End to End Network Slicing Security Deployment Algorithm for Multi Service Scenarios
-
摘要: 5G移动通信中,网络切片(NS)的引入成功解决了不同业务场景的网络资源分配不均问题。针对传统算法无法满足5G网络的多业务场景切片安全部署问题,该文提出一种针对于多业务场景的端到端网络切片安全需求(NSR)部署算法。首先,针对切片部署过程中节点的安全性进行了定义;其次,根据节点的安全性进行排序和映射,在此基础上,以最小化网络资源部署成本的同时提高部署的安全收益为目标,构建切片部署的数学模型;最后,考虑到每种类型切片的资源需求不同,提出一种针对性的部署算法实现端到端网络切片的安全部署。仿真结果表明,所提算法在满足端到端网络切片安全部署的同时,降低了部署的成本,获得了较好的部署安全收益。Abstract: In 5G mobile communication, the introduction of Network Slice (NS) solves successfully the problem of uneven network resource allocation in different business scenarios. In view of the problem that traditional algorithms can not meet the security deployment of 5G network multi business scenario slicing, an end-to-end Network Slicing security Requirement (NSR) deployment algorithm for multi business scenario is proposed. Firstly, the security of nodes in slice deployment process is defined; Secondly, the nodes are sorted and mapped according to their security. On this basis, in order to minimize the cost of network resource deployment and improve the security benefits of deployment, a mathematical model of slice deployment is constructed; Finally, considering the different resource requirements of each type of slicing, a targeted deployment algorithm is proposed to realize the secure deployment of end-to-end network slicing. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can satisfy the security deployment of end-to-end network slices, reduce the deployment cost and obtain better deployment security benefits.
-
Key words:
- 5G Network Slice (NS) /
- Security deployment /
- Multi service scenarios /
- Safety benefits
-
表 1 虚拟节点安全等级排序算法
输入:原始的节点集合$ {N^{\rm{R}}} $ 输出:排序的节点集合${{S} }({N^{\rm{R} } })$ (1) 计算所有节点的安全性NS并进行降序排列 (2) 将NS值最高的节点标记为R,并作为根节点生成BFS树 (3) 将树中的每一层节点按照式(1)中方法排序 (4) 返回排序后的节点集合${{S} }({N^{\rm{R} } })$ 表 2 切片请求中虚拟节点映射算法
输入:网络切片请求 输出:映射的节点集合 (1) for 每一个虚拟节点i do (2) if $i = {{R} }$ then (3) 映射到具有最高安全等级的物理节点上 (4) if $i \ne {{R} }$ then (5) 选择$ i $的父节点F, 物理节点P (6) 选择P的相邻节点为备用节点集合A (7) 满足节点容量的同时选择集合${{A} }$中$ {\rm{NS}} $值最大的节点 (8) end if (9) 返回节点集合 (10) end for 表 3 切片请求中虚拟链路映射算法
输入:网络切片请求 输出:映射后的链路集合 (1) 将链路的带宽进行降序排列 (2) for 每一条虚拟链路 do (3) 计算该链路的带宽,并进行链路筛选 (4) 找到虚拟链路的两端的物理节点 (5) 利用插点法寻找两个链路之间的最短路径作为虚拟链路的
映射路径(6) 返回链路集合 (7) end for 表 4 eMBB切片跨域部署实现算法
输入:eMBB类型切片$ {R^{\rm{e}}} $,网络资源$ {G^{\rm{P}}} $ 输出:部署结果 (1) 依据算法1对节点排序得到$ S\left( {{N^{\rm{R}}}} \right) $ (2) 依据算法2按照排序结果对ANs节点进行映射 (3) 依据算法2按照排序结果对CNs节点进行映射 (4) 依据算法3完成链路映射 (5) 依据链路映射结果对TNs节点进行映射 (6) 返回部署结果 表 5 mMTC切片跨域部署实现算法
输入:mMTC类型切片$ {R^{\rm{m}}} $,网络资源$ {G^{\rm{P}}} $ 输出:部署结果 (1) 依据表1算法对节点排序得到$ S\left( {{N^{\rm{R}}}} \right) $ (2) 依据表2算法按照排序结果对CNs节点进行映射 (3) 选择资源满足需求的ANs节点作为候选ANs节点 (4) 搜索CNs节点和候选ANs节点之间的候选物理链路集合,并
根据对比结果完成链路映射(5) 依据虚拟链路映射结果对TNs节点进行映射 (6) 完成ANs节点的映射 (7) 返回部署结果 表 6 uRLLC切片跨域部署实现算法
输入:uRLLC类型切片$ {R^{\rm{u}}} $,网络资源$ {G^{\rm{P}}} $ 输出:部署结果 (1) 依据表1算法对节点排序得到$ S\left( {{N^{\rm{R}}}} \right) $ (2) 依据节点安全等级选择ANs节点CNs节点作为候选节点集合 (3) 搜索候选CNs节点和候选ANs节点之间的候选物理路径集合,
并根据对比结果完成链路映射(4) 依据虚拟链路映射结果对TNs节点进行映射 (5) 完成ANs节点,CNs节点的映射 (6) 返回部署结果 -
[1] LI Taihui, ZHU Xiaorong, and LIU Xu. An end-to-end network slicing algorithm based on deep Q-Learning for 5G network[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 122229–122240. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3006502 [2] 陈山枝. 发展5G的分析与建议[J]. 电信科学, 2016, 32(7): 1–10.CHEN Shanzhi. Analysis and suggestion of future 5G directions[J]. Telecommunications Science, 2016, 32(7): 1–10. [3] FISCHER A and DE MEER H. Position paper: Secure virtual network embedding[J]. Praxis Der Informationsverarbeitung Und Kommunikation, 2011, 34(4): 190–193. [4] ALJUHANI A and ALHARBI T. Virtualized network functions security attacks and vulnerabilities[C]. Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 7th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference (CCWC), Las Vegas, USA, 2017: 1–4. [5] ZHOU Jinhe, ZHAO Wenjun, and CHEN Shuo. Dynamic network slice scaling assisted by prediction in 5G network[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 133700–133712. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3010623 [6] HARUTYUNYAN D, FEDRIZZI R, SHAHRIAR N, et al. Orchestrating end-to-end slices in 5G networks[C]. 2019 15th International Conference on Network and Service Management (CNSM), Halifax, Canada, 2019: 1–9. [7] ZHAO Hailiang, DENG Shuiguang, LIU Zijie, et al. DPoS: Decentralized, privacy-preserving, and low-complexity online slicing for multi-tenant networks[C]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, Los Alamitos, USA, 2021. [8] ZHAO Guanqun, QIN Shuang, and FENG Gang. Network slice selection in softwarization based mobile networks[C]. 2018 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Abu Dhabi, The United Arab Emirates, 2018: 1–7. [9] WANG Jingpei, SUN Bin, and NIU Xinxin. A trust model evaluation algorithm based on trusted modeling process[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University: Science and Technology, 2013, 3(12): 1699–1707. [10] 牛犇, 游伟, 汤红波. 基于安全信任的网络切片部署策略研究[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2019, 36(2): 574–579.NIU Ben, YOU Wei, and TANG Hongbo. Research on network slicing deployment strategy based on security trust[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2019, 36(2): 574–579. [11] GUAN Wanqing, WEN Xiangming, WANG Luhan, et al. A service-oriented deployment policy of end-to-end network slicing based on complex network theory[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 19691–19701. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2822398 [12] 管婉青. 基于多层复杂网络理论的网络切片协作管理研究[D]. [博士论文], 北京邮电大学, 2019GUAN Wanqing. Research on cooperative management of network slicing based on multilayer complex network theory[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2019. [13] 张子超, 郝蔚琳, 张伊凡. 一种复杂网络中节点安全重要性排序的度量方法[J]. 信息安全学报, 2019, 4(1): 79–88.ZHANG Zichao, HAO Weilin, and ZHANG Yifan. A measure approach for ranking the security importance of node security importance in complex network[J]. Journal of Cyber Security, 2019, 4(1): 79–88. [14] FREEMAN L C. A set of measures of centrality based on betweenness[J]. Sociometry, 1977, 40(1): 35–41. doi: 10.2307/3033543 [15] 荣莉莉, 郭天柱, 王建伟. 复杂网络节点中心性[J]. 上海理工大学学报, 2008, 30(3): 227–230, 236. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6735.2008.03.005RONG Lili, GUO Tianzhu, and WANG Jianwei. Centralities of nodes in complex networks[J]. Journal of University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, 2008, 30(3): 227–230, 236. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6735.2008.03.005 [16] ABBASI A N and HE Mingyi. Convolutional neural network with PCA and batch normalization for hyperspectral image classification[C]. IGARSS 2019 - 2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019: 959–962. [17] AKRAM V K, ASCI M, and DAGDEVIREN O. Design and analysis of a breadth first search based connectivity robustness estimation approach in wireless sensor networks[C]. 2018 6th International Conference on Control Engineering & Information Technology (CEIT), Istanbul, Turkey, 2018: 1–6. [18] HUANG Guanghao, LU Wei, XIE Jidong, et al. Improved route selection strategy based on K shortest path[C]. 2019 International Symposium on Networks, Computers and Communications (ISNCC), Istanbul, Turkey, 2019: 1–4. [19] ITU. IMT vision-framework and overall objectives of the future development of IMT for 2020 and beyond[R]. ITU-R M.2083-0, 2015. [20] HARRINGTON P. Machine Learning in Action[M]. Beijing: The People’s Posts and Telecommunications Press, 2013: 15–31. [21] AARTS E and KORST J. Simulated Annealing and Boltzmann Machines[M]. New York: John Wiley &Sons, 1989: 173–198. [22] YU Cunqian, HOU Weigang, GUAN Yingying, et al. Virtual 5G network embedding in a heterogeneous and multi-domain network infrastructure[J]. China Communications, 2016, 13(10): 29–43. doi: 10.1109/CC.2016.7732010 [23] MIJUMBI R, SERRAT J, GORRICHO J, et al. Design and evaluation of algorithms for mapping and scheduling of virtual network functions[C]. The 2015 1st IEEE Conference on Network Softwarization (NetSoft), London, UK, 2015: 1–9. [24] YU Minlan, YI Y, REXFORD J, et al. Rethinking virtual network embedding: Substrate support for path splitting and migration[J]. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 2008, 38(2): 17–29. doi: 10.1145/1355734.1355737 -





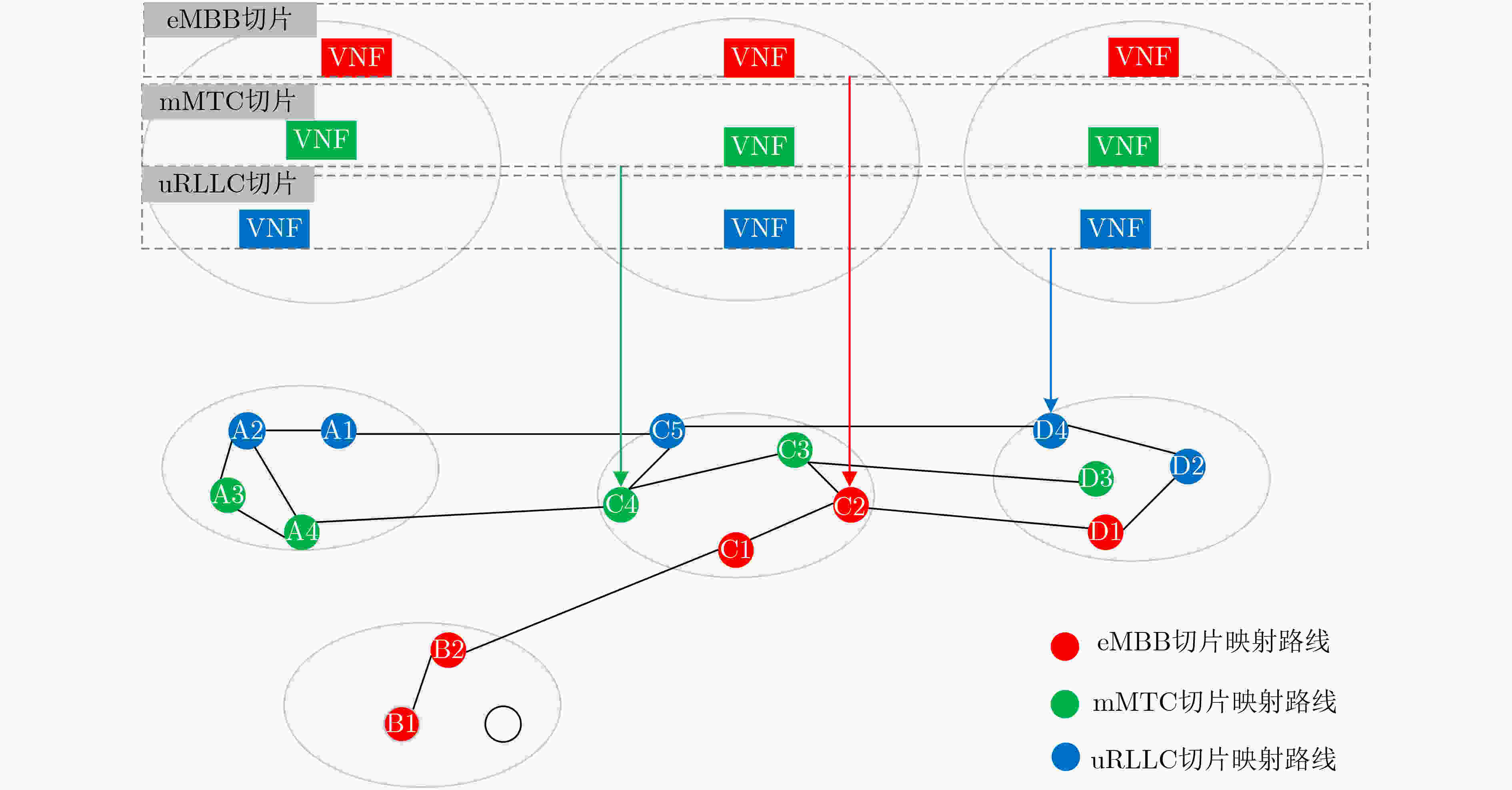
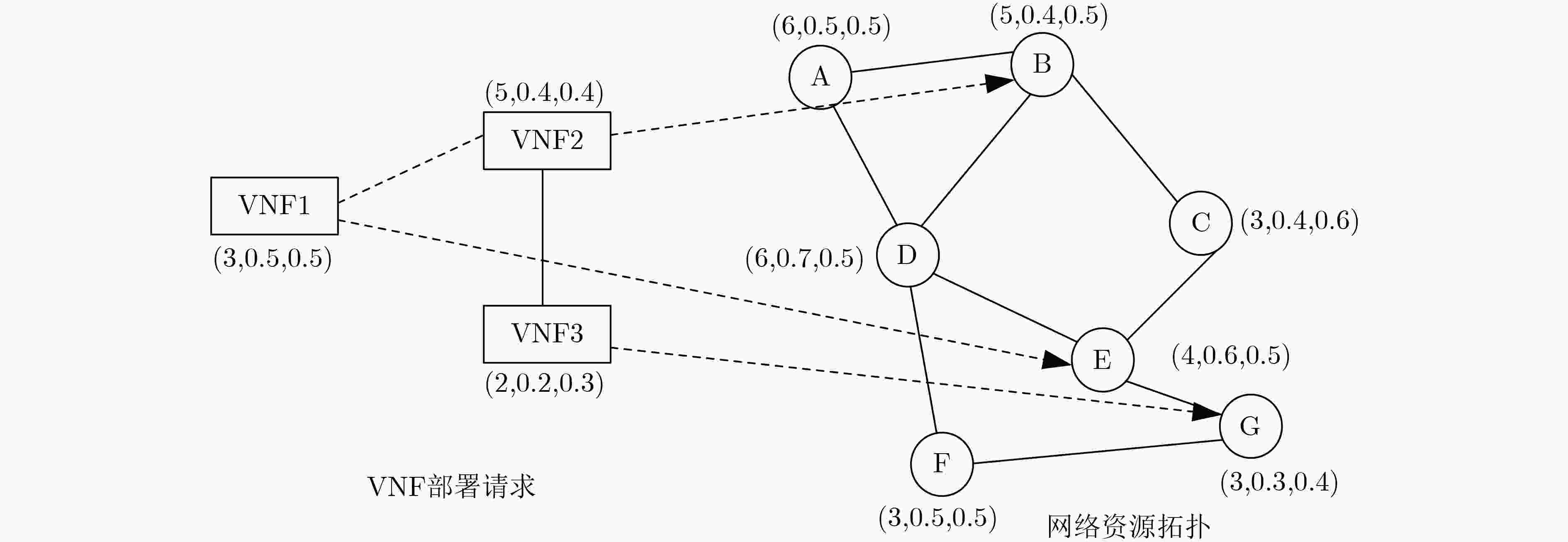
 下载:
下载:
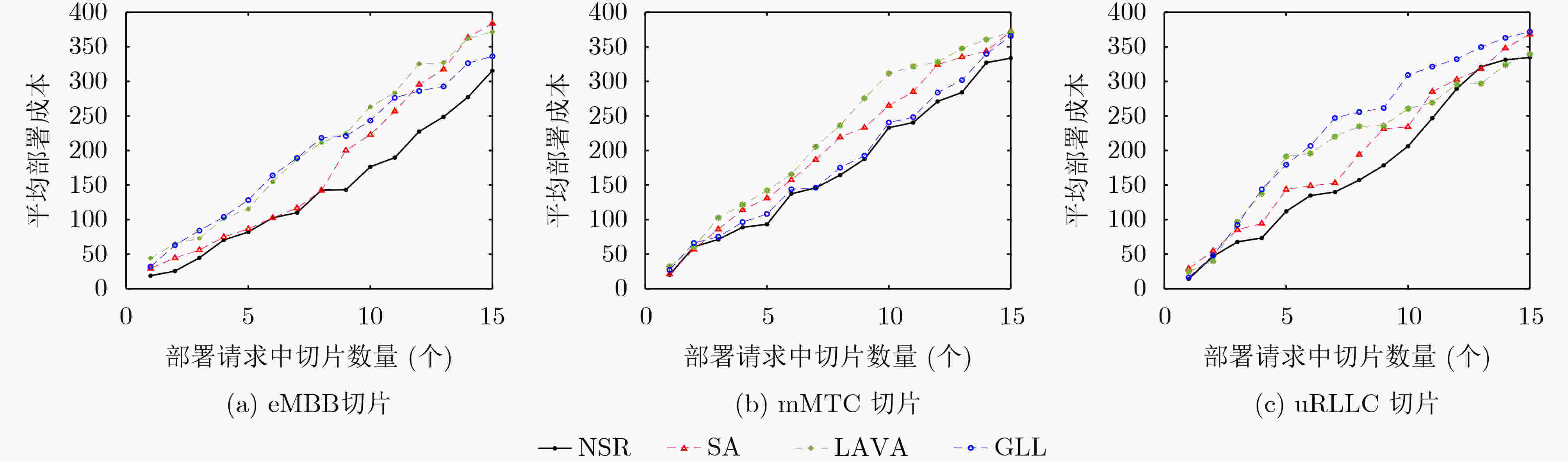
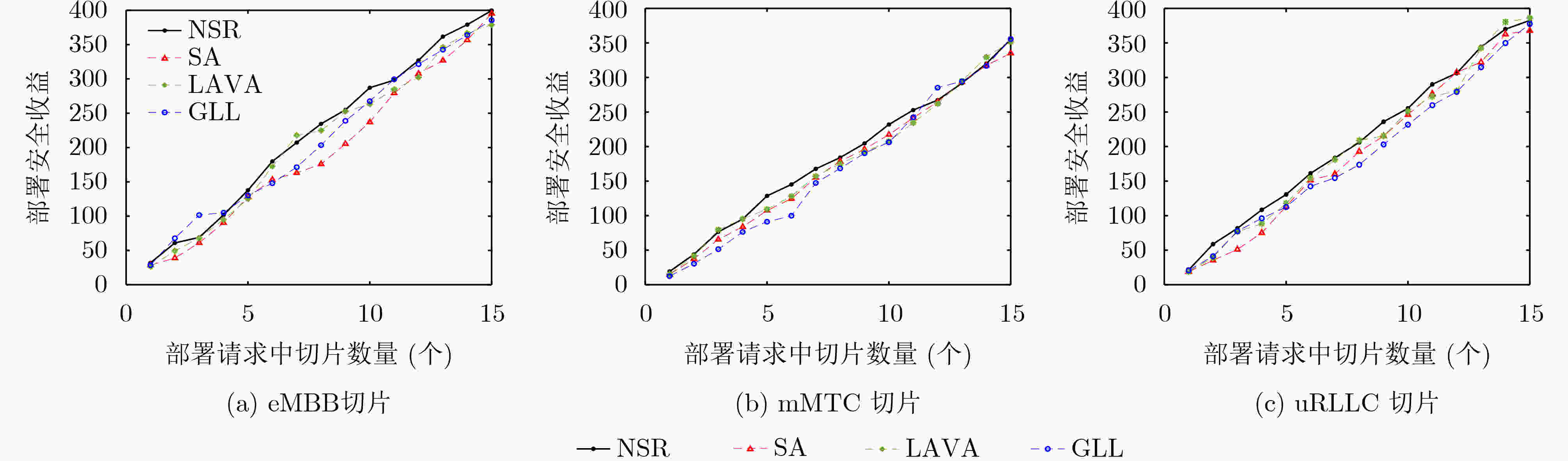


 下载:
下载:
