Research on Gesture Classification Methods in Amputee Subjects Based on Gray Theory Model
-
摘要: 针对截肢者手势动作特征提取复杂、动作识别率较低的问题,该文提出一种基于灰度模型的特征提取方法。首先对预处理后的肌电信号与加速度信号经滑动窗信号截取。然后提取表面肌电信号均值、灰度模型的驱动项系数和加速度信号的绝对值均值构成特征向量,最后对滑动窗截取信号特征进行连续的识别。该文采用NinaPro(Non invasive adaptive Prosthetics)公开数据集对提出的方法进行验证,实验表明该文算法能够有效提取肌电和加速度信号的特征,对9名截肢受试者的17类手势动作的平均识别率达到91.14%,提高了17类手势的识别准确率,为仿生假肢人机交互控制算法提供了一种新的思路。Abstract: In view of the complexity and low accuracy of feature extraction of amputees’ movement gestures, a feature extraction method based on gray model is proposed in this paper. Firstly, the pre-processed surface ElectroMyoGraphy (sEMG) and acceleration signals are intercepted by sliding window. Then, the mean value of the surface EMG signal, the driving coefficient of the gray model and the absolute mean value of the acceleration signal are extracted as features to form a feature vector. Finally, the features of the signal intercepted by sliding window are identified continuously. The proposed method is verified using NinaPro (Non Invasive Adaptive Prosthetics) public dataset, experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can effectively extract the characteristics of the electromyography and acceleration signals. An average accuracy of 91.14% is reached for 17 action gestures of 9 amputation subjects. The proposed approach provides a new way for the control algorithm of bionic limbs based human-computer interaction.
-
表 1 9位残疾人实验者在不同窗大小下的分类结果
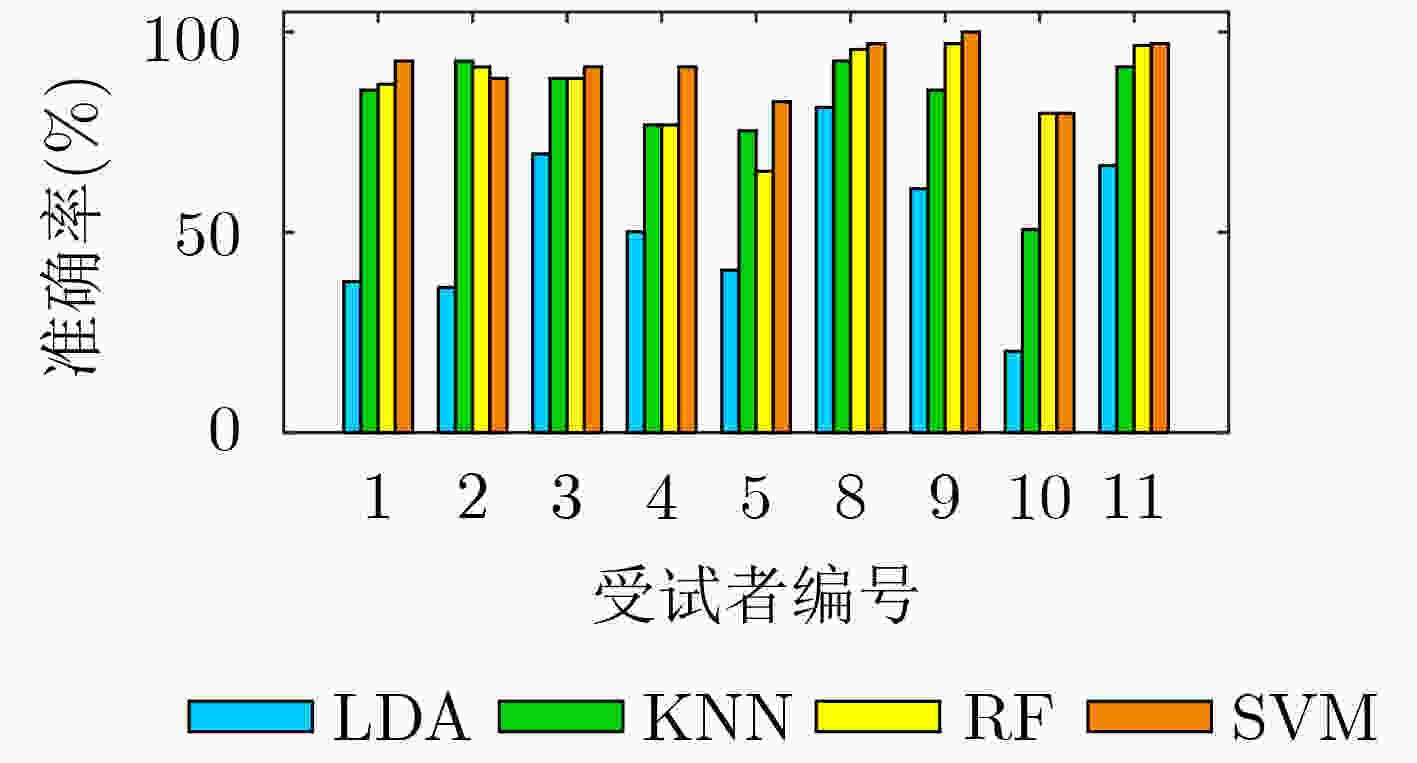
窗口长度 受试者编号 平均值 1 2 3 4 5 8 9 10 11 100 79.71 86.96 95.65 94.2 73.91 94.2 100 79.71 95.65 88.89 150 85.51 89.86 92.75 86.96 75.36 95.65 100 75.36 92.75 88.25 250 92.75 88.41 91.3 91.3 82.61 97.1 100 79.71 97.1 91.14 300 76.81 78.26 82.61 88.41 72.46 98.55 100 69.57 92.75 84.38 表 2 9位残疾人实验者分类结果
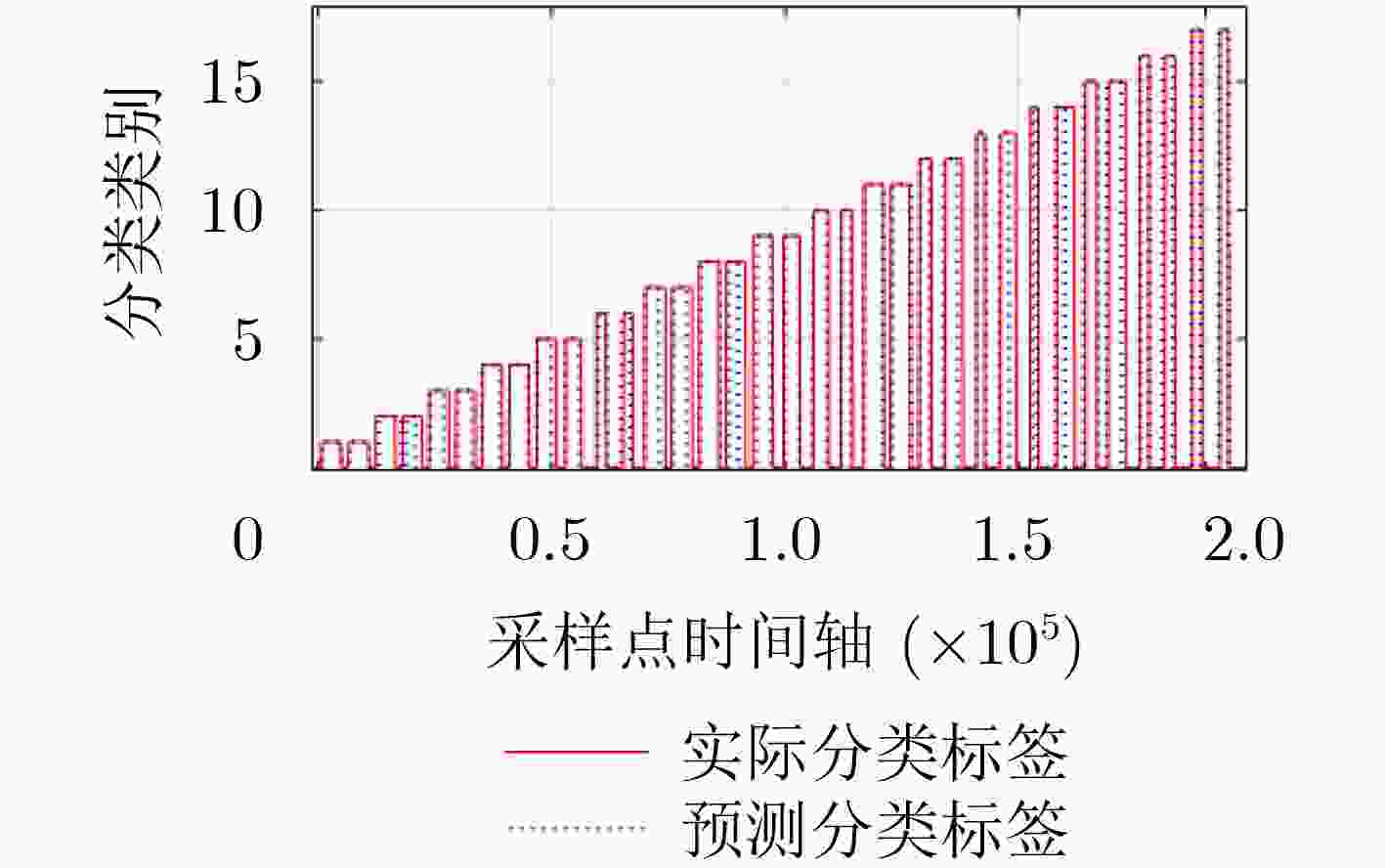
受试者编号 平均值 1 2 3 4 5 8 9 10 11 动作正确率(%) 92.75 88.41 91.30 91.3 82.61 97.1 100 79.71 97.1 91.14 MER 0.0725 0.1159 0.087 0.087 0.1739 0.029 0 0.2029 0.029 0.0886 时间轴错误率 0.2696 0.1861 0.1417 0.2368 0.4508 0.1585 0.1515 0.4364 0.1335 0.2405 表 3 本文与其他文献参数对比
文献 电极数 分类数 窗口大小 特征值 分类器 平均准确率(%) 受试者数量 受试者类型 [13] 12 10 150/50[1*] 4种时域特征 LDA 84.40 5 单截肢 [21] 8 7 250/50 MAV KNN 79.00 5 截肢者 [28] 6 8 100/NM[2*] CSSP[3*] LDA 80.30 1 截肢者 [15] 6 17 NM 功率谱密度 ANN 83.00 12 截肢者 [29] 12 17 250/50 WPT+MAVPCA SVM 88.80 9 截肢者 [16] 12 17 256/10 TD+TFD特征 RF 75.16 9 截肢者 [17] 16 17 300/10 6种特征 RVFL+ELM 63.10 10 截肢者 本文 12 17 250/50 灰度模型+Mean+MAV SVM 91.14 9 截肢者 小标说明: [1*]滑动窗口大小为150,增量为10,表3内窗口大小一列均为同格式。
[2*]NM(Not Mention):没有提到;
[3*]Common Spatio-Spectral Pattern -
[1] POLISIERO M, BIFULCO P, LICCARDO A, et al. Design and assessment of a low-Cost, electromyographically controlled, prosthetic hand[J]. Medical Devices: Evidence and Research, 2013, 2013: 97–104. doi: 10.2147/MDER.S39604 [2] 胡中旭. 虚拟场景人机交互中手势识别技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 华中科技大学, 2018.HU Zhongxu. Research on gesture recognition technology in human-computer interaction of virtual scene[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2018. [3] 曾海滨. 基于表面肌电控制的外骨骼手功能康复机器人研究[D]. [硕士论文], 山东大学, 2019.ZENG Haibin. A novel sEMG-controlled hand function exoskeleton robot for rehabilitation in post-stroke individuals[D]. [Master dissertation], Shandong University, 2019. [4] 邹俞, 晁建刚, 杨进. 航天员虚拟交互操作训练多体感融合驱动方法研究[J]. 图学学报, 2018, 39(4): 742–751.ZOU Yu, CHAO Jiangang, and YANG Jin. On multi-somatosensory driven method for virtual interactive operation training of astronaut[J]. Journal of Graphics, 2018, 39(4): 742–751. [5] 李晓宇. 基于手势交互的移动机器人三维环境探索及感知技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 哈尔滨工业大学, 2017.LI Xiaoyu. Research on unknown environment exploration and perception based on hand gesture interaction for mobile robots[D]. [Master dissertation], Harbin Institute of Technology, 2017. [6] 夏朝阳, 周成龙, 介钧誉, 等. 基于多通道调频连续波毫米波雷达的微动手势识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 164–172. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190797XIA Zhaoyang, ZHOU Chenglong, JIE Junyu, et al. Micro-motion gesture recognition based on multi-channel frequency modulated continuous wave millimeter wave radar[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 164–172. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190797 [7] 王勇, 吴金君, 田增山, 等. 基于FMCW雷达的多维参数手势识别算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(4): 822–829. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180485WANG Yong, WU Jinjun, TIAN Zengshan, et al. Gesture recognition with multi-dimensional parameter using FMCW radar[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(4): 822–829. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180485 [8] 马杰, 张绣丹, 杨楠, 等. 融合密集卷积与空间转换网络的手势识别方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(4): 951–956. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170627MA Jie, ZHANG Xiudan, YANG Nan, et al. Gesture recognition method combining dense convolutional with spatial transformer networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(4): 951–956. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170627 [9] 石欣, 朱家庆, 秦鹏杰, 等. 基于改进能量核的下肢表面肌电信号特征提取方法[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2020, 41(1): 121–128. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.j1905438SHI Xin, ZHU Jiaqing, QIN Pengjie, et al. Feature extraction method of lower limb surface EMG signal based on improved energy nucleus[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2020, 41(1): 121–128. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.j1905438 [10] SAUDABAYEV A, and VAROL H A. Sensors for robotic hands: A survey of state of the art[J]. IEEE Access, 2015, 3: 1765–1782. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2015.2482543 [11] LIU Lukai, LIU Pu, CLANCY E A, et al. Electromyogram whitening for improved classification accuracy in upper limb prosthesis control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2013, 21(5): 767–774. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2013.2243470 [12] 丁其川, 熊安斌, 赵新刚, 等. 基于表面肌电的运动意图识别方法研究及应用综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(1): 13–25. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c140563DING Qichuan, XIONG Anbin, ZHAO Xingang, et al. A review on researches and applications of sEMG-based motion intent recognition methods[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(1): 13–25. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c140563 [13] LI Guanglin, SCHULTZ A E, KUIKEN T A. Quantifying pattern recognition-based myoelectric control of multifunctional transradial prostheses[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2010, 18(2): 185–192. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2009.2039619 [14] 汪洋, 张定国. 针对上肢高位截肢者的肌电假肢设计[J]. 传感器与微系统, 2008, 37(4): 84–88, 91. doi: 10.13873/J.1000-9787(2018)04-0084-05WANG Yang and ZHANG Dingguo. Design of myoelectric upper-limb prosthesis towards amputees with high-level amputation[J]. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 2008, 37(4): 84–88, 91. doi: 10.13873/J.1000-9787(2018)04-0084-05 [15] JIRALERSPONG T, NAKANISHI E, LIU Chao, et al. Experimental study of real-time classification of 17 voluntary movements for multi-degree myoelectric prosthetic hand[J]. Applied Sciences, 2017, 7(11): 1163. doi: 10.3390/app7111163 [16] ROBINSON C P, LI Baihua, MENG Qinggang, et al. Effectiveness of surface electromyography in pattern classification for upper limb amputees[C]. Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Pattern Recognition, Beijing, China, 2018: 107–112. doi: 10.1145/3268866.3268889. [17] CENE V H and BALBINOT A. Enhancing the classification of hand movements through sEMG signal and non-iterative methods[J]. Health and Technology, 2019, 9(4): 561–577. doi: 10.1007/s12553-019-00315-6 [18] WANG Zhengxin and HAO Peng. An improved grey multivariable model for predicting industrial energy consumption in China[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2016, 40(11/12): 5745–5758. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2016.01.012 [19] 丁松, 党耀国, 徐宁. 基于虚拟变量控制的GM(1, N)模型构建及其应用[J]. 控制与决策, 2018, 33(2): 309–315. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2016.1613DING Song, DANG Yaoguo, and XU Ning. Construction and application of GM(1, N) based on control of dummy variables[J]. Control and Decision, 2018, 33(2): 309–315. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2016.1613 [20] NAIK G R, ARJUNAN S, and KUMAR D. Applications of ICA and fractal dimension in sEMG signal processing for subtle movement analysis: A review[J]. Australasian Physical & Engineering Sciences in Medicine, 2011, 34(2): 179–193. doi: 10.1007/s13246-011-0066-4 [21] CIPRIANI C, ANTFOLK C, CONTROZZI M, et al. Online myoelectric control of a dexterous hand prosthesis by transradial amputees[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2011, 19(3): 260–270. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2011.2108667 [22] 蒋贵虎, 陈万忠, 马迪, 等. 基于ITD和PLV的四类运动想象脑电分类方法研究[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2019, 40(5): 195–202. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.j1904651JIANG Guihu, CHEN Wanzhong, MA Di, et al. Research on four-class motor imagery EEG classification method based on ITD and PLV[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2019, 40(5): 195–202. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.j1904651 [23] ATZORI M, GIJSBERTS A, CASTELLINI C, et al. Effect of clinical parameters on the control of myoelectric robotic prosthetic hands[J]. Journal of Rehabilitation Research & Development, 2016, 53(3): 345–358. doi: 10.1682/JRRD.2014.09.0218 [24] GIJSBERTS A, ATZORI M, CASTELLINI C, et al. Movement error rate for evaluation of machine learning methods for sEMG-based hand movement classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2014, 22(4): 735–744. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2014.2303394 [25] 张思佳. 无线穿戴式表面肌电信号采集系统设计[D]. [硕士论文], 浙江大学, 2019.ZHANG Sijia. Design of wireless wearable surface EMG signal acquisition system[D]. [Master dissertation], Zhejiang University, 2019. [26] SMITH L H, HARGROVE L J, LOCK B A, et al. Determining the optimal window length for pattern recognition-based myoelectric control: Balancing the competing effects of classification error and controller delay[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2011, 19(2): 186–192. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2010.2100828 [27] TENORE F V G, RAMOS A, FAHMY A, et al. Decoding of individuated finger movements using surface electromyography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2009, 56(5): 1427–1434. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2008.2005485 [28] HUANG Gan, ZHANG Zhiguo, ZHANG Dingguo, et al. Spatio-spectral filters for low-density surface electromyographic signal classification[J]. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing, 2013, 51(5): 547–555. doi: 10.1007/s11517-012-1024-3 [29] 刘俊宏. 基于特征值降维与多元信号融合的手部动作识别算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 吉林大学, 2017.LIU Junhong. Recognition algorithms of hand movements based on feature dimensionality reduction and multiple signal fusion[D]. [Master dissertation], Jilin University, 2017. -






 下载:
下载:
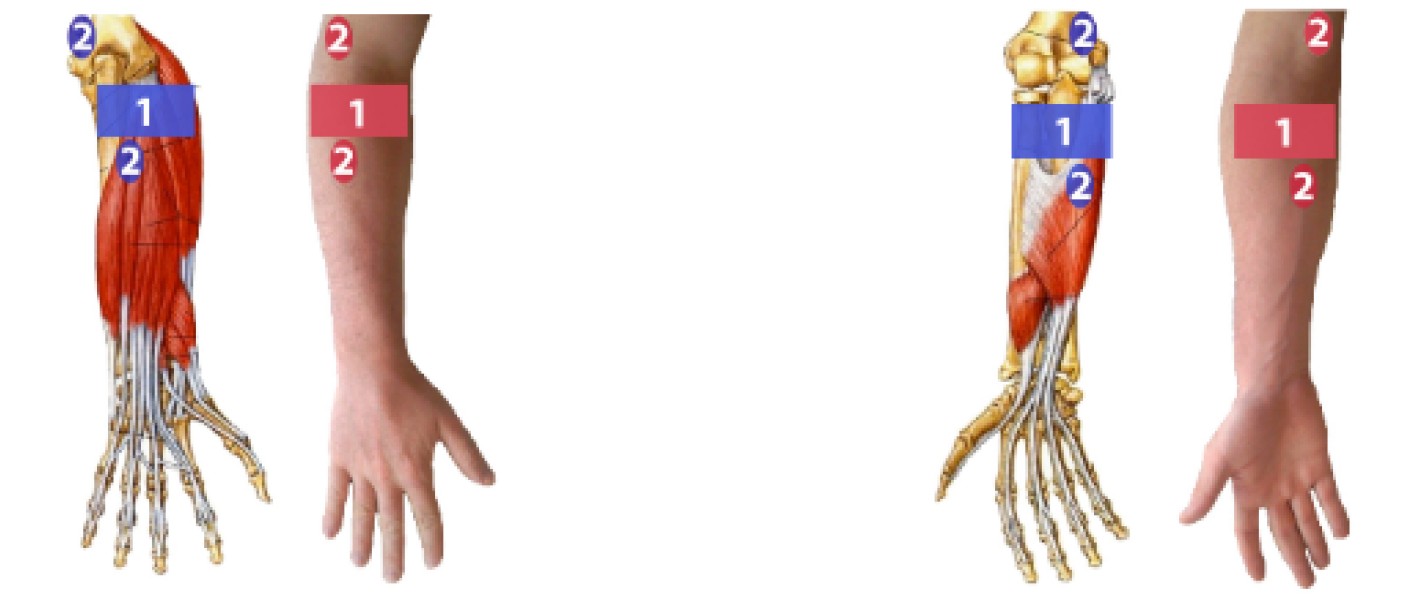

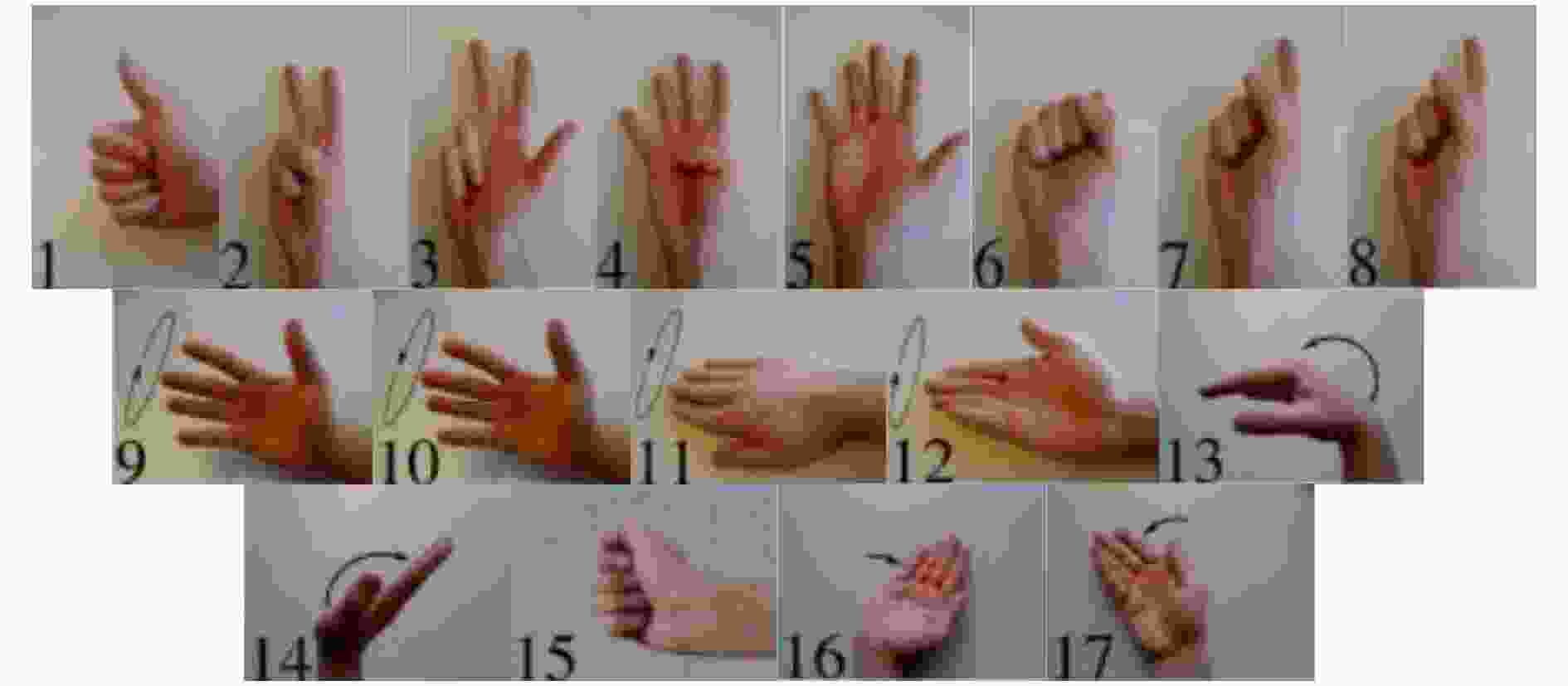
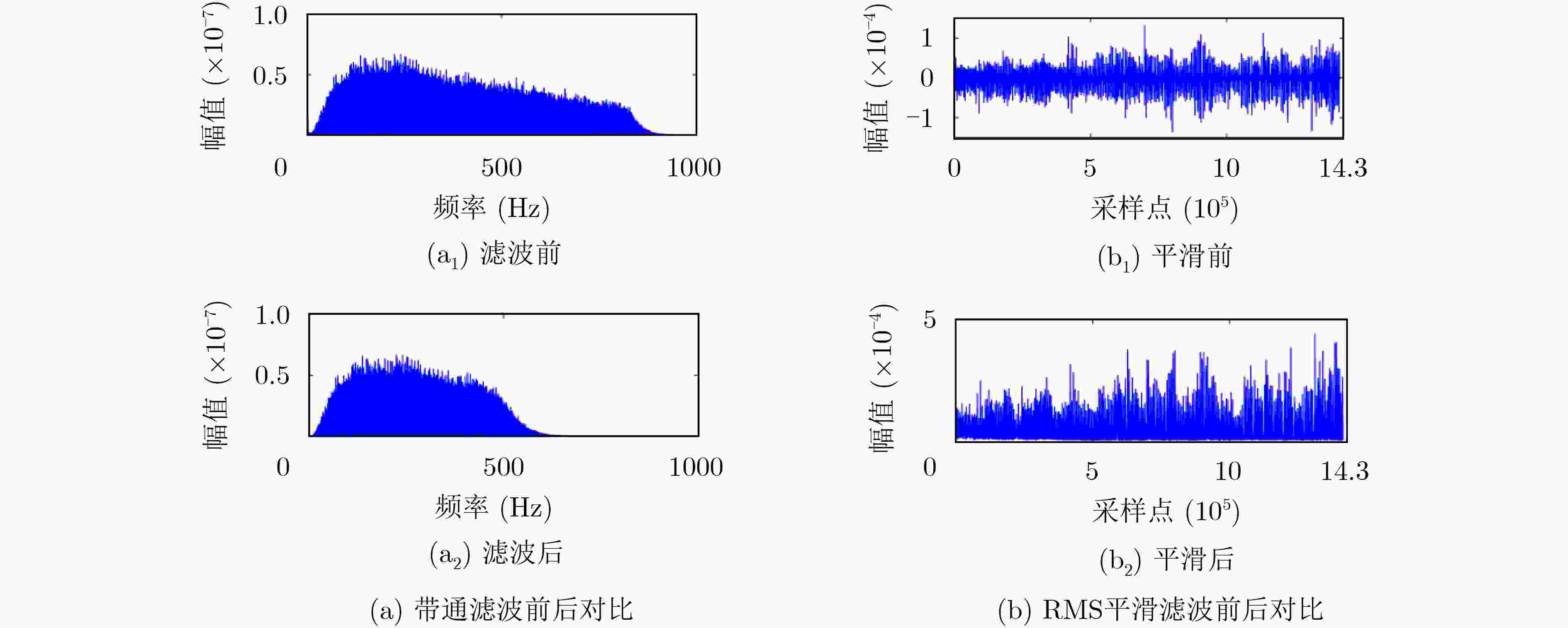
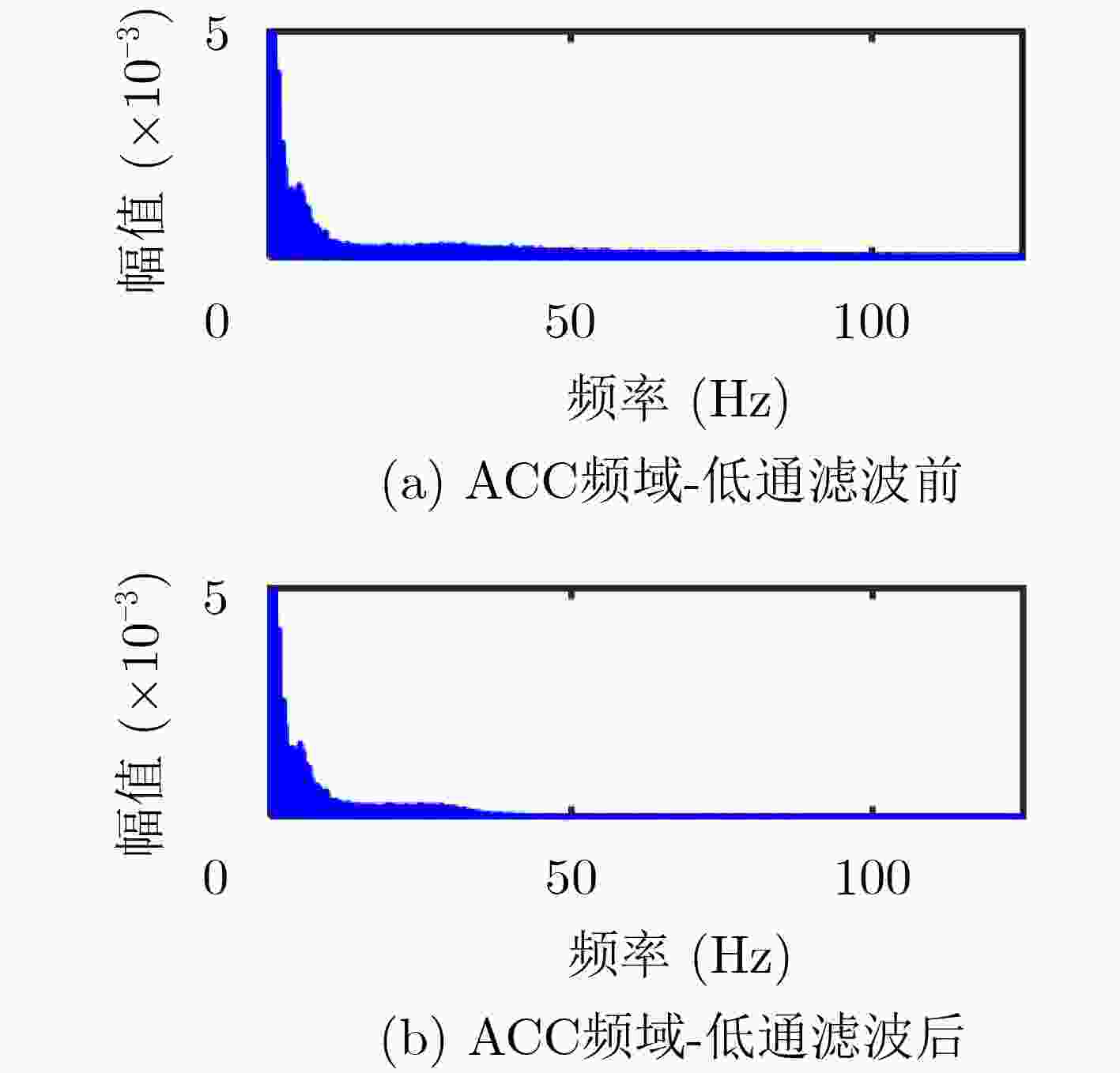
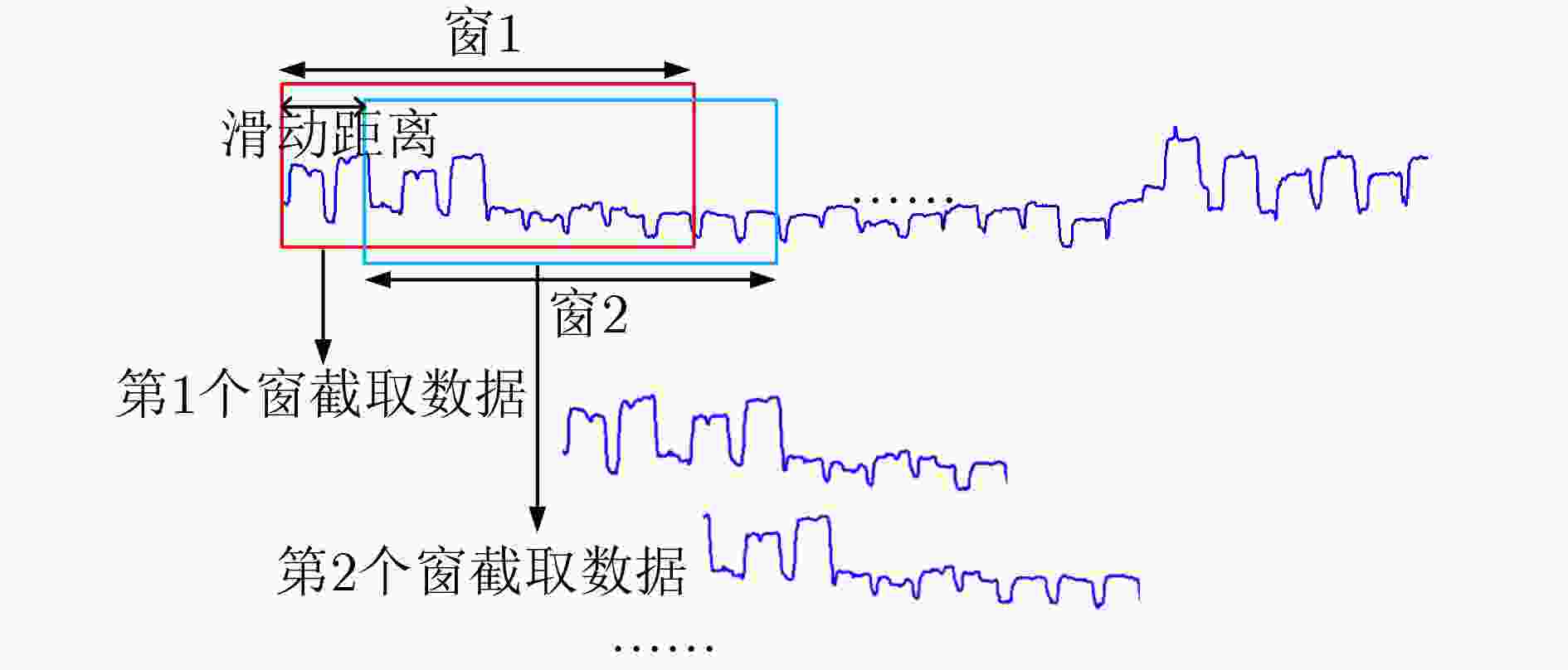


 下载:
下载:
