A Variable Step Size Least Mean p-Power Adaptive Filtering Algorithm
-
摘要: 在
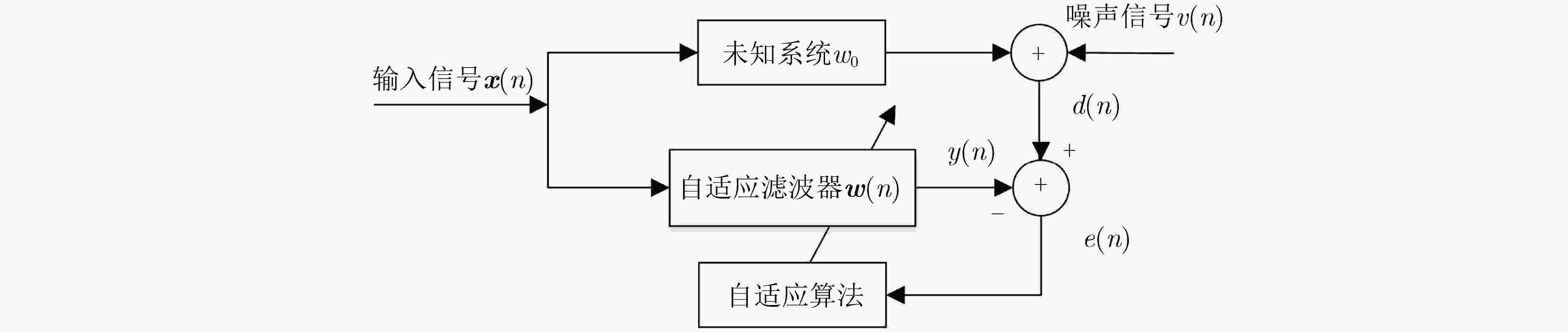
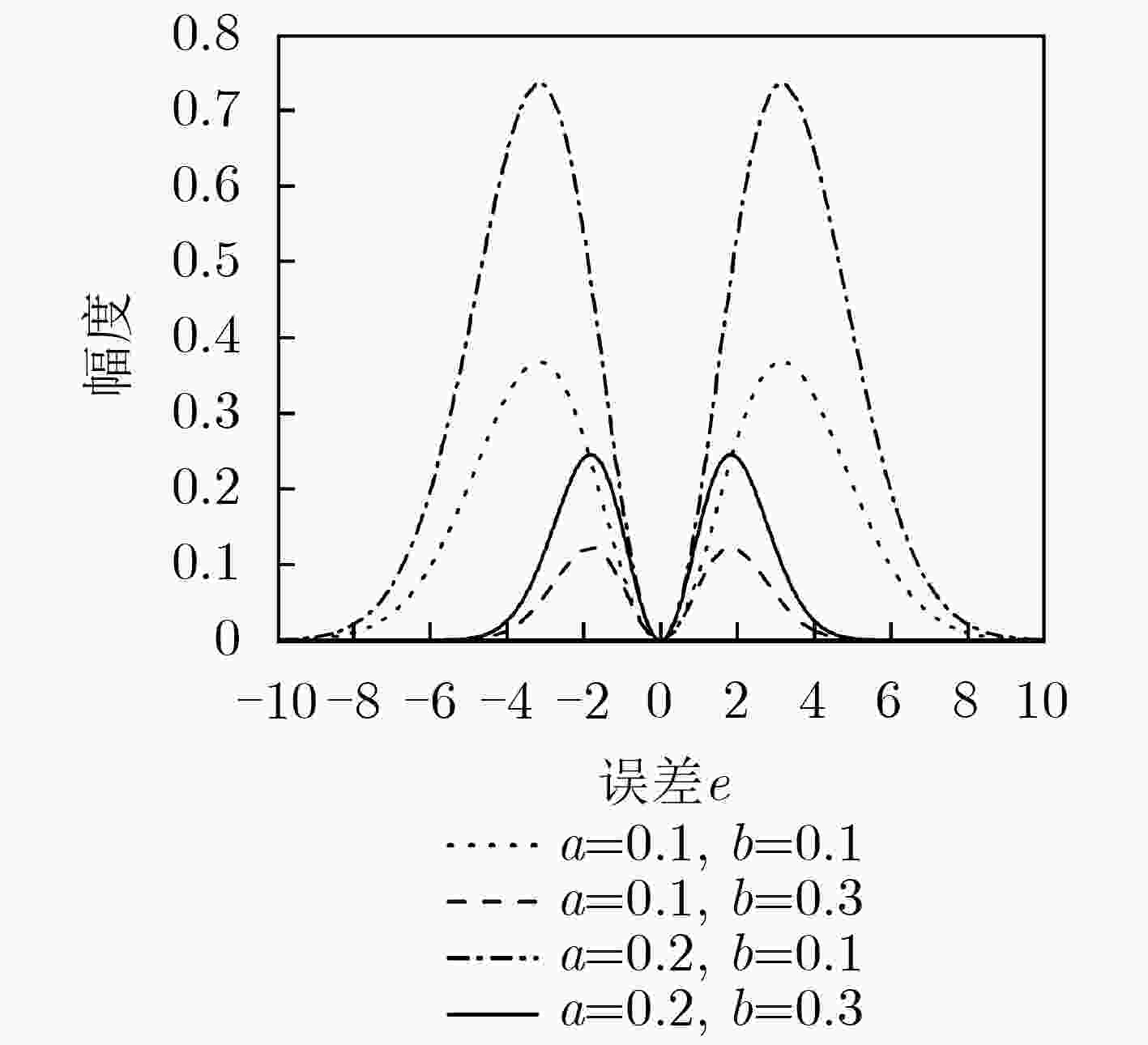
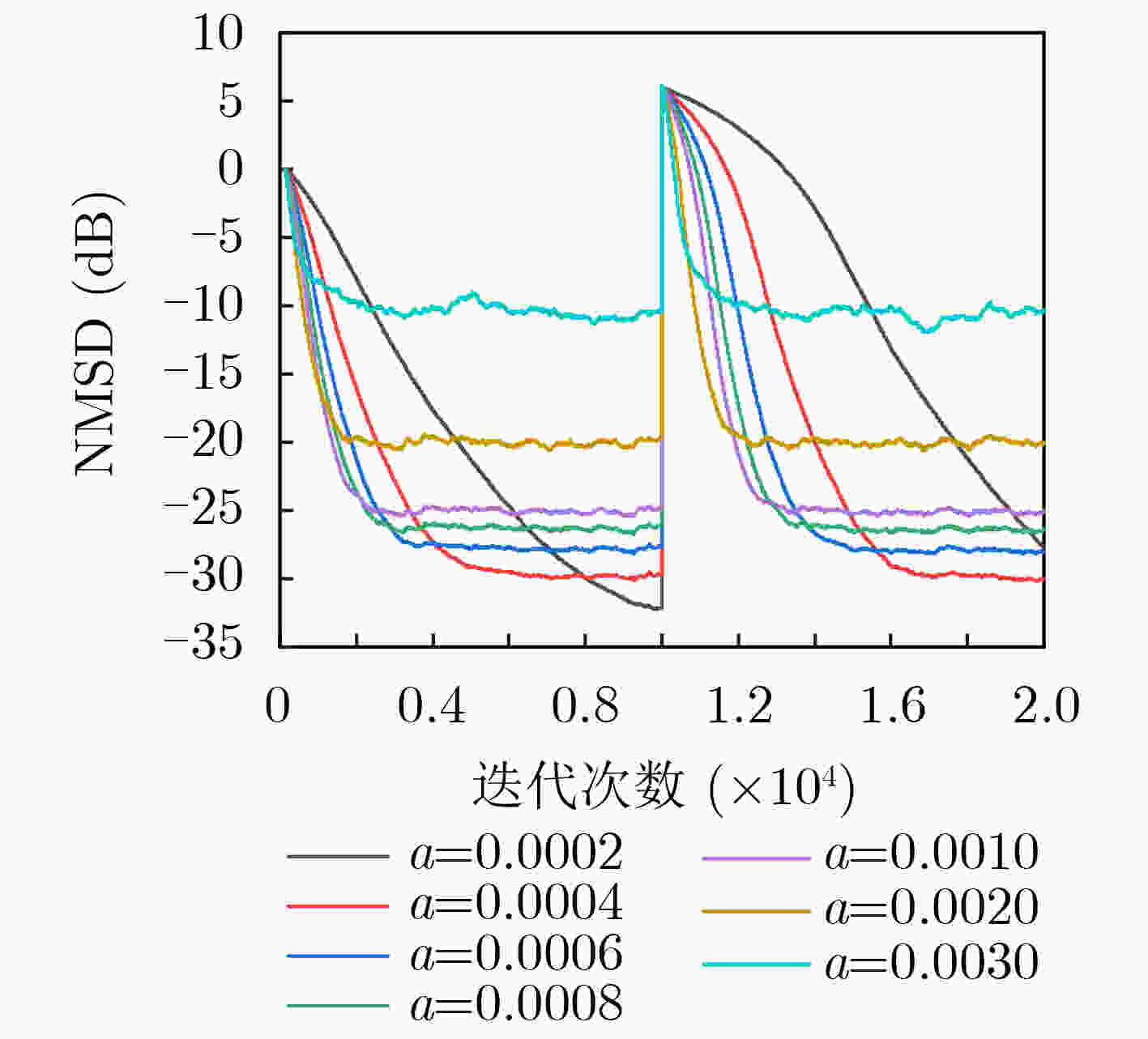
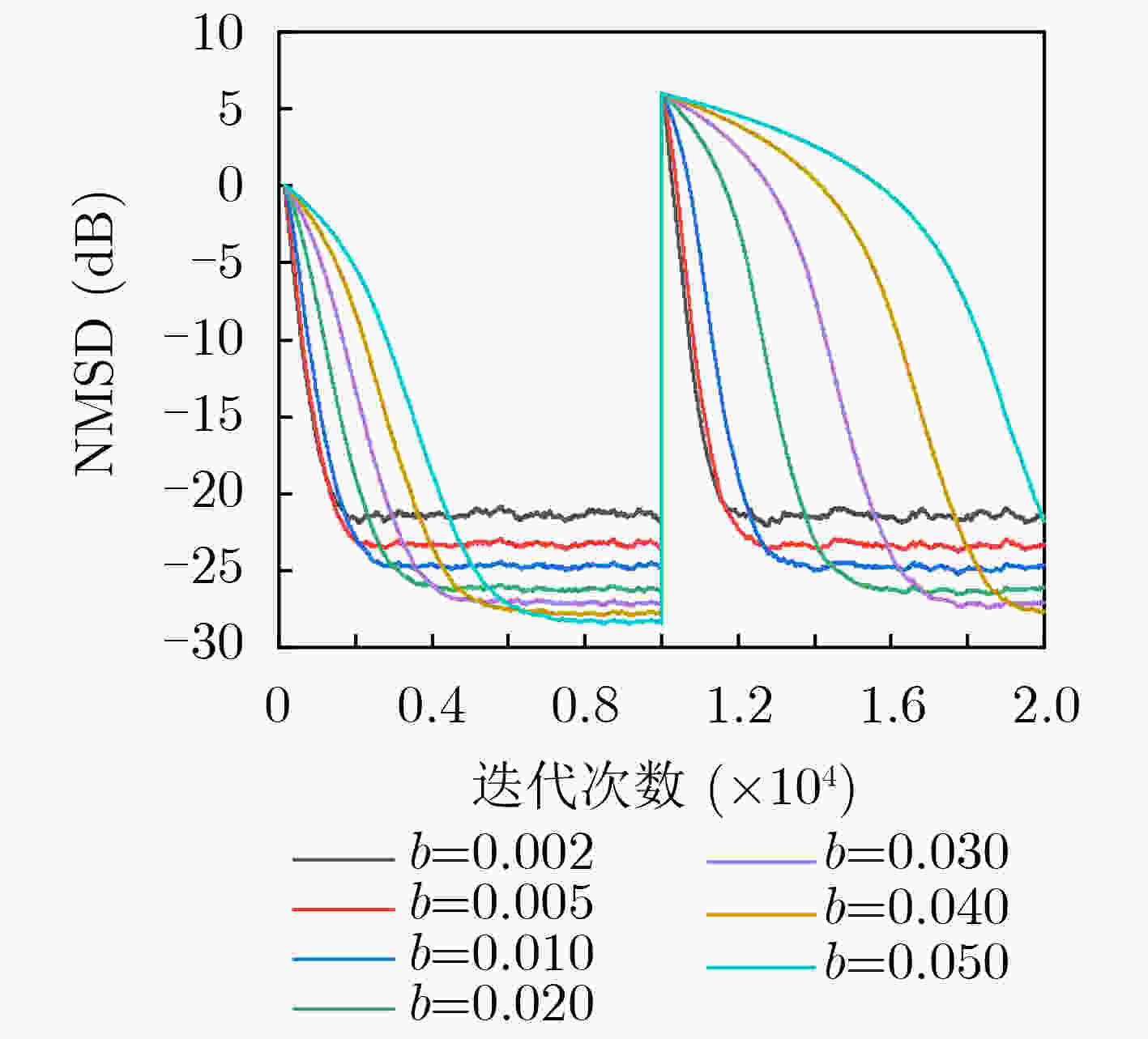
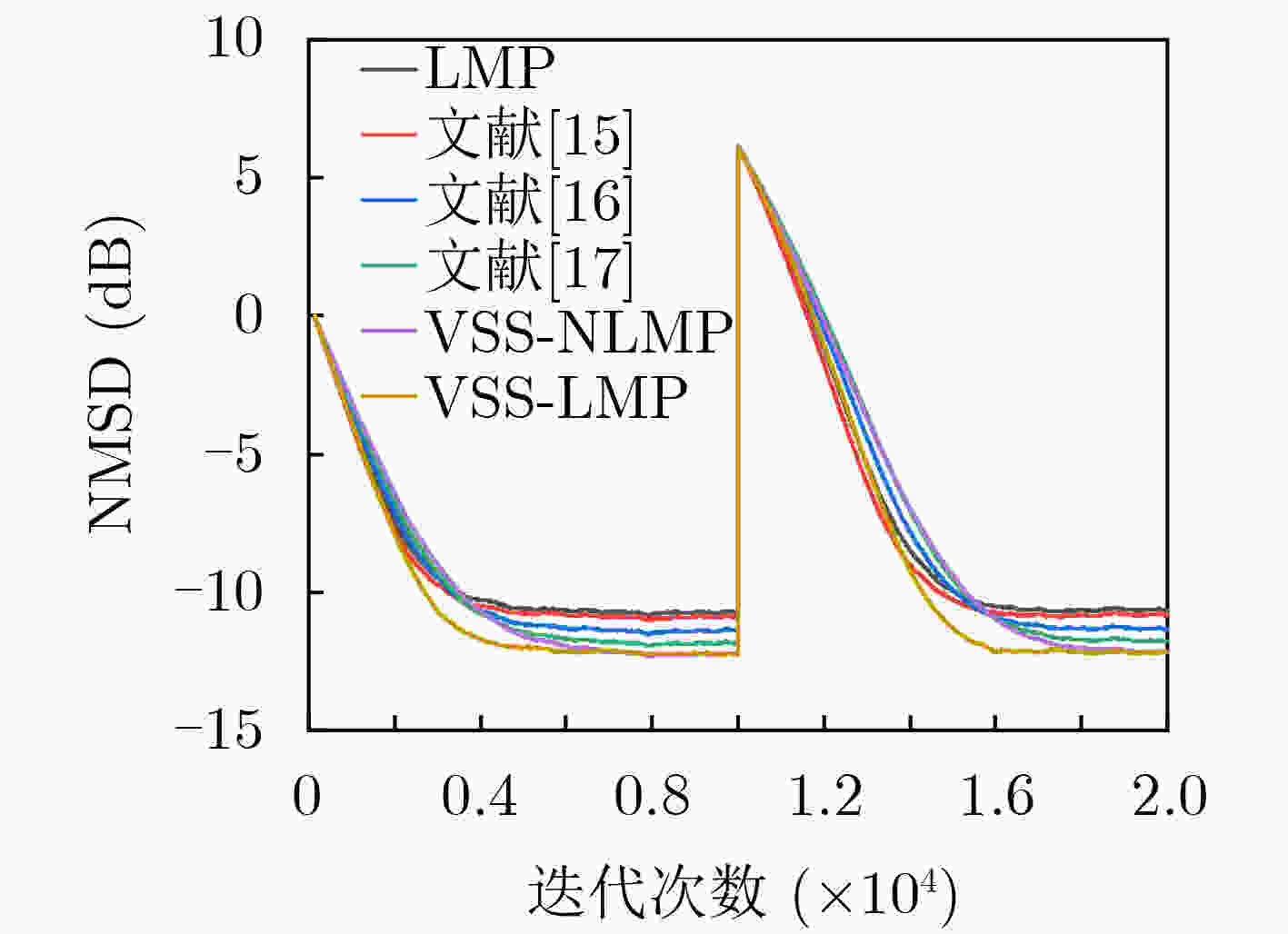
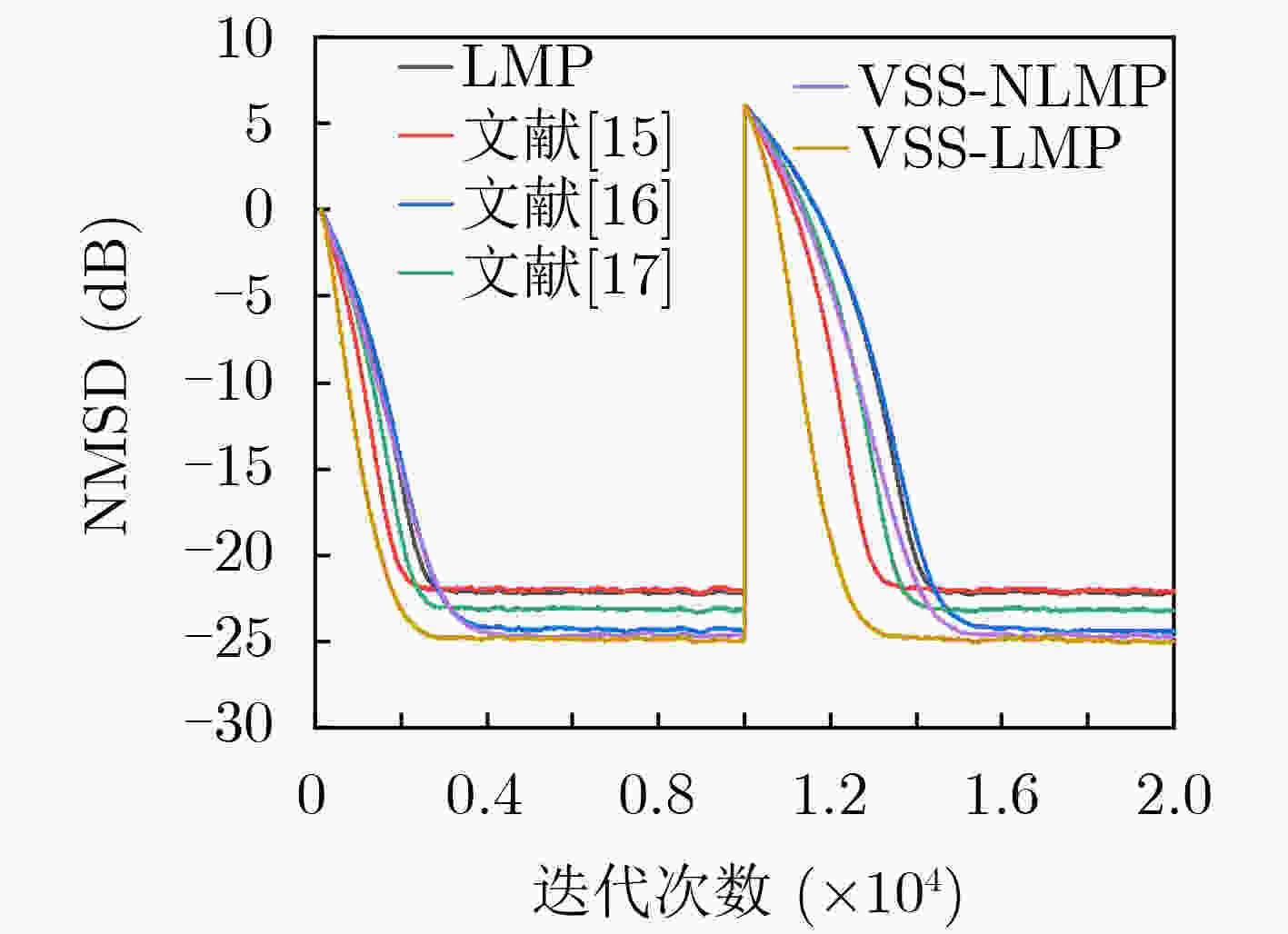
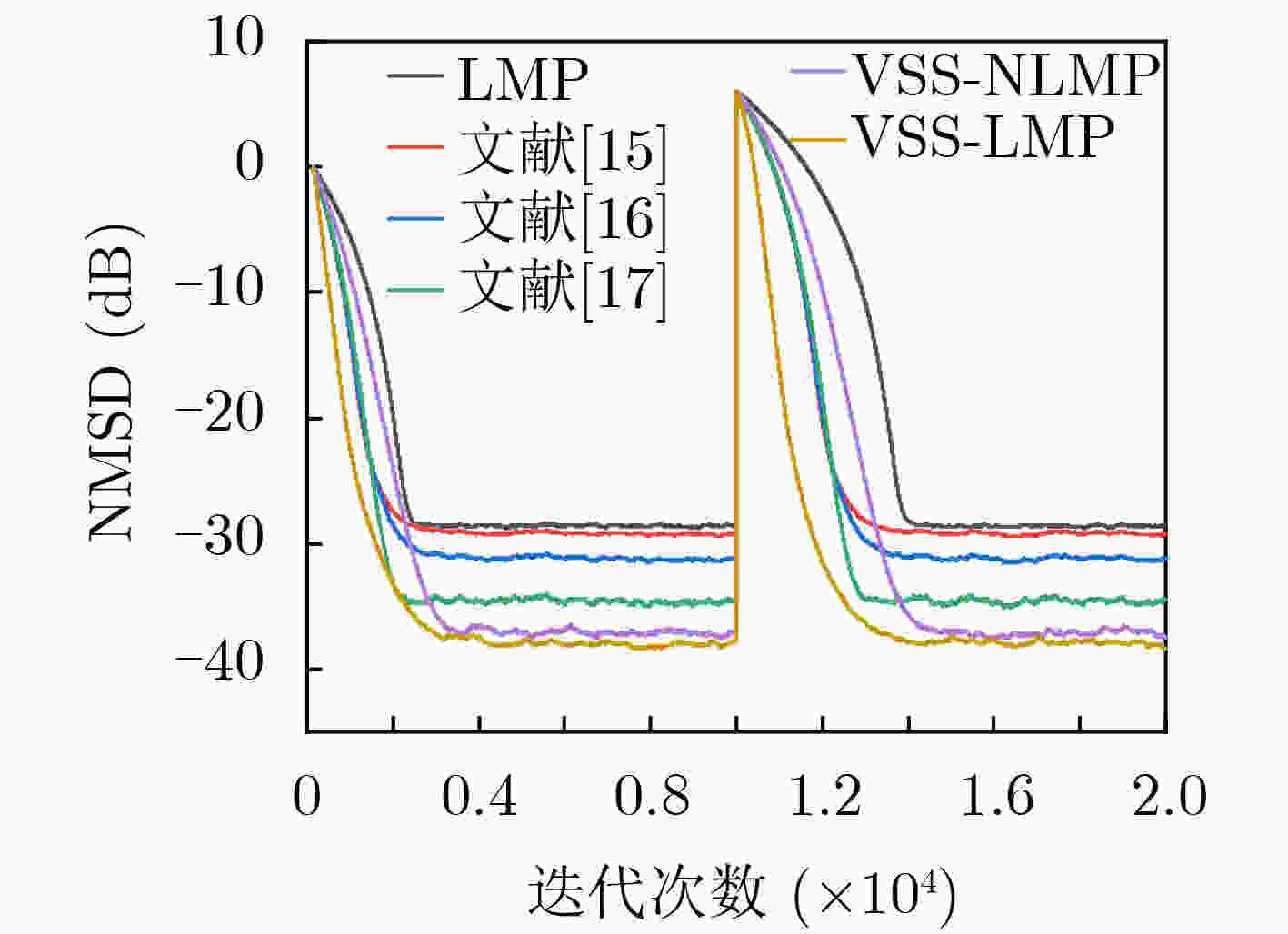
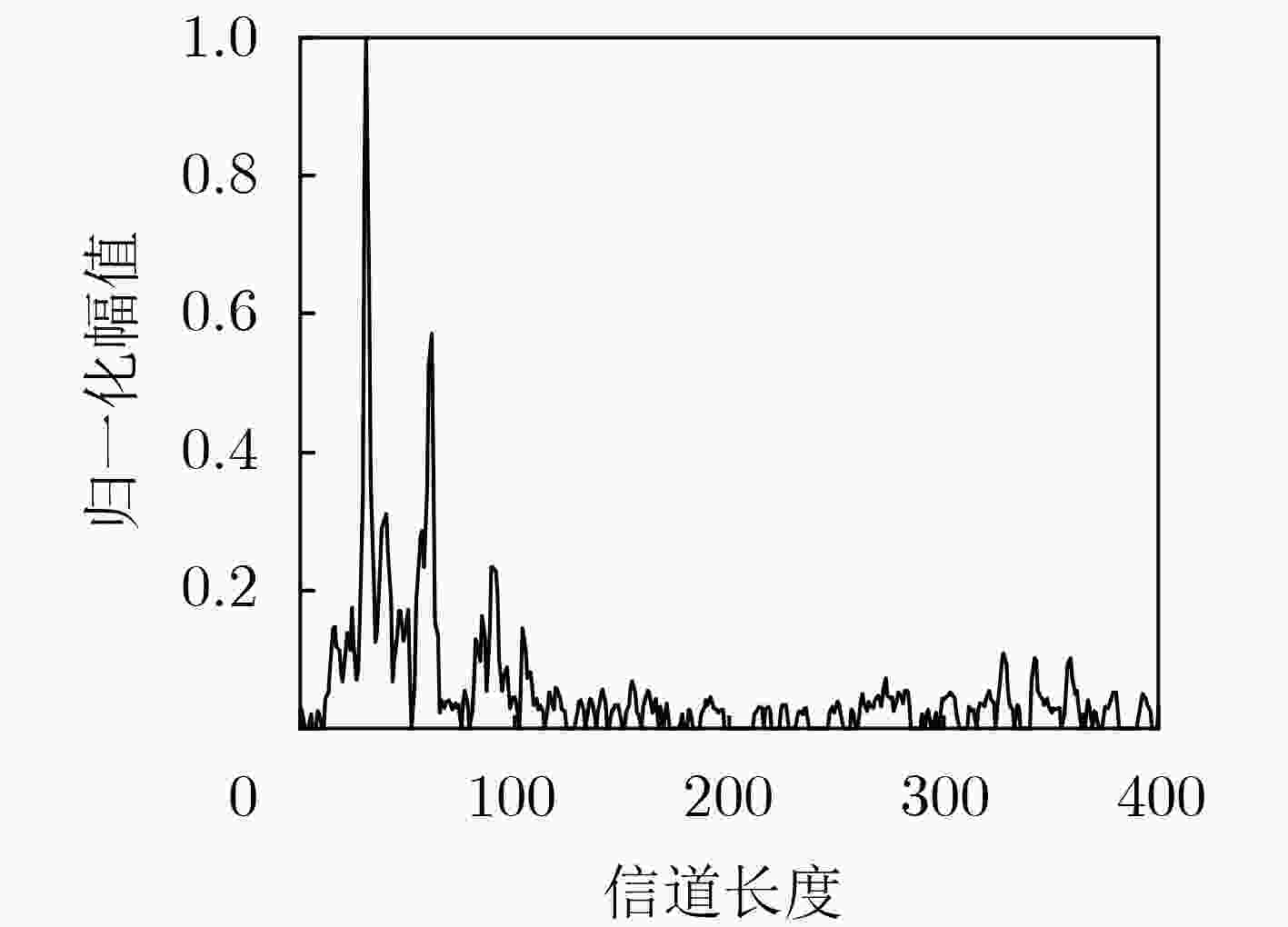
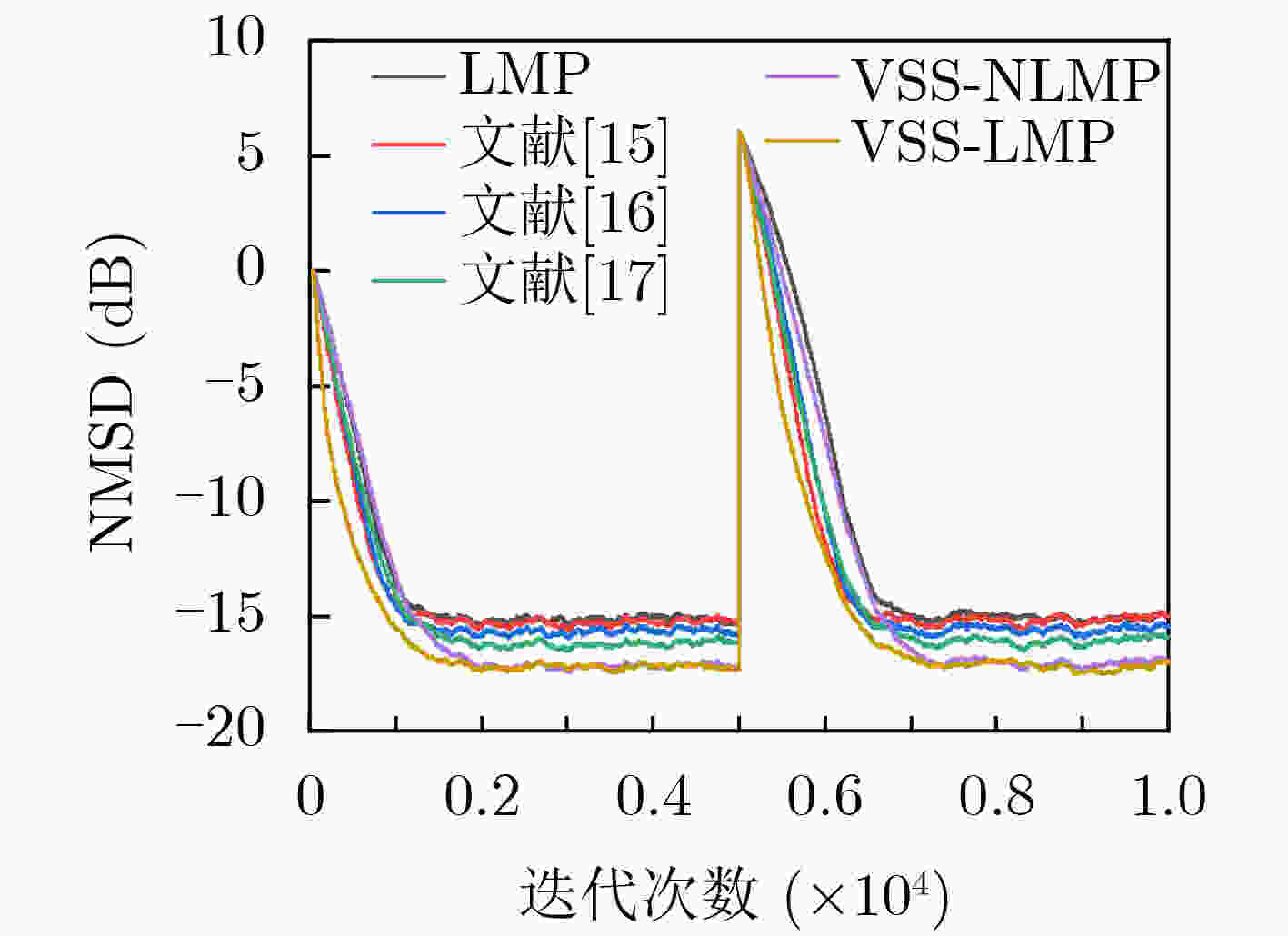
$ \alpha $ 稳定分布脉冲噪声背景下,为解决固定步长最小平均p范数(LMP)不能同时满足快收敛速度和低稳态误差的问题,该文提出一种对脉冲噪声具有鲁棒性的变步长最小平均p范数(VSS-LMP)自适应滤波算法。该算法利用改进的变形高斯函数来调节步长,采用移动平均法构造变步长函数,克服了定步长算法稳态误差高及抗噪性能差的问题。VSS-LMP算法在系统受到脉冲噪声干扰时,能维持步长稳定;当系统逐渐稳定时,能产生小步长以降低稳态误差。系统辨识仿真结果表明,在$ \alpha $ 稳定分布脉冲噪声下,VSS-LMP算法与固定步长和已有变步长算法相比,具有更快的收敛速度和更强的系统跟踪能力。Abstract: Under$ \alpha $ stable distribution impulse noise environment, in order to solve the problem that the fixed step-size Least Mean p-Power(LMP) can not satisfy the fast convergence speed and low steady-state error at the same time, a Variable Step-Size LMP (VSS-LMP) adaptive filtering algorithm with robustness to impulse noise is proposed. The algorithm uses an improved modified Gaussian function to adjust the step size, and uses a moving average method to construct a variable step size function, which overcomes the problems of high steady-state error and poor anti-noise performance of the fixed-step algorithm. When the system is disturbed by impulse noise, the VSS-LMP algorithm can maintain a stable step size; When the system is gradually stable, it can generate a small step size to reduce the steady-state error. The simulation results of system identification show that the VSS-LMP algorithm has faster convergence speed and stronger system tracking ability compared with the fixed step size and variable step size algorithm under the condition of$ \alpha $ stable distributed impulse noise. -
表 1 VSS-LMP算法框图
%初始化
μ(0)=0,初始化参数w0,a,b,β,p
For n=0,1,2,···
%计算误差
$ e(n){\rm{ = }}d(n) - {{\boldsymbol{w}}^{\rm{T}}}{\boldsymbol{x}}(n) $
%更新步长
$ \mu (e(n)) = \beta \mu (e(n - 1)) + (1 - \beta )a{\left| {e(n)} \right|^2}\exp ( - b{\left| {e(n)} \right|^2}) $
%更新权值
$ {\boldsymbol{w}}(n + 1){\rm{ = }}{\boldsymbol{w}}(n) + \mu (e(n)){\left| {e(n)} \right|^{p - 2}}e(n){\boldsymbol{x}}(n) $
End表 2 各算法比较
算法 步长 参数 信噪比5 dB 信噪比15 dB 信噪比25 dB 脉冲参数N4 定步长LMP算法 $\mu $ $\mu $ 0.0065 0.0050 0.0050 0.0004 文献[15] $ \mu {\rm{ = }}\beta \left\{ {\dfrac{1}{{1{\rm{ + }}\exp ( - \alpha {{\left| {e(n)} \right|}^m})}} - 0.5} \right\} $ α, β, m 0.10.015, 3 0.2, 0.015, 3 0.2, 0.02, 3 0.3, 0.0014, 3 文献[16] $ \mu = \beta \left\{ {1 - \dfrac{2}{{1 + \exp (\alpha {{\left| {e(n)} \right|}^\gamma })}}} \right\} $ α, β, γ 0.2, 0.006, 2 0.3, 0.005, 2 0.3, 0.01, 2 0.3, 0.0007, 2 文献[17] $ \mu = c{\rm{\{ }}1 - \exp ( - a{\left| {e(n)} \right|^b}){\rm{\} }} $ a, b, c 0.4, 2, 0.006 0.4, 2, 0.006 0.2, 2, 0.01 0.4, 2, 0.0006 VSS-NLMP $ \begin{gathered}\bar g(n) = \lambda \bar g(n - 1) + (1 - \lambda ){\rm{\{ }}{\left| {e(n)} \right|^{p - 2}}e(n){\boldsymbol{x}}(n){\rm{\} }} \hfill \\\mu (n) = \rho \mu (n - 1) + {\gamma _s}{\rm{\{ }}{\left\| {\bar g(n - 1)} \right\|^2}{\left| {e(n - 1)} \right|^p}{\rm{\} }} \hfill \\ \end{gathered} $ $ \lambda $, $ {\gamma _s} $, $ \rho $ 0.99, 0.97, 0.0004 0.99, 0.97, 0.004 0.99, 0.97,
0.0060.995, 0.97,
0.0008本文算法 $ \mu = \beta \mu (e(n - 1)) + (1 - \beta )a{\left| {e(n)} \right|^2}\exp ( - b{\left| {e(n)} \right|^2}) $ a, b, β 0.001, 0.02, 0.98 0.0008, 0.01, 0.98 0.0026, 0.015, 0.98 0.00008, 0.0009, 0.99 -
[1] KWONG R H and JOHNSTON E W. A variable step size LMS algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1992, 40(7): 1633–1642. doi: 10.1109/78.143435 [2] AU W W L and BANKS K. The acoustics of the snapping shrimp Synalpheus parneomeris in Kaneohe Bay[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1998, 103(1): 41–47. doi: 10.1121/1.423234 [3] ZHAO Haiquan, LIU Bing, and SONG Pucha. Variable step-size affine projection maximum correntropy criterion adaptive filter with correntropy induced metric for sparse system identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2020, 67(11): 2782–2786. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2020.2973764 [4] SHAO Min and NIKIAS C L. Signal processing with fractional lower order moments: Stable processes and their applications[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1993, 81(7): 986–1010. doi: 10.1109/5.231338 [5] BERSHAD N J and BERMUDEZ J C M. A switched variable step size NLMS adaptive filter[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2020, 101: 102730. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2020.102730 [6] 付柏成, 赵知劲, 尚俊娜. 一种新的变步长NLMP快速算法[J]. 计算机仿真, 2008, 25(8): 90–92, 112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2008.08.024FU Baicheng, ZHAO Zhijin, and SHANG Junna. A new variable step-size NLMP fast algorithm[J]. Computer Simulation, 2008, 25(8): 90–92, 112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2008.08.024 [7] 郝燕玲, 单志明, 吕东泽, 等. 脉冲噪声下基于梯度加权平均的变步长NLMP算法[J]. 宇航学报, 2012, 33(5): 655–660. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2012.05.019HAO Yanling, SHAN Zhiming, LV Dongze, et al. Variable step-size NLMP algorithm with a gradient-based weighted average in impulsive environments[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2012, 33(5): 655–660. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2012.05.019 [8] 陈思佳, 赵知劲. 用于稀疏系统辨识的变步长加权零吸引最小平均p范数算法[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2020, 37(5): 1103–1108. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2019.90014CHEN Sijia and ZHAO Zhijin. Variable step-size reweighted zero attracting least mean p-norm algorithm for sparse system identification[J]. Control Theory &Applications, 2020, 37(5): 1103–1108. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2019.90014 [9] WANG Weihua, ZHAO Jihong, QU Hua, et al. A correntropy inspired variable step-size sign algorithm against impulsive noises[J]. Signal Processing, 2017, 141: 168–175. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2017.05.028 [10] WANG Biao, GAO Shijie, GE Huilin, et al. A variable step size for maximum correntropy criterion algorithm with improved variable kernel width[J]. IEEJ Transactions on Electrical and Electronic Engineering, 2020, 15(10): 1465–1474. doi: 10.1002/tee.23217 [11] 赵集. Alpha稳定分布环境下自适应滤波算法研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2020. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2020.000710.ZHAO Ji. Research on adaptive filtering algorithms under alpha stable distributed environments[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2020. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2020.000710. [12] 朱晓梅, 朱卫平, 李森. 一种基于分数低阶矩的α稳定分布噪声中频谱感知方案[J]. 南京邮电大学学报:自然科学版, 2014, 34(3): 23–27, 35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5439.2014.03.004ZHU Xiaomei, ZHU Weiping, and LI Sen. An FLOM-based spectrum sensing scheme in α-stable distributed noise[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications:Natural Science, 2014, 34(3): 23–27, 35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5439.2014.03.004 [13] SHI Long, ZHAO Haiquan, and ZAKHAROV Y. An improved variable kernel width for maximum correntropy criterion algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2020, 67(7): 1339–1343. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2018.2880564 [14] 杨威, 刘宏清, 黎勇, 等. 冲击噪声下的LMS和RLS联合滤波算法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报:自然科学版, 2017, 44(2): 165–170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2017.02.028YANG Wei, LIU Hongqing, LI Yong, et al. Joint estimation algorithms based on LMS and RLS in the presence of impulsive noise[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2017, 44(2): 165–170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2017.02.028 [15] 罗小东, 贾振红, 王强. 一种新的变步长LMS自适应滤波算法[J]. 电子学报, 2006, 34(6): 1123–1126. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2006.06.030LUO Xiaodong, JIA Zhenghong, and WANG Qiang. A new variable step size LMS adaptive filtering algorithm[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2006, 34(6): 1123–1126. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2006.06.030 [16] 杜秀群, 冯西安, 杜伟. 一种应用于自适应降噪的变步长LMS算法[J]. 机械科学与技术, 2010, 29(12): 1732–1734, 1738. doi: 10.13433/j.cnki.1003-8728.2010.12.028DU Xiuqun, FENF Xi’an, and DU Wei. A variable step size LMS algorithm applied to adaptive noise cancellation[J]. Mechanical Science and Technology for Aerospace Engineering, 2010, 29(12): 1732–1734, 1738. doi: 10.13433/j.cnki.1003-8728.2010.12.028 [17] 王平波, 马凯, 武彩. 基于正态分布曲线的分段式变步长LMS算法[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2020, 42(5): 16–22. doi: 10.11887/j.cn.202005003WANG Pingbo, MA Kai, and WU Cai. Segmented variable-step-size LMS algorithm based on normal distribution curve[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2020, 42(5): 16–22. doi: 10.11887/j.cn.202005003 [18] CHITRE M A, POTTER J R, and ONG S H. Optimal and near-optimal signal detection in snapping shrimp dominated ambient noise[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2006, 31(2): 497–503. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2006.875272 [19] 王彪, 方涛, 戴跃伟. 时间反转滤波器组多载波水声通信方法[J]. 声学学报, 2020, 45(1): 38–44. doi: 10.15949/j.cnki.0371-0025.2020.01.004WANG Biao, FANG Tao, and DAI Yuewei. Method of Time reversal filter bank multicarrier underwater acoustic communication[J]. Acta Acustica, 2020, 45(1): 38–44. doi: 10.15949/j.cnki.0371-0025.2020.01.004 -







 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
