A Lattice Structure Optimization Method and Sensitivity Analysis of Finite Impulse Response Filter
-
摘要: 有限脉冲响应(FIR)滤波器是无线通信研究中多载波调制系统的主要组成单元。针对有限字长效应导致FIR滤波器性能下降问题,该文提出一种FIR滤波器格型结构改善因量化导致的滤波器系数误差,即降低系数灵敏度,利用状态空间结构表示相应改进格型结构系数,并推导分析其系数灵敏度表达式。仿真实例验证理论推导结果,即改进格型结构系数灵敏度与采样周期相关。与传统格型结构相比,在量化字长和采样周期约束下,改进格型结构频响特性曲线更接近理想频响特性曲线,系数灵敏度更小,抗有限字长效应能力更好。Abstract: Finite Impulse Response(FIR) filter is the main component of multi-carrier modulation system in wireless communication research. Considering the problem of FIR filter performance degradation caused by the finite word length effect, an FIR filter lattice structure is proposed to optimize the filter coefficient error caused by quantization, that is, to reduce the coefficient sensitivity. The state space structure is used to express the corresponding improved lattice structure coefficients, and the coefficient sensitivity expression is derived and analyzed. The simulation results show that the sensitivity of the improved lattice structure coefficient is related to the sampling period. Compared with the traditional lattice structure, under the constraints of quantization word length and sampling period, the frequency response characteristic curve of the improved lattice structure is closer to the ideal frequency response characteristic curve, the coefficient sensitivity is smaller, and the ability of resisting finite word length effect is better.
-
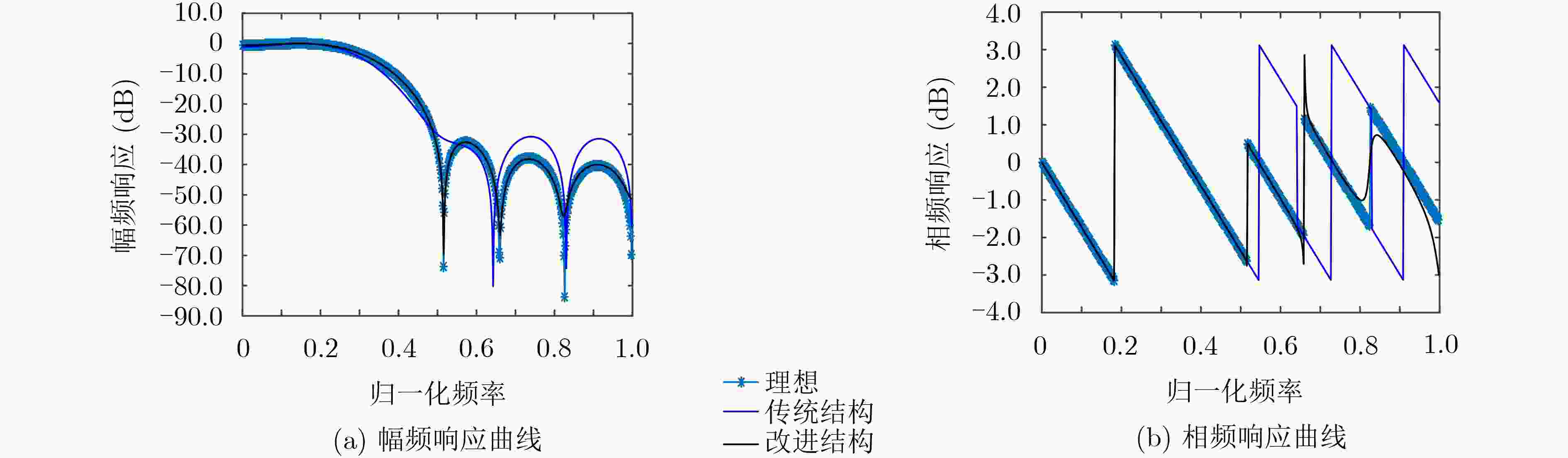
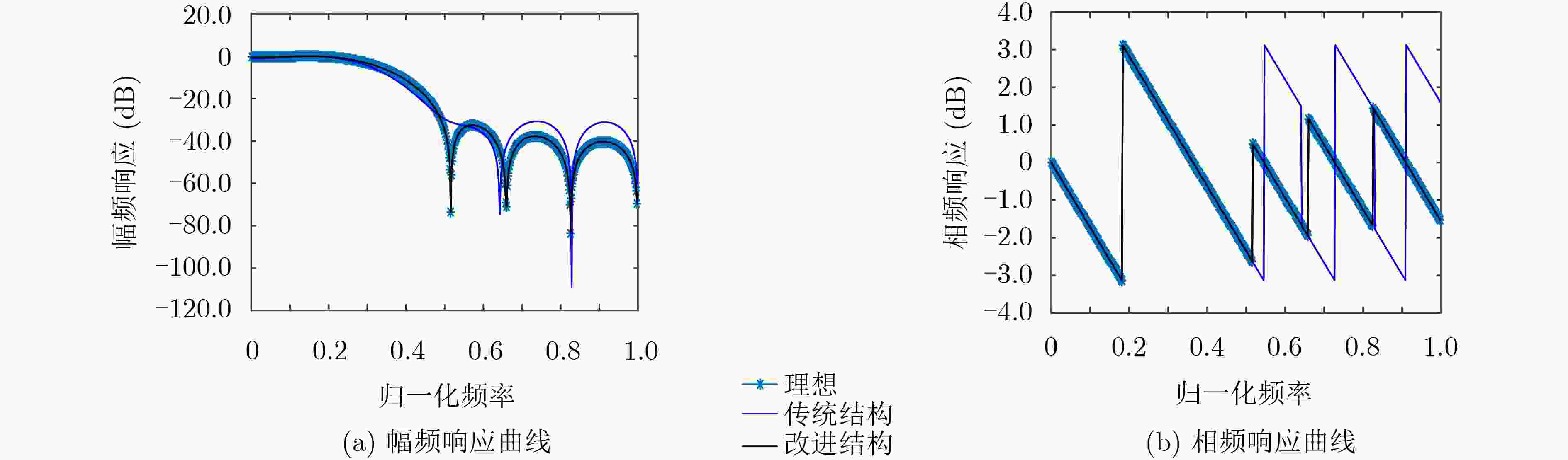
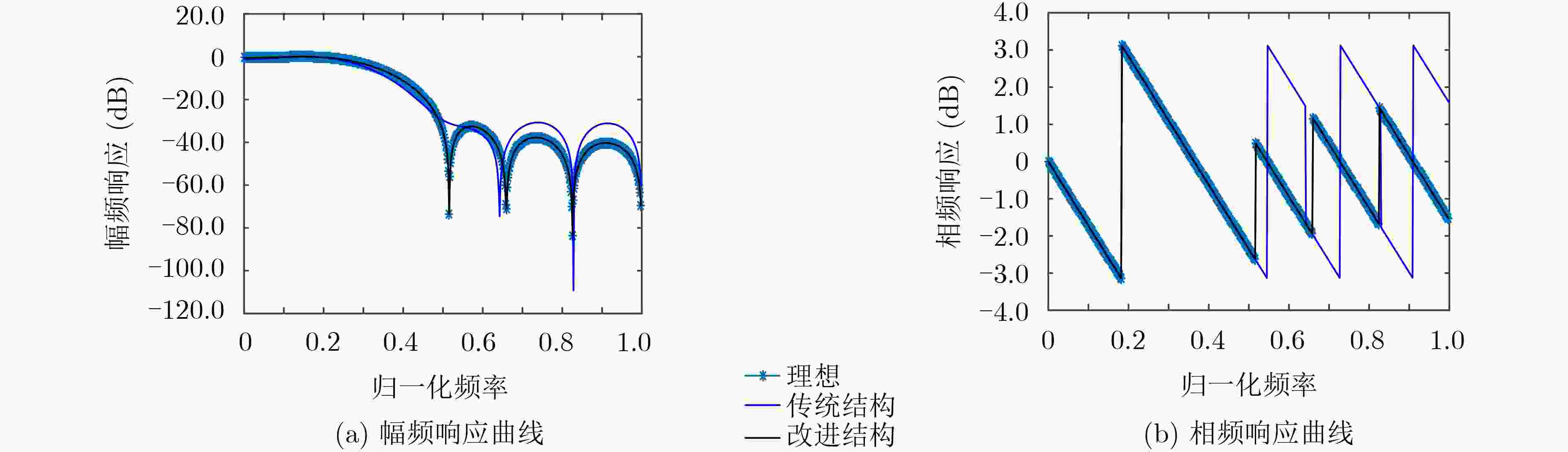
表 1 不同Ts下结构系数灵敏度
Ts (s) 10–2 10–3 10–4 10–5 Rz 12 12 12 12 Rρ 19.4761 1.1848 1.0018 1.0000 表 2 两种结构幅频响应与理想幅频响应的差值
字长Bc (bit) 采样周期Ts (s) ωRz (dB) ωRρ (dB) 8 10–2 4.9703 2.9412 10–3 4.9703 0.9399 10–4 4.9703 0.9437 10 10–2 4.6208 0.5500 10–3 4.6208 0.1509 10–4 4.6208 0.1244 16 10–2 4.7135 0.0018 10–3 4.7135 9.1602×10–4 10–4 4.7135 3.9264×10–4 -
[1] JIANG Lei, ZHANG Haijian, CHENG Shuai, et al. An overview of FIR filter design in future multicarrier communication systems[J]. Electronics, 2020, 9(4): 599. doi: 10.3390/electronics9040599 [2] 庄陵, 马靖怡, 王光宇, 等. FIR数字滤波器零极点灵敏度分析及优化实现[J]. 通信学报, 2018, 39(9): 168–177. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2018167ZHUANG Ling, MA Jingyi, WANG Guangyu, et al. Analysis and optimal realization of pole-zero sensitivity for FIR digital filters[J]. Journal on Communications, 2018, 39(9): 168–177. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2018167 [3] RAJAN A, JAMADAGNI H S, and RAO A. Minimizing quantization effects in digital filtering[C]. 2009 IEEE 13th Digital Signal Processing Workshop and 5th IEEE Signal Processing Education Workshop, Marco Island, USA, 2009: 501–506. doi: 10.1109/DSP.2009.4785975. [4] RENCZES B, KOLLÁR I, MOSCHITTA A, et al. Numerical optimization problems of sine-wave fitting algorithms in the presence of roundoff errors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2016, 65(8): 1785–1795. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2016.2562218 [5] LI Gang, GEVERS M, and SUN Youxian. Performance analysis of a new structure for digital filter implementation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Fundamental Theory and Applications, 2000, 47(4): 474–482. doi: 10.1109/81.841849 [6] HUANG Chaogeng, LI Gang, and XU Hong. Sensitivity analysis of a novel digital filter structure[C]. 2009 7th International Conference on Information, Communications and Signal Processing, Macau, China, 2009: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICICS.2009.5397476. [7] 黄朝耿, 李刚. 一种高效数字滤波器结构及其灵敏度分析[J]. 电路与系统学报, 2010, 15(2): 80–86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-0249.2010.02.015HUANG Chaogeng and LI Gang. An efficient orthogonal digital filter structure with sensitivity analysis[J]. Journal of Circuits and Systems, 2010, 15(2): 80–86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-0249.2010.02.015 [8] KO H J and TSAI J J P. Robust and computationally efficient digital IIR filter synthesis and stability analysis under finite precision implementations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 1807–1822. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.2977848 [9] LIU Yin and PARHI K K. Linear-phase lattice FIR digital filter architectures using stochastic logic[J]. Journal of Signal Processing Systems, 2018, 90(5): 791–803. doi: 10.1007/s11265-017-1224-z [10] GRAY A and MARKEL J. Digital lattice and ladder filter synthesis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Audio and Electroacoustics, 1973, 21(6): 491–500. doi: 10.1109/TAU.1973.1162522 [11] LIM Y C. On the synthesis of IIR digital filters derived from single channel AR lattice network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1984, 32(4): 741–749. doi: 10.1109/TASSP.1984.1164394 [12] LI Gang, LIM Y C, and HUANG Chaogeng. Very robust low complexity lattice filters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2010, 58(12): 6093–6104. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2077635 [13] HUANG Chaogeng, LI Gang, XU Zhixing, et al. Design of optimal digital lattice filter structures based on genetic algorithm[J]. Signal Processing, 2012, 92(4): 989–998. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2011.10.011 [14] 张玉洪, 保铮. FIR数字滤波器的简化格型实现[J]. 电子与信息学报, 1988, 10(3): 193–201.ZHANG Yuhong and BAO Zheng. Simplified lattice realization of fir digital filters[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 1988, 10(3): 193–201. [15] ANDREWS J G, BUZZI S, CHOI W, et al. What will 5G be?[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2014, 32(6): 1065–1082. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2014.2328098 -





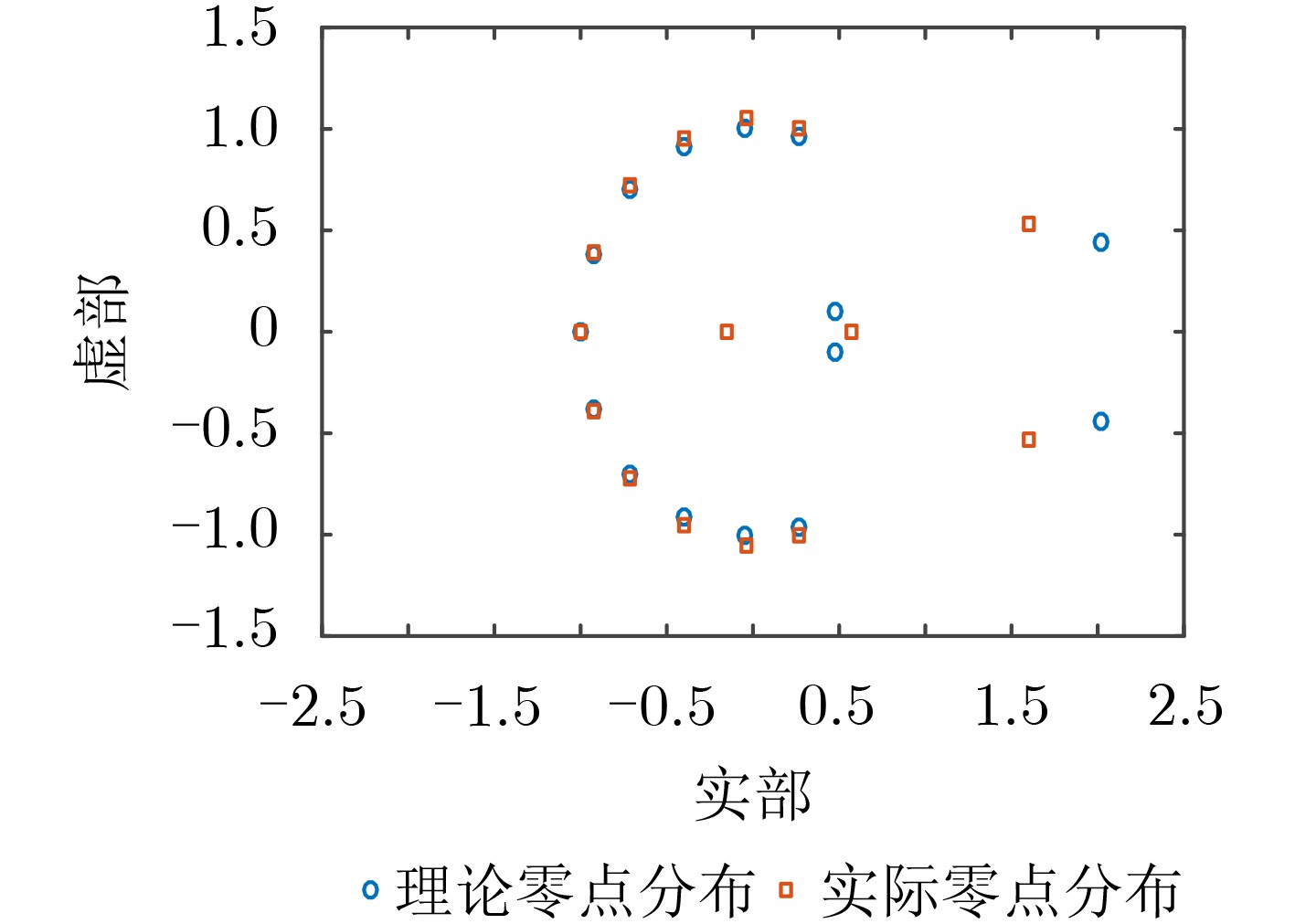
 下载:
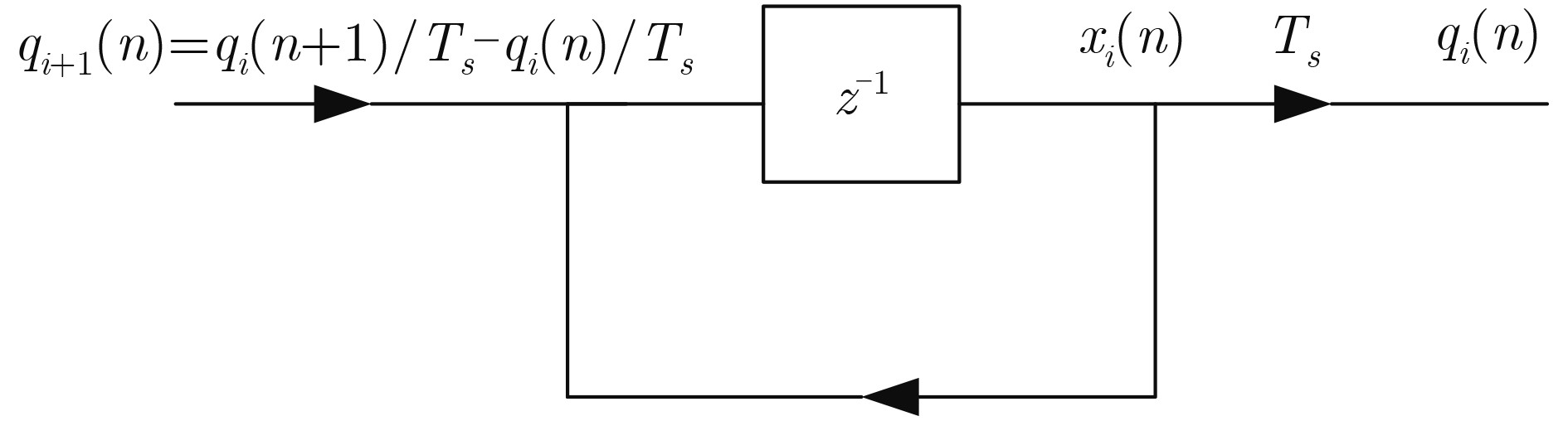
下载:
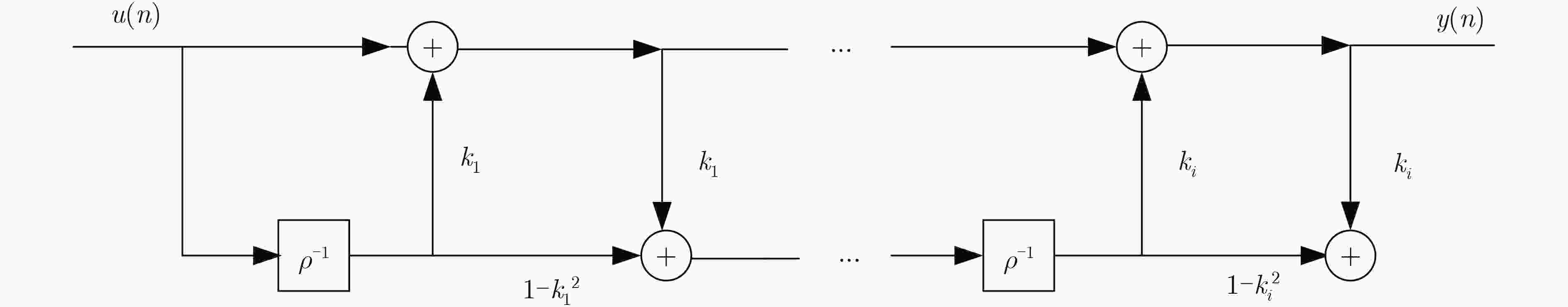
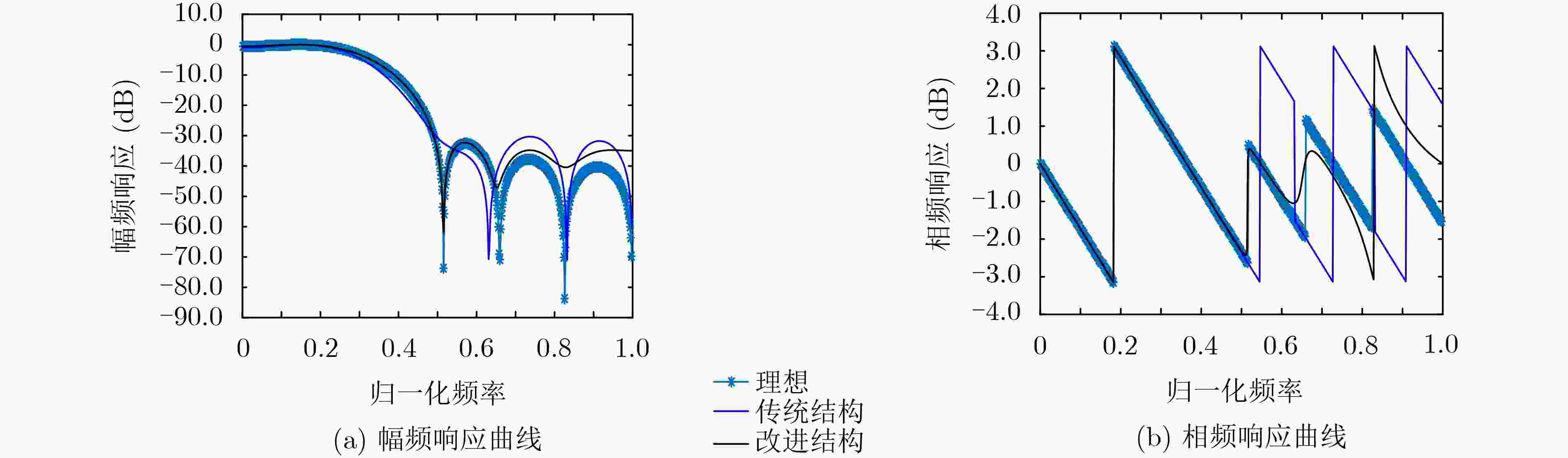


 下载:
下载:
