Two-dimensional Underwent Synthetic Aperture Radar Imaging Based on Iterative Proximal Projection
-
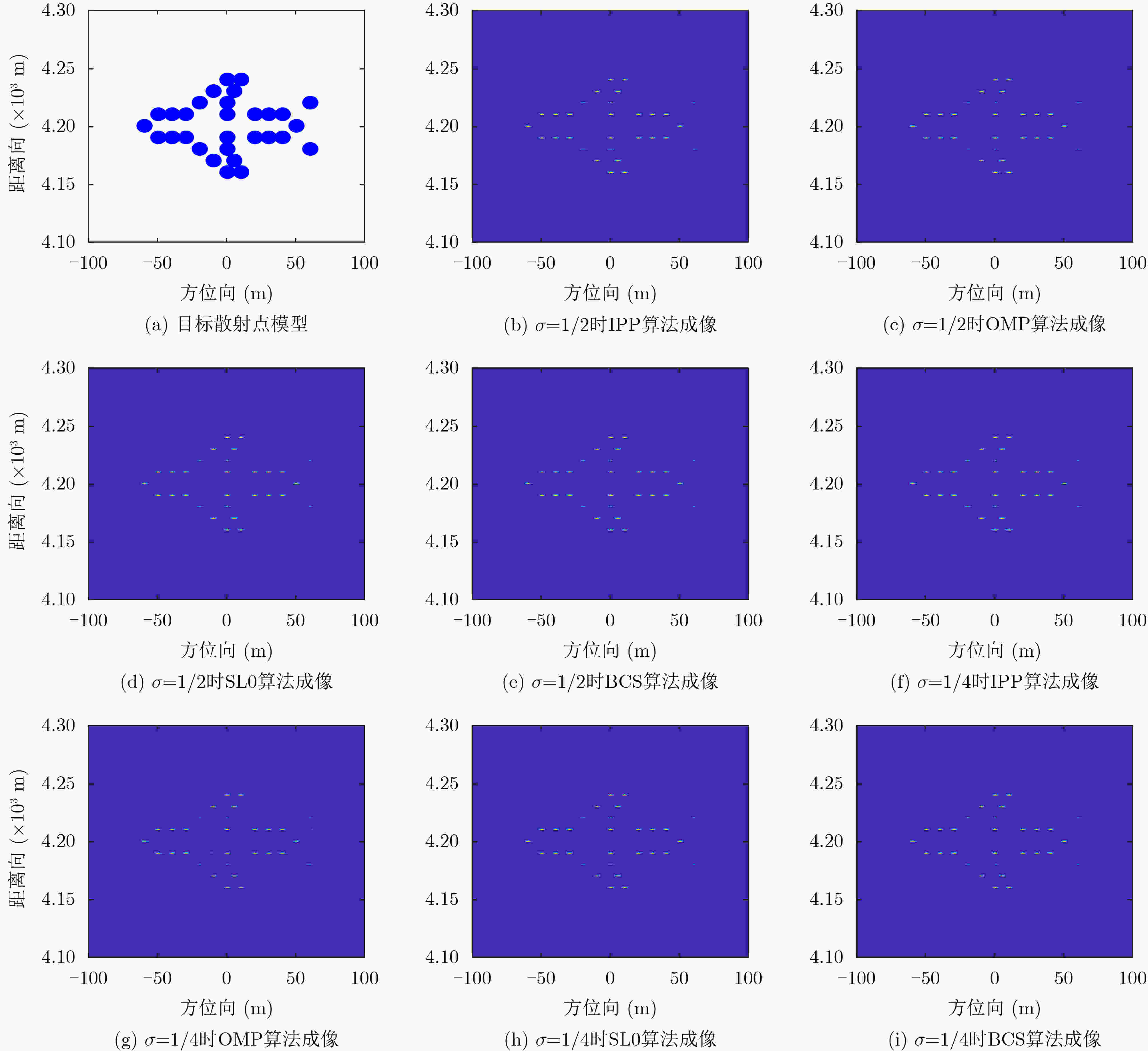
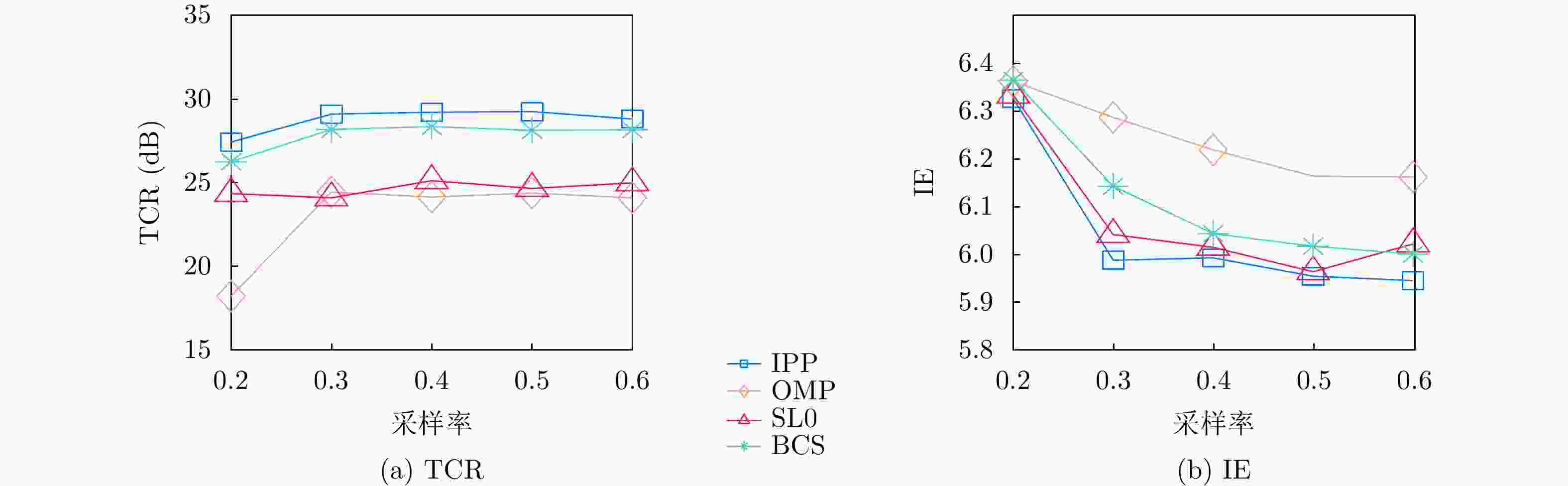
摘要: 合成孔径成像雷达(SAR)具有数据量大、采样率高等特点,针对传统压缩感知(CS)的SAR成像存在精度低及抗噪性能差的问题,该文提出一种基于迭代近端投影(IPP)的2维欠采样合成孔径雷达成像重建方法。即通过对雷达回波构建为距离频域-方位多普勒域的2维稀疏表示模型,在此基础上将成像问题转化为距离向和方位向压缩感知稀疏重构问题,利用迭代近端投影算法的函数优化模型来表示合成孔径雷达成像中的稀疏表示,最后采用平滑削边绝对偏离(SCAD)罚函数获得近端算子以求解该模型并进行成像。仿真与实测数据处理结果表明,所提方法成像效果更好。
-
关键词:
- SAR成像 /
- 压缩感知 /
- 迭代近端投影 /
- 平滑削边绝对偏离罚函数
Abstract: Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) imaging has a large amount of data volume, high sampling rate, and the problem of SAR imaging precision in traditional Compression Sensing (CS) is low, and there is a problem of poor anti-noise performance. A method of reconstruction method of two - dimensional sampling synthetic aperture rada based on Iterative Proximal Projection (IPP) is proposed. The radar echo is constructed as a two-dimensional sparse representation model in the range frequency-domain-azimuth Doppler region. On this basis, the two-dimensional imaging problem is transformed into the range and azimuth compression sensing sparse reconstruction. The function optimization model of the iterative proximal projection algorithm is used to represent the sparse representation of the synthetic aperture thunder imaging, and the proximal operator is finally obtained with the Smoothly Clipped Absolute Deviation (SCAD) penalty function to solve the model and to image. Simulation and measured data processing results show that the method of imaging is better. -
表 1 雷达仿真参数
参数 数值 雷达信号载频 3 GHz 雷达信号带宽 150 MHz 采样频率 300 MHz 雷达距目标区域中心点 4200 m 表 2 采样率为原采样率1/2时各算法成像时间
算法 时间(s) IPP 26.7381 OMP 18.7749 SL0 27.3091 BCS 178.2851 表 3 温哥华场景RADARSAT-1参数
参数 数值 距离带宽 30.3 MHz 距离向采样频率 32.317 MHz 脉冲宽度 30.111 MHz 卫星轨道半径 7186029 m 雷达波长 0.05657 m -
[1] ZHU Hongliang, LEUNG R, and HONG Minyi. Shadow compensation for synthetic aperture radar target classification by dual parallel generative adversarial network[J]. IEEE Sensors Letters, 2020, 4(8): 7002904. doi: 10.1109/LSENS.2020.3009179 [2] XIAO Peng, LIU Bo, and GUO Wei. ConGaLSAR: A constellation of geostationary and low earth orbit synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(12): 2085–2089. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2962574 [3] 杨磊, 张苏, 黄博, 等. 多任务协同优化学习高分辨SAR稀疏自聚焦成像算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(9): 2711–2719. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200300YANG Lei, ZHANG Su, HUANG Bo, et al. Multi-task learning of sparse autofocusing for high-resolution SAR imagery[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(9): 2711–2719. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200300 [4] 田鹤, 于海锋, 朱宇, 等. 基于频域稀疏压缩感知的星载SAR稀疏重航过3维成像[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(8): 2021–2028. doi: 10.11999/JEJT190638TIAN He, YU Haifeng, ZHU Yu, et al. Sparse flight 3-D imaging of spaceborne SAR based on frequency domain sparse compressed sensing[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(8): 2021–2028. doi: 10.11999/JEJT190638 [5] BU Hongxia, BAI Xia, and TAO Ran. Compressed sensing SAR imaging based on sparse representation in fractional Fourier domain[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2012, 55(8): 1789–1800. doi: 10.1007/s11432-012-4607-6 [6] PATEL V M, EASLEY G R, HEALY D M, et al. Compressed synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2010, 4(2): 244–254. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2009.2039181 [7] DONG Xiao and ZHANG Yunhua. A novel compressive sensing algorithm for SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2014, 7(2): 708–720. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2013.2291578 [8] LIU Zhixue, LI Gang, ZHANG Hao, et al. SAR imaging of dominant scatterers using cascading StOMP[C]. Proceedings of 2011 IEEE CIE International Conference on Radar, Chengdu, China, 2011: 1676–1679. [9] BU Hongxia, TAO Ran, BAI Xia, et al. A novel SAR imaging algorithm based on compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(5): 1003–1007. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2372319 [10] 徐建平, 皮亦鸣, 曹宗杰. 基于贝叶斯压缩感知的合成孔径雷达高分辨成像[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2011, 33(12): 2863–2868. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.01377XU Jianping, PI Yiming, and CAO Zongjie. SAR imaging based on Bayesian compressive sensing[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2011, 33(12): 2863–2868. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.01377 [11] 梁美美. 基于压缩感知的SAR成像算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 哈尔滨工程大学, 2014.LIANG Meimei. Research of SAR imaging arithmetic based on compressed sensing[D]. [Master dissertation], Harbin Engineering University, 2014. [12] LI Shiyong, ZHAO Guoqiang, LI Houmin, et al. Near-field radar imaging via compressive sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2015, 63(2): 828–833. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2014.2381262 [13] GHAYEM F, SADEGHI M, BABAIE-ZADEH M, et al. Sparse signal recovery using iterative proximal projection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(4): 879–894. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2778695 [14] CHEN Jinli, ZHENG Yao, ZHANG Tingxiao, et al. Iterative reweighted proximal projection based DOA estimation algorithm for monostatic MIMO radar[J]. Signal Processing, 2020, 172: 107537. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107537 [15] FAN Jianqing and LI Runze. Variable selection via Nonconcave penalized likelihood and its oracle properties[J]. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 2001, 96(456): 1348–1360. doi: 10.1198/016214501753382273 [16] 卜红霞, 白霞, 赵娟, 等. 基于压缩感知的矩阵型联合SAR成像与自聚焦算法[J]. 电子学报, 2017, 45(4): 874–881. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.04.016BU Hongxia, BAI Xia, ZHAO Juan, et al. Joint matrix form SAR imaging and autofocus based on compressed sensing[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2017, 45(4): 874–881. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.04.016 [17] TSENG P. Convergence of a block coordinate descent method for nondifferentiable minimization[J]. Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications, 2001, 109(3): 475–494. doi: 10.1023/A:1017501703105 [18] 徐楚, 朱栋强, 汪玲, 等. 基于零空间 ${l_1}$ 范数最小化的ISAR成像方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2020, 42(2): 315–321. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2020.02.09XU Chu, ZHU Dongqiang, WANG Ling, et al. ISAR imaging using null space l1 norm minimization[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(2): 315–321. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2020.02.09 -





 下载:
下载:

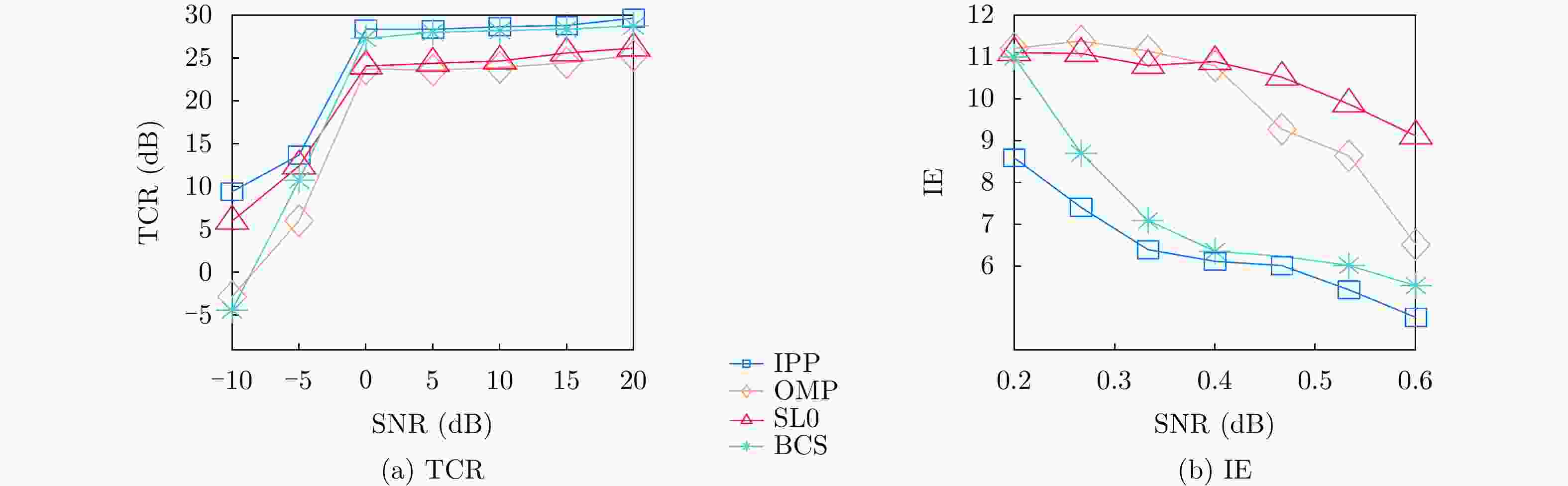
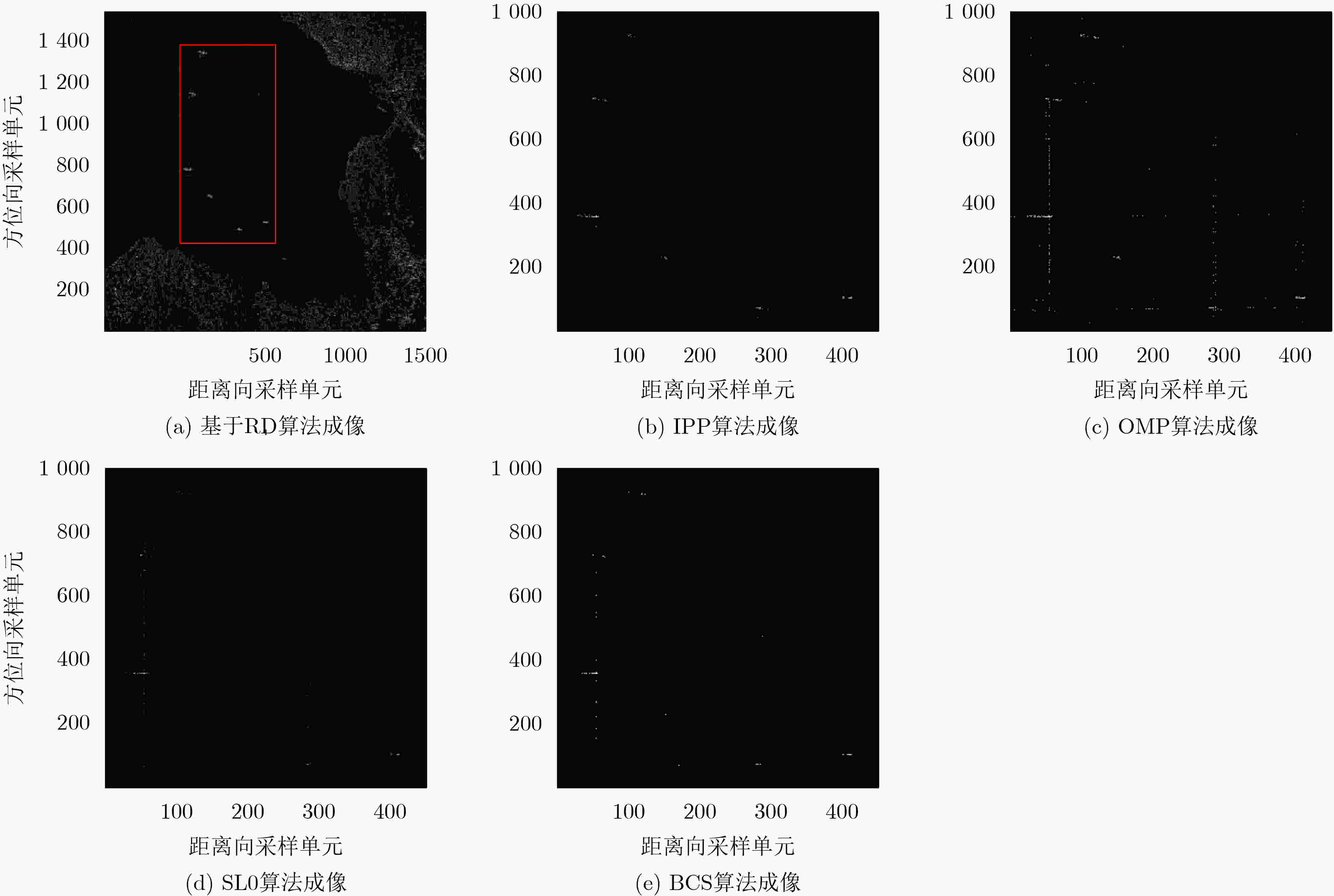



 下载:
下载:
