New Method of Task Offloading in Mobile Edge Computing for Vehicles Based on Simulated Annealing Mechanism
-
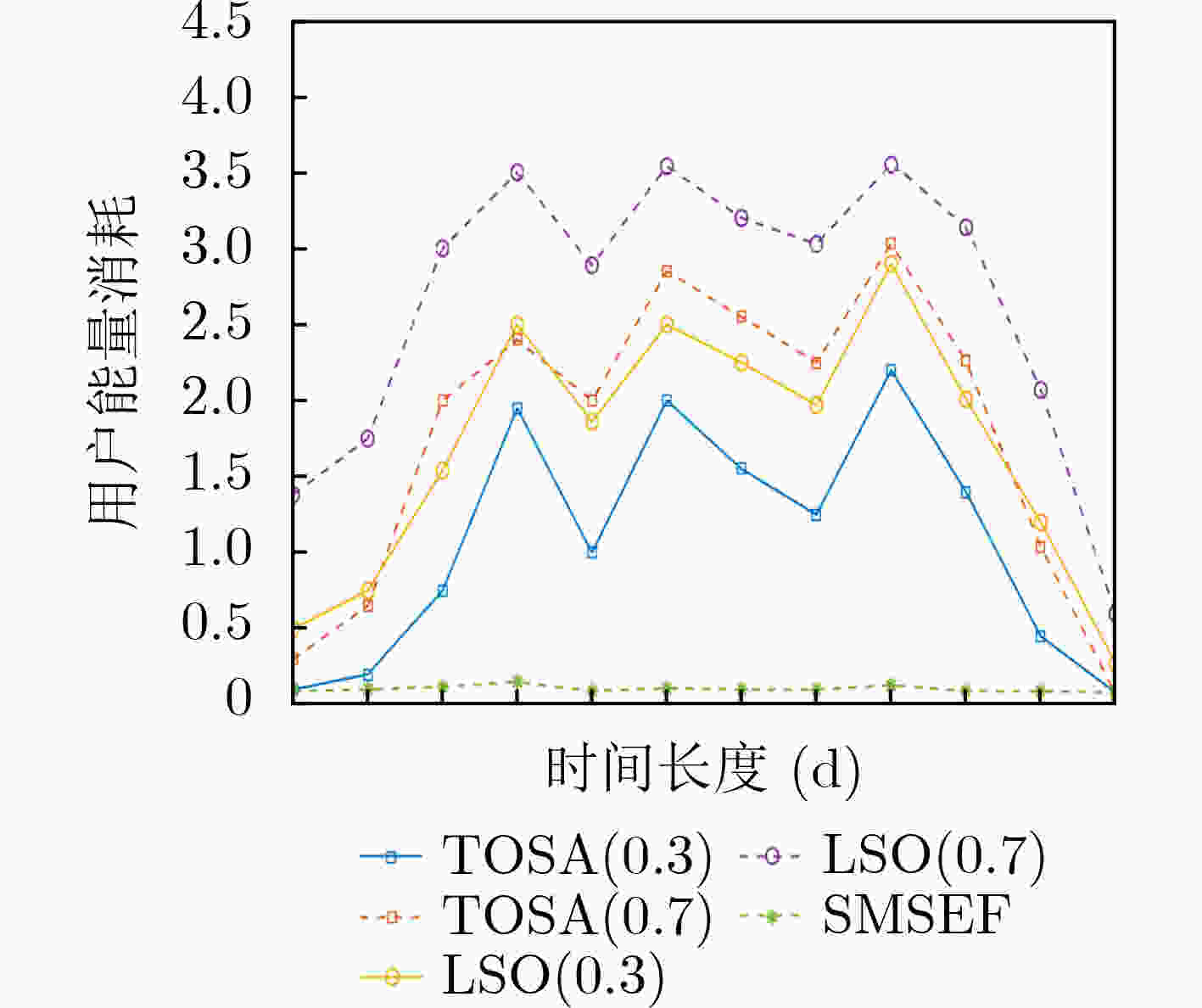
摘要: 在车联网(IOV)环境中,如果将车辆的计算任务都放置在云平台执行,无法满足对于信息处理的实时性,考虑移动边缘计算技术以及任务卸载策略,将用户的计算任务卸载到靠近设备边缘的服务器去执行。但是在密集的环境下,如果所有的任务都卸载到附近的边缘服务器去执行,同样会给边缘服务器带来巨大的负载。该文提出基于模拟退火机制的车辆用户移动边缘计算任务卸载新方法,通过定义用户的任务计算卸载效用,综合考虑时耗和能耗,结合模拟退火机制,根据当前道路的密集程度对系统卸载效用进行优化,改变用户的卸载决策,选择在本地执行或者卸载到边缘服务器上执行,使得在给定的环境下的所有用户都能得到满足低时延高质量的服务。仿真结果表明,该算法在减少用户任务计算时间的同时降低了能量消耗。Abstract: For Internet Of Vehicles(IOV), if all the computing tasks of vehicles are placed on the cloud platform, it can not meet the real-time requirement of information processing. Considering the mobile edge computing technology and task offloading method, the computing tasks are offloaded to the server near the edge of the device. However, in a dense environment, if all the tasks are offloaded, it would also bring large pressure to the edge server. A new method for offloading mobile edge computing tasks for vehicle users based on simulated annealing mechanism is proposed in this paper. By defining the user's task to calculate the offloading utility, comprehensively considering the time consumption and energy consumption, combining with simulated annealing, the utility of system offloading is optimized according to the current road density, and the user's offloading decision is changed. The offloading is executed locally or on the edge server, so that all users in a given environment can get high-quality service with low delay. The simulation results show that the algorithm can reduce the user task computing time and energy consumption at the same time.
-
Key words:
- Internet Of Vehicles(IOV) /
- Edge computing /
- Task offloading /
- Optimal /
- Simulated annealing mechanism
-
表 1 变量符号及含义
变量符号 含义 $ V $ 用户 $ M $ 服务器 $ {T}_{v} $ 用户计算任务 $ {t}_{v}^{\mathrm{l}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{c}} $ 用户在本地执行任务时耗 $ {e}_{v}^{\mathrm{l}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{c}} $ 用户在本地执行任务能耗 $ {E}_{v,m}^{n} $ 用户选择服务器上任意频带n进行传输 ${{\boldsymbol{p}}}_{v}^{\mathrm{t}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{n} }$ 用户输出功率 $ {C}_{v,m} $ 信息传送速率 $ {t}_{v}^{\text{tran}} $ 用户将任务上传所需时间 $ {t}_{v}^{\mathrm{c}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{m}} $ 任务在服务器的执行时间 $ {t}_{v}^{\mathrm{o}\mathrm{f}\mathrm{f}} $ 任务卸载到边缘的时间消耗 $ {e}_{v}^{\mathrm{t}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{n}} $ 任务卸载到边缘的时间能耗 $ {Q}_{v} $ 用户卸载效用 $ {\lambda }_{1} $ 时耗偏好 $ {\lambda }_{2} $ 能耗偏好 表 2 生成初始温度(算法1)
输入:v, m, n //初始用户数量,边缘服务器数量,每个边缘服务器子频带数量 offload(v,m,n)=zeros(v,m,n) //所有用户都没有卸载任务 Qv_old=0; //此时所有用户的卸载效用为0 for user=1:v for server=1:m for sub_server=1:n //每个边缘服务器配置7个子频带
$ {Q}_{v}=\left({\lambda }_{1}\dfrac{{t}_{v}^{\mathrm{l}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{c}}-{t}_{v}^{\mathrm{o}\mathrm{f}\mathrm{f}}}{{t}_{v}^{\mathrm{l}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{c}}}+{\lambda }_{2}\dfrac{{e}_{v}^{\mathrm{l}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{c}}-{e}_{v}^{\mathrm{t}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{n}}}{{e}_{v}^{\mathrm{l}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{c}}}\right){\displaystyle\sum }_{m\in M}{E}_{v,m},\forall v\in V $//根据式(12),用户选择满足自身卸载效用最大的方式执行任务 if (Qv_new>Qv_old) offload(v,m,n)=0 else offload(v,m,n)=1 end //如果卸载效用低于之前的效用则不进行卸载 end end end 输出:offload(v,m,n) //得到用户初始的任务卸载策略 表 3 状态转换(算法2)
输入:offload(v, m, n) //当前任务卸载策略,初始用户数量,边缘服务器数量,每个边
缘服务器子频带数量v_change=unidrnd(v) //选择改变执行方式的用户 [thism,thisn]=find(v,m,n) //找到用户当前的任务执行方式 if(change>rand) //改变任务在本地/服务器执行 offload(v,thism,thisn)=1-offload(v,thism,thisn) else if (offload(v,thism,thisn)==1) if(M_change>rand) nowm =unidrnd(m) //改变所选的卸载的服务器 offload(v,thism,thisn)=0 offload(v,nowm,thisn)=1 else //改变当前服务器所选择的子频带 nown=unidrnd(n) offload(v,thism,thisn)=0 offload(v,thism,nown)=1 end end 输出:offload(v, m, n) //新的卸载策略 表 4 基于模拟退火机制的边缘计算任务卸载算法(算法3)
输入:v, m, n, paras //初始用户数量,边缘服务器数量,每个边缘服务器子频带数
量,其他设定参数Offload=Offload_old=getORI(v,m,n) //根据算法1,得到初始卸载策略 Q=Q_old=getQ(offload_old,paras) //根据式(15),计算出卸载效用,并看作当前“最优解” while(T>T_end && i<i_end) //如果没有达到设定的终止温度,在规定的迭代次数范围内 for usr=1:k //定义每次改变策略的用户数量为k offload_new=changeoff(v,m,n) Q_new=getQ(offload_new,paras) deltQ=Q_new-Qold if(delQ>0) //如果本次策略卸载效用高于上一次,则接受本次策略 offload_old=offload_new Q_old=Q_new if(Q_new>Q) //如果本次策略卸载效用高于目前的最优解,则替代之前的解 Q=Q_new offload=offload_new end else if getP>rand //根据式(16)计算降温概率并判断是否接受本次策略 offload_old=offload_new Q_old=Q_new end end T=aT //根据降温系数改变温度 end 输出:Q,Offload //当达到终止温度或者规定的迭代次数,终止退火,此时得到
的用户卸载效用即是函数的最优解。表 5 仿真参数
仿真参数 取值 服务器个数(个) 4,9,16,25 车流量大小(辆) 30–Vmax
V3max = 110每个服务器的子频带数量(个) 7 计算任务大小(kb) 480 服务器间距(km) 1 能耗系数(J/bit) $ {5.0\times 10}^{-27} $ 服务器带宽(MHz) 75 终止温度 $ {10}^{-9} $ 温度下降率 0.97 领域解空间大小 5 权重$ {\mathit{\lambda }}_{1}{,\mathit{\lambda }}_{2} $ 1/2,1/2 -
[1] MELAOUENE N and ROMADI R. An enhanced routing algorithm using ant colony optimization and VANET infrastructure[J]. MATEC Web of Conferences, 2019, 259: 02009. doi: 10.1051/matecconf/201925902009 [2] BRENNAND C A R L, DE SOUZA A M, MAIA G, et al. An intelligent transportation system for detection and control of congested roads in urban centers[C]. 2015 IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communication (ISCC), Larnaca, Cyprus, 2015: 663–668. [3] CHEN Jieqiong, MAO Guoqiang, LI Changle, et al. Capacity of cooperative vehicular networks with infrastructure support: Multiuser case[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(2): 1546–1560. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2753772 [4] XU Xiaolong, LI Yuancheng, HUANG Tao, et al. An energy-aware computation offloading method for smart edge computing in wireless metropolitan area networks[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2019, 133: 75–85. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2019.02.008 [5] ZHANG Ke, MAO Yuming, LENG Supeng, et al. Mobile-edge computing for vehicular networks: A promising network paradigm with predictive off-loading[J]. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 2017, 12(2): 36–44. doi: 10.1109/MVT.2017.2668838 [6] ZHANG Degan, LIU Si, ZHANG Ting, et al. Novel unequal clustering routing protocol considering energy balancing based on network partition & distance for mobile education[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2017, 88: 1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2017.03.025 [7] ZHANG Degan, ZHANG Ting, and LIU Xiaohuan. Novel self-adaptive routing service algorithm for application in VANET[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2019, 49(5): 1866–1879. doi: 10.1007/s10489-018-1368-y [8] ZHANG Degan, WANG Xiang, SONG Xiaodong, et al. A novel approach to mapped correlation of ID for RFID anti-collision[J]. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, 2014, 7(4): 741–748. doi: 10.1109/TSC.2014.2370642 [9] YANG Junnan, DING Ming, MAO Guoqiang, et al. Optimal base station antenna downtilt in downlink cellular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(3): 1779–1791. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2897296 [10] ZHANG Degan, ZHANG Ting, DONG Yue, et al. Novel optimized link state routing protocol based on quantum genetic strategy for mobile learning[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2018, 122: 37–49. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2018.07.018 [11] ZHANG Degan, GE Hui, ZHANG Ting, et al. New multi-hop clustering algorithm for vehicular ad hoc networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2019, 20(4): 1517–1530. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2018.2853165 [12] ZHANG Ting, ZHANG Degan, YAN Haoran, et al. A new method of data missing estimation with FNN-based tensor heterogeneous ensemble learning for internet of vehicle[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 420: 98–110. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.09.042 [13] CHEN Jieqiong, MAO Guoqiang, LI Changle, et al. A topological approach to secure message dissemination in vehicular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2020, 21(1): 135–148. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2018.2889746 [14] DUAN Peibo, MAO Guoqiang, LIANG Weifa, et al. A unified spatio-temporal model for short-term traffic flow prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2019, 20(9): 3212–3223. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2018.2873137 [15] SARDELLITTI S, SCUTARI G, and BARBAROSSA S. Distributed joint optimization of radio and computational resources for mobile cloud computing[C]. 2014 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Cloud Networking (CloudNet), Luxembourg, 2014: 211–216. [16] OUEIS J, STRINATI E C, and BARBAROSSA S. The fog balancing: Load distribution for small cell cloud computing[C]. 2015 IEEE 81st Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), Glasgow, UK, 2015: 1–6. [17] WEI Feng, CHEN Sixuan, and ZOU Weixia. A greedy algorithm for task offloading in mobile edge computing system[J]. China Communications, 2018, 15(11): 149–157. doi: 10.1109/CC.2018.8543056 [18] TRAN T X and POMPILI D. Joint task offloading and resource allocation for multi-server mobile-edge computing networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(1): 856–868. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2881191 [19] KAO Y H, KRISHNAMACHARI B, RA M R, et al. Hermes: Latency optimal task assignment for resource-constrained mobile computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2017, 16(11): 3056–3069. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2017.2679712 [20] ZHANG Jiao, HU Xiping, NING Zhaolong, et al. Energy-latency tradeoff for energy-aware offloading in mobile edge computing networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2018, 5(4): 2633–2645. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2017.2786343 [21] WU Xinzhou, SUBRAMANIAN S, GUHA R, et al. Vehicular communications using DSRC: Challenges, enhancements, and evolution[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2013, 31(9): 399–408. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2013.SUP.0513036 [22] ZHAO Junhui, CHEN Yan, and GONG Yi. Study of connectivity probability of vehicle-to-vehicle and vehicle-to-infrastructure communication systems[C]. 2016 IEEE 83rd Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), Nanjing, China, 2016: 1–4. [23] ZHANG Hongli, ZHANG Qiang, DU Xiaojiang, et al. Toward vehicle-assisted cloud computing for smartphones[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2015, 64(12): 5610–5618. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2015.2480004 [24] RAZA S, WANG Shangguang, AHMED M, et al. Corrigendum to “a survey on vehicular edge computing: Architecture, applications, technical issues, and future directions”[J]. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2019, 2019: 6104671. doi: 10.1155/2019/6104671 [25] SHAHAPUR S and DASGUPTA S. Future scope for 5G with respect to the Indian telecommunication sector and proposed solution of setting up 5G in rural areas using unmanned aerial vehicles[C]. 2019 6th International Conference on Computing for Sustainable Global Development, New Delhi, India, 2019: 199–204. [26] KAVITHA A and VELUSAMY R L. Simulated annealing and genetic algorithm-based hybrid approach for energy-aware clustered routing in large-range multi-sink wireless sensor networks[J]. International Journal of Ad Hoc and Ubiquitous Computing, 2020, 35(2): 96–116. doi: 10.1504/IJAHUC.2020.109800 [27] WANG Hui, LI Kangshun, and PEDRYCZ W. A routing algorithm based on simulated annealing algorithm for maximising wireless sensor networks lifetime with a sink node[J]. International Journal of Bio-Inspired Computation, 2020, 15(4): 264–275. doi: 10.1504/IJBIC.2020.108596 -





 下载:
下载:
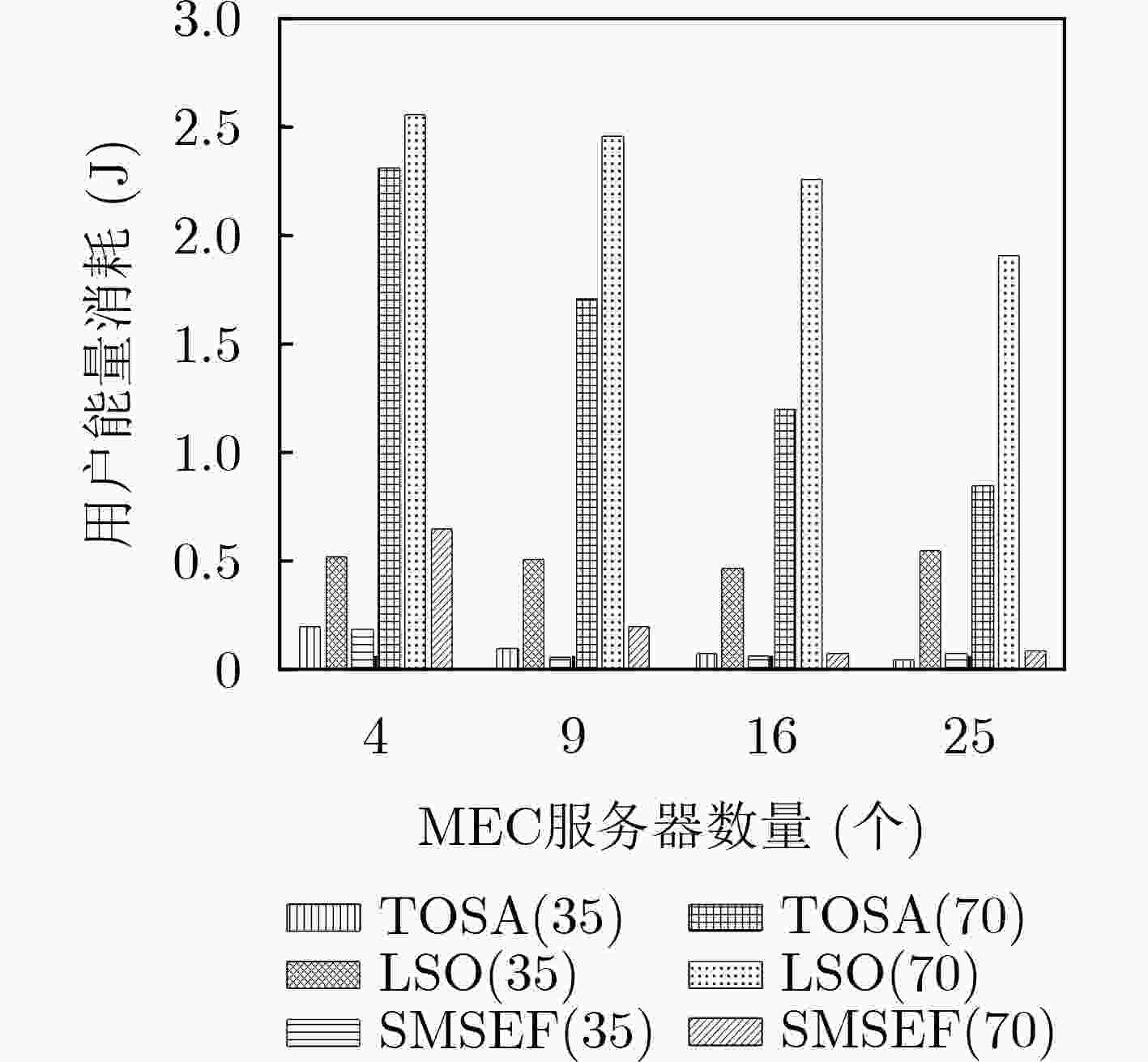
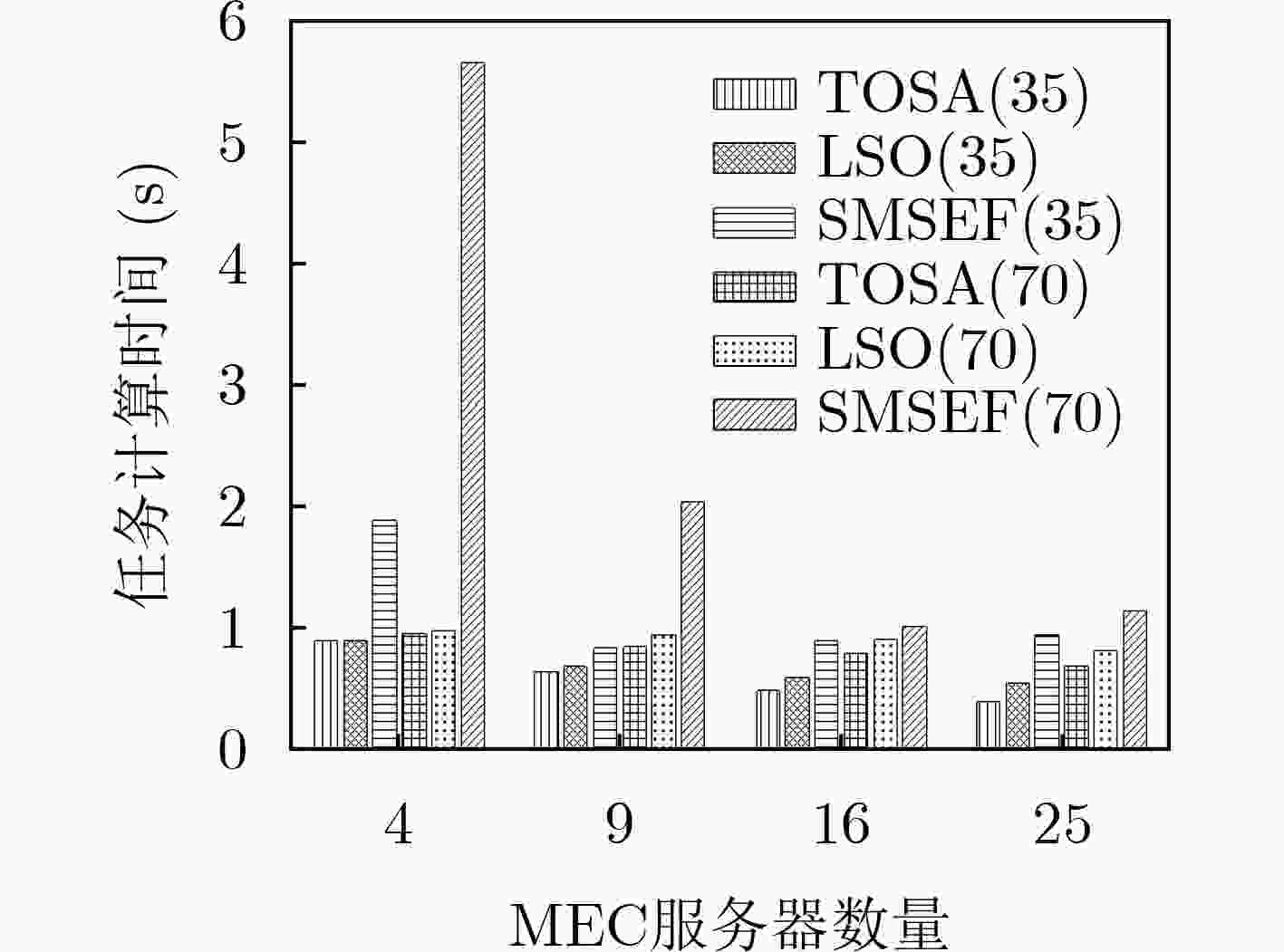
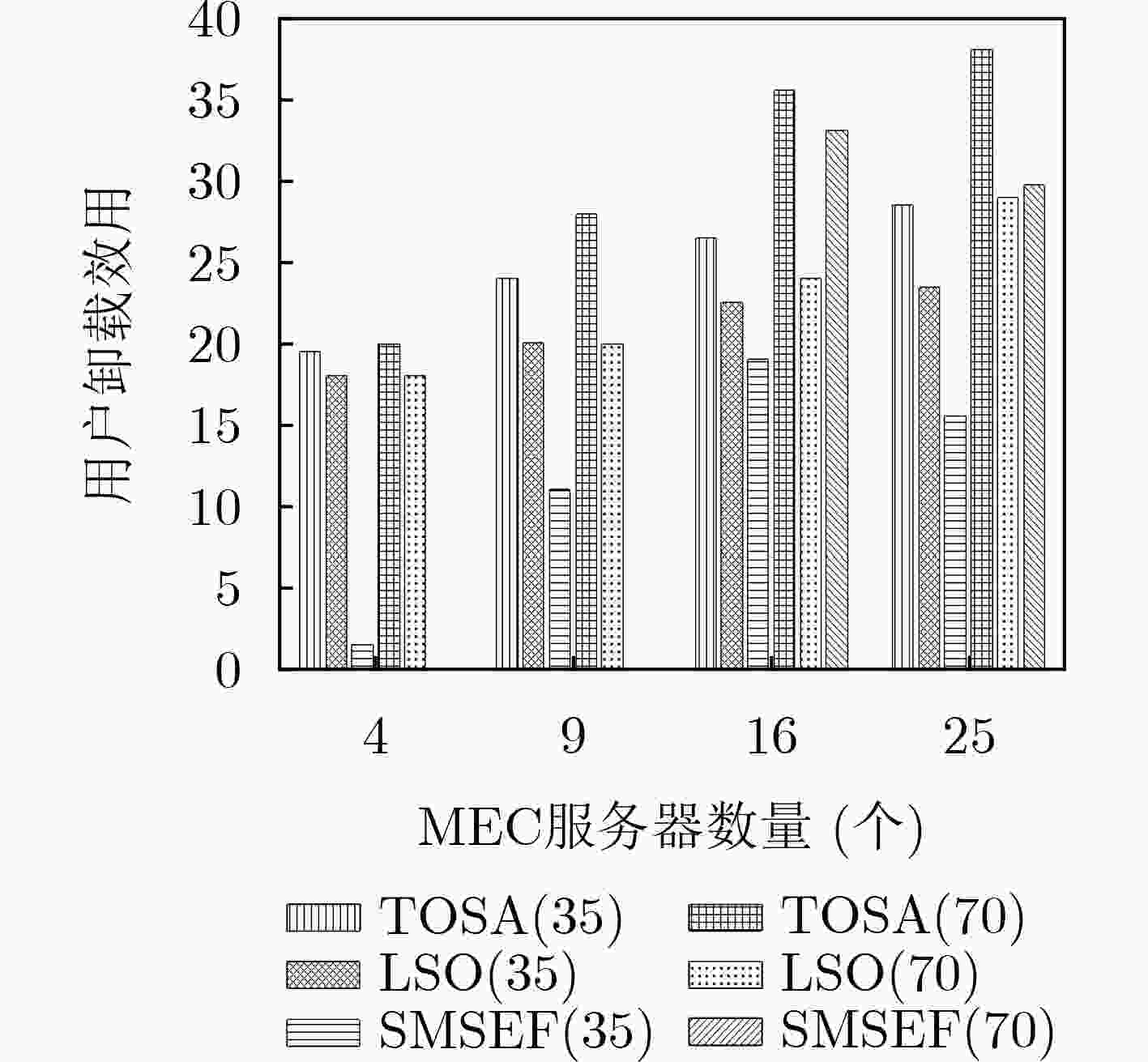
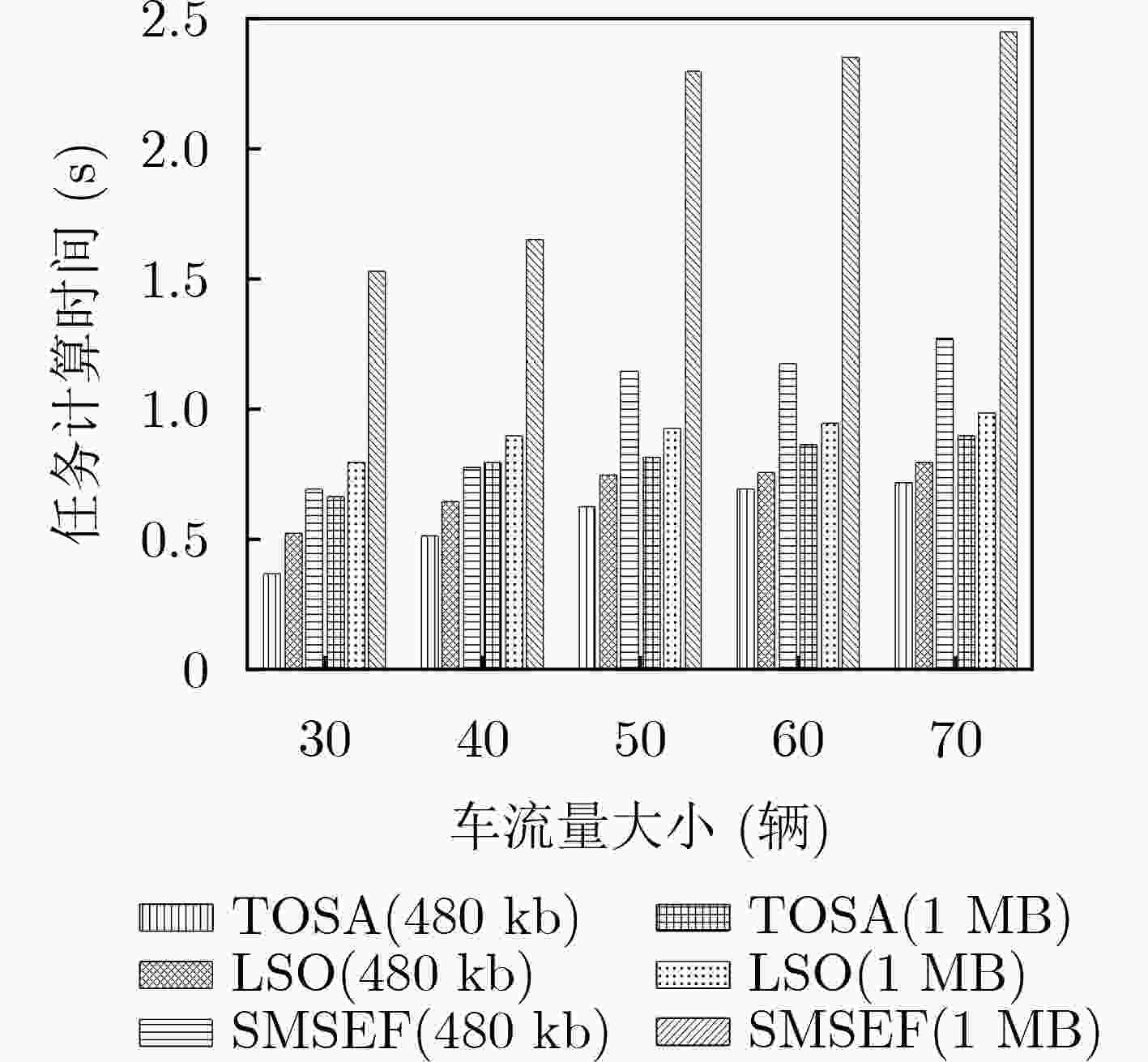
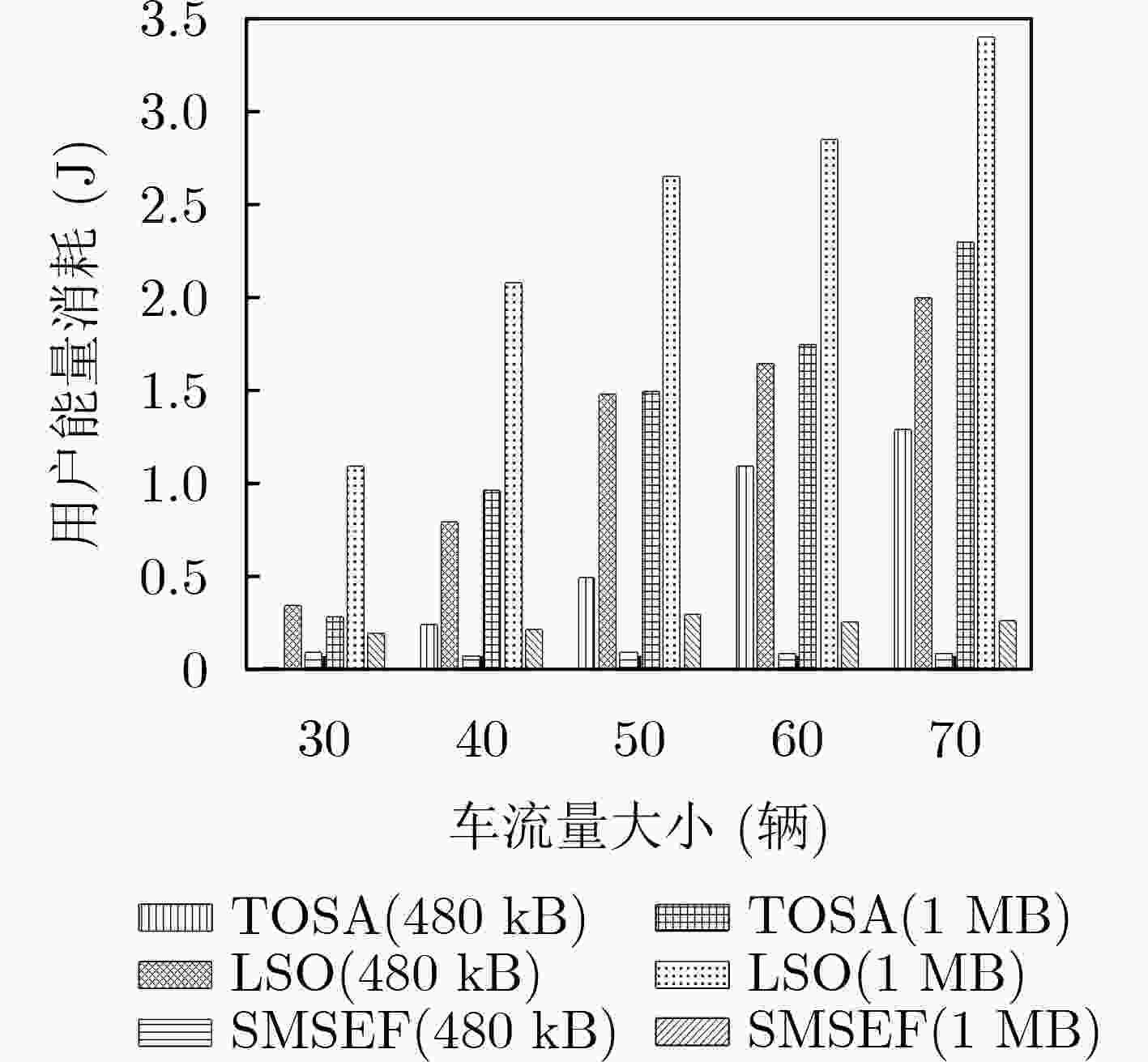
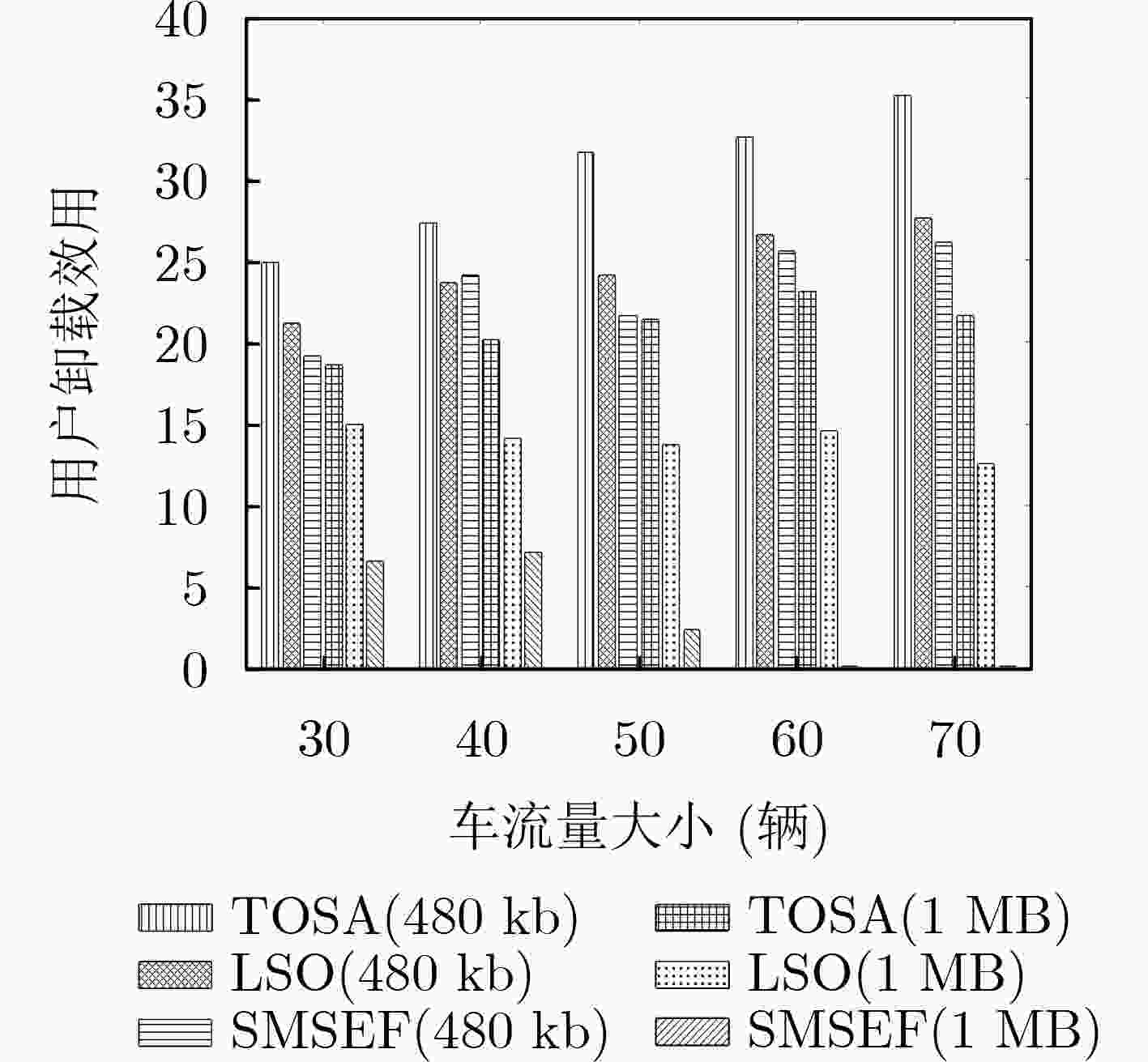
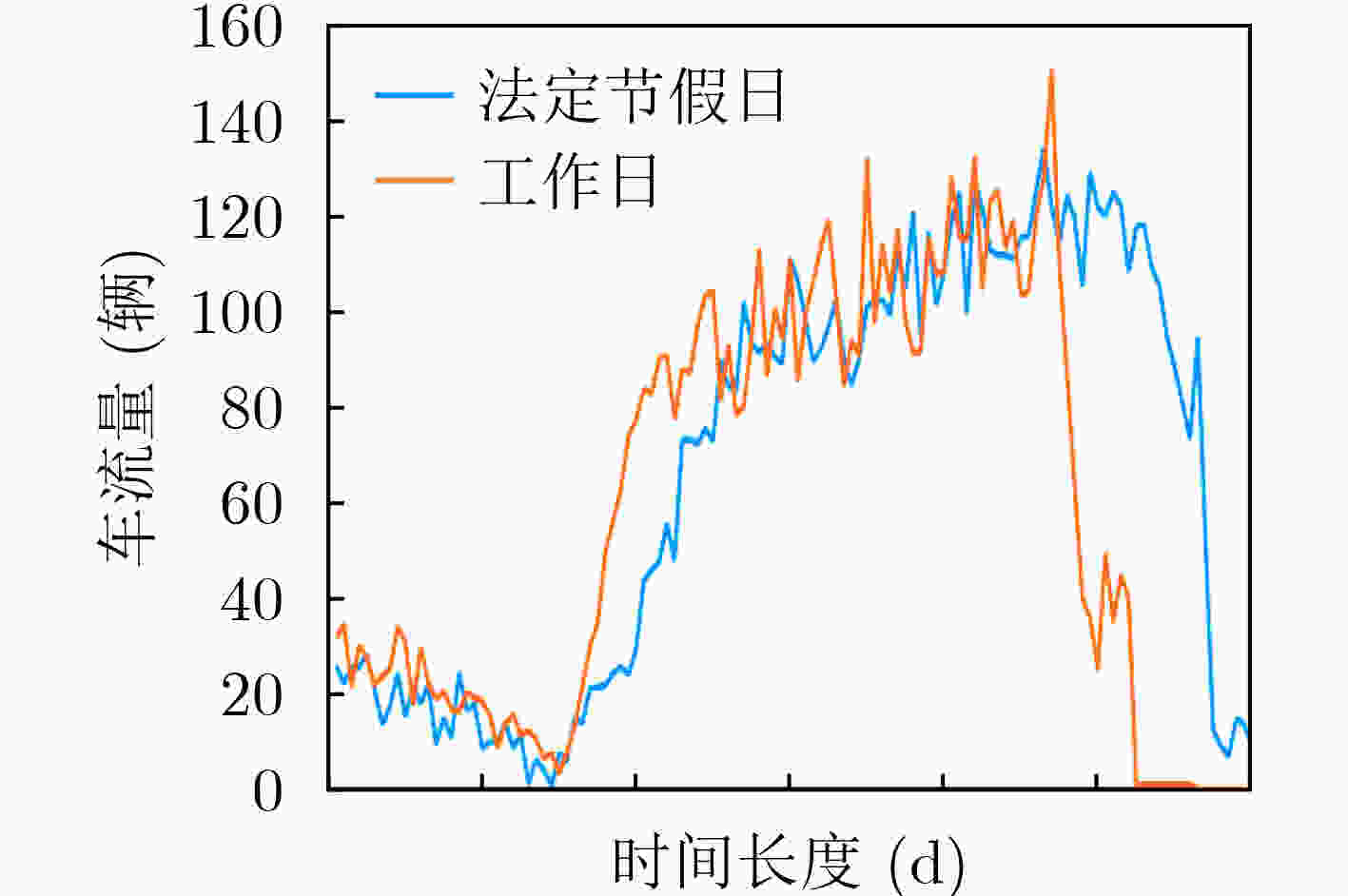
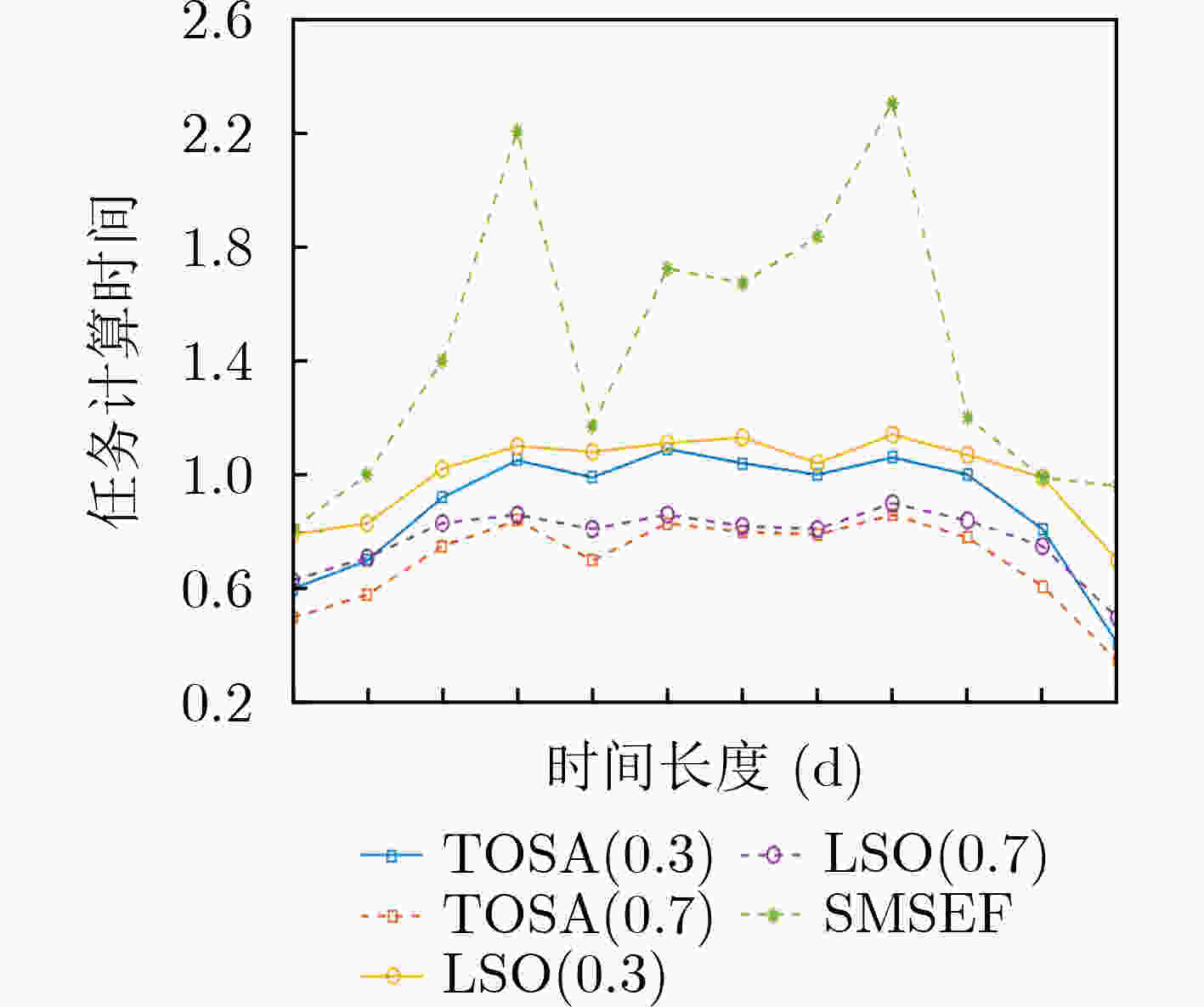


 下载:
下载:
