Load Balancing User Association and Resource Allocation Strategy in Time and Wavelength Division Multiplexed Passive Optical Network and Cloud Radio Access Network Joint Architecture
-
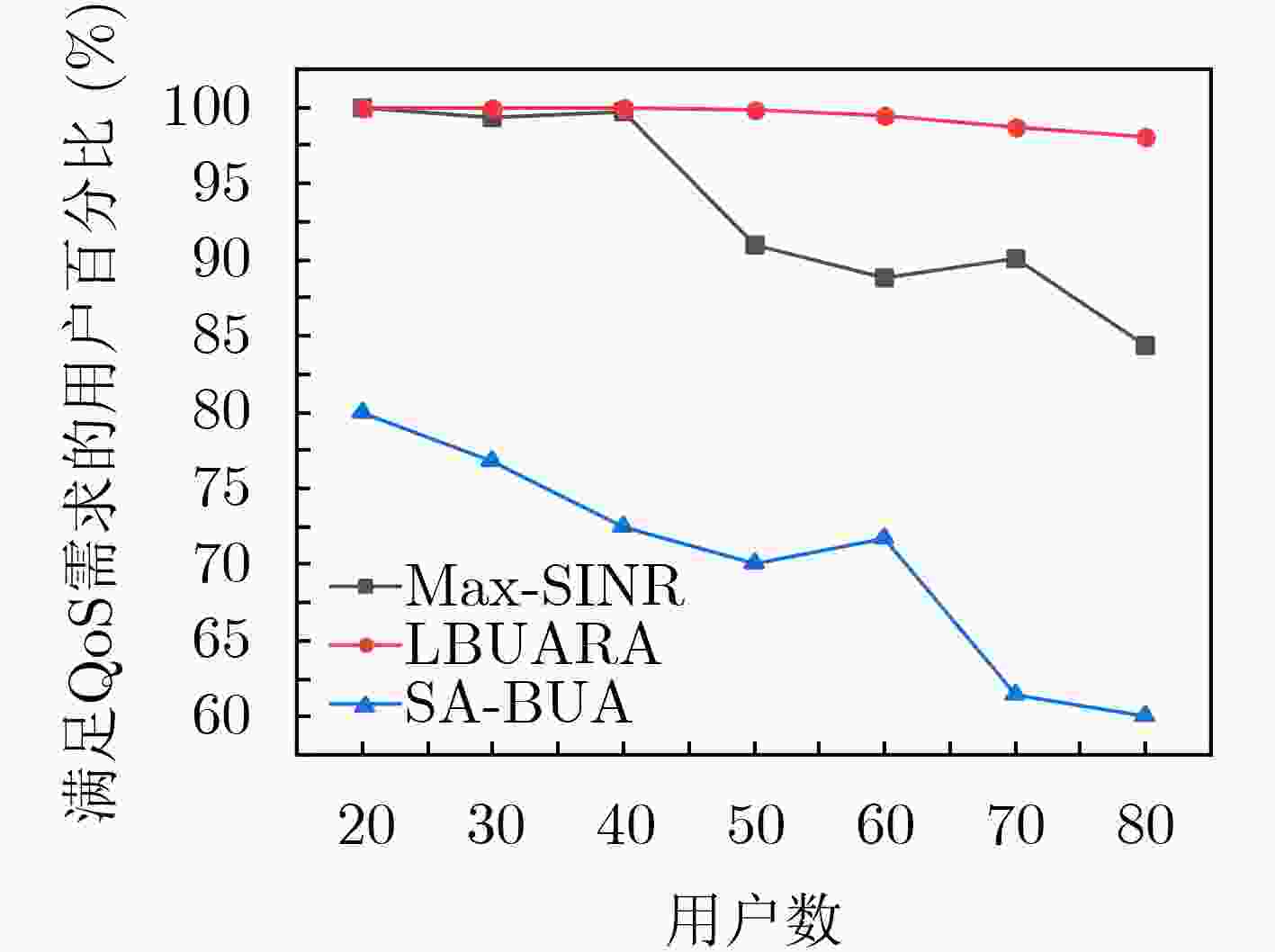
摘要: 在时分波分无源光网络(TWDM-PON)与云无线接入网(C-RAN)的联合架构中,由于无线域的负载不均衡问题,限制了网络整体的传输效率。为了充分利用TWDM-PON与C-RAN联合架构的网络资源,并保证用户的服务质量(QoS),该文提出一种负载平衡的用户关联与资源分配算法(LBUARA)。首先根据不同用户的服务质量需求以及分布式无线射频头端(RRH)的负载对用户的影响,构建用户收益函数。进而,在保证用户服务质量的前提下,根据网络状态建立随机博弈模型,并基于多智能体Q学习提出负载均衡的用户关联和资源分配算法,从而获得最优的用户关联与资源分配方案。仿真结果表明,所提的用户关联和资源分配策略能够实现网络的负载均衡,保证用户的服务质量,并提高网络吞吐量。Abstract: The load imbalance in the wireless domain limits the overall transmission efficiency of the network in the joint architecture of Time and Wavelength Division Multiplexed Passive Optical Network (TWDM-PON) and Cloud Radio Access Network (C-RAN). A Load Balancing User Association and Resource Allocation (LBUARA) algorithm is proposed to ensure the Quality of Service(QoS) of users, and make full use of network resources TWDM-PON jointly with C-RAN architecture. Firstly, the user revenue function is constructed according to the service quality requirements of different users and the impact of Remote Radio Head (RRH) load on users. Furthermore, a random game model is established according to the network state, under the premise of ensuring the quality of user service. A user association and resource allocation algorithm based on multi-agent Q-learning load balancing is proposed to obtain the optimal user association and resource allocation plan. The simulation results show that users association and resource allocation strategies mentioned can achieve load balancing network to ensure quality of service users, and improve network throughput.
-
表 1 负载均衡的用户关联和资源分配算法
(1) 初始化episode,每个用户的Q值${Q_i}(s,{a_i})$以及${\phi _i}({s_i},{a_i})$ (2) for each step of an episode to t steps do (3) for each UE i do (4) 在状态${s_i}$时通过式(21)选择动作${a_i}$ (5) 通过式(7)计算为每个用户分配的RB数量 (6) 通过式(13)计算Vi (7) 每个用户获取关联状态$s'$,设置 $s' \to s$ (8) 通过式(20)更新${Q_i}(s,{a_i})$ (9) 更新${\phi _i}({s_i},{a_i})$ (10) end for (11) if 当前状态集合$S = \{ 1,1,···,1\} $ (12) break (13) end if (14) 最终所有的用户得到关联策略$({s_i},{a_i})$ -
[1] REN Hong, LIU Nan, PAN Cunhua, et al. Low-latency C-RAN: An next-generation wireless approach[J]. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 2018, 13(2): 48–56. doi: 10.1109/MVT.2018.2811244 [2] ZHAO Wentao and WANG Shaowei. Traffic density-based RRH selection for power saving in C-RAN[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2016, 34(12): 3157–3167. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2016.2600414 [3] KALIL M, Al-DWEIK A, SHARKH M A, et al. A framework for joint wireless network virtualization and cloud radio access networks for next generation wireless networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 20814–20827. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2746666 [4] SIMEONE O, MAEDER A, PENG Mugen, et al. Cloud radio access network: Virtualizing wireless access for dense heterogeneous systems[J]. Journal of Communications and Networks, 2016, 18(2): 135–149. doi: 10.1109/JCN.2016.000023 [5] ZHANG Zhiguo, CHEN Yanxu, CAI Shanyong, et al. Colorless-light and tunable-light-source schemes for TWDM and WDM PONs[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2018, 56(8): 120–128. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2018.1700751 [6] WANG Xinbo, CAVDAR C, WANG Lin, et al. Virtualized cloud radio access network for 5G transport[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2017, 55(9): 202–209. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2017.1600866 [7] 王汝言, 徐宁宁, 吴大鹏. 能耗和时延感知的虚拟化云无线接入网络资源分配机制[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(1): 83–90. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180063WANG Ruyan, XU Ningning, and WU Dapeng. Energy consumption and delay-aware resource allocation mechanism for virtualization cloud radio access network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(1): 83–90. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180063 [8] ALNOMAN A, CARVALHO G H S, ANPALAGAN A, et al. Energy efficiency on fully cloudified mobile networks: Survey, challenges, and open issues[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2018, 20(2): 1271–1291. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2017.2780238 [9] WU Dapeng, ZHANG Zhihao, WU Shaoen, et al. Biologically inspired resource allocation for network slices in 5G-enabled internet of things[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(6): 9266–9279. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2888543 [10] ALI M, RABBANI Q, NAEEM M, et al. Joint user association, power allocation, and throughput maximization in 5G H-CRAN networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(10): 9254–9262. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2715229 [11] 王汝言, 李宏娟, 吴大鹏. 基于Stackelberg博弈的虚拟化无线传感网络资源分配策略[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(2): 377–384. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180277WANG Ruyan, LI Hongjuan, and WU Dapeng. Stackelberg game-based resource allocation strategy in virtualized wireless sensor network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(2): 377–384. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180277 [12] ELHATTAB M K, ELMESALAWY M M, and ISMAIL T. Fronthaul-aware user association in 5G heterogeneous cloud radio access networks: A matching game perspective[C]. 2018 International Symposium on Networks, Computers and Communications (ISNCC), Rome, Italy, 2018. doi: 10.1109/ISNCC.2018.8531056. [13] WU Dapeng, LIU Jia, and YANG Zhigang. Bilateral satisfaction aware participant selection with MEC for mobile crowd sensing[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 48110–48122. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2978774 [14] SU Gongchao, CHEN Bin, LIN Xiaohui, et al. A sequential auction game for QoS-aware user association in heterogeneous cellular networks[C]. Proceedings of 2018 Tenth International Conference on Ubiquitous and Future Networks (ICUFN), Prague, Czech Republic, 2018: 464–468. doi: 10.1109/ICUFN.2018.8436793. [15] GE Xin, LI Xiuhua, JIN Hu, et al. Joint user association and user scheduling for load balancing in heterogeneous networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2018, 17(5): 3211–3225. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2018.2808488 [16] PROSKOCHYLO A, ZRIAKHOV M, and AKULYNICHEV A. The effects of queueing algorithms on QoS for real-time traffic in process of load balancing[C]. 2018 International Scientific-Practical Conference Problems of Infocommunications. Science and Technology (PIC S&T), Kharkiv, Ukraine, 2018: 575–580. doi: 10.1109/INFOCOMMST.2018.8632161. [17] WANG Feng, CHEN Wen, TANG Hongying, et al. Joint optimization of user association, subchannel allocation, and power allocation in multi-cell multi-association OFDMA heterogeneous networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2017, 65(6): 2672–2684. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2017.2678986 [18] AWAIS M, AHMED A, NAEEM M, et al. Efficient joint user association and resource allocation for cloud radio access networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 1439–1448. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2663758 [19] 王汝言, 池文祥, 张鸿. WOBAN中基于令牌桶算法的自适应流量整形策略[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(6): 1401–1408. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160974WANG Ruyan, CHI Wenxiang, and ZHANG Hong. Adaptive traffic shaping policy based on token bucket algorithm of wireless-optical broadband access network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(6): 1401–1408. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160974 [20] WANG Kaidi, LIU Yuanwei, DING Zhiguo, et al. User association and power allocation for multi-cell non-orthogonal multiple access networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(11): 5284–5298. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2935433 [21] SCHERER W T, ADAMS S, and BELING P A. On the practical art of state definitions for Markov decision process construction[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 21115–21128. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2819940 [22] JANG B, KIM M, HARERIMANA G, et al. Q-learning algorithms: A comprehensive classification and applications[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 133653–133667. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2941229 [23] LI Dong, ZHANG Haijun, LONG Keping, et al. User association and power allocation based on q-learning in ultra dense heterogeneous networks[C]. 2019 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Waikoloa, USA, 2019: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/GLOBECOM38437.2019.9013455. [24] ZHAO Nan, LIANG Yingchang, NIYATO D, et al. Deep reinforcement learning for user association and resource allocation in heterogeneous cellular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(11): 5141–5152. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2933417 [25] CHEN Xianfu, ZHAO Zhifeng, and ZHANG Honggang. Stochastic power adaptation with multiagent reinforcement learning for cognitive wireless mesh networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2013, 12(11): 2155–2166. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2012.178 [26] SEDIQ A B, GOHARY R H, SCHOENEN R, et al. Optimal tradeoff between sum-rate efficiency and Jain’s fairness index in resource allocation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2013, 12(7): 3496–3509. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2013.061413.121703 -





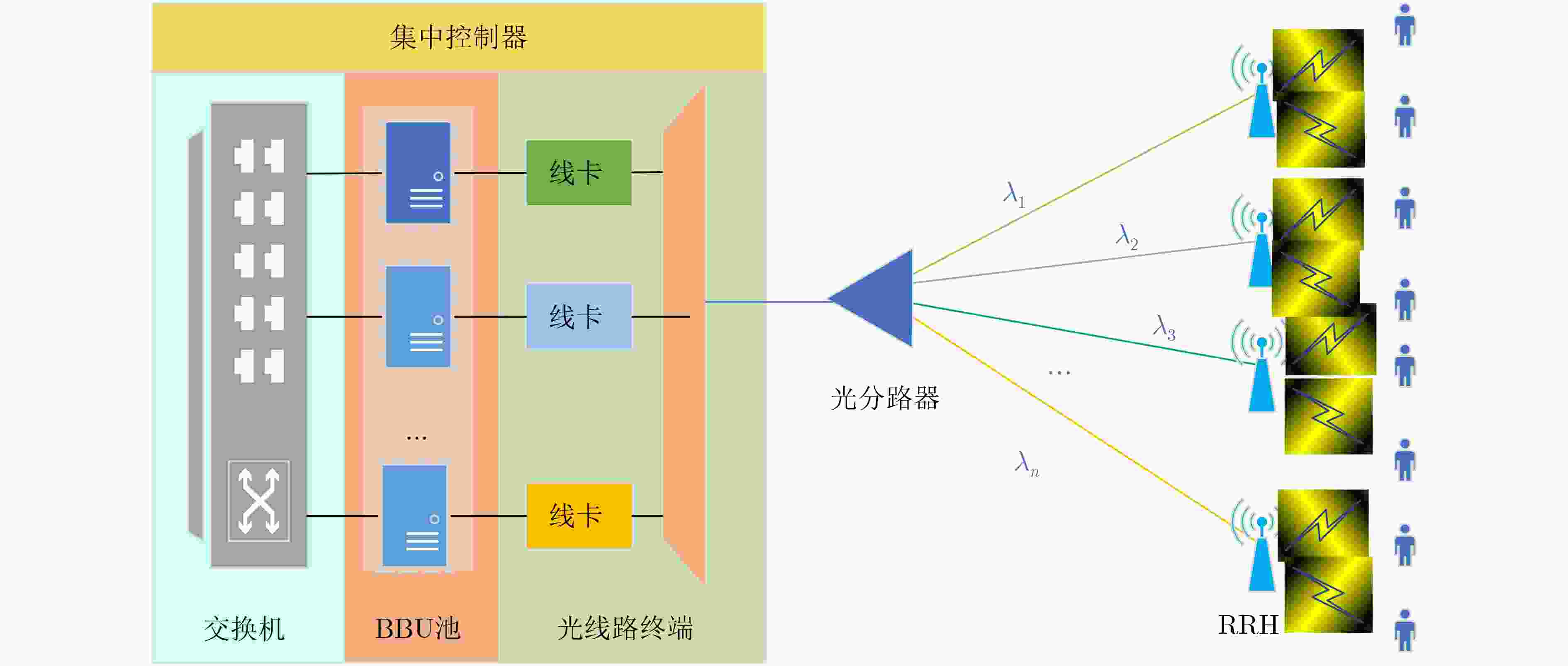
 下载:
下载:
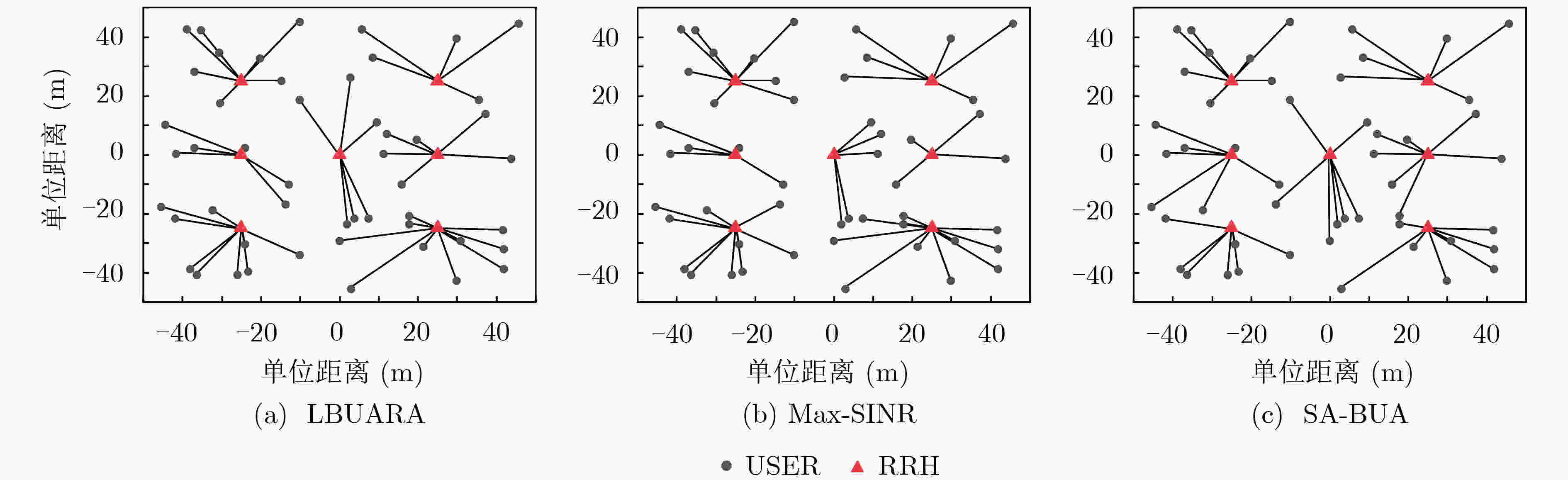
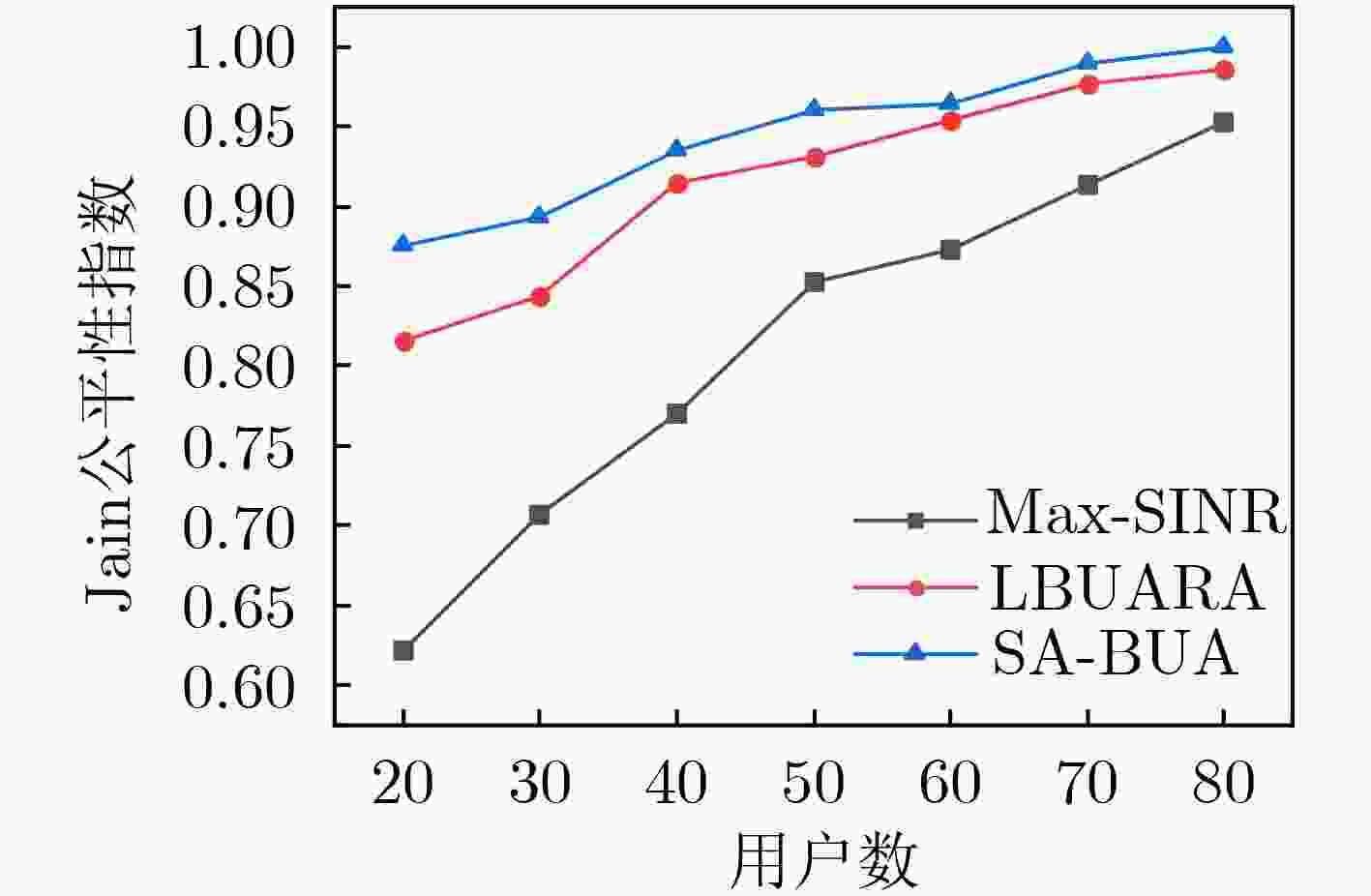
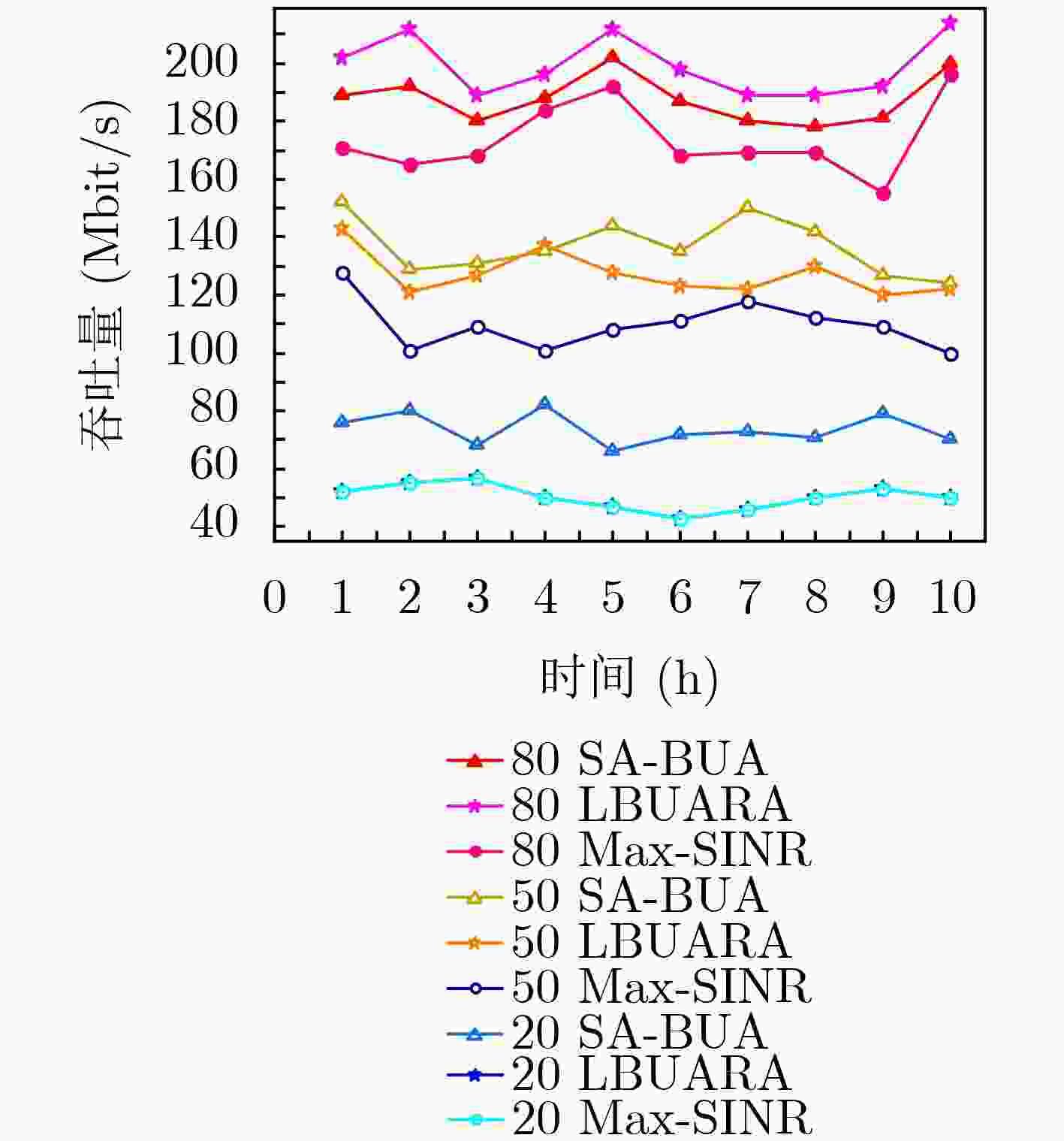


 下载:
下载:
