Person Re-identification Based on Stepped Feature Space Segmentation and Local Attention Mechanism
-
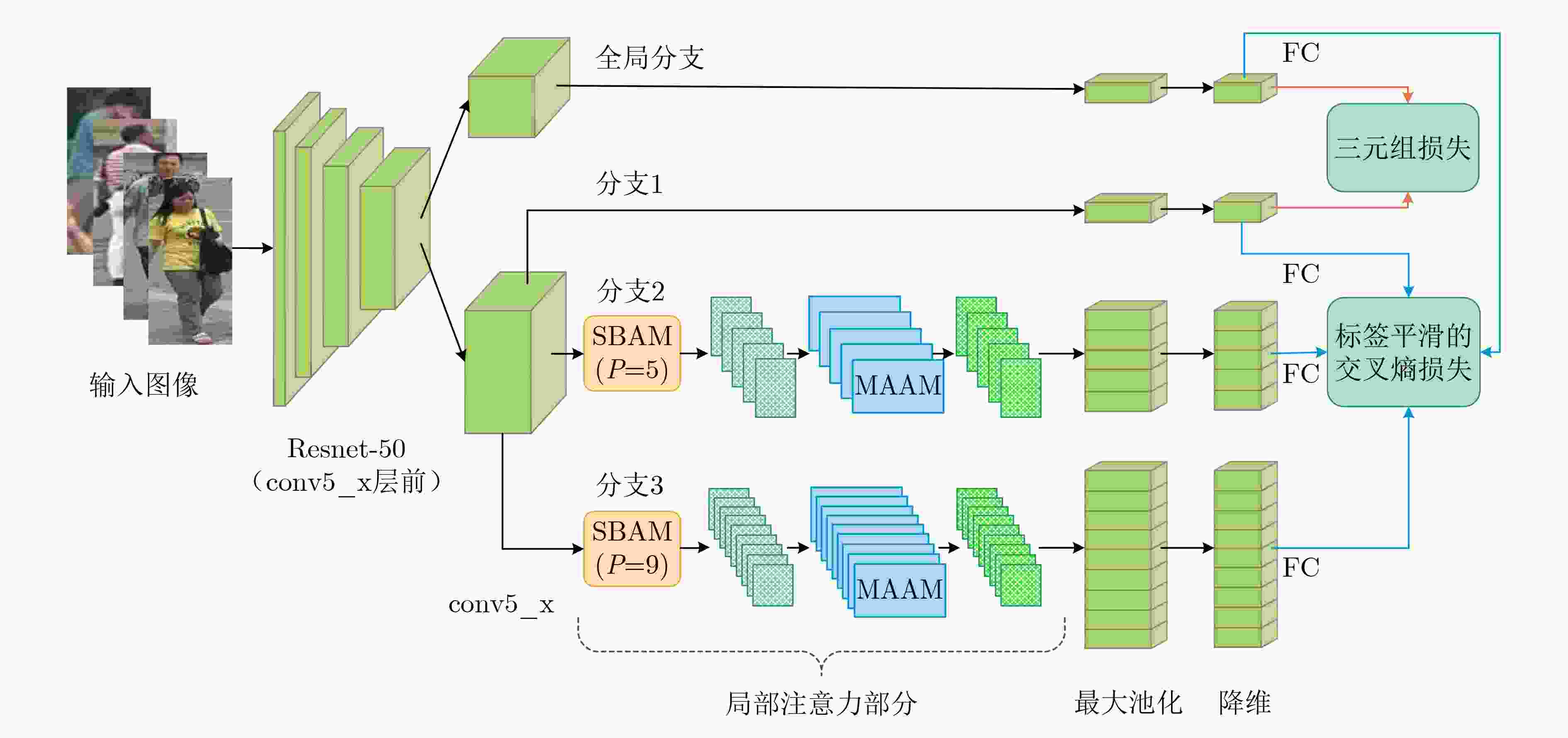
摘要: 为了让网络捕捉到更有效的内容来进行行人的判别,该文提出一种基于阶梯型特征空间分割与局部分支注意力网络(SLANet)机制的多分支网络来关注局部图像的显著信息。首先,在网络中引入阶梯型分支注意力模块,该模块以阶梯型对特征图进行水平分块,并且使用了分支注意力给每个分支分配不同的权重。其次,在网络中引入多尺度自适应注意力模块,该模块对局部特征进行处理,自适应调整感受野尺寸来适应不同尺度图像,同时融合了通道注意力和空间注意力筛选出图像重要特征。在网络的设计上,使用多粒度网络将全局特征和局部特征进行结合。最后,该方法在3个被广泛使用的行人重识别数据集Market-1501,DukeMTMC-reID和CUHK03上进行验证。其中在Market-1501数据集上的mAP和Rank-1分别达到了88.1%和95.6%。实验结果表明,该文所提出的网络模型能够提高行人重识别准确率。Abstract: In order to make the network capture more effective content distinguish pedestrians, this paper proposes a multi-branch network based on Stepped feature space segmentation and Local Branch Attention Network (SLANet) mechanism to pay attention to the salient information of local images. First of all, a stepped branch attention module is introduced into the network. This module blocks the feature map horizontally in a stepped manner, and branch attention is used to assign different weights to each branch. Secondly, a multi-scale adaptive attention module is introduced into the network, which processes local features and adapts the size of the receptive field to adapt to images of different scales. Meanwhile, channel attention and spatial attention are combined to screen out the important features of the image. In the design of network, the multi-granularity network is used to combine the global feature with the local feature. Finally, the method is validated on three widely used person re-identification data sets Market-1501, DukeMTMC-reID and CUHK03. Among them, mAP and Rank-1 on market-1501 data set reach 88.1% and 95.6% respectively. The experimental results show that the proposed network model can improve the accuracy of person re-identification.
-
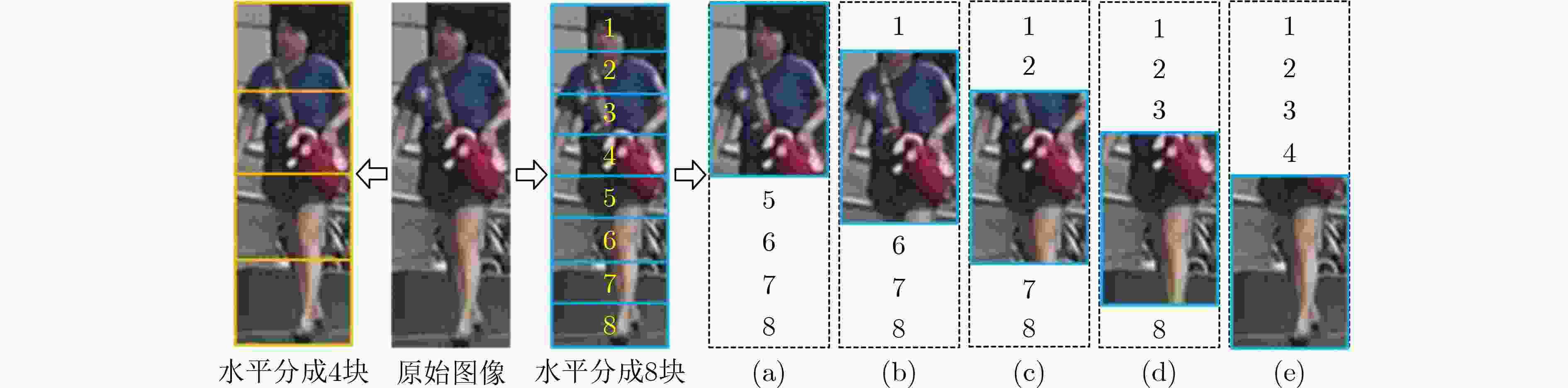
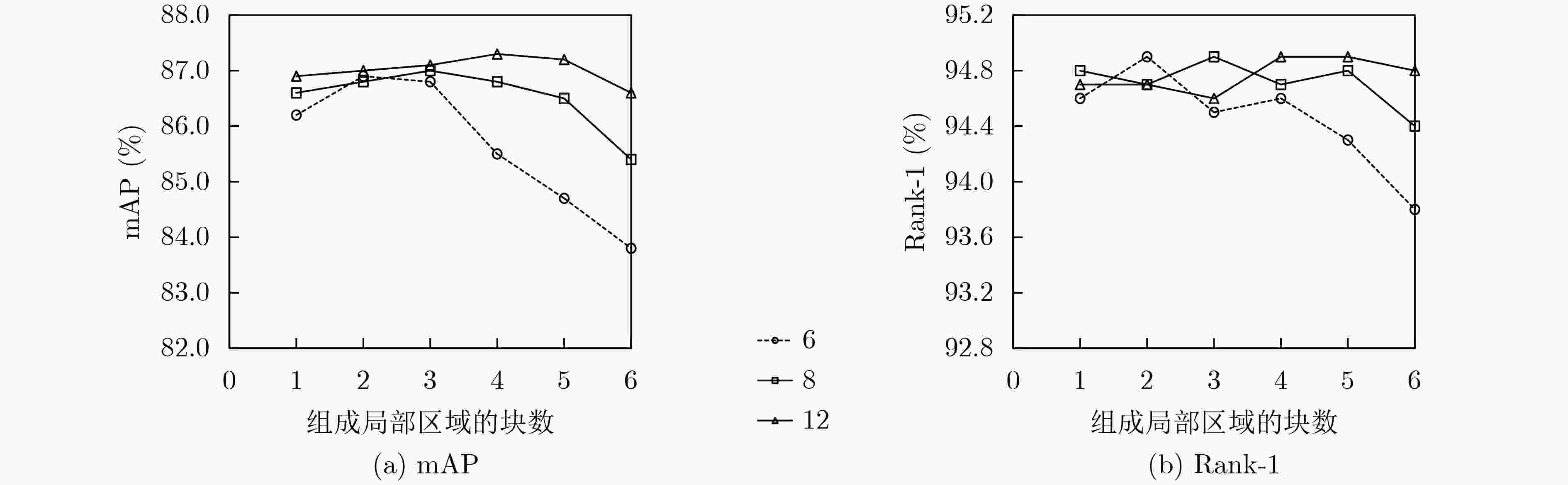
表 1 多粒度分块方法比较(%)
分块方式 mAP Rank-1 Rank-5 Rank-10 6_3 + 6_2 87.6 95.0 98.4 99.1 6_3 + 8_3 87.1 94.9 98.3 98.9 6_3 + 12_4 87.3 94.9 98.4 99.0 8_4 + 6_2 87.4 95.1 98.4 99.0 8_4 + 8_3 87.1 94.9 98.3 99.0 8_4 + 12_4 87.7 95.3 98.5 99.2 12_6 + 6_2 87.5 95.0 98.4 99.1 12_6 + 8_3 87.7 95.2 98.4 99.1 12_6 + 12_4 87.4 95.2 98.4 99.2 表 2 阶梯型多分支的有效性(%)
分块方式 mAP Rank-1 Rank-5 Rank-10 全局特征 77.3 90.5 96.4 97.8 8_4 86.8 94.7 98.4 99.0 12_4 87.3 94.9 98.4 99.1 8_4 + 12_4 87.7 95.3 98.5 99.2 8_4 + 12_4 + 8_2 87.8 95.1 98.4 99.2 8_4 + 12_4 + 12_3 87.3 94.9 98.4 99.1 表 3 联合训练的有效性(%)
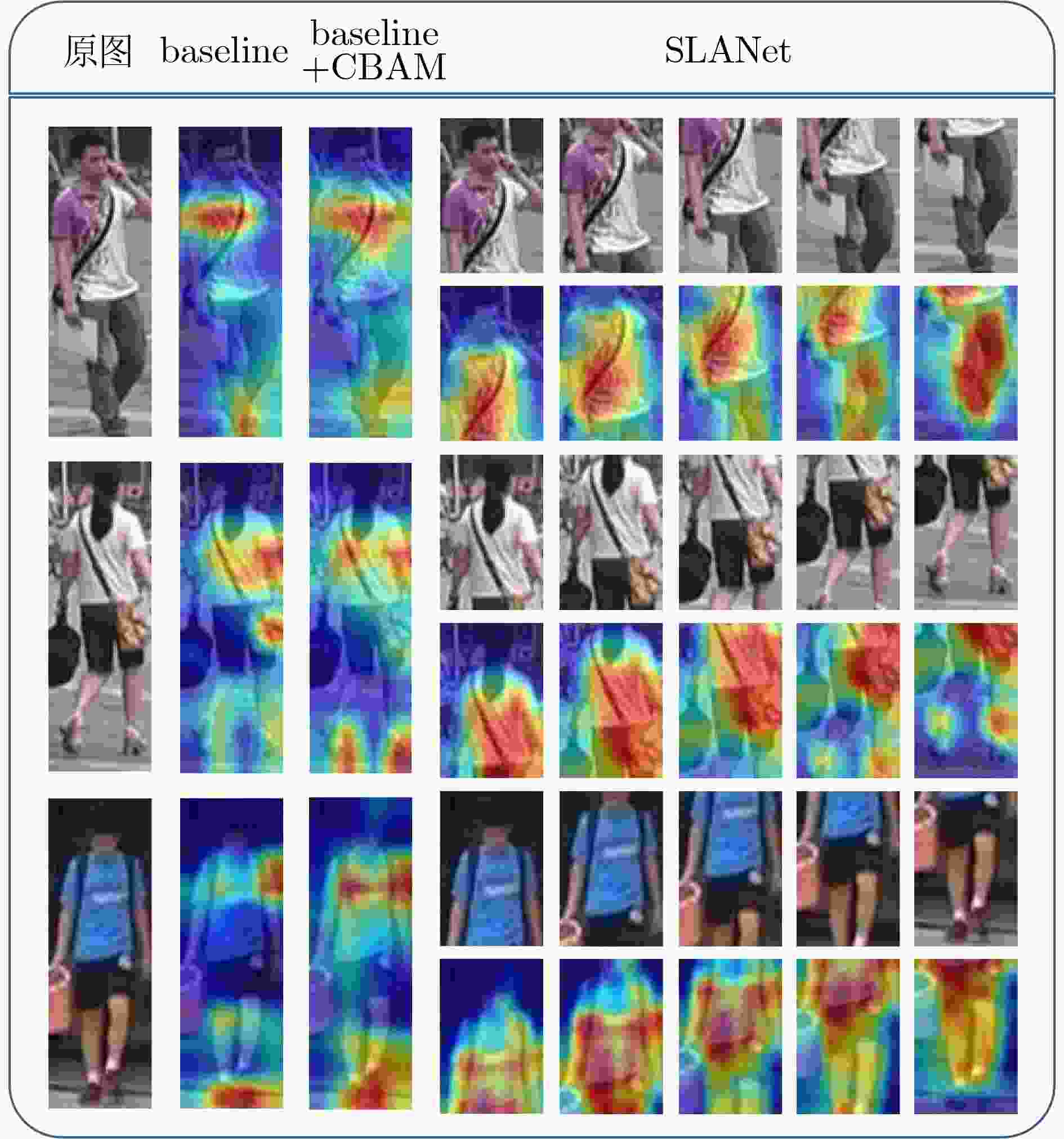
方法 mAP Rank-1 Rank-5 Rank-10 baseline 77.3 90.5 96.4 97.8 + SBAM 87.7 95.3 98.5 99.2 + SBAM + MAAM 88.1 95.6 98.6 99.2 表 4 在Market-1501数据集上的性能比较(%)
表 5 在DukeMTMC-reID数据集上的性能比较(%)
-
[1] 周智恒, 刘楷怡, 黄俊楚, 等. 一种基于等距度量学习策略的行人重识别改进算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(2): 477–483. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180336ZHOU Zhiheng, LIU Kaiyi, HUANG Junchu, et al. Improved metric learning algorithm for person re-identification based on equidistance[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(2): 477–483. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180336 [2] 陈莹, 许潇月. 基于双向参考集矩阵度量学习的行人再识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(2): 394–402. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190159CHEN Ying and XU Xiaoyue. Matrix metric learning for person re-identification based on bidirectional reference set[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(2): 394–402. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190159 [3] HE Botao and YU Shaohua. Ring-push metric learning for person reidentification[J]. Journal of Electronic Imaging, 2017, 26(3): 033005. doi: 10.1117/1.JEI.26.3.033005 [4] GOODFELLOW I J, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative adversarial nets[C]. Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2014: 2672–2680. [5] 杨锋, 许玉, 尹梦晓, 等. 基于深度学习的行人重识别综述[J]. 计算机应用, 2020, 40(5): 1243–1252. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2019091703YANG Feng, XU Yu, YIN Mengxiao, et al. Review on deep learning-based pedestrian re-identification[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2020, 40(5): 1243–1252. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2019091703 [6] ZHENG Zhedong, ZHENG Liang, and YANG Yi. Unlabeled samples generated by GAN improve the person re-identification baseline in vitro[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 3774–3782. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.405. [7] SUN Yifan, ZHENG Liang, YANG Yi, et al. Beyond part models: Person retrieval with refined part pooling (and a strong convolutional baseline)[C]. Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 480–496. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01225-0_30. [8] WANG Guanshuo, YUAN Yufeng, CHEN Xiong, et al. Learning discriminative features with multiple granularities for person Re-identification[C]. Proceedings of the 26th ACM international conference on Multimedia, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2018: 274–282. doi: 10.1145/3240508.3240552. [9] ZHAO Haiyu, TIAN Maoqing, SUN Shuyang, et al. Spindle Net: Person re-identification with human body region guided feature decomposition and fusion[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 907–915. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.103. [10] MIAO Jiaxu, WU Yu, LIU Ping, et al. Pose-guided feature alignment for occluded person re-identification[C]. Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 542–551. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00063. [11] SONG Chunfeng, HUANG Yan, OUYANG Wanli, et al. Mask-guided contrastive attention model for person re-identification[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 1179–1188. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00129. [12] LI Wei, ZHU Xiatian, and GONG Shaogang. Harmonious attention network for person re-identification[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 2285–2294. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00243. [13] LI Xiang, WANG Wenhai, HU Xiaolin, et al. Selective kernel networks[C]. Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 510–519. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00060. [14] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[C]. Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 3–19. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_1. [15] LUO Hao, GU Youzhi, LIAO Xingyu, et al. Bag of tricks and a strong baseline for deep person re-identification[C]. Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 1487–1495. doi: 10.1109/CVPRW.2019.00190. [16] HERMANS A, BEYER L, and LEIBE B. In defense of the triplet loss for person re-identification[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1703.07737, 2017. [17] ZHENG Liang, SHEN Liyue, TIAN Lu, et al. Scalable person re-identification: A benchmark[C]. Proceedings of 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1116–1124. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.133. [18] RISTANI E, SOLERA F, ZOU R, et al. Performance measures and a data set for multi-target, multi-camera tracking[C]. Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 17–35. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-48881-3_2. [19] LI Wei, ZHAO Rui, XIAO Tong, et al. DeepReID: Deep filter pairing neural network for person re-identification[C]. Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 152–159. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2014.27. [20] SUN Yifan, ZHENG Liang, DENG Weijian, et al. SVDNet for pedestrian retrieval[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 3820–3828. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.410. [21] FU Yang, WEI Yunchao, ZHOU Yuqian, et al. Horizontal pyramid matching for person re-identification[C]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, USA, 2019: 8295–8302. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v33i01.33018295. [22] CHEN Binghui, DENG Weihong, and HU Jiani. Mixed high-order attention network for person re-identification[C]. Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 371–381. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00046. [23] CHANG Xiaobin, HOSPEDALES T M, and XIANG Tao. Multi-level factorisation net for person re-identification[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 2109–2118. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00225. [24] ZHONG Zhun, ZHENG Liang, CAO Donglin, et al. Re-ranking person re-identification with k-reciprocal encoding[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 3652–3661. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.389. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
