L21 Nonnegative Matrix Factorization for Hyperspectral Unmixing Based on Subspace Structure Regularization
-
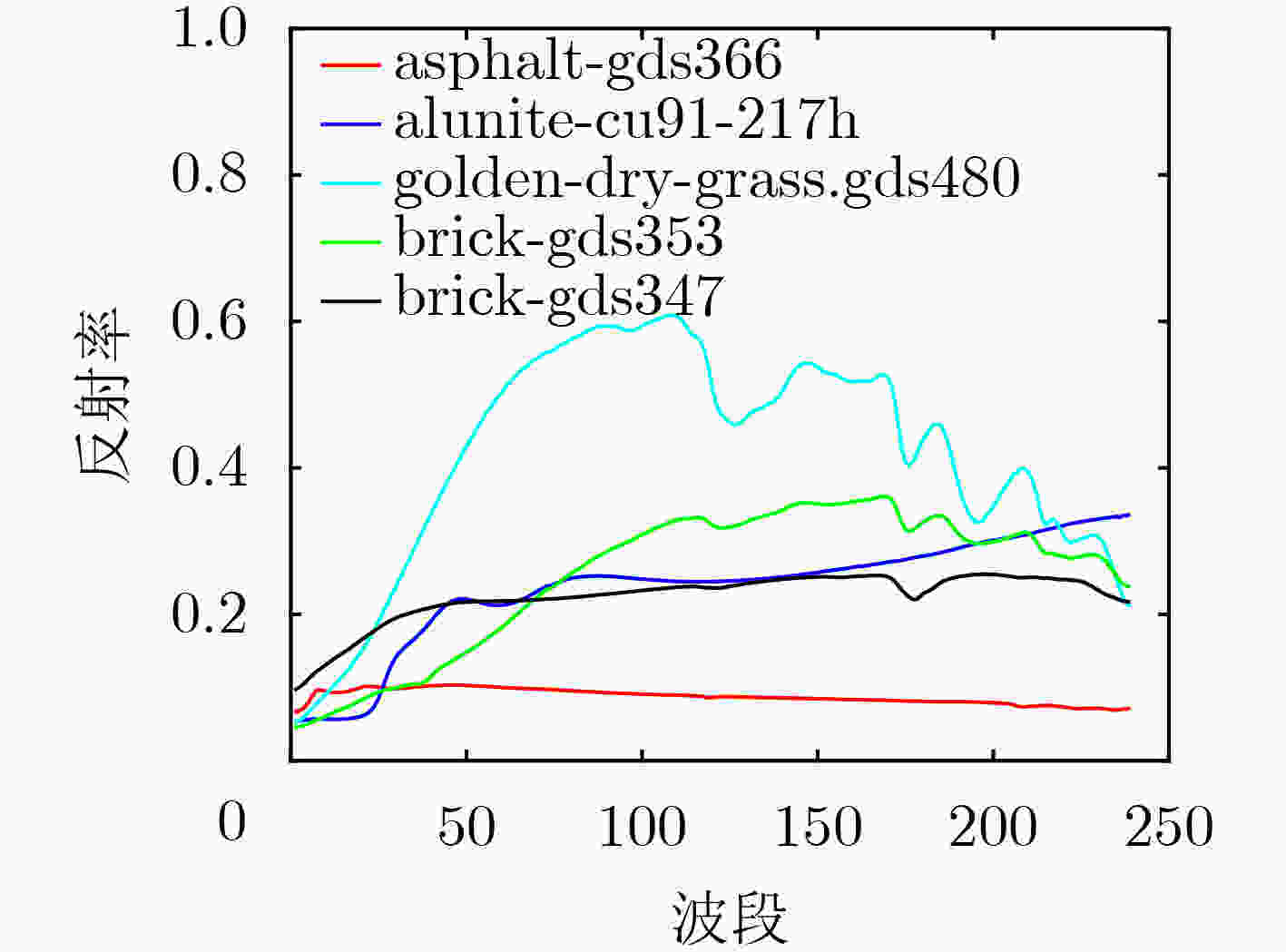
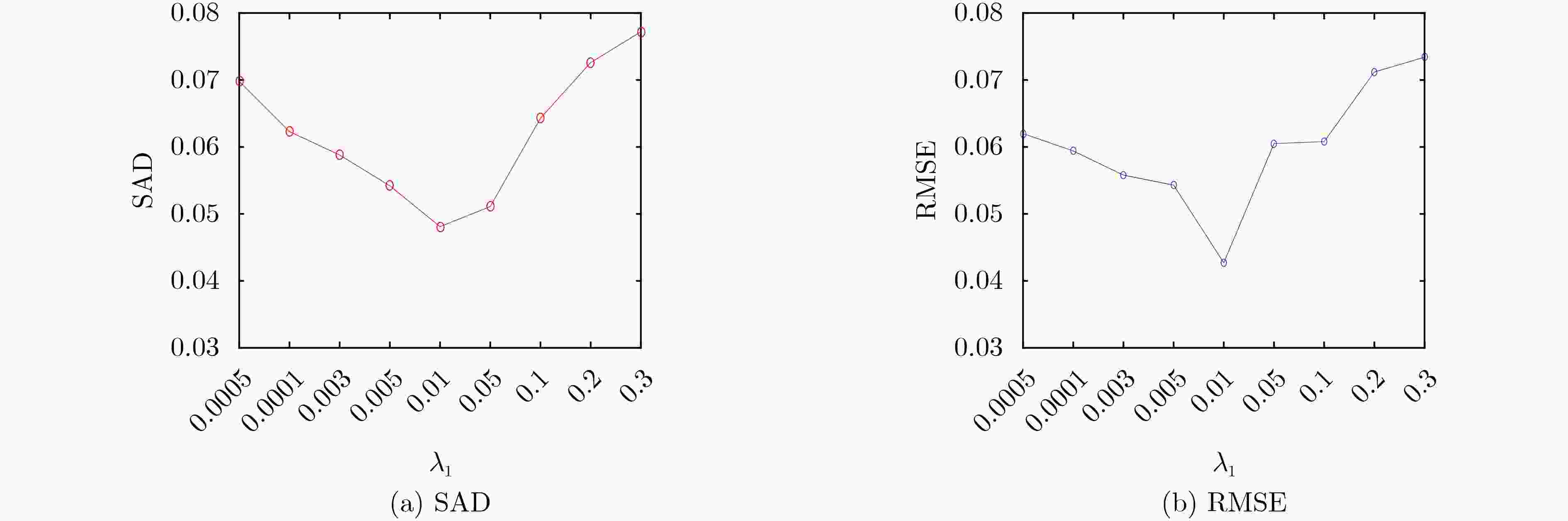
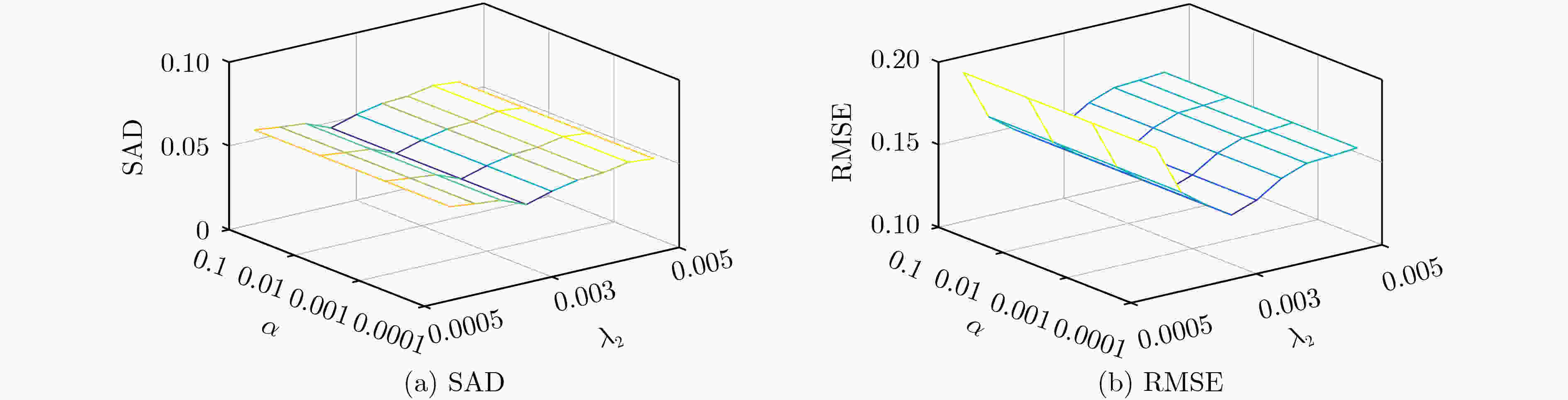
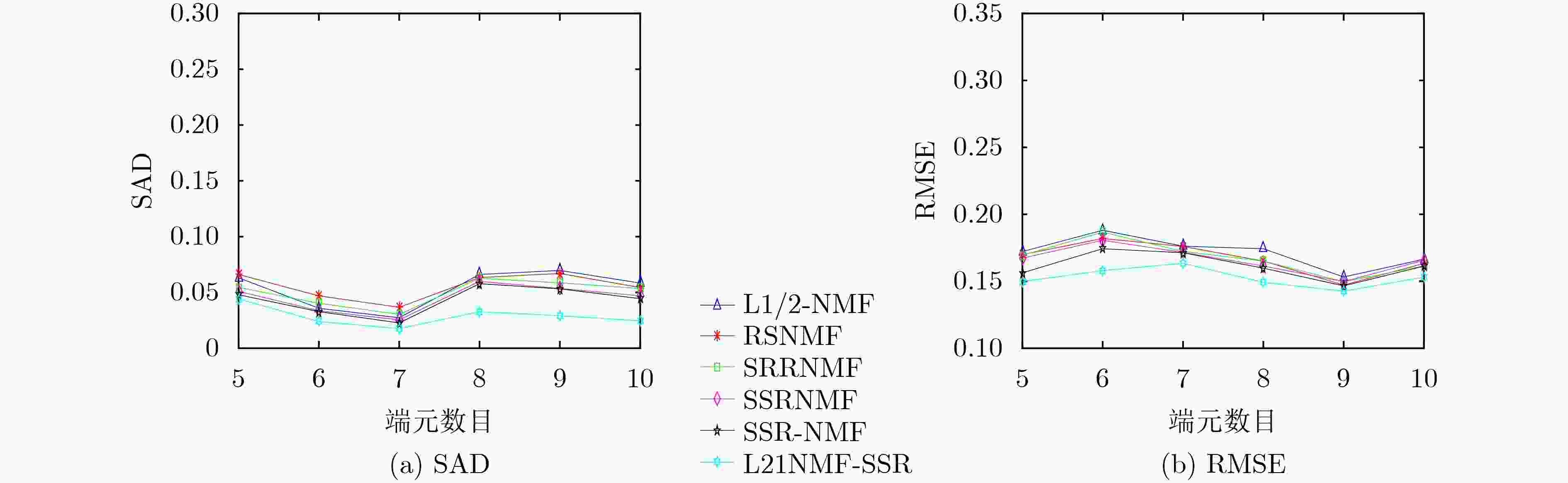
摘要: 标准的非负矩阵分解(NMF)应用于高光谱解混时,容易受到噪声和异常值的干扰,解混效果较差。为了提高分解性能,该文将L21范数引入标准的NMF算法中,对模型进行了改进,从而提高算法的鲁棒性。其次,为了提高分解后丰度矩阵的稀疏性,将双重加权稀疏约束引入L21NMF模型中,使其中一个权值提高每个像元对应的丰度向量上的稀疏性,另一个权值提高每个端元对应的丰度向量上的稀疏性。同时,为了利用像元的全局空间分布信息,观察地物在不同图像中的真实分布情况,引入子空间结构正则项,提出了基于子空间结构正则化的L21非负矩阵分解(L21NMF-SSR)算法。通过在模拟数据集和真实数据集与其他经典算法的比较,验证了该算法具有更好的性能,同时具有去噪能力。Abstract: When the standard Nonnegative Matrix Factorization (NMF) is applied to hyperspectral unmixing, it is easy to be interfered by noise and outliers, and the unmixing effect is poor. In order to improve the factorized performance, the L21 norm is introduced into the standard NMF algorithm, and the model is improved to improve the robustness of the algorithm. Secondly, in order to improve the sparsity of the factorized abundance matrix, the double reweighted sparse constraint is introduced into the L21NMF model, so that one of the weights increases sparsity along the abundance vector corresponding to each pixel, and the other weight promotes the sparsity along the abundance vector corresponding to each endmember. Meanwhile, in order to utilize the global spatial distribution information of the pixels and observe the true distribution of materials in different images, the subspace structure regularization is introduced, and the L21 Nonnegative Matrix Factorization based on Subspace Structure Regularization (L21NMF-SSR) is proposed. The better performance and denoising ability of the proposed method are demonstrated by comparing with other classical methods on both synthetic and real datasets.
-
表 1 L21NMF-SSR算法(算法1)
输入:高光谱图像矩阵${\boldsymbol{Y}}$ 输出:端元矩阵${\boldsymbol{E}}$,丰度矩阵${\boldsymbol{A}}$和自表达矩阵${\boldsymbol{Z}}$ 步骤1:使用VCA-FCLS初始化${\boldsymbol{E}}$和${\boldsymbol{A}}$,利用LRR计算${\boldsymbol{Z}}$,且
${\boldsymbol{L}} = {\boldsymbol{Z}}$;步骤2:利用式(20)更新${\boldsymbol{E}}$; 步骤3:用${{\boldsymbol{Y}}_f}$和${{\boldsymbol{E}}_f}$替换${\boldsymbol{Y}}$和${\boldsymbol{E}}$; 步骤4:利用式(24)、式(26)更新${\boldsymbol{A}}$和${\boldsymbol{Z}}$; 步骤5:用SVT更新${\boldsymbol{L}}$; 步骤6:直到满足停止条件; 表 2 不同算法在不同信噪比级别下的SAD值的比较
SNR(dB) L1/2-NMF RSNMF SRRNMF SSRNMF SSR-NMF L21NMF-SSR 15 0.1933 0.1896 0.1795 0.1622 0.1447 0.1025 20 0.1490 0.1293 0.1127 0.0939 0.0653 0.0528 25 0.0998 0.0965 0.0898 0.0800 0.0491 0.0391 30 0.0952 0.0853 0.0639 0.0561 0.0267 0.0160 35 0.0612 0.0514 0.0462 0.0265 0.0094 0.0073 表 3 不同算法在不同信噪比级别下的RMSE值的比较
SNR(dB) L1/2-NMF RSNMF SRRNMF SSRNMF SSR-NMF L21NMF-SSR 15 0.3669 0.3352 0.3247 0.2821 0.2619 0.1796 20 0.2754 0.2488 0.1793 0.1614 0.1541 0.0996 25 0.1172 0.1067 0.1125 0.0926 0.0659 0.0560 30 0.1093 0.0901 0.0724 0.0642 0.0462 0.0318 35 0.0861 0.0623 0.0522 0.0456 0.0312 0.0186 表 4 不同算法在Jasper Ridge数据集的SAD值对比
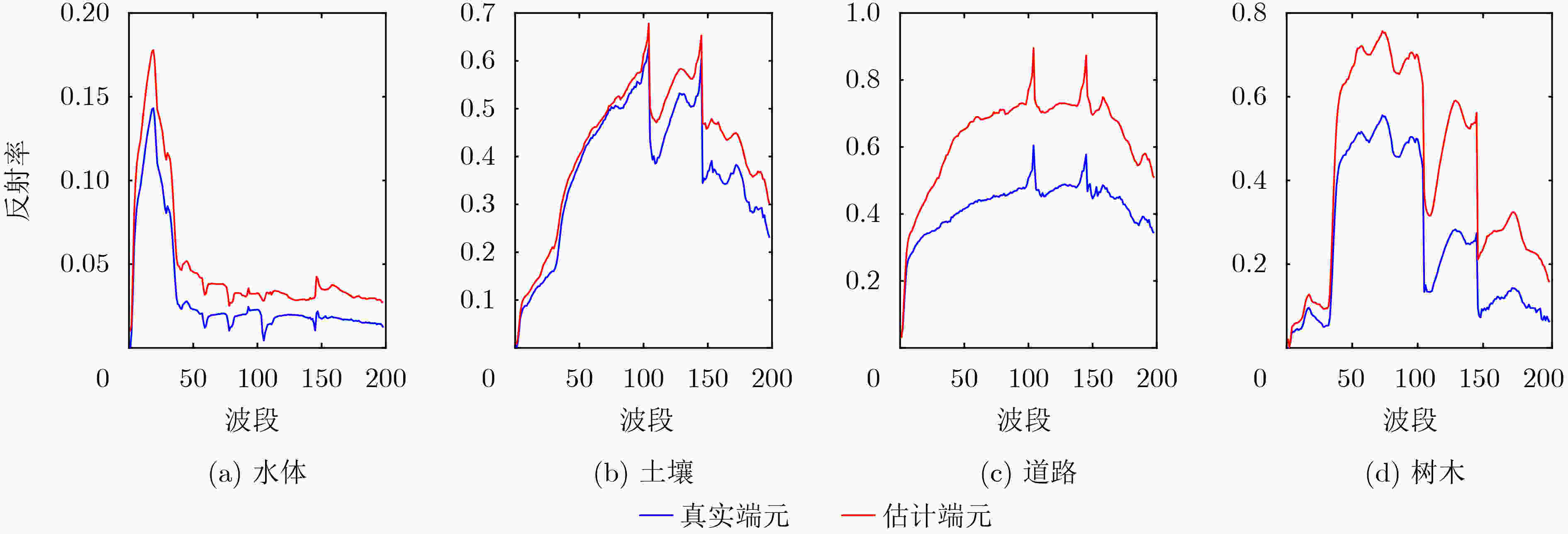
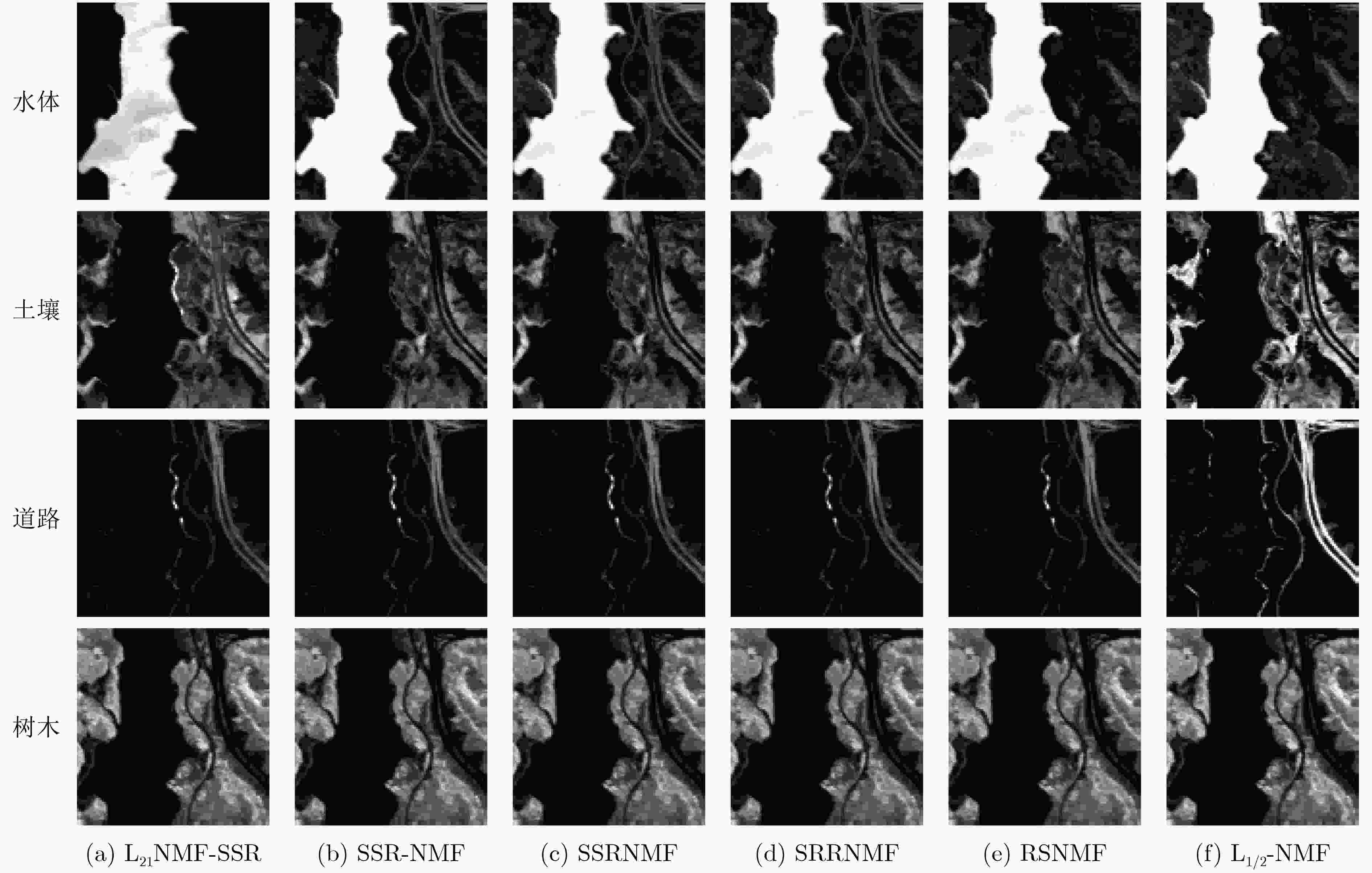
L1/2-NMF RSNMF SRRNMF SSRNMF SSR-NMF L21NMF-SSR 树木 0.1284 0.1721 0.1306 0.1338 0.1131 0.1224 水体 0.0816 0.1061 0.0862 0.1195 0.0958 0.0307 土壤 0.1533 0.1584 0.1545 0.1189 0.1445 0.1711 道路 0.1174 0.1050 0.1212 0.1123 0.0723 0.0494 均值 0.1202 0.1217 0.1231 0.1211 0.1064 0.0934 表 5 不同算法在Jasper Ridge数据集的RMSE值对比
L1/2-NMF RSNMF SRRNMF SSRNMF SSR-NMF L21NMF-SSR RMSE 0.2126 0.2080 0.2124 0.1564 0.1415 0.1311 表 6 不同算法在Urban数据集的SAD值对比
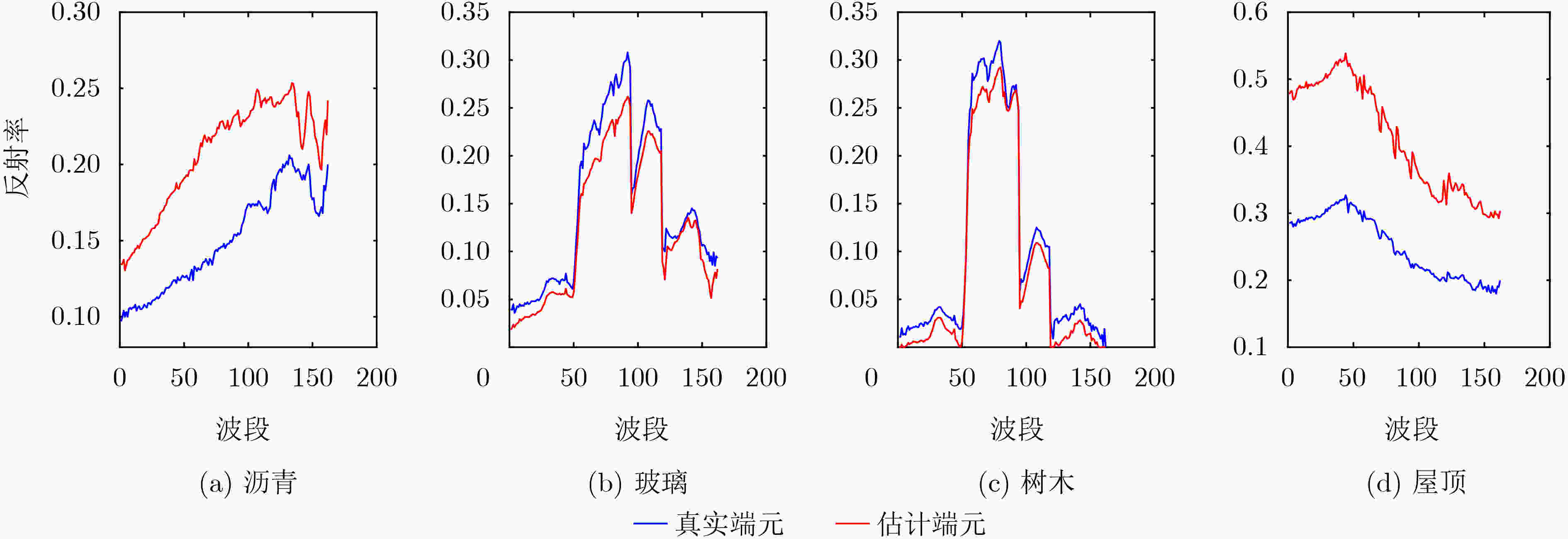
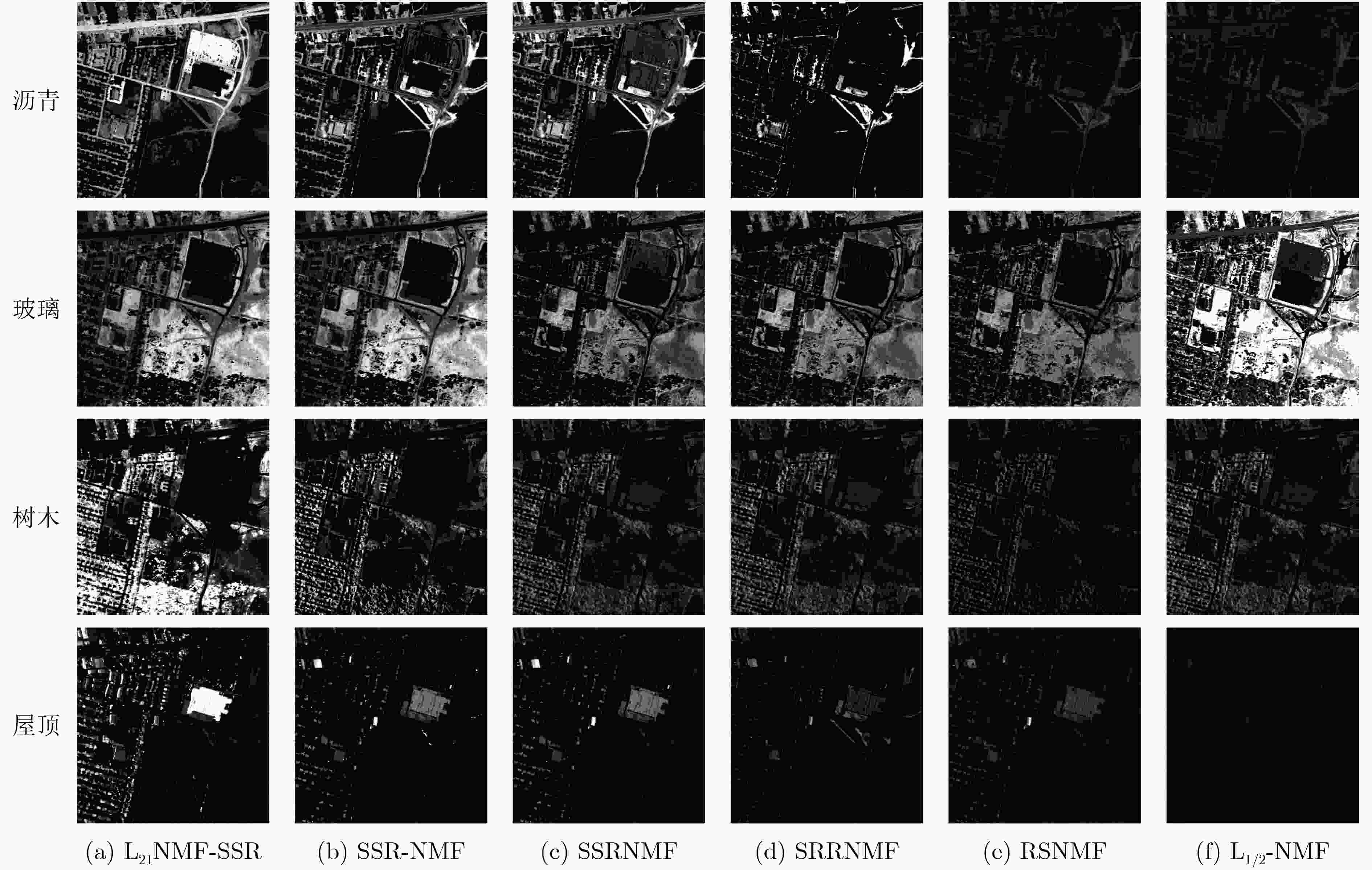
L1/2-NMF RSNMF SRRNMF SSRNMF SSR-NMF L21NMF-SSR 沥青 0.3629 0.2631 0.2515 0.2661 0.1734 0.1324 玻璃 0.3278 0.2389 0.2839 0.2196 0.2009 0.1574 树木 0.2018 0.1975 0.1956 0.1409 0.1106 0.1130 屋顶 0.1409 0.2064 0.1783 0.1851 0.1463 0.1194 均值 0.2584 0.2265 0.2273 0.2029 0.1578 0.1306 表 7 不同算法在Urban数据集的RMSE值对比
L1/2-NMF RSNMF SRRNMF SSRNMF SSR-NMF L21NMF-SSR RMSE 0.3567 0.3493 0.3411 0.3283 0.2787 0.2581 -
[1] 祝伟, 王雪, 黄岩, 等. 重加权稀疏和全变差约束下的深度非负矩阵分解高光谱解混[J]. 遥感学报, 2020, 24(4): 401–416.ZHU Wei, WANG Xue, HUANG Yan, et al. Reweighted sparsity regularized deep nonnegative matrix factorization with total variation toward hyperspectral unmixing[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2020, 24(4): 401–416. [2] LE Dong, YUAN Yuan, and LUXS X. Spectral–spatial joint sparse NMF for hyperspectral unmixing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(3): 2391–2402. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3006109 [3] 陈晋, 马磊, 陈学泓, 等. 混合像元分解技术及其进展[J]. 遥感学报, 2016, 20(5): 1102–1109.CHEN Jin, MA Lei, CHEN Xuehong, et al. Research progress of spectral mixture analysis[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2016, 20(5): 1102–1109. [4] YUAN Yuan, ZHANG Zihan, and WANG Qi. Improved collaborative non-negative matrix factorization and total variation for hyperspectral unmixing[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 998–1010. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.2977399 [5] BIOUCAS-DIAS J M, PLAZA A, DOBIGEON N, et al. Hyperspectral unmixing overview: Geometrical, statistical, and sparse regression-based approaches[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2012, 5(2): 354–379. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2012.2194696 [6] LI Jun and BIOUCAS-DIAS J M. Minimum volume simplex analysis: A fast algorithm to unmix hyperspectral data[C]. IGARSS 2008 - 2008 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Boston, USA, 2008: 250–253. [7] CHAN T H, CHI C Y, HUANG Yumin, et al. A convex analysis-based minimum-volume enclosing simplex algorithm for hyperspectral unmixing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(11): 4418–4432. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2009.2025802 [8] BERMAN M, KIIVERI H, LAGERSTROM R, et al. ICE: A statistical approach to identifying endmembers in hyperspectral images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2004, 42(10): 2085–2095. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2004.835299 [9] 袁博. 空间与谱间相关性分析的NMF高光谱解混[J]. 遥感学报, 2018, 22(2): 265–276.YUAN Bo. NMF hyperspectral unmixing algorithm combined with spatial and spectral correlation analysis[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2018, 22(2): 265–276. [10] WANG Nan, DU Bo, ZHANG Liangpei, et al. An abundance characteristic-based independent component analysis for hyperspectral unmixing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(1): 416–428. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2322862 [11] HE Wei, ZHANG Hongyan, and ZHANG Liangpei. Sparsity-regularized robust non-negative matrix factorization for hyperspectral unmixing[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(9): 4267–4279. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2519498 [12] 徐光宪, 王延威, 马飞, 等. 基于最小体积稀疏正则的高光谱解混方法的研究[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2020, 57(24): 241010.XU Guangxian, WANG Yanwei, MA Fei, et al. Based on method of Hyperspectral unmixing minimum volume of sparse regularization[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2020, 57(24): 241010. [13] WANG Nan, DU Bo, and ZHANG Liangpei. An endmember dissimilarity constrained non-negative matrix factorization method for hyperspectral unmixing[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2013, 6(2): 554–569. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2013.2242255 [14] QIAN Yuntao, JIA Sen, ZHOU Jun, et al. Hyperspectral unmixing via L1/2 sparsity-constrained nonnegative matrix factorization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(11): 4282–4297. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2144605 [15] CANDÈS E J, WAKIN M B, and BOYD S P. Enhancing sparsity by reweighted l1 minimization[J]. Journal of Fourier Analysis and Applications, 2008, 14(5): 877–905. [16] QU Kewen and BAO Wenxing. Multiple-Priors ensemble constrained nonnegative matrix factorization for spectral unmixing[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 963–975. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.2976602 [17] LU Xiaoqiang, WU Hao, YUAN Yuan, et al. Manifold regularized sparse NMF for hyperspectral unmixing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(5): 2815–2826. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2213825 [18] LU Xiaoqiang, DONG Le, and YUAN Yuan. Subspace clustering constrained sparse NMF for hyperspectral unmixing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(5): 3007–3019. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2946751 [19] ZHOU Lei, ZHANG Xueni, WANG Jianbo, et al. Subspace structure regularized nonnegative matrix factorization for hyperspectral unmixing[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 4257–4270. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.3011257 [20] HUANG Risheng, LI Xiaorun, and ZHAO Liaoying. Spectral–spatial robust nonnegative matrix factorization for hyperspectral unmixing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(10): 8235–8254. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2919166 [21] 周昌, 李向利, 李俏霖, 等. 基于余弦相似度的稀疏非负矩阵分解算法[J]. 计算机科学, 2020, 47(10): 108–113. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.190700112ZHOU Chang, LI Xiangli, LI Qiaolin, et al. Sparse non-negative matrix factorization algorithm based on cosine similarity[J]. Computer Science, 2020, 47(10): 108–113. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.190700112 [22] LIU Guangcan, LIN Zhouchen, YAN Shuicheng, et al. Robust recovery of subspace structures by low-rank representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(1): 171–184. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.88 [23] CAI Jianfeng, CANDÈS E J, and SHEN Zuowei. A singular value thresholding algorithm for matrix completion[J]. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 2010, 20(4): 1956–1982. doi: 10.1137/080738970 [24] HE Wei, ZHANG Hongyan, and ZHANG Liangpei. Total variation regularized reweighted sparse nonnegative matrix factorization for hyperspectral unmixing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(7): 3909–3921. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2683719 [25] http://www.ehu.es/ccwintco/index.php/Hyperspectral_Imagery_Synthesis tools for MATLAB, 2020. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
