Execution Delay Minimization in Wireless Powered Mobile Edge Computing Networks
-
摘要: 针对无线供能移动边缘计算(MEC)网络,该文将计算时延定义为数据卸载与计算所消耗的时间,并提出一种节点计算时延之和最小化的多维资源分配方法。首先,在节点能量因果约束下,通过联合优化专用能量站工作时长、任务分割系数、节点计算频率和发射功率来建立一个计算时延之和最小化的多维资源分配问题。由于存在优化变量耦合与max-max函数,所建问题非凸且无法采用凸优化工具获取最优解。为此,通过引入一系列松弛变量和辅助变量来进行优化问题简化以及优化变量解耦,并在此基础上,通过深入分析简化问题的结构特性,提出一种基于二分法的迭代算法来求解原问题的最优解。最后,计算机仿真验证了所提迭代算法的正确性以及所提资源分配方法在计算时延方面的优越性。
-
关键词:
- 无线供能移动边缘网络 /
- 计算时延 /
- 能量因果约束 /
- 资源分配方法
Abstract: For a wireless powered MEC (Mobile Edge Computing) network, the execution delay as the time for data offloading and data execution is defined, and a multidimensional resource allocation scheme is proposed to minimize the execution delay of all nodes. Firstly, an execution delay minimization based multidimensional optimization problem is formulated by jointly optimizing the operation time of a power beacon, the portions of task bits for local computing and offloading, the computing frequency and the transmit power of per node, subject to the energy-causality constraint of nodes. As the formulated optimization problem includes couplings among optimization variables and the max-max function, it is non-convex and can not be solved by the existing convex tools. Therefore, a series of slack variables and auxiliary variables are introduced to simplify the optimization problem and decouple the coupled variables. Then after carefully inspecting the structure of the simplified problem, a dichotomy based iterative algorithm is proposed to obtain the optimal solution. Finally, computer simulations validate the correctness of the devised iterative algorithm and the advantages of the proposed resource allocation in terms of the execution delay. -
表 1 仿真参数
含义 参数 数值 用户数 K 4 专用能量站最大发射功率 P0 23 dBm 带宽 W 400 kHz 噪声功率谱密度 $ {{{\sigma ^{\text{2}}}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{\sigma ^{\text{2}}}} W}} \right. } W} $ –120 dBm/Hz 节点k最小所需计算的任务比特数 Lk 5 kbit 节点k发送信息的电路损耗 $ {p_{k,c}} $ 1 mW 节点k本地计算时最大计算频率 $ f_k^{\max } $ 500 MHz 节点k本地计算时有效电容系数 $ {\varepsilon _k} $ 10–26 节点k计算一个比特所需要的CPU 时钟周期数 Gk 1000 Cycles/bit -
[1] Key drivers and research challenges for 6G ubiquitous wireless intelligence[EB/OL]. http://jultika.oulu.fi/files/isbn9789526223544.pdf, 2019. [2] 谢人超, 廉晓飞, 贾庆民, 等. 移动边缘计算卸载技术综述[J]. 通信学报, 2018, 39(11): 138–155. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2018215XIE Renchao, LIAN Xiaofei, JIA Qingmin, et al. Survey on computation offloading in mobile edge computing[J]. Journal on Communications, 2018, 39(11): 138–155. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2018215 [3] ZENG Ming, HAO Wanming, DOBRE O A, et al. Delay minimization for massive MIMO assisted mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(6): 6788–6792. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.2979434 [4] BI Suzhi and ZHANG Yingjun. Computation rate maximization for wireless powered mobile-edge computing with binary computation offloading[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2018, 17(6): 4177–4190. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2018.2821664 [5] WANG Feng, XU Jie, WANG Xin, et al. Joint offloading and computing optimization in wireless powered mobile-edge computing systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2018, 17(3): 1784–1797. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2017.2785305 [6] ZHOU Fuhui, WU Yongpeng, HU R Q, et al. Computation rate maximization in UAV-enabled wireless-powered mobile-edge computing systems[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2018, 36(9): 1927–1941. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2018.2864426 [7] HU Xiaoyan, WONG K K, and YANG Kun. Wireless powered cooperation-assisted mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2018, 17(4): 2375–2388. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2018.2794345 [8] HU Xiaoyan, WONG K K, and ZHANG Yangyang. Wireless-powered edge computing with cooperative UAV: Task, time scheduling and trajectory design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(12): 8083–8098. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3019097 [9] ZHOU Fuhui and HU R Q. Computation efficiency maximization in wireless-powered mobile edge computing networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(5): 3170–3184. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.2970920 [10] 施丽琴, 叶迎晖, 卢光跃. 无线供能边缘计算网络中系统计算能效最大化资源分配方案[J]. 通信学报, 2020, 41(10): 59–69. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2020182SHI Liqin, YE Yinghui, and LU Guangyue. Computation energy efficiency maximization based resource allocation scheme in wireless powered mobile edge computing network[J]. Journal on Communications, 2020, 41(10): 59–69. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2020182 [11] SHI Liqin, YE Yinghui, CHU Xiaoli, et al. Computation energy efficiency maximization for a NOMA-based WPT-MEC network[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(13): 10731–10744. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3048937 [12] REN Jinke, YU Guanding, HE Yinghui, et al. Collaborative cloud and edge computing for latency minimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(5): 5031–5044. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2904244 [13] WU Yuan, QIAN Liping, NI Kejie, et al. Delay-minimization nonorthogonal multiple access enabled multi-user mobile edge computation offloading[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2019, 13(3): 392–407. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2019.2893057 [14] DING Zhiguo, NG D W K, SCHOBER R, et al. Delay minimization for NOMA-MEC offloading[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2018, 25(12): 1875–1879. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2018.2876019 [15] YE Yinghui, SHI Liqin, CHU Xiaoli, et al. On the outage performance of ambient backscatter communications[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(8): 7265–7278. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.2984449 [16] CHI Kaikai, ZHU Yihua, LI Yanjun, et al. Minimization of transmission completion time in wireless powered communication networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2017, 4(5): 1671–1683. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2017.2689777 -





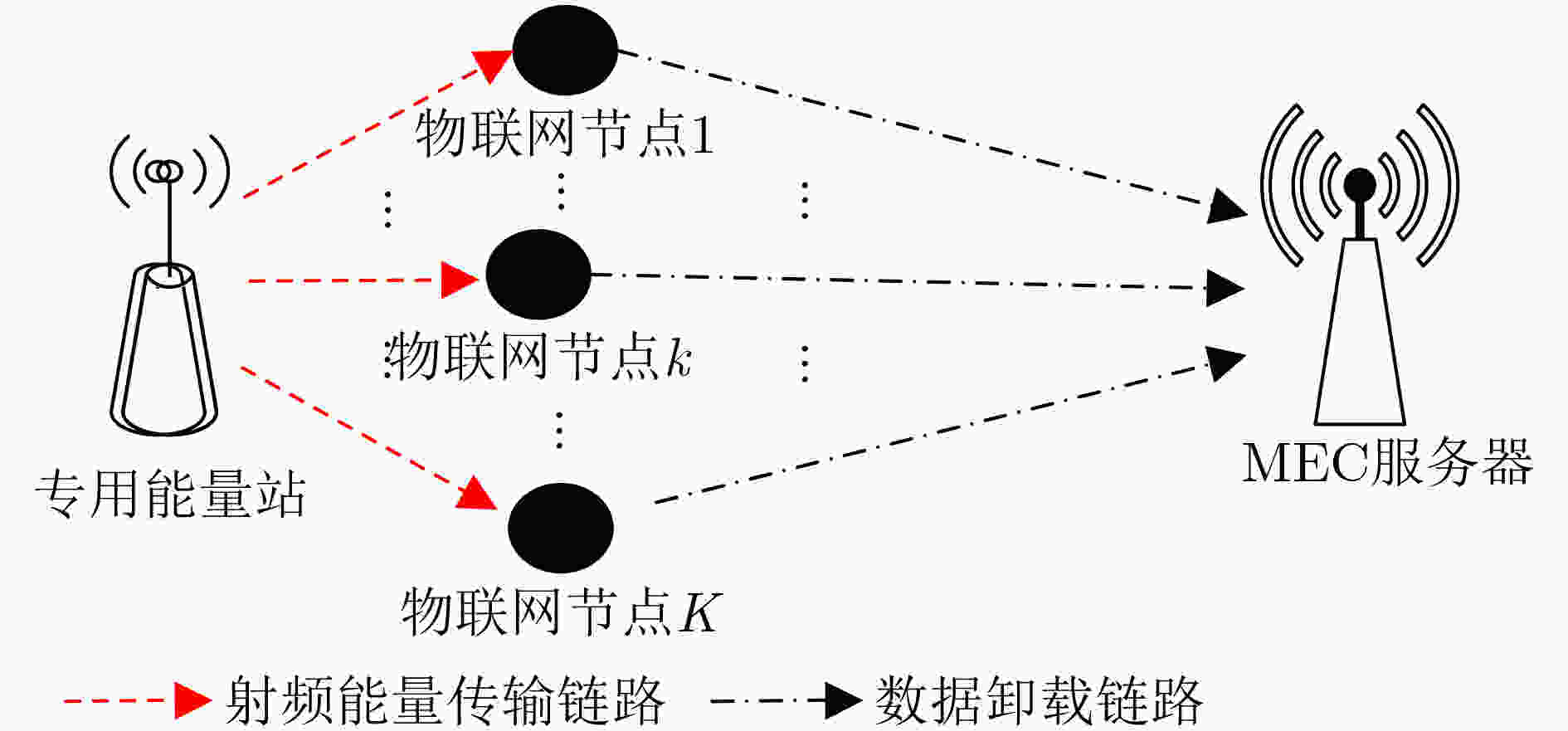
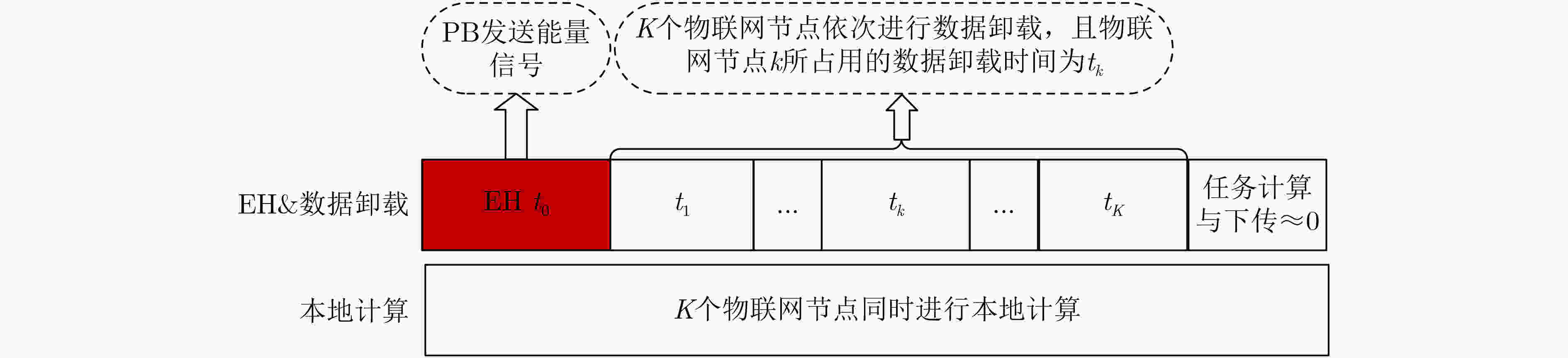
 下载:
下载:
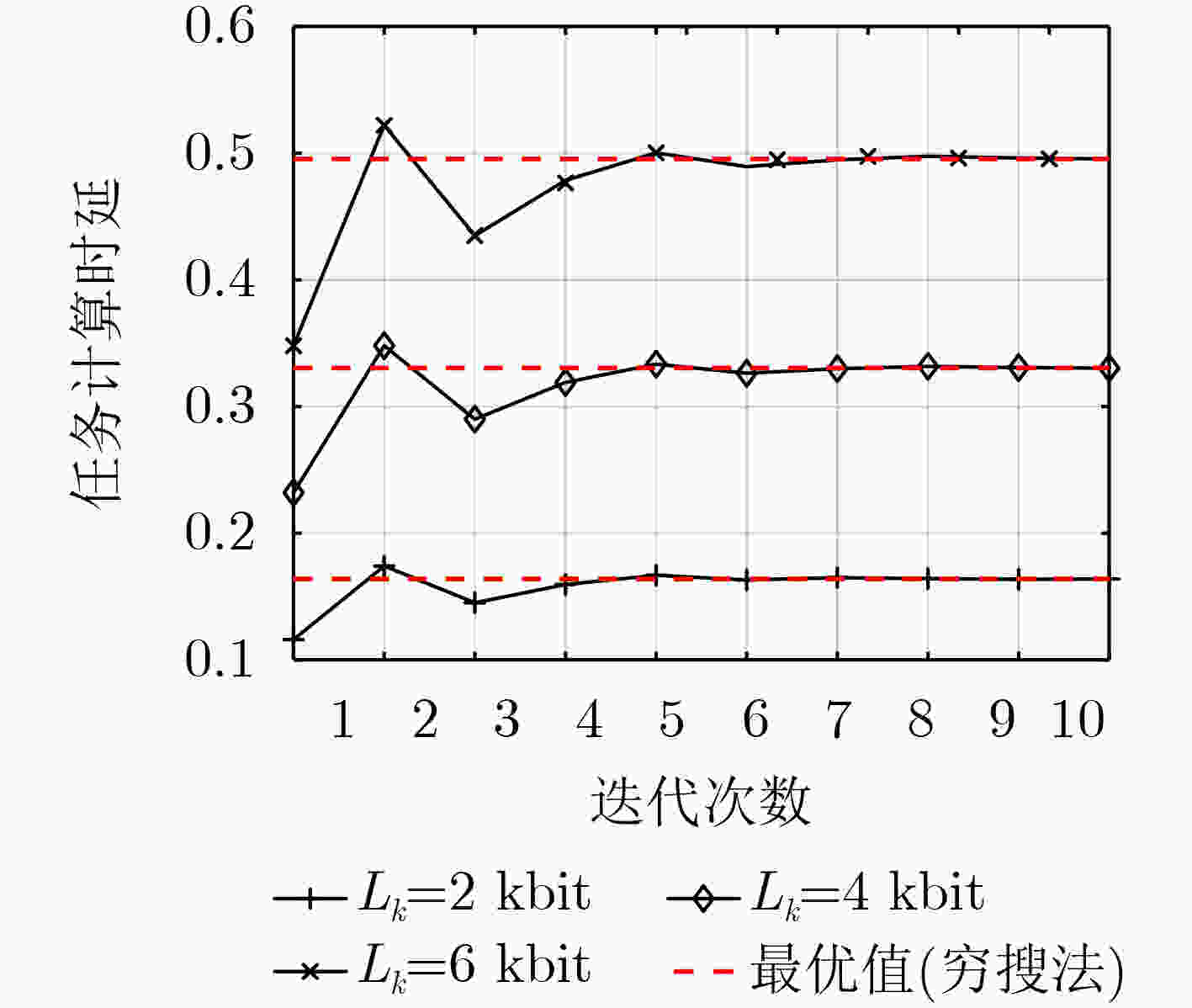
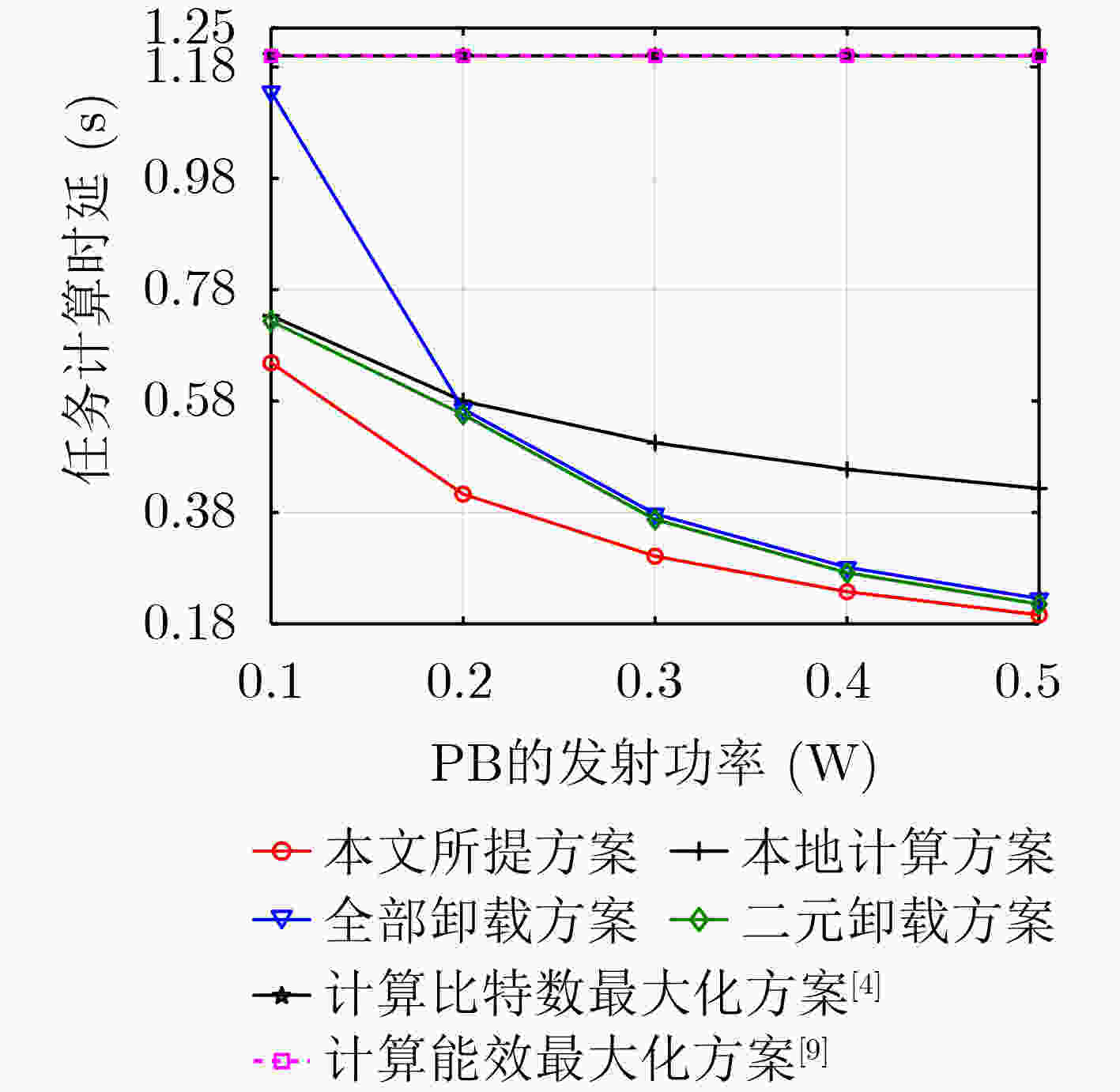


 下载:
下载:
