Link Prediction in Knowledge Graphs Based on Hyperbolic Graph Attention Networks
-
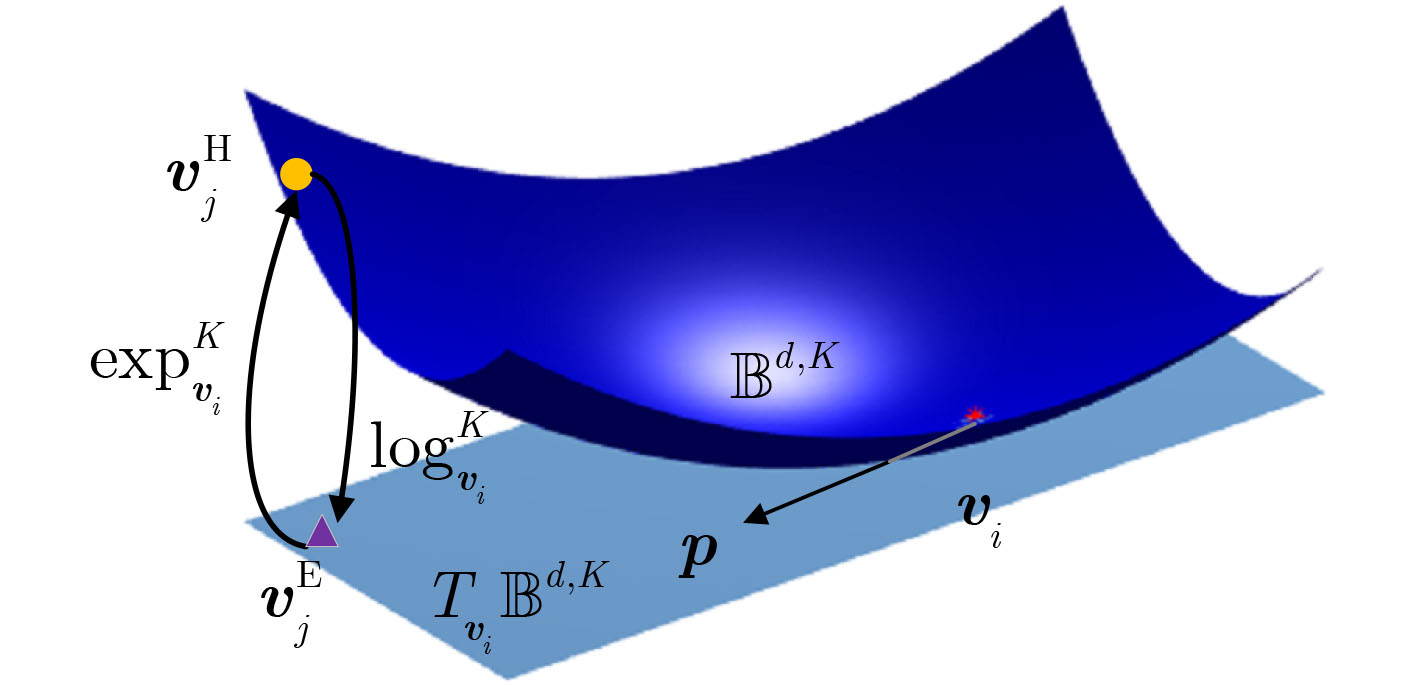
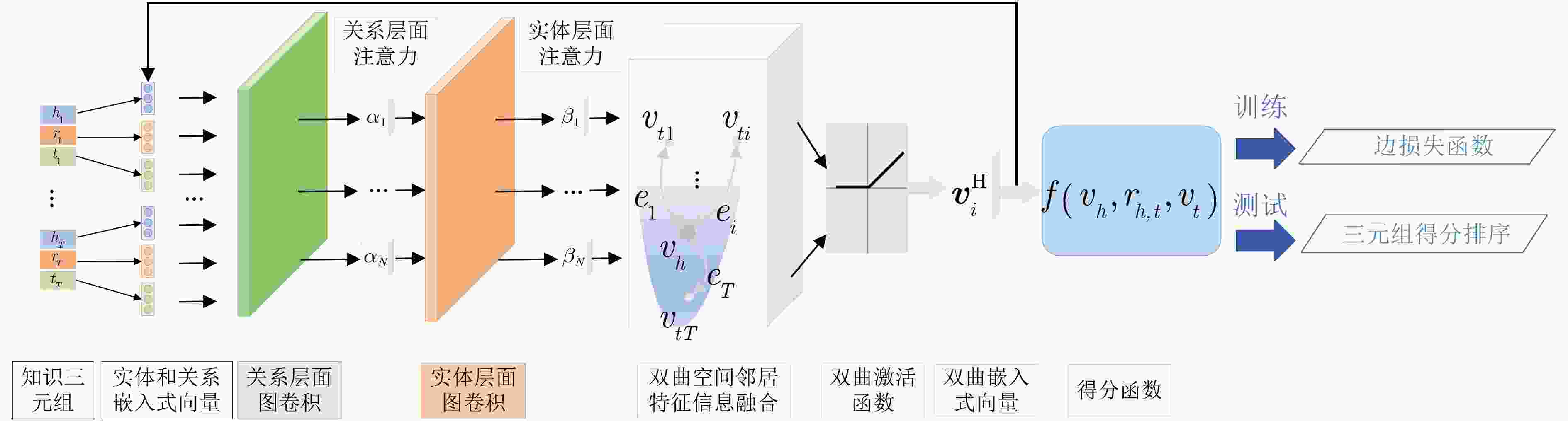
摘要: 现有的大多数知识表示学习模型孤立地看待每个知识三元组,未能发现和利用实体周围邻域特征信息,并且将树状层级结构的知识图谱嵌入到欧式空间,会带来嵌入式向量高度失真的问题。为解决上述问题,该文提出了一种基于双曲图注意力网络的知识图谱链路预测方法(HyGAT-LP)。首先将知识图谱嵌入到负常数曲率的双曲空间中,从而更契合知识图谱的树状层级结构;然后在所给实体领域内基于实体和关系两种层面的注意力机制聚合邻域特征信息,将实体嵌入到低维的双曲空间;最后利用得分函数计算每个三元组的得分值,并以此作为判定该三元组成立的依据完成知识图谱上的链路预测任务。实验结果表明,与基准模型相比,所提方法可显著提高知识图谱链路预测性能。Abstract: Most existing knowledge representation learning models treat knowledge triples independently, it fail to cover and leverage the feature information in any given entity’s neighborhood. Besides, embedding knowledge graphs with tree-like hierarchical structure in Euclidean space would incur a large distortion in embeddings. To tackle such issues, a link prediction method based on Hyperbolic Graph ATtention networks for Link Prediction in knowledge graphs (HyGAT-LP) is proposed. Firstly, knowledge graphs are embedded in hyperbolic space with constant negative curvature, which is more suited for knowledge graphs’ tree-like hierarchical structure. Then the proposed method aggregates feature information in the given entity’s neighborhood with both entity-level and relation-level attention mechanisms, and further, embeds the given entity in low dimensional hyperbolic space. Finally, every triple’s score is computed by a scoring function, and links in knowledge graphs are predicted based on the scores indicating the probabilities that predicted triples are correct. Experimental results show that, compared with baseline models, the proposed method can significantly improve the performance of link prediction in knowledge graphs.
-
Key words:
- Knowledge graphs /
- Link prediction /
- Hyperbolic space /
- Graph attention networks
-
表 1 FB15k-237数据集和WN18RR数据集统计量信息
数据集 $ \left| {\mathbf{V}} \right| $ $ \left| {\mathbf{R}} \right| $ 三元组数 $ \rho $ 训练集$ {{\mathbf{E}}_{{\text{Train}}}} $ 验证集$ {{\mathbf{E}}_{{\text{Valid}}}} $ 测试集$ {{\mathbf{E}}_{{\text{Test}}}} $ 总三元组数$ {\mathbf{E}} $ FB15k-237 14541 237 272115 17535 20466 310116 1308.5 WN18RR 40943 11 86835 3034 3134 93003 8454.8 表 2 FB15k-237数据集和WN18RR数据集上知识图谱链路预测结果
流形 模型 FB15k-237 WN18RR MRR Hits@1 Hits@3 Hits@10 MRR Hits@1 Hits@3 Hits@10 $ \mathbb{R} $ TransE 0.294 0.186 0.321 0.465 0.226 0.427 0.441 0.532 DistMult 0.241 0.155 0.263 0.419 0.444 0.412 0.470 0.504 ConvE 0.325 0.237 0.356 0.501 0.456 0.419 0.470 0.531 ConvKB 0.289 0.198 0.324 0.471 0.265 0.058 0.445 0.558 MuRE 0.336 0.245 0.370 0.521 0.475 0.436 0.487 0.554 TuckER 0.358 0.266 0.394 0.544 0.471 0.443 0.482 0.526 RGHAT 0.522 0.462 0.546 0.631 0.483 0.425 0.499 0.588 $ \mathbb{C} $ ComplEx 0.247 0.158 0.275 0.428 0.449 0.409 0.469 0.530 RotatE 0.338 0.241 0.375 0.533 0.476 0.428 0.492 0.571 $ \mathbb{B} $ MuRP 0.335 0.243 0.367 0.518 0.481 0.440 0.495 0.566 ATTH 0.384 0.252 0.384 0.540 0.486 0.443 0.498 0.573 HyGAT-LP 0.529 0.467 0.566 0.650 0.521 0.441 0.511 0.619 表 3 在WN18RR数据集中每类关系的统计量信息
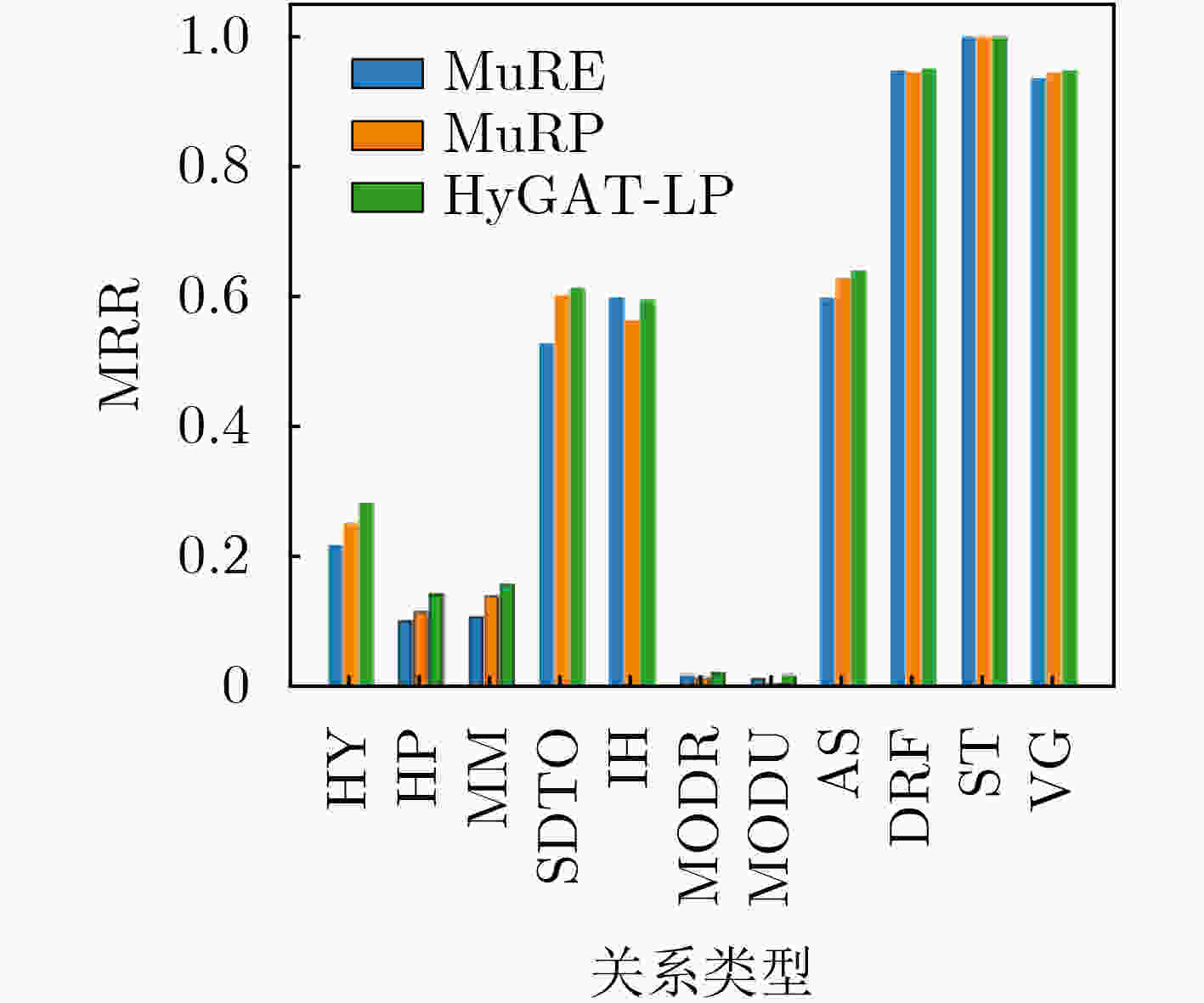
关系名 简记 总三元组数 Khs $ {\xi _{\text{G}}} $ hypernym HY 37221 1.00 –2.46 has_part HP 5142 1.00 –1.43 member_meronym MM 7928 1.00 –2.90 synset_domain_topic_of SDTO 3335 0.99 –0.69 instance_hypernym IH 3150 1.00 –0.82 member_of_domain_region MODR 983 1.00 –0.78 member_of_domain_usage MODU 675 1.00 –0.74 also_see AS 1396 0.36 –2.09 derivationally_related_form DRF 31867 0.04 –3.84 similar_to ST 86 0 –1.00 verb_group VG 1220 0 –0.50 表 4 预测排名前10尾实体情况
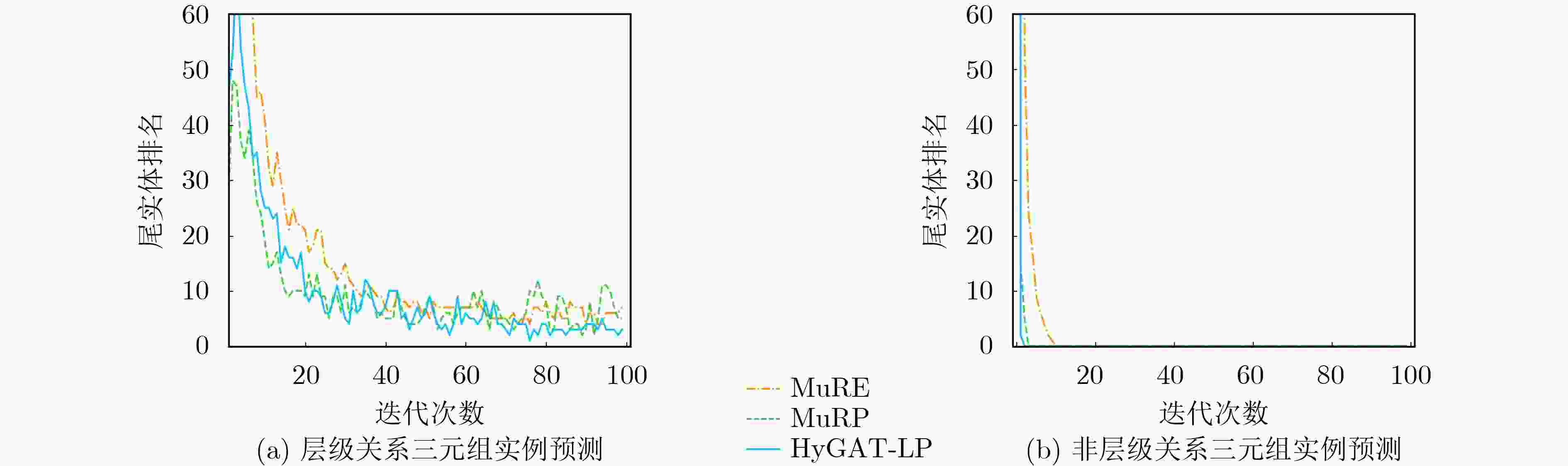
(european_union,member_meronym,?) (geology,derivationally_related_form,?) 排序 MuRE MuRP HyGAT-LP MuRE MuRP HyGAT-LP 1 england noway bulgaria geologist geologist geologist 2 poland bulgaria denmark give scientist paleontologist 3 scotland denmark europe psychologist anatomist doctor 4 switzerland switzerland noway explorer meteorologist scientist 5 denmark poland iceland religionist film biologist 6 noway iceland belarus theologian biologist geophysicist 7 bulgaria scotland switzerland ophthalmologist geomorphologic geomorphologic 8 united_states croatia hungary philosopher paleontologist philosopher 9 europe belarus ireland diagnostician chronologize physicist 10 turkey united_states czechoslovakia specialist geophysicist musician -
[1] 王昊奋, 漆桂林, 陈华钧. 知识图谱: 方法、实践与应用[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2019: 1–3.WANG Haofen, QI Guilin, and CHEN Huajun. Knowledge Graph[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics History, 2019: 1–3. [2] REINANDA R, MEIJ E, and DE RIJKE M. Knowledge graphs: An information retrieval perspective[J]. Foundations and Trends® in Information Retrieval, 2020, 14(4): 289–444. doi: 10.1561/1500000063 [3] 张崇宇. 基于知识图谱的自动问答系统的应用研究与实现[D]. [硕士论文], 北京邮电大学, 2019.ZHANG Chongyu. Application research and implementation of automatic question answering system based on knowledge graph[D]. [Master dissertation], Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2019. [4] 秦川, 祝恒书, 庄福振, 等. 基于知识图谱的推荐系统研究综述[J]. 中国科学:信息科学, 2020, 50(7): 937–956. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2019-0274QIN Chuan, ZHU Hengshu, ZHUANG Fuzhen, et al. A survey on knowledge graph-based recommender systems[J]. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2020, 50(7): 937–956. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2019-0274 [5] BRONSTEIN M M, BRUNA J, LECUN Y, et al. Geometric deep learning: Going beyond Euclidean data[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2017, 34(4): 18–42. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2017.2693418 [6] WANG Quan, MAO Zhendong, WANG Bin, et al. Knowledge graph embedding: A survey of approaches and applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2017, 29(12): 2724–2743. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2017.2754499 [7] BORDES A, USUNIER N, GARCIA-DURÁN A, et al. Translating Embeddings for modeling multi-relational data[C]. Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Lake Tahoe, USA, 2013: 2787–2795. [8] SUN Zhiqing, DENG Zhihong, NIE Jianyun, et al. RotatE: Knowledge graph embedding by relational rotation in complex space[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1902.10197, 2019. [9] NICKEL M, TRESP V, and KRIEGEL H. A three-way model for collective learning on multi-relational data[C]. Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Bellevue, USA, 2011: 809–816. [10] YANG Bishan, YIH W T, HE Xiaodong, et al. Embedding entities and relations for learning and inference in knowledge bases[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6575, 2015. [11] TROUILLON T, WELBL J, RIEDEL S, et al. Complex embeddings for simple link prediction[C]. Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), New York, USA, 2016: 2071–2080. [12] BALAZEVIC I, ALLEN C, and HOSPEDALES T. TuckER: Tensor factorization for knowledge graph completion[C]. Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP), Hong Kong, China, 2019: 5184–5194. [13] DETTMERS T, MINERVINI P, STENETORP P, et al. Convolutional 2D knowledge graph embeddings[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1707.01476, 2018. [14] NGUYEN D Q, NGUYEN D Q, NGUYEN T D, et al. A convolutional neural network-based model for knowledge base completion and its application to search personalization[J]. Semantic Web, 2019, 10(5): 947–960. doi: 10.3233/SW-180318 [15] SCHLICHTKRULL M, KIPF T N, BLOEM P, et al. Modeling relational data with graph convolutional networks[C]. 15th International Conference on The Semantic Web, Heraklion, Greece, 2018: 593–607. [16] ZHANG Zhao, ZHUANG Fuzhen, ZHU Hengshu, et al. Relational graph neural network with hierarchical attention for knowledge graph completion[C]. The AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), Palo Alto, USA, 2020: 9612–9619. [17] WU Zonghan, PAN Shirui, CHEN Fengwen, et al. A comprehensive survey on graph neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 32(1): 4–24. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.2978386 [18] 王强, 江昊, 羿舒文, 等. 复杂网络的双曲空间表征学习方法[J]. 软件学报, 2021, 32(1): 93–117. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.006092WANG Qiang, JIANG Hao, YI Shuwen, et al. Hyperbolic representation learning for complex networks[J]. Journal of Software, 2021, 32(1): 93–117. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.006092 [19] ZHANG Chengkun and GAO Junbin. Hype-HAN: Hyperbolic hierarchical attention network for semantic embedding[C]. Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI), Yokohama, Japan, 2020: 3990–3996. [20] BALAŽEVIC I, ALLEN C, and HOSPEDALES T. Multi-relational poincaré graph embeddings[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.09791, 2019. [21] CHAMI I, WOLF A, JUAN Dacheng, et al. Low-dimensional hyperbolic knowledge graph embeddings[C]. Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), Seattle, USA, 2020: 6901–6914. [22] BONNABEL S. Stochastic gradient descent on Riemannian manifolds[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2013, 58(9): 2217–2229. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2013.2254619 [23] SAKAI H and IIDUKA H. Riemannian adaptive optimization algorithm and its application to natural language processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(1): 1–12. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2021.3049845. [24] ADCOCK A B, SULLIVAN B D, and MAHONEY M W. Tree-like structure in large social and information networks[C]. IEEE 13th International Conference on Data Mining, Dallas, USA, 2013: 1–10. [25] KRACKHARDT D. Computational Organization Theory[M]. London: Psychology Press, 1994: 89–111. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
