A PET-CT Lung Tumor Segmentation Method Based on Active Contour Model
-
摘要: 针对PET-CT肺肿瘤分割中存在的没有充分将医生临床经验融入到算法设计的问题,该文利用PET高斯分布先验,结合区域可伸缩拟合(RSF)模型和最大似然比分类(MLC)准则,提出一种基于变分水平集的混合活动轮廓模型RSF_ML。进一步,借鉴人工勾画肺肿瘤过程中融合图像的重要价值,提出了基于RSF_ML的PET-CT肺肿瘤融合图像分割方法。实验表明,所提出方法较好地实现了有代表性的非小细胞肺肿瘤(Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, NSCLC)的精确分割,主客观结果优于对比方法,可为临床提供有效的计算机辅助分割结果。Abstract: To solve the problem that the doctors' clinical experience is not fully integrated into the algorithm design in PET-CT lung tumor segmentation, a hybrid active contour model named RSF_ML based on variational level set is proposed by combining with the PET Gaussian distribution prior, Region Scalable Fitting (RSF) model and Maximum Likelihood ratio Classification (MLC) criterion. Furthermore, referring to the important value of fusion image in the process of lung tumor manual delineation, a segmentation method for PET-CT lung tumor fusion image based on RSF_ML is proposed. Experiments show that the proposed method can achieve accurate segmentation of representative Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC), and the subjective and objective results are better than the comparison method, which can provide effective computer-aided segmentation results for clinic.
-
表 1 基于RSF_ML模型的图像分割
输入:待分割图像像 输出:分割后的图像 步骤1:将水平集函数$ \scriptstyle\phi $初始化为二进制阶跃函数
$\scriptstyle \varphi (x,t=0)= $$\scriptstyle{\left\{\begin{aligned}& r,\quad\;\; x{\rm{在} }C{\text{内部} }\\ & -r,\quad {\text{其它} } \end{aligned}\right.}$,其中常量$ \scriptstyle r > 0 $;
步骤2:初始化水平集演化参数,如:迭代次数,$ \scriptstyle{\lambda _1} $, $\scriptstyle {\lambda _2} $, $\scriptstyle \mu $,
$ \scriptstyle\nu $, w, $ \scriptstyle\sigma $, r, $ \scriptstyle\Delta t $等;步骤3:根据式(10)—式(13)更新均值和方差; 步骤4:基于式(18)更新水平集函数$ \phi $; 步骤5:如果达到收敛,则终止迭代,否则返回步骤3。 表 2 各方法的DSC
图像 RSF_ML RSF RSF&LoG PET-CT PET CT PET-CT PET CT PET-CT PET CT I1 0.9585 0.9109 0.9390 0.9616 0.9112 0.9427 0.9627 0.9113 0.9543 I2 0.9945 0.8298 0.9941 0.9482 0.8301 0.9389 0.9660 0.8320 0.9394 I3 0.9970 0.8120 0.9800 0.9636 0.7859 0.9542 0.9821 0.8147 0.9689 I4 0.9898 0.8238 – 0.9635 0.7992 – 0.9661 0.8242 – I5 0.9823 0.8313 – 0.9112 0.6206 – 0.9144 0.6459 – I6 0.9498 0.9267 – 0.9191 0.8709 – 0.9214 0.8795 – I7 0.9899 0.9493 – 0.8825 0.9043 – 0.9273 0.9239 – I8 0.9814 0.7475 – 0.6731 0.7363 – 0.7795 0.7441 – I9 0.9902 0.8477 – 0.8874 0.7366 – 0.9637 0.8347 – mean±
std0.9815±
0.01640.8532±
0.06400.9710±
0.02860.9011±
0.09120.7995±
0.09330.9453±
0.00800.9315±
0.06170.8234±
0.08590.9542±
0.0147表 3 各方法的HD
图像 RSF_ML RSF RSF&LoG PET-CT PET CT PET-CT PET CT PET-CT PET CT I1 0.0693 0.0871 0.0681 0.0739 0.0881 0.0865 0.0817 0.0855 0.0879 I2 0.0117 0.0884 0.0137 0.0781 0.0864 0.0820 0.0576 0.0864 0.0806 I3 0.0020 0.0580 0.0239 0.0408 0.0531 0.0439 0.0203 0.0595 0.0298 I4 0.0257 0.2119 – 0.0825 0.2016 – 0.0775 0.2096 – I5 0.1362 0.3594 – 0.2976 0.6549 – 0.2692 0.6444 – I6 0.0192 0.0275 – 0.0273 0.0511 – 0.0273 0.0452 – I7 0.0164 0.0325 – 0.0869 0.0699 – 0.0688 0.0523 – I8 0.0568 0.2503 – 0.3604 0.2607 – 0.2744 0.2486 – I9 0.0364 0.2044 – 0.1859 0.3187 – 0.1022 0.2061 – mean±
std0.0415±
0.04160.1466±
0.11490.0352±
0.02890.1371±
0.11850.1983±
0.19710.0708±
0.02340.1088±
0.09590.1820±
0.18990.0661±
0.0317 -
[1] COSMA L, SOLLAKU S, FRANTELLIZZI V, et al. Early 18F-FDG PET/CT in COVID-19[J]. Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology, 2020, 64(5): 671–673. doi: 10.1111/1754-9485.13099 [2] SONG Yang, CAI Weidong, and FENG D D. Global context inference for adaptive abnormality detection in PET-CT images[C]. Proceedings of the 9th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Barcelona, Spain, 2012: 482–485. doi: 10.1109/ISBI.2012.6235589. [3] DONG Yunyun, YANG Wenkai, WANG Jiawen, et al. An improved supervoxel 3D region growing method based on PET/CT multimodal data for segmentation and reconstruction of GGNs[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2020, 79(3): 2309–2338. doi: 10.1007/s11042-019-08250-4 [4] JU Wei, XIANG Deihui, ZHANG Bin, et al. Random walk and graph cut for Co-segmentation of lung tumor on PET-CT images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(12): 5854–5867. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2488902 [5] LIAN Chunfeng, RUAN Su, DENŒUX T, et al. Joint tumor segmentation in PET-CT images using co-clustering and fusion based on belief functions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(2): 755–766. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2872908 [6] LI Laquan, LU Wei, TAN Yihua, et al. Variational PET/CT tumor co-segmentation integrated with PET restoration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Radiation and Plasma Medical Sciences, 2020, 4(1): 37–49. doi: 10.1109/TRPMS.2019.2911597 [7] FOSTER B, BAĞCI U, MANSOOR A, et al. A review on segmentation of positron emission tomography images[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2014, 50: 76–96. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2014.04.014 [8] LI Laquan, ZHAO Xiangming, LU Wei, et al. Deep learning for variational multimodality tumor segmentation in PET/CT[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 392: 277–295. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.10.099 [9] ZHAO Xiangming, LI Laquan, LU Wei, et al. Tumor co-segmentation in PET/CT using multi-modality fully convolutional neural network[J]. Physics in Medicine & Biology, 2019, 64(1): 015011. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/aaf44b [10] 叶锋, 李婉茹, 陈家祯, 等. 基于显著性区域检测和水平集的图像快速分割算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(11): 2661–2668. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170214YE Feng, LI Wanru, CHEN Jiazhen, et al. Image fast segmentation algorithm based on saliency region detection and level set[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(11): 2661–2668. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170214 [11] SONG Yangyang, PENG Guohua, SUN Dongwei, et al. Active contours driven by Gaussian function and adaptive-scale local correntropy-based K-means clustering for fast image segmentation[J]. Signal Processing, 2020, 174: 107625. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107625 [12] JIN Ri and WENG Guirong. Active contour model based on improved fuzzy c-means algorithm and adaptive functions[J]. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 2019, 78(11): 3678–3691. doi: 10.1016/j.camwa.2019.06.010 [13] GUO Lu, SHEN Shuming, HARRIS E, et al. A tri-modality image fusion method for target delineation of brain tumors in radiotherapy[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(11): e112187. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112187 [14] BALLANGAN C, WANG Xiuying, FULHAM M, et al. Lung tumor delineation in PET-CT images using a downhill region growing and a Gaussian mixture model[C]. Proceedings of the 18th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 2011: 2173–2176. doi: 10.1109/ICIP.2011.6116042. [15] LI Chunming, KAO C Y, GORE J C, et al. Minimization of region-scalable fitting energy for image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2008, 17(10): 1940–1949. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2008.2002304 [16] ZONG Jingjing, QIU Tianshuang, LI Weidong, et al. Automatic ultrasound image segmentation based on local entropy and active contour model[J]. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 2019, 78(3): 929–943. doi: 10.1016/j.camwa.2019.03.022 [17] DING Keyan, XIAO Linfang, and WENG Guirong. Active contours driven by region-scalable fitting and optimized Laplacian of Gaussian energy for image segmentation[J]. Signal Processing, 2017, 134: 224–233. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2016.12.021 -





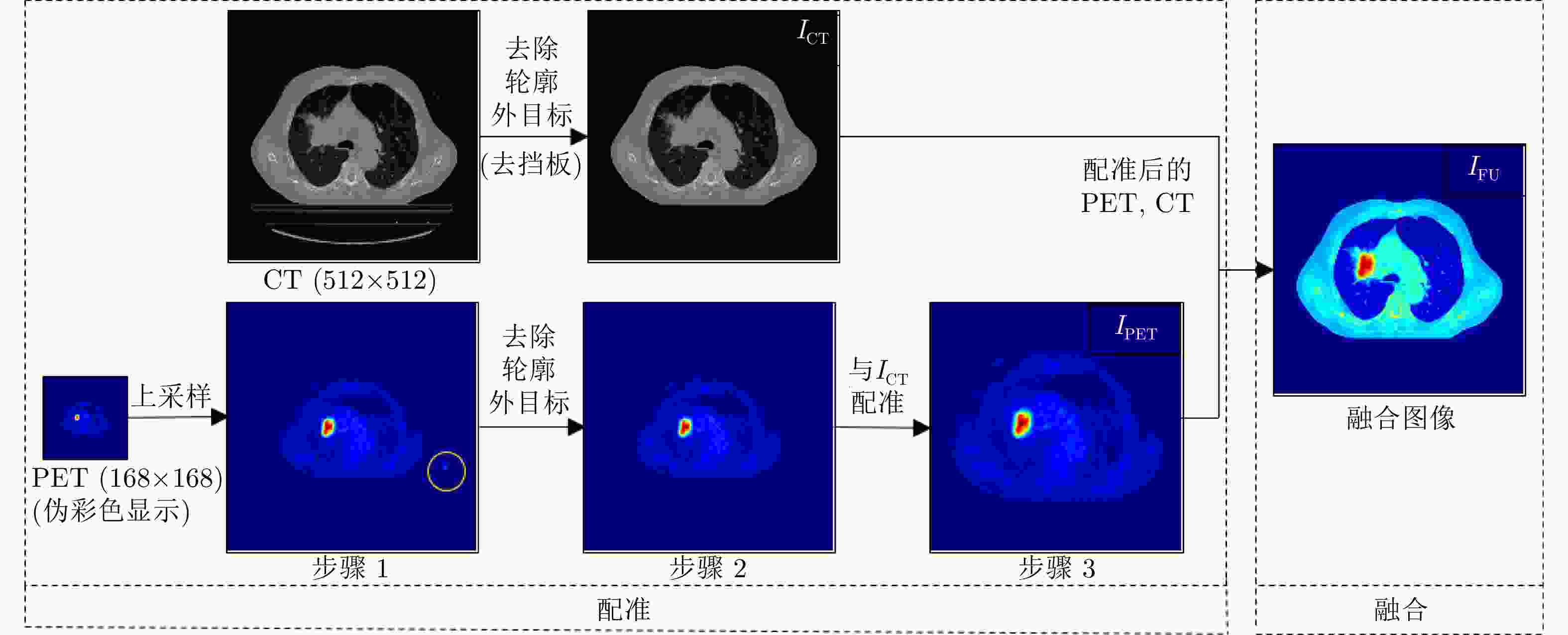
 下载:
下载:
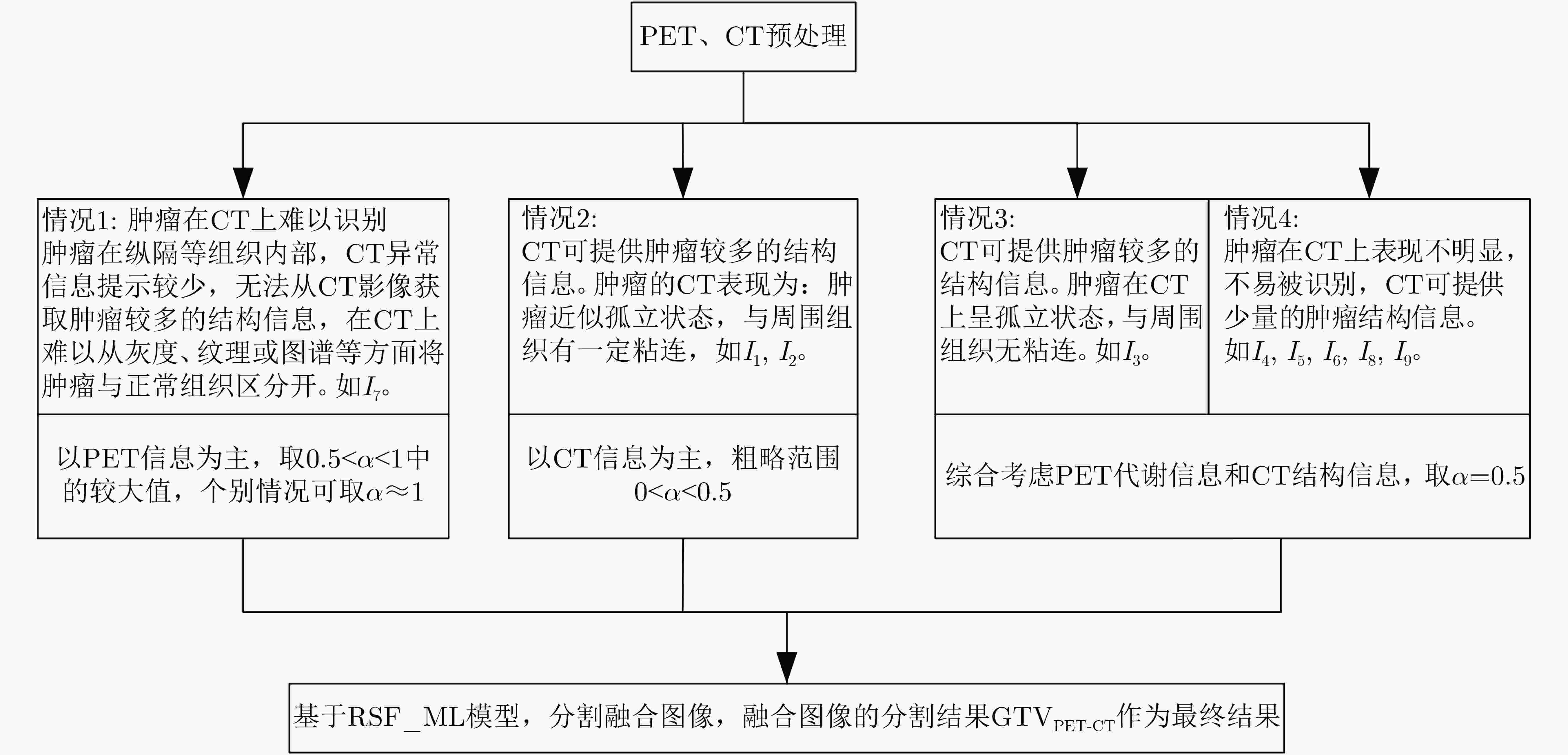
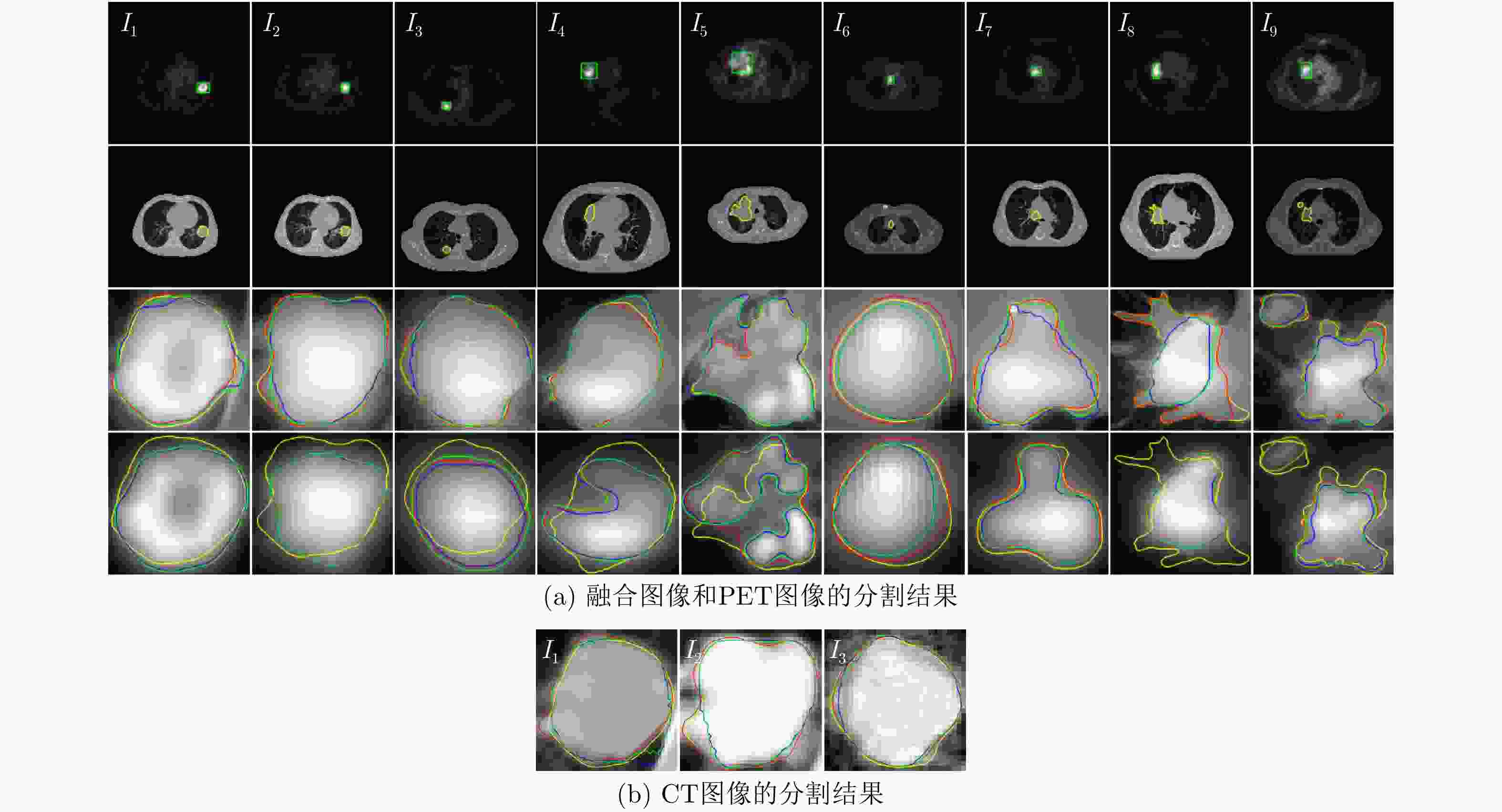


 下载:
下载:
