Three-Dimensional Palmprint Recognition Technology Based on the Fusion of Surface Type and Deep Learning
-
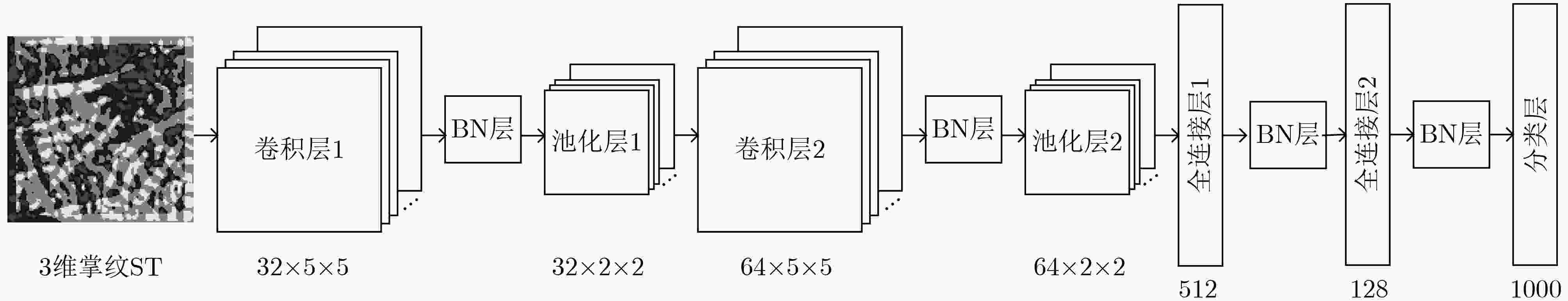
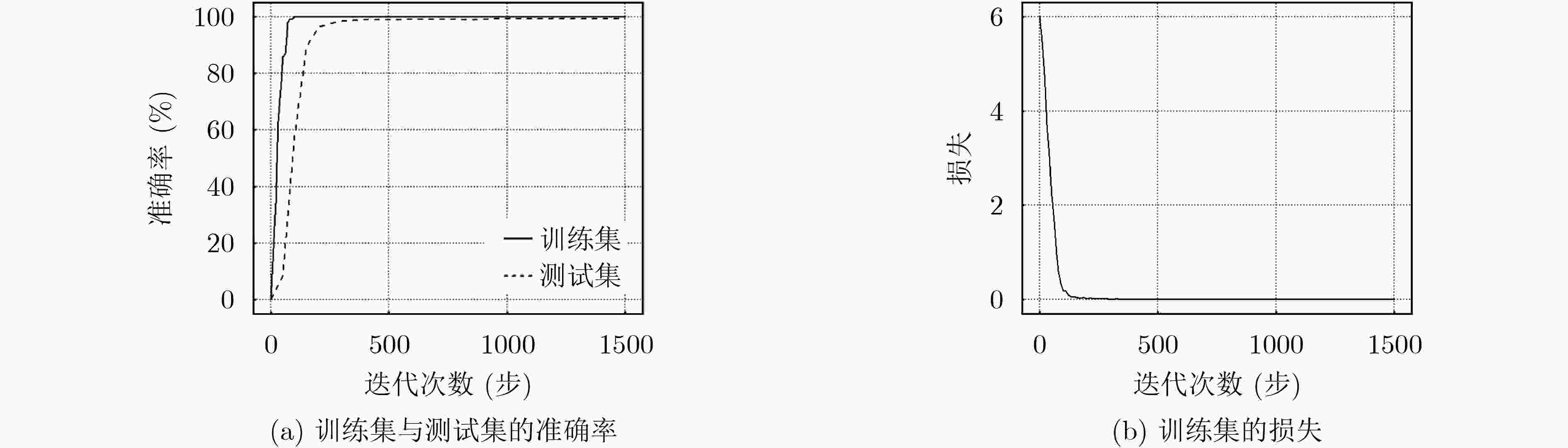
摘要: 传统的2维掌纹识别在图像采集时容易受到干湿度、残影和压力等影响,使得其鲁棒性和准确性降低。为解决这些问题,3维掌纹识别技术应运而生。现有的3维掌纹身份认证技术需要将掌纹的特征提取与匹配识别分开进行,不仅延缓了识别时间,更增加了不同方法优化组合的难度。该文提出一种基于曲面类型(ST)与深度学习融合的3维掌纹识别方法。该方法利用ST图像表示3维掌纹特征,并将其作为卷积神经网络(CNN)的输入,实现网络的训练。测试图像可自行提取掌纹图像特征信息并在网络中直接完成识别。实验结果表明,该文方法在公开数据集上得到了99.43%的准确率和28 ms的识别时间,与传统3维掌纹识别方法相比均有提高,实现了3维掌纹的快速高精度识别。Abstract: Traditional Two-Dimensional (2D) palmprint recognition is susceptible to the effects of dry humidity, residual image and pressure during image acquisition, which reduces its robustness and accuracy. To solve these problems, Three-Dimensional (3D) palmprint recognition technology is widely studied. The existing 3D palmprint identity authentication technology needs to separate palmprint feature extraction and matching recognition, which not only delays the recognition time, but also increases the difficulty of optimizing the combination of different methods. A 3D palmprint recognition method is proposed based on the fusion of Surface Type (ST) and deep learning. ST images is used to represent 3D palmprint features and to be as input of Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) to realize training. The test image can be automatically extracted the feature information of the palmprint image and complete the identification directly. The experimental results show that the proposed method has an accuracy of 99.43% and a recognition time of 28 ms on the public data set, which has high performance of accuracy and speed compared with the traditional 3D palmprint recognition methods.
-
表 1 由曲率得到的9类ST
$K > 0$ $K = 0$ $K < 0$ $H < 0$ 峰
(ST=1)岭
(ST=2)鞍岭
(ST=3)$H = 0$ 无
(ST=4)平坦
(ST=5)低点
(ST=6)$H > 0$ 坑
(ST=7)谷
(ST=8)鞍谷
(ST=9)表 2 2维掌纹及3维掌纹不同特征表示方法的对比实验结果
不同特征 识别率(%) 识别时间(ms) 2维掌纹ROI 94.75 29 GCI 95.53 30 CST 98.88 28 MCI 99.05 29 ST 99.43 28 表 3 不同网络的对比实验结果
网络 识别率(%) 训练时间(ms) 识别时间(ms) LeNet+ST 78.85 142000 31 AlexNet+ST[11] 99.40 151000 35 改进LeNet5+ST 99.43 128000 28 -
[1] 王会勇, 唐士杰, 丁勇, 等. 生物特征识别模板保护综述[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2020, 57(5): 1003–1021. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2020.20190371WANG Huiyong, TANG Shijie, DING Yong, et al. Survey on biometrics template protection[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2020, 57(5): 1003–1021. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2020.20190371 [2] 李新春, 马红艳, 林森. 基于局部邻域四值模式的掌纹掌脉融合识别[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 32(4): 630–638. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2020.04.016LI Xinchun, MA Hongyan, and LIN Sen. Palmprint and palm vein fusion recognition based on local neighbor quaternary pattern[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications:Natural Science Edition, 2020, 32(4): 630–638. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2020.04.016 [3] POONIA P, AJMERA P K, and SHENDE V. Palmprint recognition using robust template matching[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2020, 167: 727–736. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2020.03.338 [4] 赵士伟, 张如彩, 王月明, 等. 生物特征识别技术综述[J]. 中国安防, 2015, 29(7): 79–86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7873.2015.07.026ZHAO Shiwei, ZHANG Rucai, WANG Yueming, et al. Overview of biometric recognition technology[J]. China Security &Protection, 2015, 29(7): 79–86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7873.2015.07.026 [5] 孙冬梅, 裘正定. 生物特征识别技术综述[J]. 电子学报, 2001, 29(S1): 1744–1748. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2001.z1.004SUN Dongmei and QIU Zhengding. A survey of the emerging biometric technology[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2001, 29(S1): 1744–1748. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2001.z1.004 [6] 王曦, 盖绍彦, 达飞鹏. 融合几何信息和方向信息的三维掌纹识别方法[J]. 图学学报, 2020, 41(3): 390–398. doi: 10.11996/JG.j.2095-302X.2020030390WANG Xi, GAI Shaoyan, and DA Feipeng. Fusion of geometric and orientation information for 3D palmprint recognition[J]. Journal of Graphics, 2020, 41(3): 390–398. doi: 10.11996/JG.j.2095-302X.2020030390 [7] 陆展鸿, 单鲁斌, 苏立循, 等. 基于U-Net的掌纹图像增强与ROI提取[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(9): 1807–1816. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2020.0309LU Zhanhong, SHAN Lubin, SU Lixun, et al. Palmprint enhancement and ROI extraction based on U-Net[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(9): 1807–1816. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2020.0309 [8] LI Wei, ZHANG D, LU Guangming, et al. A novel 3-D palmprint acquisition system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics - Part A:Systems and Humans, 2012, 42(2): 443–452. doi: 10.1109/TSMCA.2011.2164066 [9] ZHANG D, LU Guangming, LI Wei, et al. Three dimensional palmprint recognition using structured light imaging[C]. 2008 IEEE Second International Conference on Biometrics: Theory, Applications and Systems, Washington, USA, 2008: 1–6. [10] BAI Xuefei, GAO Nan, ZHANG Zonghua, et al. 3D palmprint identification combining blocked ST and PCA[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2017, 100: 89–95. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2017.10.008 [11] 杨冰, 莫文博, 姚金良. 融合局部特征与深度学习的三维掌纹识别[J]. 浙江大学学报:工学版, 2020, 54(3): 540–545. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2020.03.014YANG Bing, MO Wenbo, and YAO Jinliang. 3D palmprint recognition by using local features and deep learning[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University:Engineering Science, 2020, 54(3): 540–545. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2020.03.014 [12] BESL P J and JAIN R C. Segmentation through variable-order surface fitting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1988, 10(2): 167–192. doi: 10.1109/34.3881 [13] 文成林, 吕菲亚. 基于深度学习的故障诊断方法综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 234–248. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190715WEN Chenglin and LÜ Feiya. Review on deep learning based fault diagnosis[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 234–248. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190715 [14] LECUN Y, BOTTOU L, BENGIO Y, et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278–2324. doi: 10.1109/5.726791 [15] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on ImageNet classification[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015. [16] IOFFE S and SZEGEDY C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[C]. The 32nd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 2015. [17] PolyU 2D and 3D palmprint database[EB/OL]. http://www.comp.polyu.edu.hk/~biometrics/, 2016. [18] ZHANG D, LU Guangming, LI Wei, et al. Palmprint recognition using 3-D information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C (Applications and Reviews) , 2009, 39(5): 505–519. doi: 10.1109/TSMCC.2009.2020790 [19] ZHANG Lin, SHEN Ying, LI Hongyu, et al. 3D palmprint identification using block-wise features and collaborative representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(8): 1730–1736. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2372764 [20] 白雪飞, 高楠, 张宗华, 等. 基于分块ST与主成分分析的三维掌纹识别[J]. 天津大学学报:自然科学与工程技术版, 2018, 51(6): 631–637. doi: 10.11784/tdxbz201704065BAI Xuefei, GAO Nan, ZHANG Zonghua, et al. Three dimensional palmprint identification based on blocked ST and PCA[J]. Journal of Tianjin University:Science and Technology, 2018, 51(6): 631–637. doi: 10.11784/tdxbz201704065 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
