Cooperative Spectrum Sensing Method Based on Deep Convolutional Neural Network
-
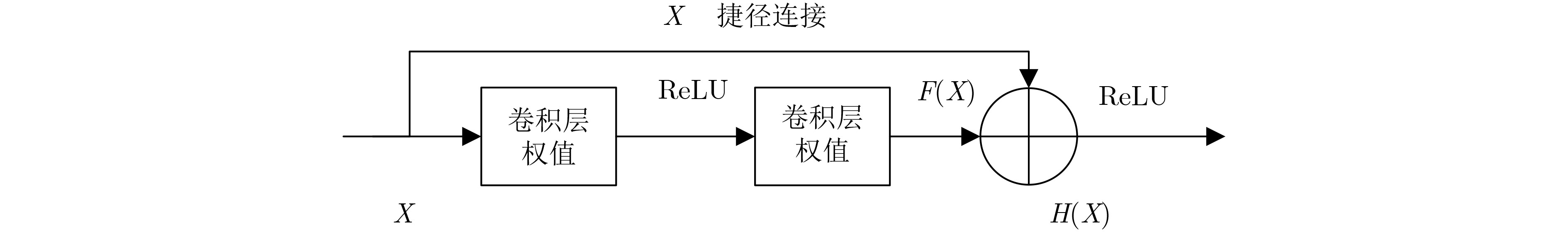
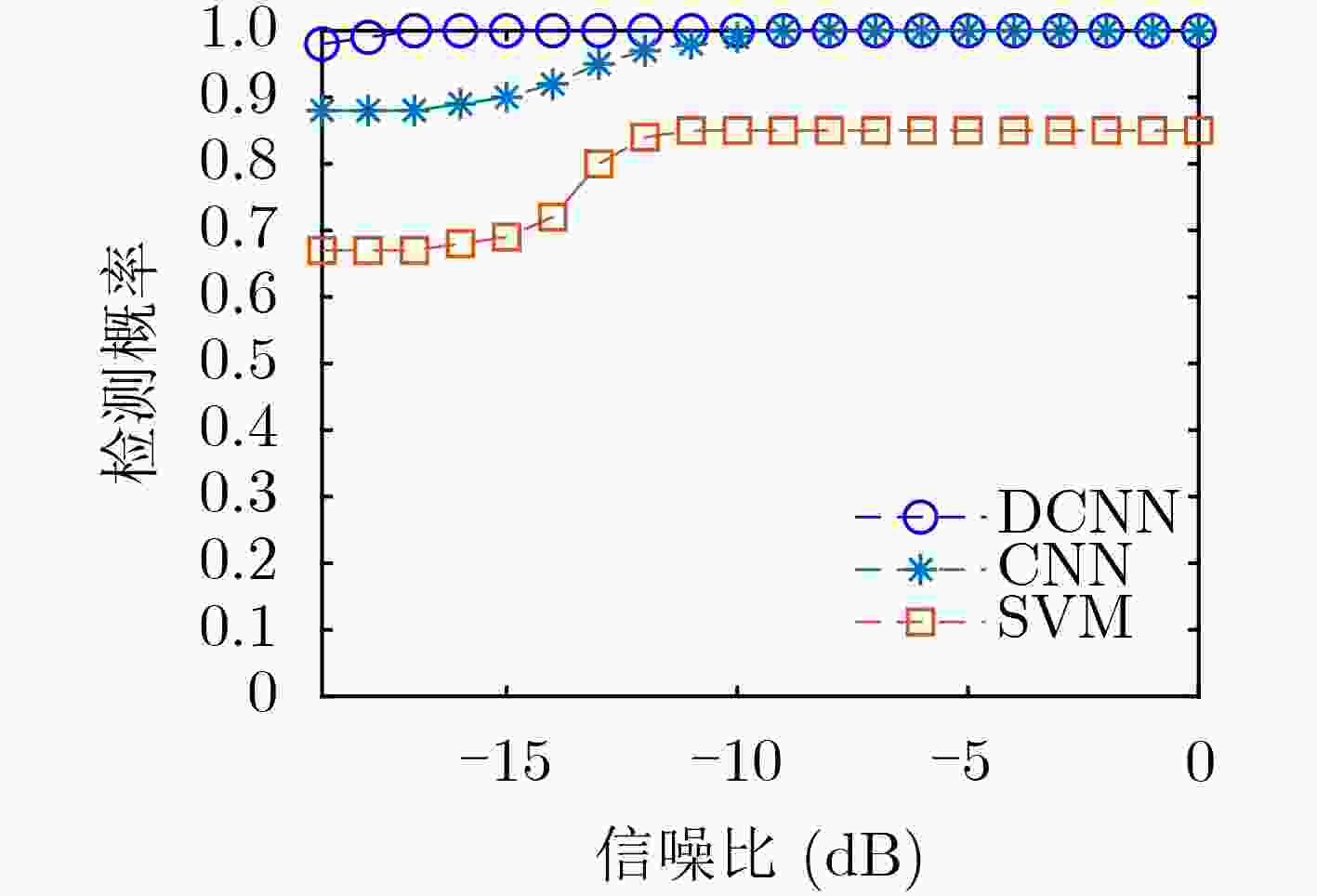
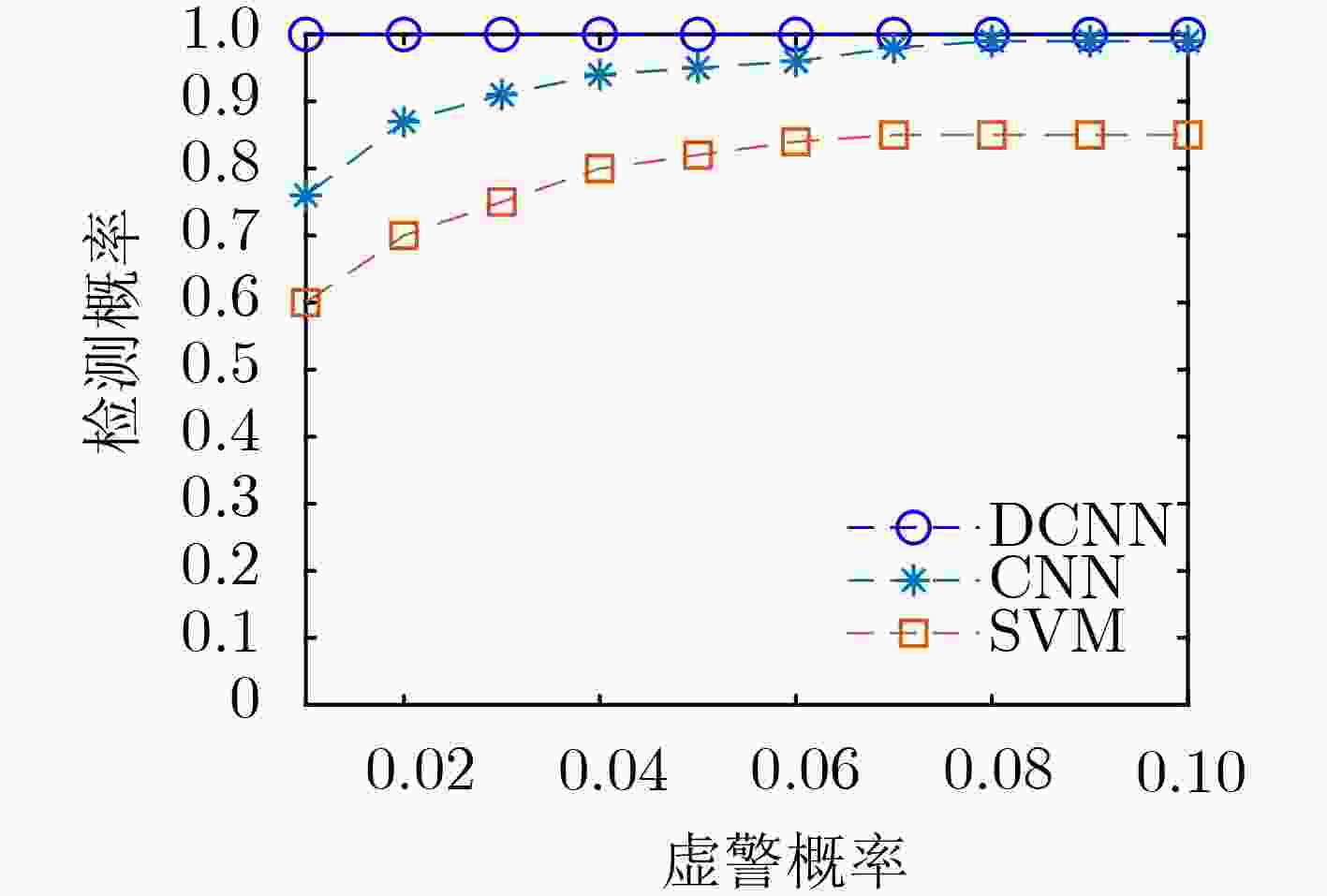
摘要: 针对传统卷积神经网络(CNN)频谱感知方法提取特征能力受限于网络结构简单,增加网络结构又容易出现梯度消失等问题,该文通过在传统卷积神经网络中添加捷径连接,实现输入层恒等映射更深的网络,提出一种基于深度卷积神经网络(DCNN)的协作频谱感知方法。该方法将频谱感知问题转化为图像二分类问题,对正交相移键控(QPSK)信号的协方差矩阵进行归一化灰度处理,并作为深度卷积神经网络的输入,通过残差学习训练深度卷积神经网络模型,提取2维灰度图像的深层特征,将测试数据输入到训练好的模型中,完成基于图像分类的频谱感知。实验结果表明:与传统的频谱感知方法相比,在低信噪比(SNR)下、多用户协作感知时,所提方法具有更高的检测概率和更低的虚警概率。Abstract: The traditional spectrum sensing method of Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) has a simple network structure which limits the ability of feature extraction. To solve the problem of gradient disappearance, a cooperative spectrum sensing method based on Deep Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN) is proposed in this paper, in which shortcut connections are added to the CNN to realize the deeper network of input level identity radiation. This method transforms the spectrum sensing problem into the image binary classification problem, and performs normalized gray level processing on the covariance matrix of Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK) signal as the input of DCNN, which trains DCNN model through residual learning and extracts the deep image features of the two-dimensional grayscale image. The testing data is input into the trained model and spectrum sensing based on image classification is completed. The experimental results show that the proposed method has higher detection probability and lower false alarm probability than the traditional spectrum sensing method when the Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) is low and multiple users collaborate in sensing.
-
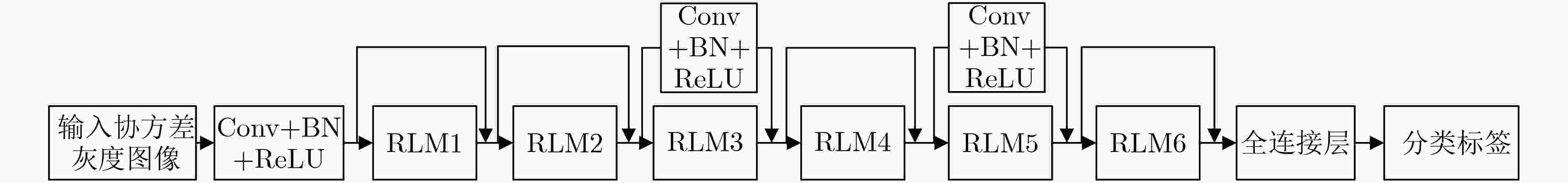
表 1 DCNN的结构参数
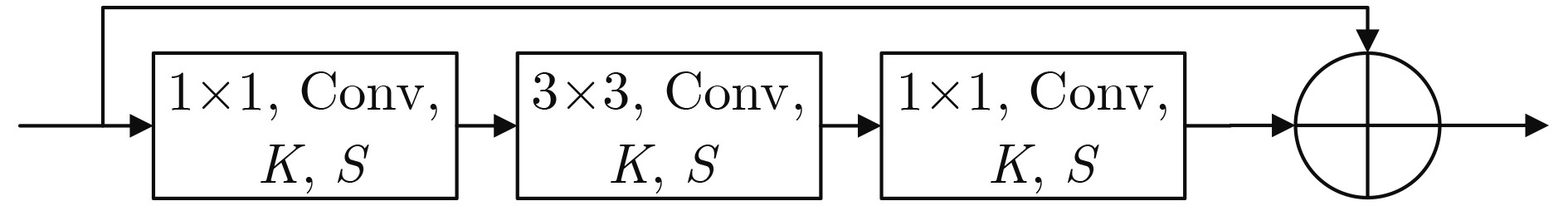
输入:采样协方差矩阵 (维度: 40 × 40) DCNN的各层卷积核大小 输入层 Null 卷积层 8@(3×3) RLM1 8@(1×1)8@(3×3)8@(1×1) RLM2 8@(1×1)8@(3×3)8@(1×1) 捷径连接卷积层1 16@(1×1) RLM3 16@(1×1)16@(3×3)16@(1×1) RLM4 16@(1×1)16@(3×3)16@(1×1) 捷径连接卷积层2 32@(1×1) RLM5 32@(1×1)32@(3×3)32@(1×1) RLM6 32@(1×1)32@(3×3)32@(1×1) 全连接2 × 1 输出:特征向量 (维度: 2 × 1) 表 2 基于DCNN的协作频谱感知算法
输入:训练样本$\{ ({ {\boldsymbol{x} }^{(1)} },{ {\boldsymbol{y} }^{(1)} }), \cdots ({ {\boldsymbol{x} }^{(m)} },{ {\boldsymbol{y} }^{(m)} })\}$,权值${\boldsymbol{W}}$,测试样本$\{ ({ {\boldsymbol{x} }^{(m + 1)} },{ {\boldsymbol{y} }^{(m + 1)} }), \cdots, ({ {\boldsymbol{x} }^{(m + n)} },{ {\boldsymbol{y} }^{(m + n)} })\}$ 输出:检测概率${P_{\rm{d}}}$和虚警概率${P_{{\rm{af}}}}$ 步骤1:(训练阶段)输入训练样本$\{ ({ {\boldsymbol{x} }^{(1)} },{ {\boldsymbol{y} }^{(1)} }), \cdots,({ {\boldsymbol{x} }^{(m)} },{ {\boldsymbol{y} }^{(m)} })\}$。 步骤2:Loop ${{\boldsymbol{x}}_{\rm{0}}}{\rm{ = }}f{(}{{\boldsymbol{W}}_{{\rm{ - 1}}}} \times {{\boldsymbol{x}}^{(m)}})$ 迭代计算l = 0, 3, 6, 9, 12, 15时的输出 ${ {\boldsymbol{x} }_L} = { {\boldsymbol{x} }_l} + \displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = l}^{L - 1} {F({ {\boldsymbol{x} }_i},\{ { {\boldsymbol{W} }_i}{\rm{\} } })}$,L=l+3 依次得到${{\boldsymbol{x}}_3}$, ${{\boldsymbol{x}}_6}$, ${{\boldsymbol{x}}_9}$, ${{\boldsymbol{x}}_{12}}$, ${{\boldsymbol{x}}_{15}}$, ${{\boldsymbol{x}}_{18}}$ 按照式(16)更新$ {\widehat{y}}^{(m)}$ Until ${\rm{loss}} = \dfrac{1}{2}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{k = 1}^c { { {\left\| { { { {\hat{\boldsymbol y} } }^{(m)} }(k) - { {\boldsymbol{y} }^{(m)} }(k)} \right\|}^{ {\rm{ } }2} } }$收敛 步骤3:(测试阶段)将测试集数据$\{ ({ {\boldsymbol{x} }^{(m + 1)} },{ {\boldsymbol{y} }^{(m + 1)} }),\cdots, ({ {\boldsymbol{x} }^{(m + n)} },{ {\boldsymbol{y} }^{(m + n)} })\}$输入训练好的DCNN模型中,正确识别授权用户发射信号的样本数为${k_{{\rm{signal}}}}$,正确识别纯噪声的样本数为${k_{{\rm{noise}}}}$。 步骤4:计算检测概率${P_{\rm{d} } } = { { {k_{ {\rm{signal} } } } } }/{n}$,虚警概率${P_{ {\rm{af} } } } = ({ {n - {k_{ {\rm{noise} } } } } })/{n}$。 表 3 3种算法的离线训练时间和在线检测时间(s)
离线训练时间 在线检测时间 DCNN_5L 19.26 1.66 CNN_5L 22.46 2.68 DCNN_21L 33.92 3.82 CNN_21L 229.93 4.87 SVM 14.00 4.70 -
[1] DIGHAM F F, ALOUINI M S, and SIMON M K. On the energy detection of unknown signals over fading channels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2007, 55(1): 21–24. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2006.887483 [2] YANG Mingchuan, LI Yuan, LIU Xiaofeng, et al. Cyclostationary feature detection based spectrum sensing algorithm under complicated electromagnetic environment in cognitive radio networks[J]. China Communications, 2015, 12(9): 35–44. doi: 10.1109/CC.2015.7275257 [3] ZHANG Xinzhi, GAO Feifei, CHAI Rong, et al. Matched filter based spectrum sensing when primary user has multiple power levels[J]. China Communications, 2015, 12(2): 21–31. doi: 10.1109/CC.2015.7084399 [4] 王磊, 郑宝玉, 李雷. 基于随机矩阵理论的协作频谱感知[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2009, 31(8): 1925–1929. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2008.01154WANG Lei, ZHENG Baoyu, and LI Lei. Cooperative spectrum sensing based on random matrix theory[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2009, 31(8): 1925–1929. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2008.01154 [5] 许炜阳, 李有均, 徐宏乾, 等. 基于随机矩阵非渐近谱理论的协作频谱感知算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(1): 123–129. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170309XU Weiyang, LI Youjun, XU Hongqian, et al. Study on cooperative spectrum sensing algorithm based on random matrix non-asymptotic spectral theory[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(1): 123–129. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170309 [6] ZHOU Fuhui, BEAULIEU N C, LI Zan, et al. Feasibility of maximum eigenvalue cooperative spectrum sensing based on Cholesky factorisation[J]. IET Communications, 2016, 10(2): 199–206. doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2015.0252 [7] THILINA K M, CHOI K W, SAQUIB N, et al. Machine learning techniques for cooperative spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2013, 31(11): 2209–2221. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2013.131120 [8] BAO Jianrong, NIE Jianyuan, LIU Chao, et al. Improved blind spectrum sensing by covariance matrix cholesky decomposition and RBF-SVM decision classification at low SNRs[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 97117–97129. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2929316 [9] 陈思吉, 王欣, 申滨. 一种基于支持向量机的认知无线电频谱感知方案[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报: 自然科学版, 2019, 31(3): 313–322. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2019.03.005CHEN Siji, WANG Xin, and SHEN Bin. A support vector machine based spectrum sensing for cognitive radios[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications:Natural Science Edition, 2019, 31(3): 313–322. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2019.03.005 [10] YU Chunyan, ZHAO Meng, SONG Meiping, et al. Hyperspectral image classification method based on CNN architecture embedding with hashing semantic feature[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2019, 12(6): 1866–1881. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2019.2911987 [11] YU Chunyan, HAN Rui, SONG Meiping, et al. A simplified 2D-3D CNN architecture for hyperspectral image classification based on spatial–spectral fusion[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 2485–2501. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.2983224 [12] MAFFEI A, HAUT J M, PAOLETTI M E, et al. A single model CNN for hyperspectral image denoising[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(4): 2516–2529. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2952062 [13] CHEN Yushi, ZHU Kaiqiang, ZHU Lin, et al. Automatic design of convolutional neural network for hyperspectral image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(9): 7048–7066. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2910603 [14] LIU Chang, WANG Jie, LIU Xuemeng, et al. Deep CM-CNN for spectrum sensing in cognitive radio[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2019, 37(10): 2306–2321. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2019.2933892 [15] LEE W, KIM M, and CHO D H. Deep cooperative sensing: Cooperative spectrum sensing based on convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(3): 3005–3009. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2891291 [16] 张孟伯, 王伦文, 冯彦卿. 基于卷积神经网络的OFDM频谱感知方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41(1): 178–186. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.01.25ZHANG Mengbo, WANG Lunwen, and FENG Yanqing. OFDM spectrum sensing method based on convolutional neural networks[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(1): 178–186. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.01.25 [17] MARSHALL J A. Neural networks for pattern recognition: By Albert Nigrin, MIT Press, Cambridge, MA: 1993, $45.00 413 pp., ISBN 0-262-14054-3[J]. Neural Networks, 1995, 8(3): 493–494. doi: 10.1016/0893-6080(95)90002-0 [18] JAMES D A. Reviewed work: Modern applied statistics with S-PLUS by W. N. Venables, B. D. Ripley[J]. Technometrics, 1996, 38(1): 77–78. doi: 10.2307/1268908 [19] WITTEK P. Pattern Recognition and Neural Networks[M]. WITTEK P. Quantum Machine Learning. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2014: 63–71. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-800953-6.00006-2. [20] 孙月驰, 李冠. 基于卷积神经网络嵌套模型的人群异常行为检测[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2019, 36(3): 196–201, 276. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2019.03.036SUN Yuechi and LI Guan. Abnormal behavior detection of crowds based on nested model of convolutional neural network[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2019, 36(3): 196–201, 276. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2019.03.036 -






 下载:
下载:
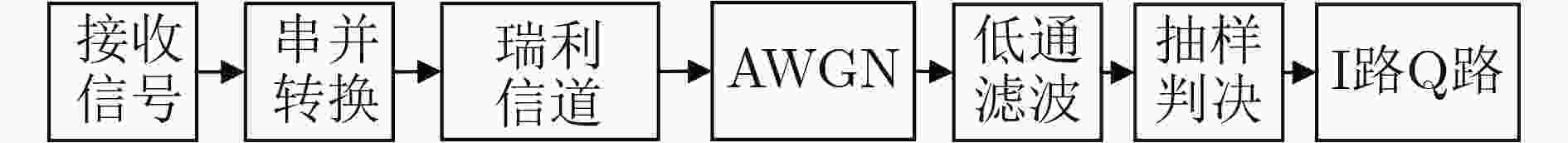

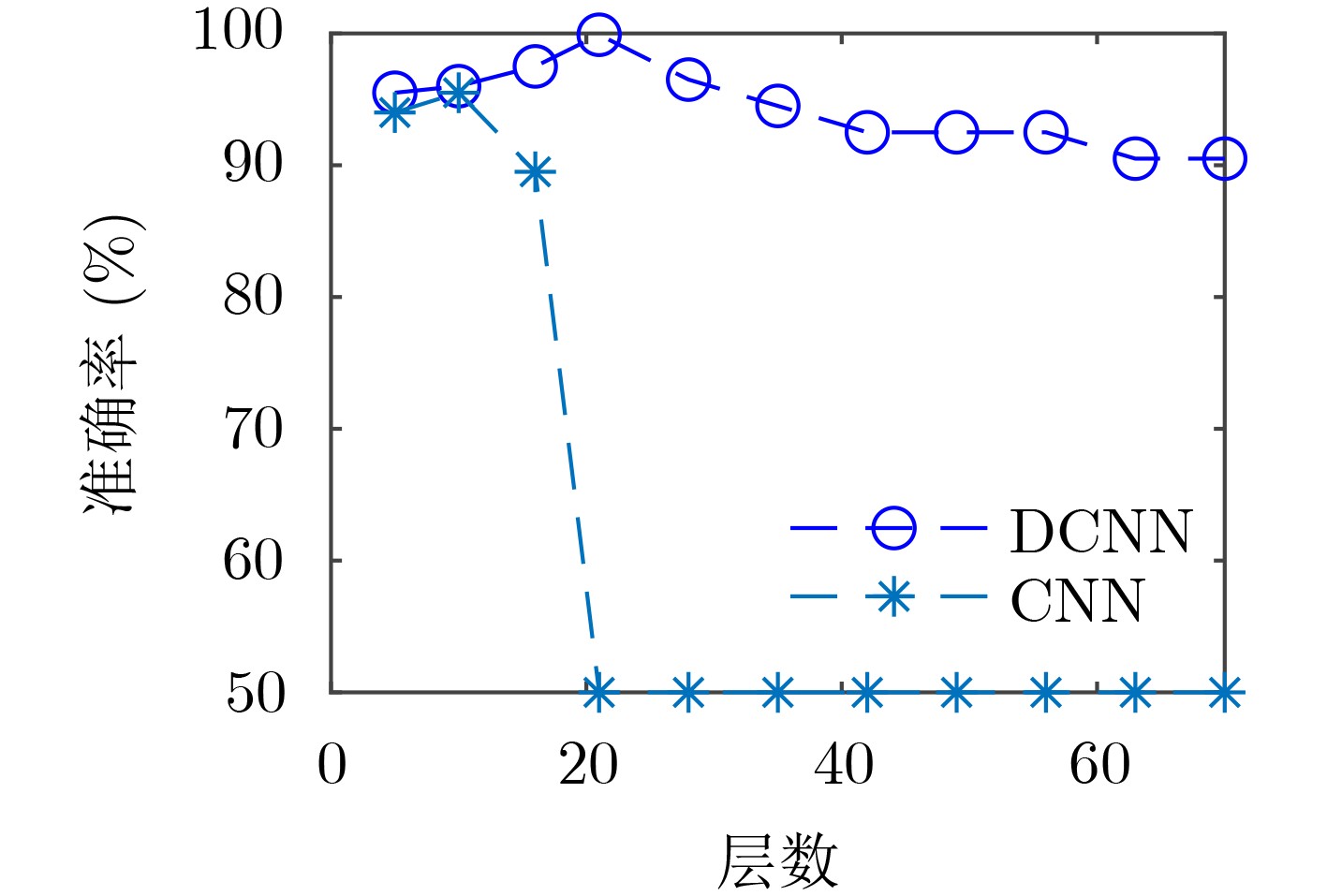
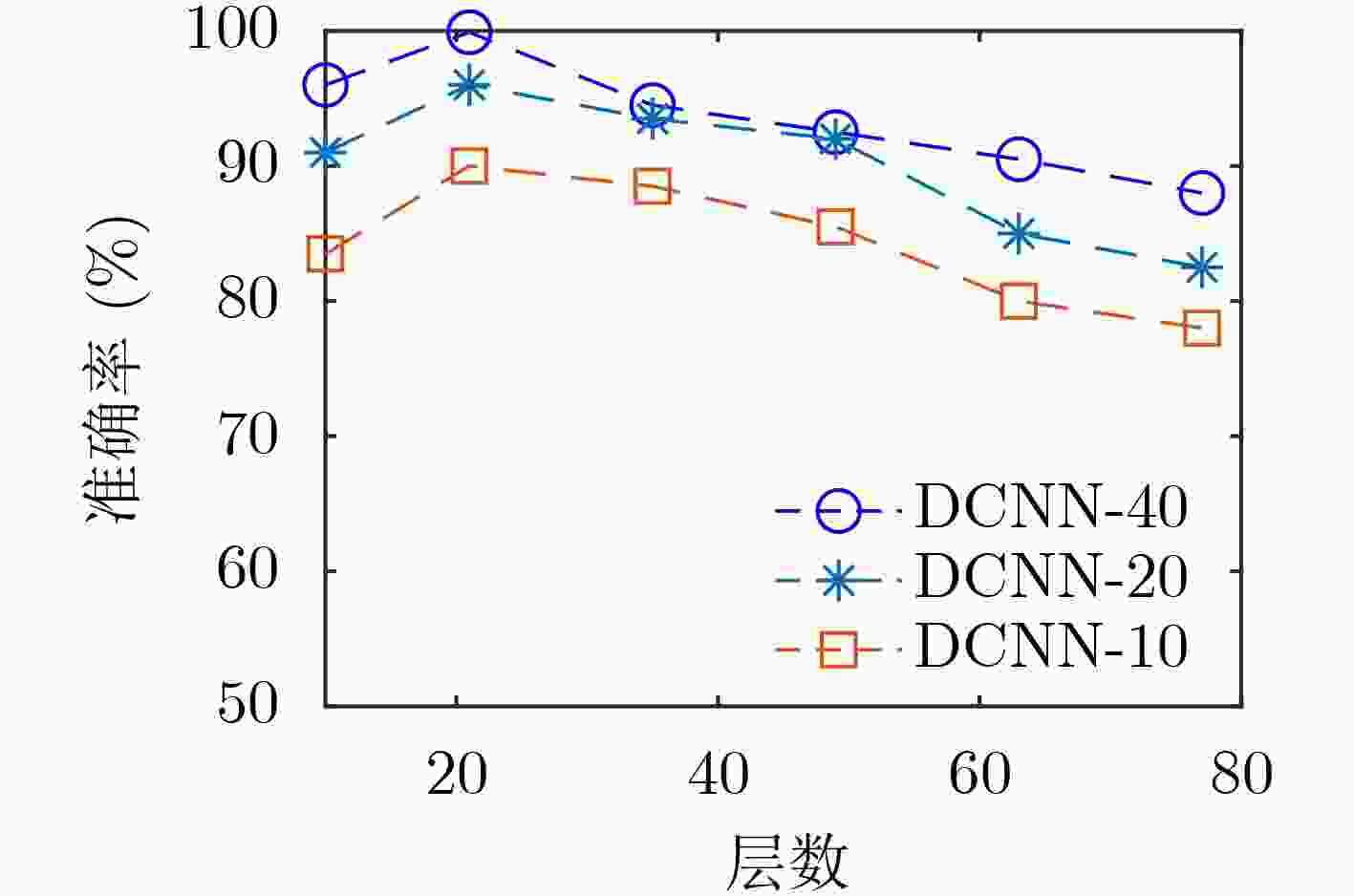
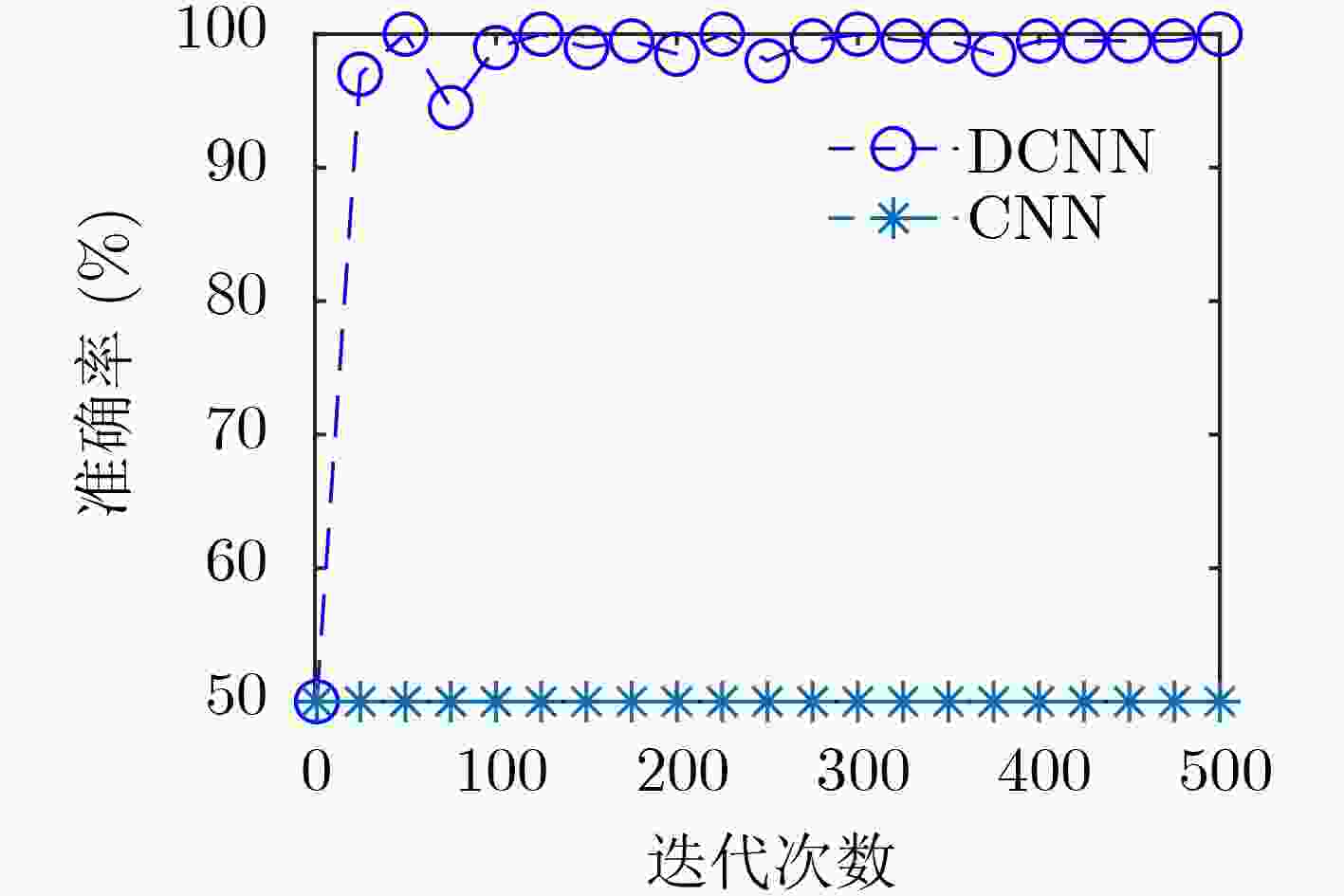
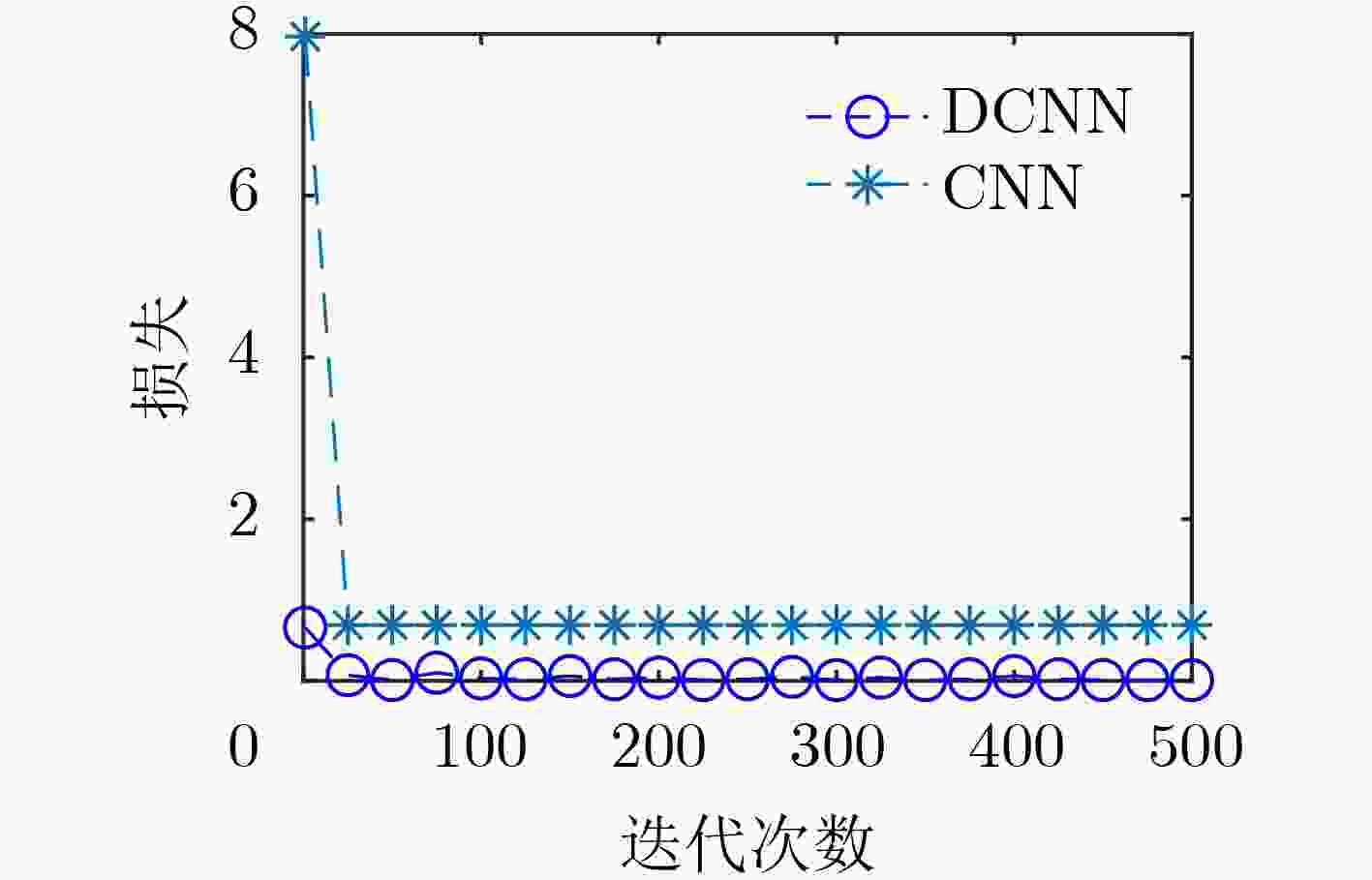


 下载:
下载:
