 mAP 40.3/17.2 43.0/17.9 42.7/19.2 42.2/18.2 42.4/18.8 42.1/18.1 42.2/18.9 雨噪声 Rank-1 75.5/15.9 74.9/16.5 75.9/16.6 76.2/17.5 76.6/17.8 75.9/16.8 76.8/18.1 mAP 51.4/14.6 51.3/15.4 51.7/15.5 52.0/16.0 52.1/16.4 51.8/15.7 63.4/16.8 无噪声 Rank-1 78.9/22.2 76.2/22.3 79.1/22.4 77.7/22.3 79.0/22.4 78.9/22.3 79.2/22.5 mAP 55.0/21.0 52.4/21.8 65.1/22.5 53.8/22.0 64.7/22.6 64.4/22.2 66.8/22.9 表 2 不同图像增强方法的指标平均增益(%)
表 3 消融实验结果
3元组网络 Triplet loss Contrastive loss reranking Rank-1 (%) mAP (%) 常规 改进 √ √ √ √ 76.7 65.3 √ √ 74.9 53.2 √ √ √ 76.5 54.6 √ √ √ √ 78.7 67.8 表 4 Market-1501数据集各方法的Rank-1和mAP(%)
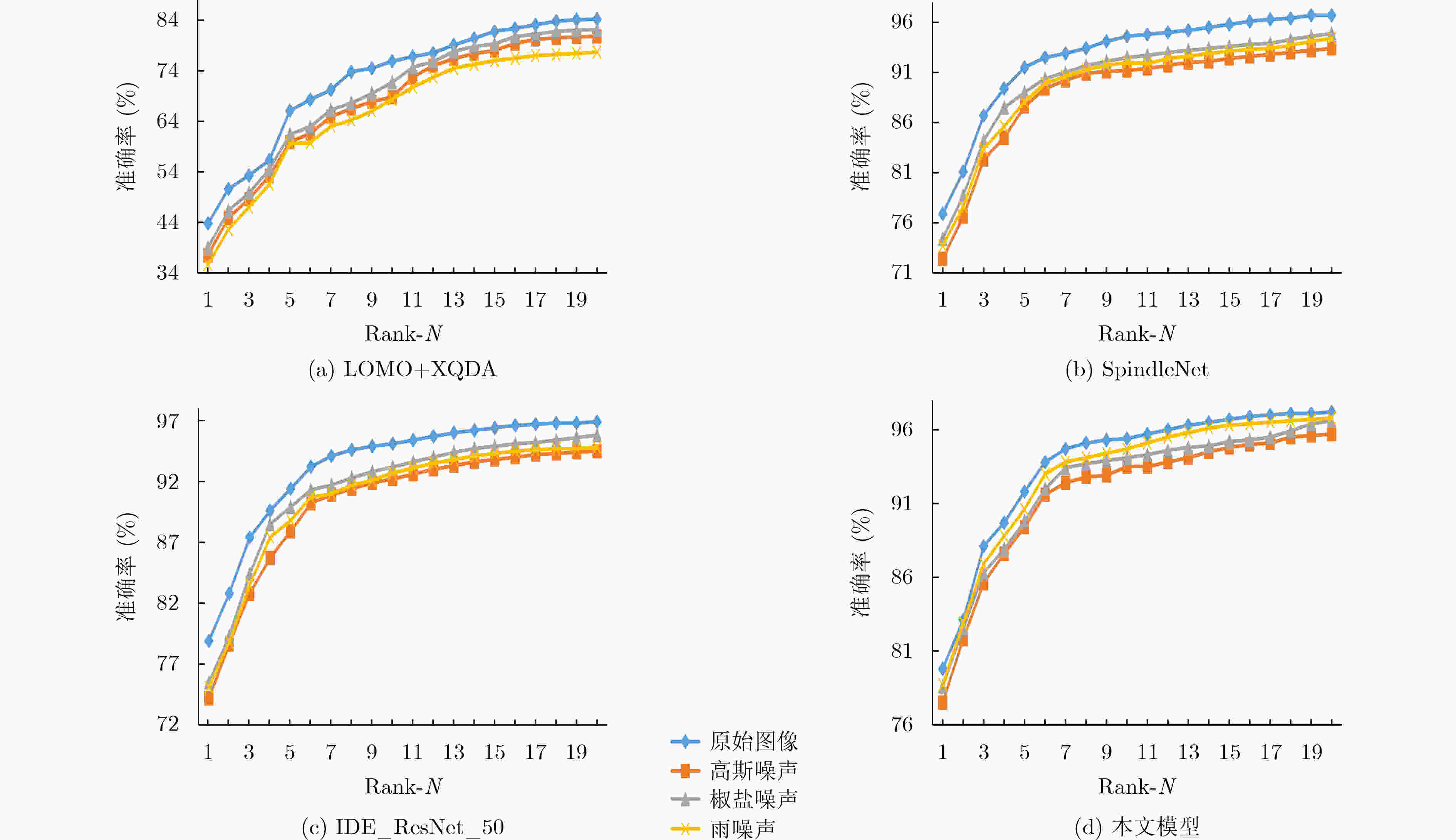
方法 原始图像 高斯噪声 椒盐噪声 雨噪声 Rank-1 mAP Rank-1 mAP Rank-1 mAP Rank-1 mAP LOMO+XQDA[2] 43.8 22.7 37.5 19.5 39 21.6 35.7 20.3 SpindleNet[7] 76.9 / 72.4 / 74.4 / 73.7 / IDE_ResNet_50[12] 78.9 55 74.2 49.4 75.5 51.9 75.1 50.6 SVDNet[20] 82.3 62.1 78.6 58.4 80.3 59.2 78.1 57.5 APR[21] 84.3 64.7 79.2 60.2 81.4 61.9 80.8 60.8 PIE[6] 79.3 56.0 74.8 50.5 76.1 53.0 77.1 54.2 本文模型 79.8 68.3 77.5 65.8 78.6 67.1 78.7 67.8 表 5 Market-1501数据集各方法Rank-1和mAP的平均下降率(%)
表 6 CUHK03数据集各方法的Rank-1和mAP(%)
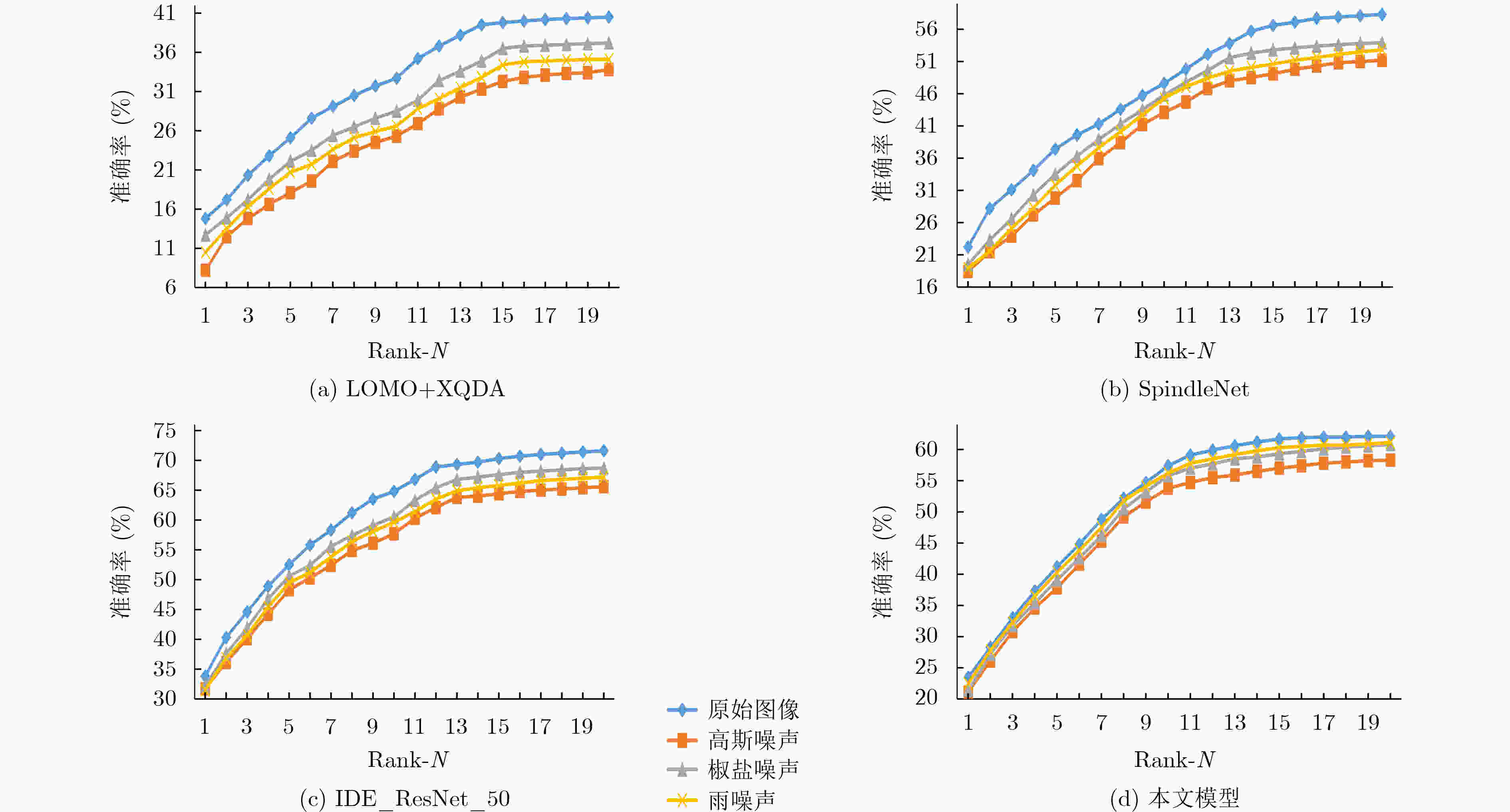
方法 原始图像 高斯噪声 椒盐噪声 雨噪声 Rank-1 mAP Rank-1 mAP Rank-1 mAP Rank-1 mAP LOMO+XQDA[2] 14.8 13.6 8.2 9.5 12.7 10.8 10.5 10.1 SpindleNet[7] 33.8 / 31.7 / 32.2 / 31.5 / IDE_ResNet_50[12] 22.2 21.0 18.4 17.6 19.5 18.8 18.9 17.8 SVDNet[20] 40.9 37.8 37.2 28.8 38.4 31.6 36.4 27.1 APR[21] 45.7 46.8 42.4 41.6 43.3 42.7 42.8 42.1 PIE[6] 34.2 31.1 31.4 25.8 33.1 29.6 29.4 22.6 本文模型 23.5 22.7 21.1 19.8 21.4 20.2 22.5 21.5 -
[1] 何果财, 刘峡壁. 基于图像三元组挖掘的无监督视觉表示学习[J]. 计算机学报, 2018, 42(12): 2787–2803. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2018.02787HE Guocai and LIU Xiabi. Unsupervised visual representation learning with image triplets mining[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2018, 42(12): 2787–2803. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2018.02787 [2] LIAO Shengcai, HU Yang, ZHU Xiangyu, et al. Person re-identification by local maximal occurrence representation and metric learning[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 2197–2206. [3] 桑海峰, 王传正, 吕应宇, 等. 基于多信息流动卷积神经网络的行人再识别[J]. 电子学报, 2019, 47(2): 351–357. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.02.014SANG Haifeng, WANG Chuanzheng, LÜ Yingyu, et al. Person re-identification based on multi-information flow convolutional neural network[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2019, 47(2): 351–357. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.02.014 [4] LUO Hao, JIANG Wei, ZHANG Xuan, et al. AlignedReID++: Dynamically matching local information for person re-identification[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2019, 94: 53–61. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2019.05.028 [5] 刘一敏, 蒋建国, 齐美彬, 等. 融合生成对抗网络和姿态估计的视频行人再识别方法[J]. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(3): 576–584. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180054LIU Yimin, JIANG Jianguo, QI Meibin, et al. Video-based person re-identification method based on GAN and pose estimation[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(3): 576–584. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180054 [6] ZHENG Liang, HUANG Yujia, LU Huchuan, et al. Pose-invariant embedding for deep person re-identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(9): 4500–4509. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2910414 [7] ZHAO Haiyu, TIAN Maoqing, SUN Shuyang, et al. Spindle net: Person re-identification with human body region guided feature decomposition and fusion[C]. The 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 907–915. [8] KÖSTINGER M, HIRZER M, WOHLHART P, et al. Large scale metric learning from equivalence constraints[C]. 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, USA, 2012: 2288–2295. [9] HERMANS A, BEYER L, and LEIBE B. In defense of the triplet loss for person re-identification[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1703.07737. 2017. [10] CHEN Weihua, CHEN Xiaotang, ZHANG Jianguo, et al. Beyond triplet loss: A deep quadruplet network for person re-identification[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 1320–1329. [11] XIAO Jinsheng, ZOU Wentao, CHEN Yunhua, et al. Single image rain removal based on depth of field and sparse coding[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2018, 116: 212–217. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2018.10.006 [12] ZHONG Zhun, ZHENG Liang, CAO Donglin, et al. Re-ranking person re-identification with k-reciprocal encoding[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 3652–3661. [13] AHARON M, ELAD M, and BRUCKSTEIN A. K-SVD: An algorithm for designing overcomplete dictionaries for sparse representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(11): 4311–4322. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2006.881199 [14] HUANG Dean, KANG Liwei, YANG Minchun, et al. Context-aware single image rain removal[C]. 2012 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, Melbourne, Australia, 2012: 164–169. [15] KANG Liwei, LIN C W, and FU Y H. Automatic single-image-based rain streaks removal via image decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(4): 1742–1755. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2011.2179057 [16] LUO Yu, XU Yong, and JI Hui. Removing rain from a single image via discriminative sparse coding[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 3397–3405. [17] SON C H and ZHANG Xioaping. Rain detection and removal via shrinkage-based sparse coding and learned rain dictionary[J]. Journal of Imaging Science and Technology, 2020, 64(3): 30501. doi: 10.2352/J.ImagingSci.Technol.2020.64.3.030501 [18] 肖进胜, 李文昊, 姜红, 等. 基于双域滤波的三维块匹配视频去噪算法[J]. 通信学报, 2015, 36(9): 91–97. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2015245XIAO Jinsheng, LI Wenhao, JIANG Hong, et al. Three dimensional block-matching video denoising algorithm based on dual-domain filtering[J]. Journal on Communications, 2015, 36(9): 91–97. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2015245 [19] 陈巧媛, 陈莹. 基于困难样本三元组损失的多任务行人再识别[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2019, 31(7): 1156–1165. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1089.2019.17463CHEN Qiaoyuan and CHEN Ying. TriHard loss based multi-task person re-identification[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design &Computer Graphics, 2019, 31(7): 1156–1165. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1089.2019.17463 [20] SUN Yifan, ZHENG Liang, DENG Weijian, et al. SVDNet for pedestrian retrieval[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 3820–3828. [21] LIN Yutian, ZHENG Liang, ZHENG Zhedong, et al. Improving person re-identification by attribute and identity learning[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2019, 95: 151–161. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2019.06.006 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
