The Range-angle Estimation of Target Based on Time-invariant and Spot Beam Optimization
-
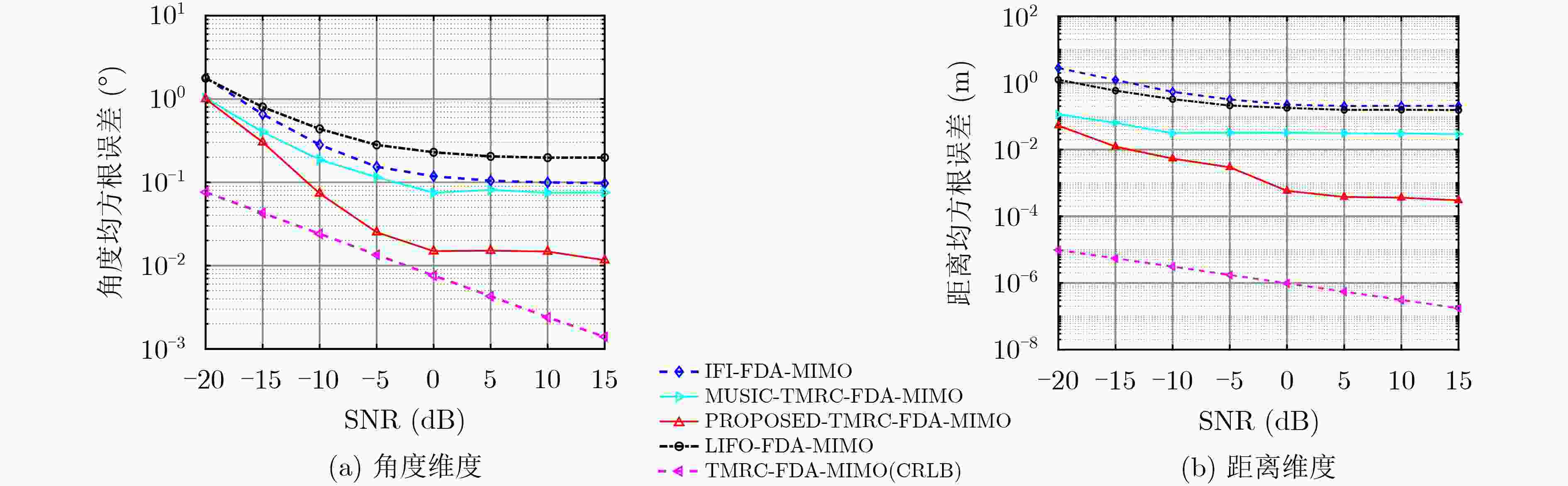
摘要: 应用频控阵式多输入多输出(FDA-MIMO)雷达实现目标距离-角度联合估计越来越受到人们的重视,利用FDA同时获得发射波束图在角度和距离的自由度。但其性能因波束图的周期性和时变性而降低。因此,该文基于时间调制和距离补偿FDA-MIMO(TMRC-FDA-MIMO)雷达的新波形合成模型,提出了一种改进的基于旋转不变技术的信号参数估计(ESPRIT)算法。最后,通过距离和角度估计的克拉美罗下界和均方根误差,与固定频偏FDA-MIMO、对数频偏FDA-MIMO雷达系统和多信号分类(MUSIC)算法进行了对比,验证了所提方法的优异性能。Abstract: The application of Frequency Diverse Array and Multiple Input Multiple Output (FDA-MIMO) radar to achieve range-angle estimation of target has attracted more and more attention. The FDA can simultaneously obtain the degree of freedom of transmitting beam pattern in angle and range. However, its performance is degraded due to the periodicity and time-varying of the beam pattern. Therefore, an improved Estimating Signal Parameter via Rotational Invariance Techniques (ESPRIT) algorithm to estimate the target’s parameters based on a new waveform synthesis model of the Time Modulation and Range Compensation FDA-MIMO (TMRC-FDA-MIMO) radar is proposed. Finally, the proposed method is compared with identical frequency increment FDA-MIMO radar system, logarithmically increased frequency offset FDA-MIMO radar system and MUltiple SIgnal Classification (MUSIC) algorithm through the Cramer Rao lower bound and root mean square error of range and angle estimation, and the excellent performance of the proposed method is verified.
-
表 1 距离-角度联合估计算法步骤
步骤1 将接收信号矩阵${{U}}$分为两个子阵,
${{{U}}_{\rm{1}}}$和${{{U}}_{\rm{2}}}$两个子阵;步骤2 根据公式(25)的旋转矩阵${{{\varPsi }}_r}$估计目标角度$ {\stackrel{\wedge }{\theta }}_{p},p\in \left\{1,2,\cdots ,P\right\}$,其中$P$代表目标数量; 步骤3 根据式(25)计算第$p$个目标的权重矢量${{{w}}_p}$; 步骤4 根据式(30)的矩阵${{{\varPsi '}}_t}$估计出目标的距离值${{\mathop r\limits^ \wedge } _p}$,
然后就可以获得目标距离、角度坐标$\left( {{{{\mathop r\limits^ \wedge} }_p},{{\mathop \theta \limits^ \wedge }_p}} \right)$;步骤5 重复步骤3和步骤4来估计其他目标的参数。 -
[1] DING Xiao, CHENG Youfeng, SHAO Wang, et al. A wide-angle scanning planar phased array with pattern reconfigurable magnetic current element[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2017, 65(3): 1434–1439. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2016.2637863 [2] ANTONIK P, WICKS M C, GRIFFITHS H D, et al. Frequency diverse array radars[C]. Proceedings of 2006 IEEE Conference on Radar, Verona, USA, 2006: 215–217. [3] 王文钦, 邵怀宗, 陈慧. 频控阵雷达: 概念、原理与应用[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(4): 1000–1011.WANG Wenqin, SHAO Huaizong, and CHEN Hui. Frequency diverse array radar: Concept, principle and application[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(4): 1000–1011. [4] SECMEN M, DEMIR S, HIZAL A, et al. Frequency diverse array antenna with periodic time modulated pattern in range and angle[C]. 2007 IEEE Radar Conference, Waltham, USA, 2007: 427–430. [5] YANG Kaikai, HONG Sheng, ZHU Qi, et al. Maximum likelihood angle-range estimation for monostatic FDA-MIMO radar with extended range ambiguity using subarrays[J]. International Journal of Antennas and Propagation, 2020, 2020: 4601208. [6] WANG Cheng, ZHENG Wang, GONG Pan, et al. Joint angle and range estimation in the fda-mimo radar: The reduced-dimension root music algorithm[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2020, 115(3): 2515–2533. doi: 10.1007/s11277-020-07694-4 [7] WANG Cheng, LI Zheng, and ZHANG Xiaofei. FDA-MIMO for joint angle and range estimation: Unfolded coprime framework and parameter estimation algorithm[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2020, 14(6): 917–926. [8] TANG Wengen, JIANG Hong, and ZHANG Qi. Range-angle decoupling and estimation for FDA-MIMO radar via atomic norm minimization and accelerated proximal gradient[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2020, 27: 366–370. [9] WANG Cheng, ZHANG Xiaofei, and LI Jianfeng. FDA-MIMO radar for 3D localization: Virtual coprime planar array with unfolded coprime frequency offset framework and TRD-MUSIC algorithm[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2021, 113: 103017. [10] KHAN W, QURESHI I M, and SAEED S. Frequency diverse array radar with logarithmically increasing frequency offset[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2014, 14: 499–502. [11] YAN Yisheng, CAI Jingye, and WANG Wenqin. Two-stage ESPRIT for unambiguous angle and range estimation in FDA-MIMO radar[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2019, 92: 151–165. [12] YAO Amin, WU Wen, and FANG Dagang. Frequency diverse array antenna using time-modulated optimized frequency offset to obtain time-invariant spatial fine focusing beampattern[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2016, 64(10): 4434–4446. [13] CHU Wei, LIU Yunqing, LI Xiaolong, et al. Optimization of emission waveform by accelerated particle swarm algorithm based on logarithmic frequency offset mathematical model[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2020, 113(1): 167–187. [14] 王伟伟, 吴孙勇, 许京伟, 等. 基于频率分集阵列的机载雷达距离模糊杂波抑制方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(10): 2321–2327.WANG Weiwei, WU Sunyong, XU Jingwei, et al. Range ambiguity clutter suppression for airborne radar based on frequency diverse array[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2015, 37(10): 2321–2327. [15] WANG Wenqin. Range-angle dependent transmit beampattern synthesis for linear frequency diverse arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2013, 61(8): 4073–4081. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2013.2260515 [16] RAO B D and HARI K V S. Performance analysis of ESPRIT and TAM in determining the direction of arrival of plane waves in noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1989, 37(12): 1990–1995. [17] GUI Ronghua, WANG Wenqin, CUI Can, et al. Coherent pulsed-FDA radar receiver design with time-variance consideration: SINR and CRB analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(1): 200–214. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2764860 -





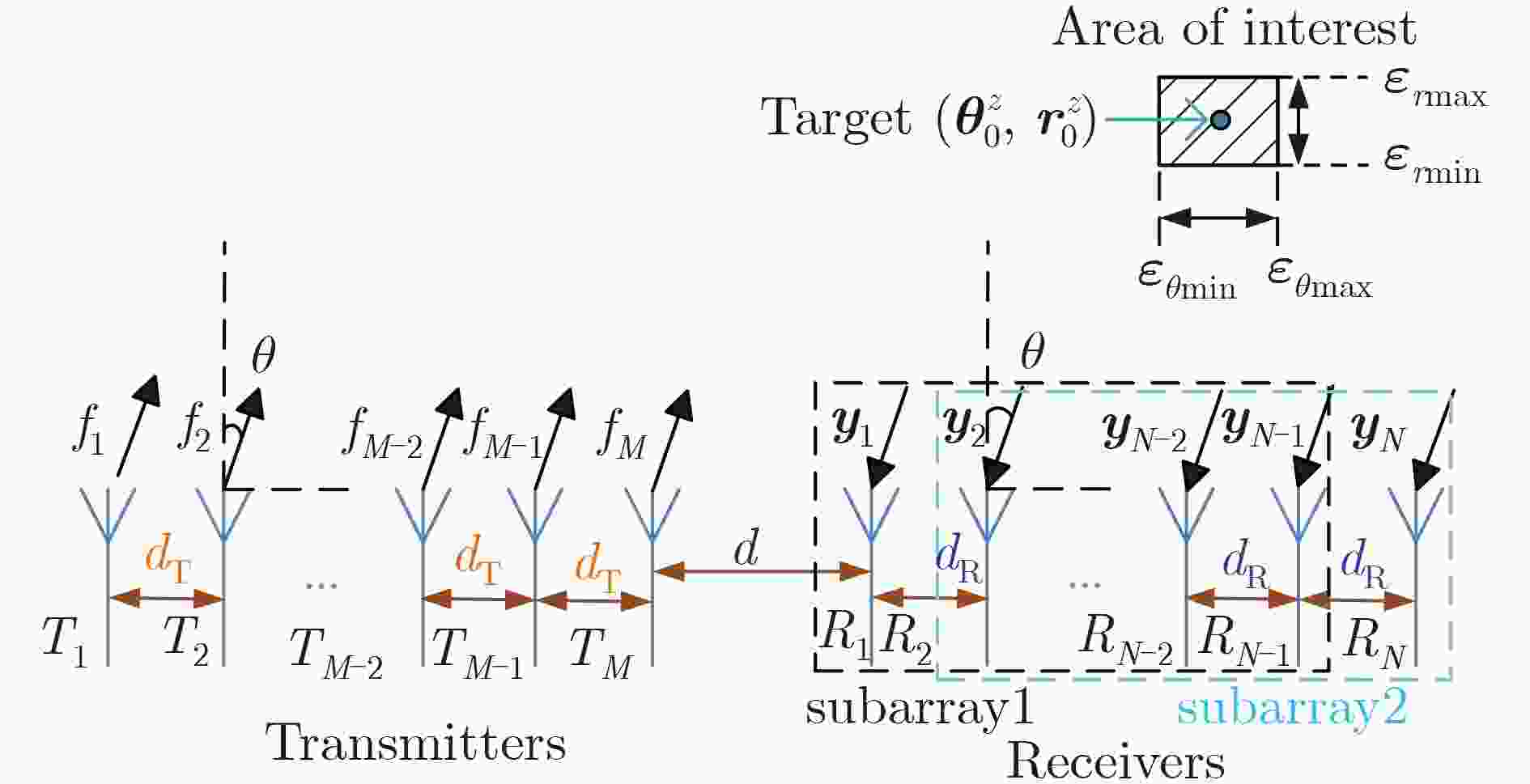
 下载:
下载:
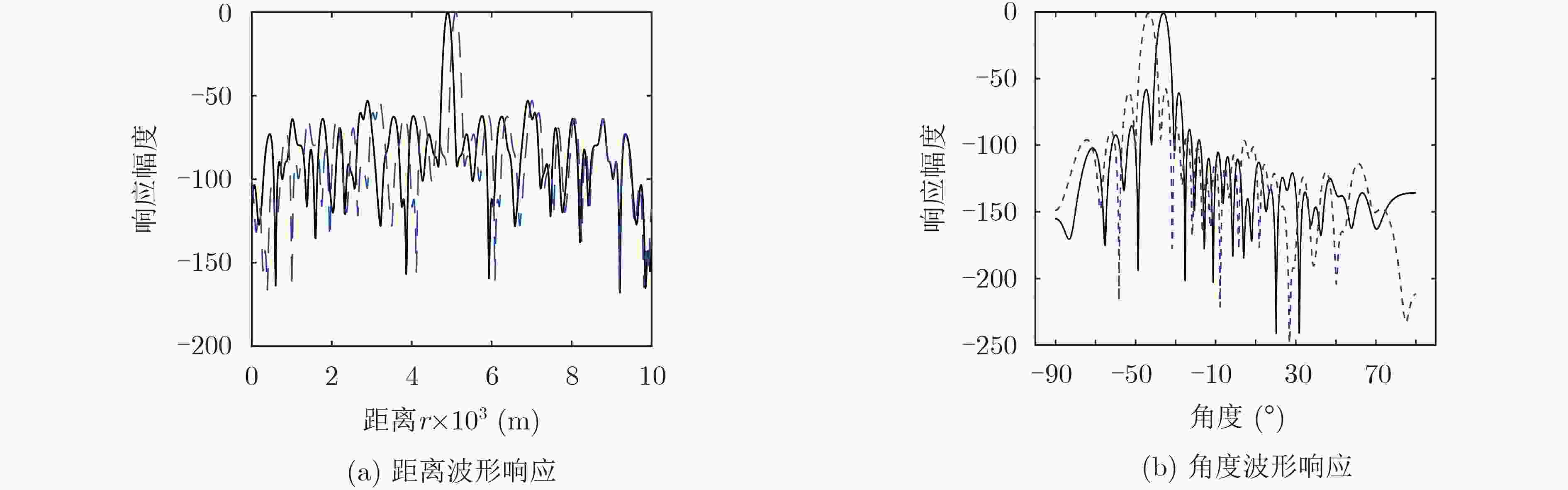
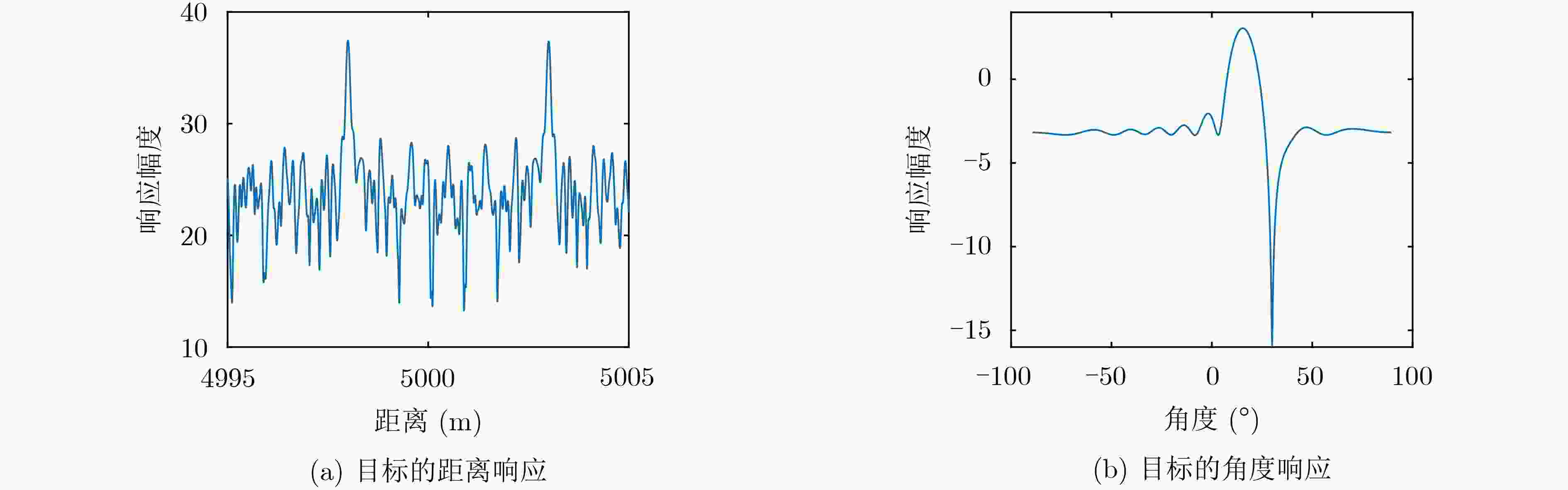
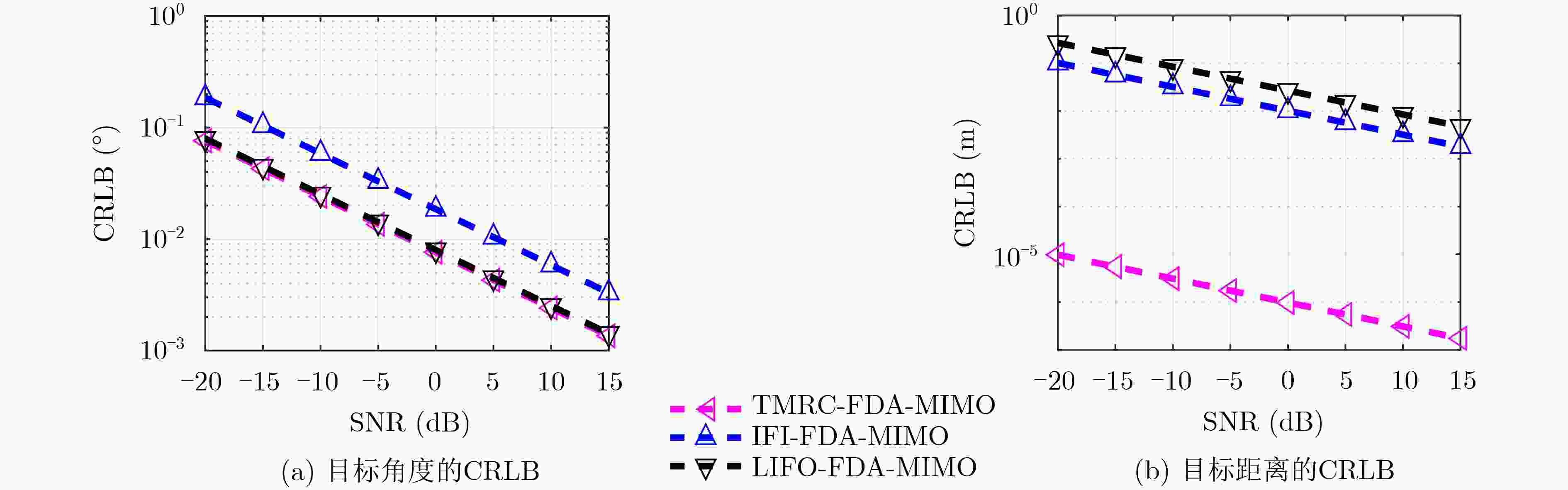


 下载:
下载:
