An Automatic Decision Algorithm for Foreign Objects Debris Based on Duffing Oscillator
-
摘要: 基于毫米波雷达的机场异物(FOD)检测技术具有高分辨率和低功耗的特点,但是传统恒虚警(CFAR)类检测算法在低信杂比(SCR)情况下虚警过高。该文提出一种基于Duffing振子的FOD检测算法。该算法首先利用杂波图CFAR检测算法将雷达接收机接收回波中的背景杂波初步分离,获得目标(包含虚警)的距离信息,并利用该信息构造Duffing方程,之后将此方程作为系统检测模型,输入接收回波信号,求解输出信号方差,采用方差极值法区分目标和虚警。仿真结果表明,在低信杂比情况下,即使虚警概率为10–3,该文检测算法也可以降低虚警率,实现目标与虚警的自动判决。与传统CFAR检测算法相比,该算法的检测概率高于传统检测算法且随信杂比的下降减小速度缓慢,即使在信杂比–30 dB的情况下所提算法仍然可以保持84%的检测概率。Abstract: The Foreign Objects Debris (FOD) detection technology based on millimeter wave radar has the advantages of high resolution and low power consumption, but the traditional Constant False Alarm Rate (CFAR) detection algorithm has high false alarm probability under the condition of low Signal-to-Clutter Ratio (SCR). A FOD detection method based on Duffing oscillator is proposed. In this method, the clutter map CFAR detection method is firstly used to separate the background clutter from the received echo signal in the radar receiver, after that the distance information of target (including false alarm) can be acquired, and the Duffing equations are constructed by using the distance information. Then the Duffing equations are used as the system detection model, and the received echo signal is considered as the input. Therefore, the output variance can be calculated by solving the Duffing equations. Finally the target can be distinguished from the false alarm by using the variance extremum method. Simulation results show that, even if the false alarm probability is 10–3, the detection method in this paper can distinguish the target from the false alarm automatically under the condition of low SCR. Furthermore, it can also reduce the false alarm probability. Compared with the traditional CFAR detection algorithm, the detection probability of this method is higher and reduces more slowly with the decrease of SCR. Meanwhile, the detection probability can be maintained at 84% under the condition of SCR=–30 dB.
-
表 1 LFMCW雷达检测系统参数
参数名称 参数值 参数名称 参数值 带宽 1.5 GHz 天线增益 20 dBi 调频周期 128 μs 水平波束宽度 1.9° 累计时间 60 ms 垂直波束宽度 5° 脉冲累计数 468 方位角波束宽度 120° 最远探测距离 70 m 向下波束宽度 28° 距离分辨率 0.1 m 角距 12°/s -
[1] MAZOUNI K, KOHMURA A, FUTATSUMORI S, et al. 77 GHz FM-CW radar for FODs detection[C]. The 7th European Radar Conference, Paris, France, 2010: 451–454. [2] 王洪, 汪学刚. 机场跑道异物监测雷达关键技术[J]. 电讯技术, 2011, 51(2): 7–10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2011.02.002WANG Hong and WANG Xuegang. Key technologies of radar for Foreign Objects Debris (FOD) detection on runways[J]. Telecommunication Engineering, 2011, 51(2): 7–10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2011.02.002 [3] 张思睿, 葛万成, 汪亮友, 等. 恶劣天气下可见光和红外图像融合算法设计[J]. 信息技术, 2016(6): 33–36. doi: 10.13274/j.cnki.hdzj.2016.06.010ZHANG Sirui, GE Wancheng, WANG Liangyou, et al. Design of the image fusion algorithm with infrared image and visible image under severe weather conditions[J]. Information Technology, 2016(6): 33–36. doi: 10.13274/j.cnki.hdzj.2016.06.010 [4] 李华琼, 张中仅, 王雨果, 等. CFAR方法在机场跑道FOD检测中的性能分析[J]. 无线电工程, 2015, 45(9): 53–57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2015.09.14LI Huaqiong, ZHANG Zhongjin, WANG Yuguo, et al. Performance analysis and comparison of CFAR methods for FOD detection in airport runway environment[J]. Radio Engineering, 2015, 45(9): 53–57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2015.09.14 [5] TOM A and VISWANATHAN R. Switched order statistics CFAR test for target detection[C]. 2008 IEEE Radar Conference, Rome, Italy, 2008: 1–5. [6] ZATTOUTA B, FARROUKI A, and BARKAT M. Automatic censoring detection using binary clutter-map estimation for NonGaussian environments[C]. 2007 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing and Communications, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 2007: 205–208. [7] NITZBERG R. Clutter map CFAR analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1986, AES-22(4): 419–421. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1986.310777 [8] CONTE E, LONGO M, and LOPS M. Modelling and simulation of non-Rayleigh radar clutter[J]. IEE Proceedings F (Radar and Signal Processing) , 1991, 138(2): 121–130. doi: 10.1049/ip-f-2.1991.0018 [9] SCHLEHER D C. Radar detection in Weibull clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1976, AES-12(6): 736–743. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1976.308352 [10] 邓冬虎, 张群, 罗迎, 等. Duffing振子在低信噪比雷达目标微动特征提取中的应用[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(2): 453–458.DENG Donghu, ZHANG Qun, LUO Ying, et al. The application of duffing oscillators to micro-motion feature extraction of radar target under low SNR[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2014, 36(2): 453–458. [11] 杨绍清, 韩东, 贾传荧. 基于混沌特征的高分辨雷达目标识别[J]. 火力与指挥控制, 2006, 31(6): 38–40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2006.06.011YANG Shaoqing, HAN Dong, and JIA Chuanying. A practical method of target recognition based on chaotic feature for high-resolution radar[J]. Fire Control &Command Control, 2006, 31(6): 38–40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2006.06.011 [12] COSTA A H, ENRÍQUEZ-CALDERA R, TELLO-BELLO M, et al. High resolution time-frequency representation for chirp signals using an adaptive system based on duffing oscillators[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2016, 55: 32–43. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2016.04.008 [13] 冀常鹏, 许素娜, 冀雯靖. 基于Duffing振子的微弱信号参数估计[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 32(2): 263–270.JI Changpeng, XU Suna, and JI Wenjing. Estimation of weak signal parameters based on Duffing oscillator[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications (Natural Science Edition) , 2020, 32(2): 263–270. [14] 刘海波, 吴德伟, 戴传金, 等. 基于Duffing振子的弱正弦信号检测方法研究[J]. 电子学报, 2013, 41(1): 8–12.LIU Haibo, WU Dewei, DAI Chuanjin, et al. A new weak sinusoidal signal detection method based on Duffing oscillators[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2013, 41(1): 8–12. [15] 朱来普, 张陆勇, 谢文凤, 等. 基于Duffing混沌振子的微弱信号检测研究[J]. 无线电工程, 2012, 42(1): 17–20.ZHU Laipu, ZHANG Luyong, XIE Wenfeng, et al. Research of weak signal detection based on Duffing chaotic oscillator[J]. Radio Engineering, 2012, 42(1): 17–20. [16] 朱志强, 侯健, 闫晓鹏, 等. 超低信噪比调频连续波引信信号小周期态Duffing振子检测[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2019, 45(10): 2069–2078. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0032ZHU Zhiqiang, HOU Jian, YAN Xiaopeng, et al. Small-scale periodic state Duffing oscillator FMCW fuze signal detection at ultra-low SNR[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019, 45(10): 2069–2078. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0032 [17] NIE Chunyan, SHI Yaowu, WANG Zhuwen, et al. A detection method of signal frequency based on optimization theory[C]. SPIE 6357, Sixth International Symposium on Instrumentation and Control Technology: Signal Analysis, Measurement Theory, Photo-Electronic Technology, and Artificial Intelligence, Beijing, China, 2006: 635701. [18] WANG Baoshuai and ZHANG Wei. FOD detection based on millimeter wave radar using higher order statistics[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing, Xiamen, China, 2017. [19] WANG Guanyu, CHEN Dajun, LIN Jianya, et al. The application of chaotic oscillators to weak signal detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 1999, 46(2): 440–444. doi: 10.1109/41.753783 [20] WANG Wei, LI Qiang, and ZHAO Guojie. Novel approach based on chaotic oscillator for machinery fault diagnosis[J]. Measurement, 2008, 41(8): 904–911. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2008.01.001 [21] 李国正, 张波. 基于Duffing振子检测频率未知微弱信号的新方法[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2017, 38(1): 181–189.LI Guozheng and ZHANG Bo. Novel method for detecting weak signal with unknown frequency based on duffing oscillator[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2017, 38(1): 181–189. -





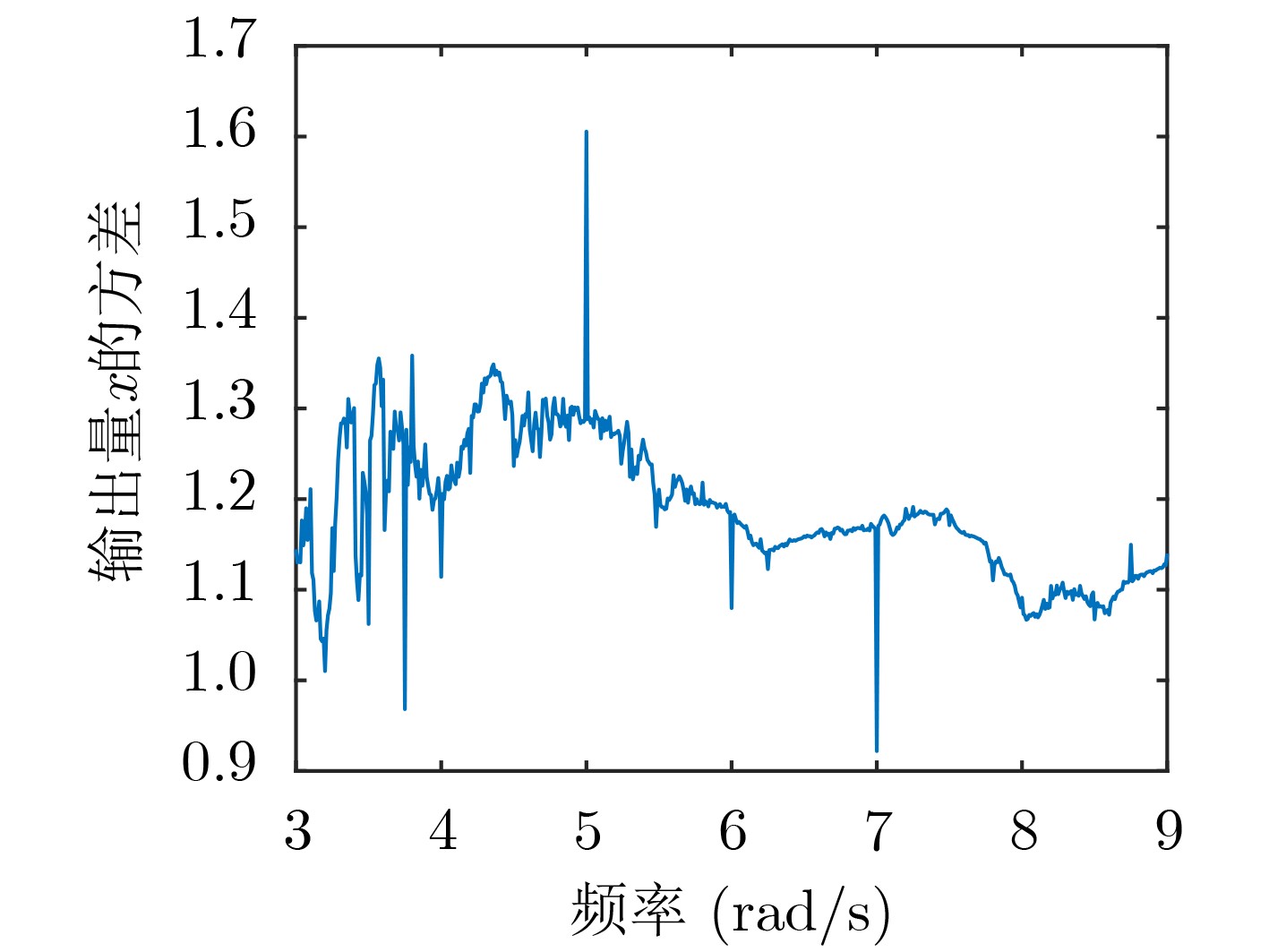
 下载:
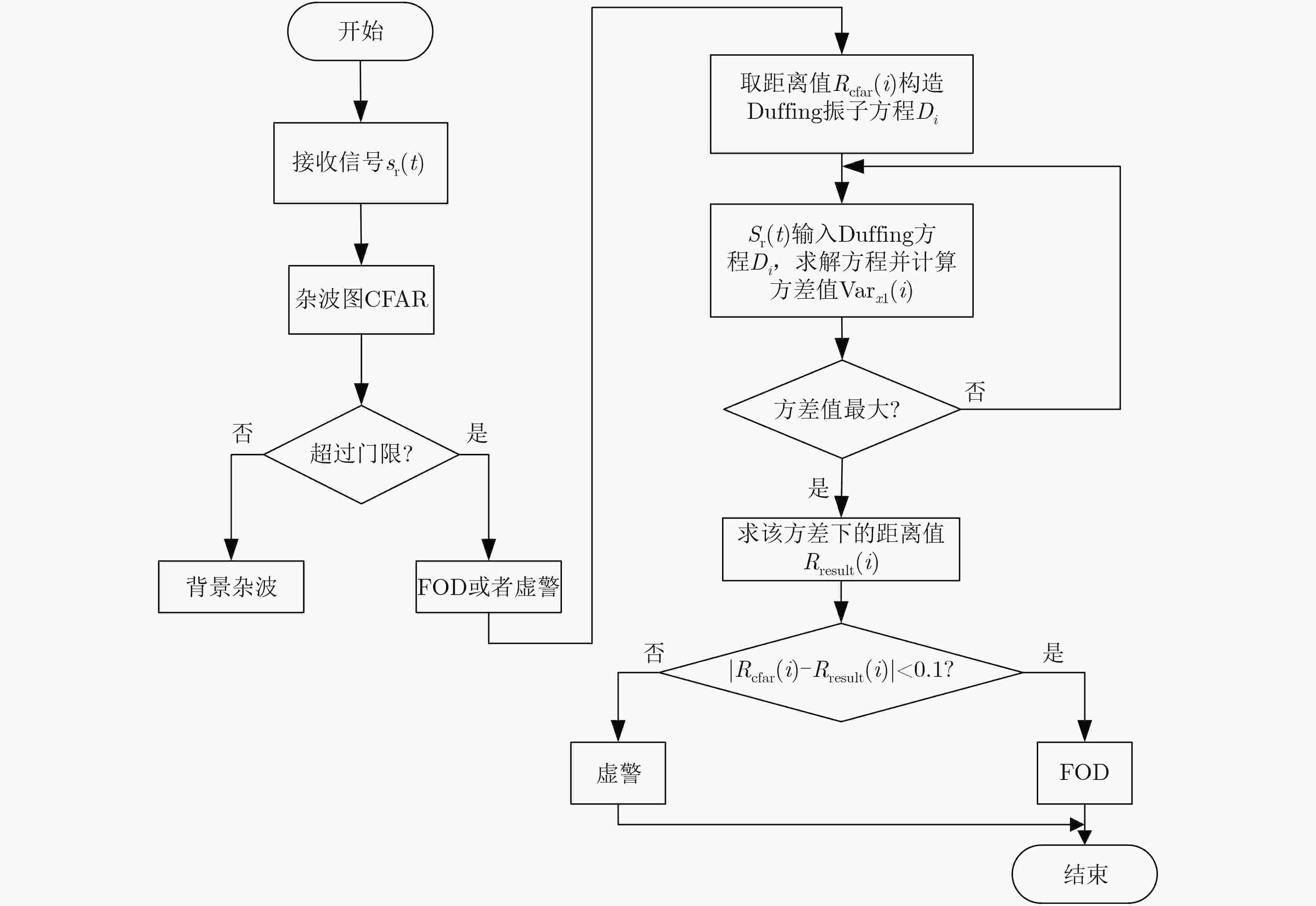
下载:

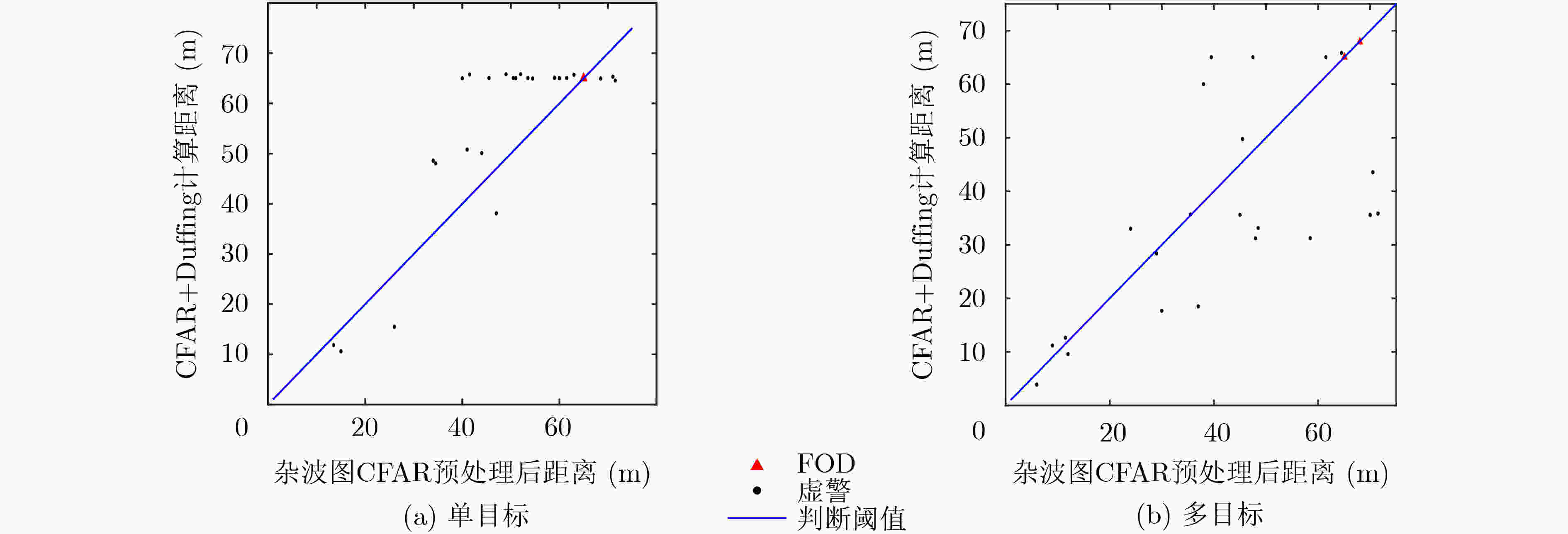

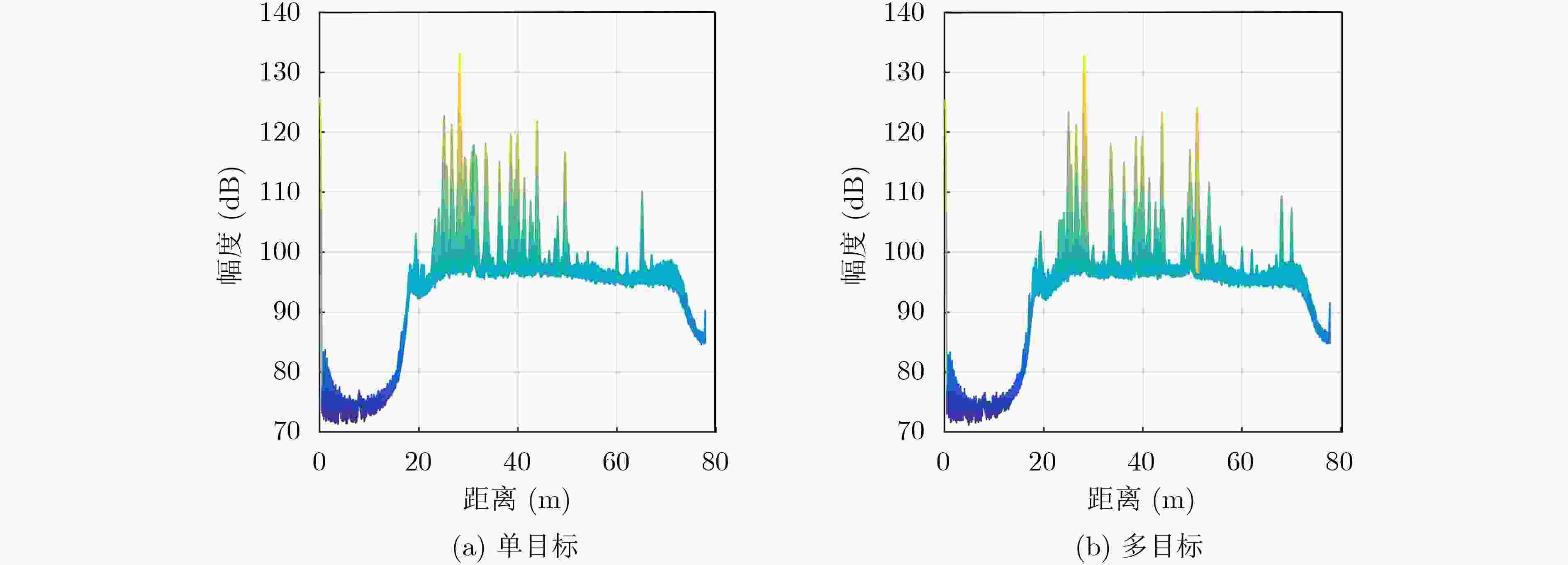
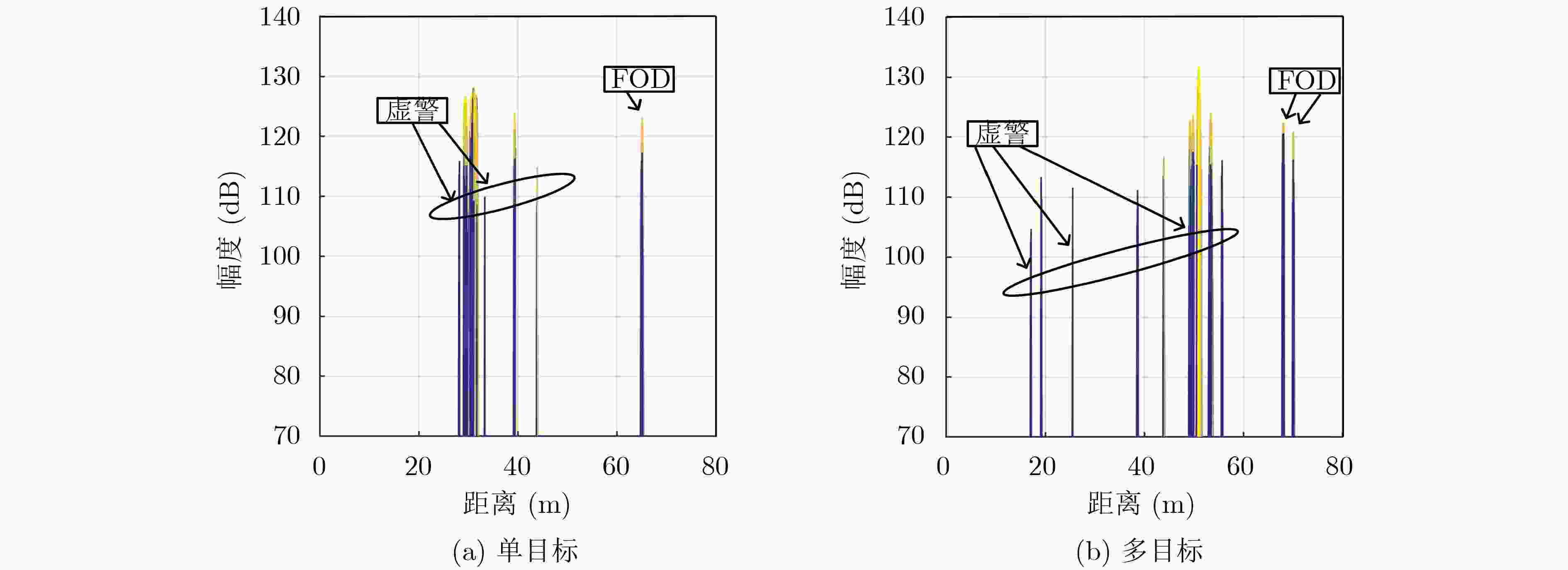

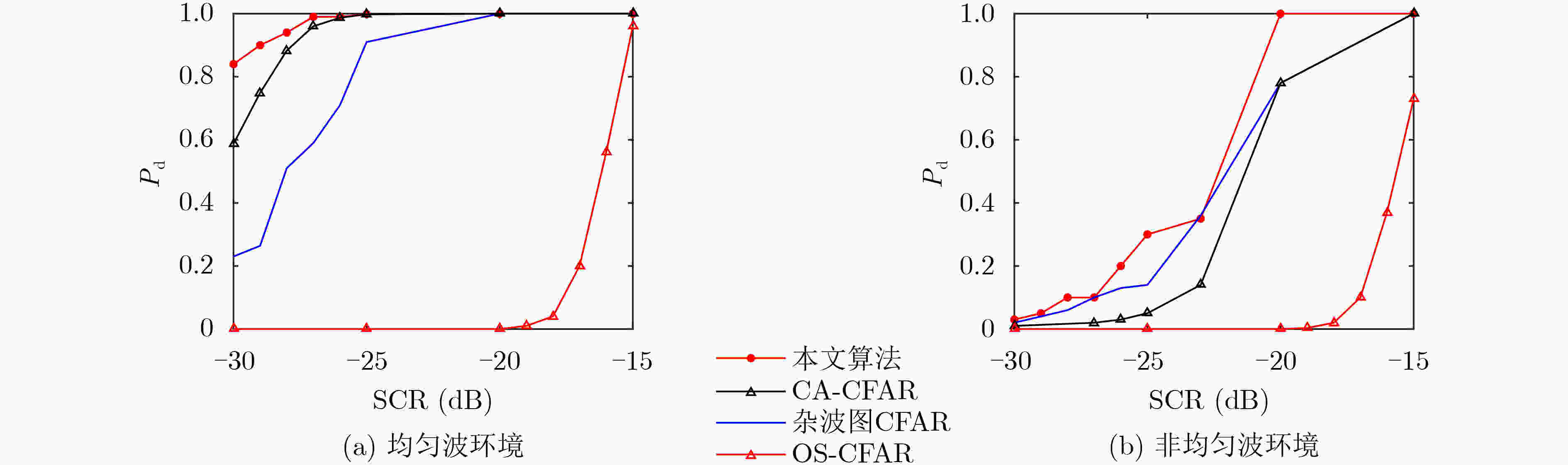


 下载:
下载:
