| [1] |
HAYKIN S. Cognitive radar: A way of the future[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2006, 23(1): 30–40. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2006.1593335
|
| [2] |
黎湘, 范梅梅. 认知雷达及其关键技术研究进展[J]. 电子学报, 2012, 40(9): 1863–1870. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2012.09.025LI Xiang and FAN Meimei. Research advance on cognitive radar and its key technology[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2012, 40(9): 1863–1870. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2012.09.025
|
| [3] |
HAYKIN S. Cognition is the key to the next generation of radar systems[C]. The 2009 IEEE 13th Digital Signal Processing Workshop and 5th IEEE Signal Processing Education Workshop, Marco Island, USA, 2009: 463–467.
|
| [4] |
赵国庆. 雷达对抗原理[M]. 2版. 西安: 西安电子科技大学出版社, 2012.ZHAO Guoqing. Principle of Radar Countermeasure[M]. 2nd ed. Xi’an: Xidian University Press, 2012.
|
| [5] |
李光久, 李昕. 博弈论简明教程[M]. 镇江: 江苏大学出版社, 2013.LI Guangjiu and LI Xin. A Brief Tutorial on Game Theory[M]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University Press, 2013.
|
| [6] |
TOPKIS D M. Supermodularity and Complementarity[M]. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1998: 212–214.
|
| [7] |
邹鲲. 认知雷达的未知目标检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(1): 166–172. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170254ZOU Kun. Unknown target detection for cognitive radar[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(1): 166–172. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170254
|
| [8] |
XUE Yanbo. Cognitive radar: Theory and simulations[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], The McMaster University, 2010.
|
| [9] |
HAYKIN S, XUE Yanbo, and SETOODEH P. Cognitive radar: Step toward bridging the gap between neuroscience and engineering[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2012, 100(11): 3102–3130. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2012.2203089
|
| [10] |
GUERCI J R. Cognitive Radar: The Knowledge-Aided Fully Adaptive Approach[M]. Boston: Artech House, 2010.
|
| [11] |
左群声, 王彤. 认知雷达导论[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2017.ZUO Qunsheng and WANG Tong. Introduction to Cognitive Radar[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2017.
|
| [12] |
张良, 祝欢, 杨予昊, 等. 机载预警雷达技术及信号处理方法综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(12): 3298–3306. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161007ZHANG Liang, ZHU Huan, YANG Yuhao, et al. Overview on airborne early warning radar technology and signal processing methods[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(12): 3298–3306. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161007
|
| [13] |
SHARAGA N, TABRIKIAN J, and MESSER H. Optimal cognitive beamforming for target tracking in MIMO radar/sonar[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2015, 9(8): 1440–1450. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2015.2467354
|
| [14] |
BEN KILANI M, NIJSURE Y, GAGNON G, et al. Cognitive waveform and receiver selection mechanism for multistatic radar[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2016, 10(2): 417–425. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2015.0319
|
| [15] |
YAO Yu, MIAO Pu, and CHEN Zhimin. Cognitive waveform optimization for phase-modulation-based joint radar-communications system[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 33276–33288. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2974787
|
| [16] |
ESMAEILI-NAJAFABADI H, LEUNG H, and MOO P W. Unimodular waveform design with desired ambiguity function for cognitive radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(3): 2489–2496. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2942411
|
| [17] |
BELL K L, BAKER C J, SMITH G E, et al. Cognitive radar framework for target detection and tracking[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2015, 9(8): 1427–1439. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2015.2465304
|
| [18] |
GUI Ronghua, WANG Wenqin, PAN Ye, et al. Cognitive target tracking via angle-range-Doppler estimation with transmit subaperturing FDA radar[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2018, 12(1): 76–89. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2018.2793761
|
| [19] |
WEN Cai, HUANG Yan, WU Jianxin, et al. Cognitive anti-deception-jamming for airborne array radar via phase-only pattern notching with nested ADMM[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 153660–153674. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2948507
|
| [20] |
KIRK B H, NARAYANAN R M, GALLAGHER K A, et al. Avoidance of time-varying radio frequency interference with software-defined cognitive radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 55(3): 1090–1107. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2886614
|
| [21] |
KARIMI V, MOHSENI R, and SAMADI S. Adaptive OFDM waveform design for cognitive radar in signal-dependent clutter[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2020, 14(3): 3630–3640. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2019.2943809
|
| [22] |
LIU Xinghua, XU Zhenhai, WANG Luoshengbin, et al. Cognitive dwell time allocation for distributed radar sensor networks tracking via cone programming[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(10): 5092–5101. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.2970280
|
| [23] |
DU Yi, LIAO Kefei, OUYANG Shan, et al. Time and aperture resource allocation strategy for multitarget ISAR imaging in a radar network[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(6): 3196–3206. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2954711
|
| [24] |
KRISHNAMURTHY V, ANGLEY D, EVANS R, et al. Identifying cognitive radars - inverse reinforcement learning using revealed preferences[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 4529–4542. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.3013516
|
| [25] |
GOGINENI S and NEHORAI A. Game theoretic approach for polarimetric MIMO radar waveform design[C]. 2012 International Waveform Diversity & Design Conference, Kauai, USA, 2012: 59–62.
|
| [26] |
Dix J P. Game-theoretic applications[J]. IEEE Spectrum, 1968, 5(4): 108–117. doi: 10.1109/MSPEC.1968.5214595.
|
| [27] |
ZETTERBERG L H. Signal detection under noise interference in a game situation[J]. IRE Transactions on Information Theory, 1962, 8(5): 47–52. doi: 10.1109/TIT.1962.1057773
|
| [28] |
LIPFORD J. A game theoretic method of obtaining a given return from a minimum weight of radar reflectors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1963, 11(2): 193. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1963.1137988
|
| [29] |
SPEYER J L. A stochastic differential game with controllable statistical parameters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems Science and Cybernetics, 1967, 3(1): 17–20. doi: 10.1109/TSSC.1967.300103
|
| [30] |
徐友云, 李大鹏, 钟卫, 等. 认知无线电网络资源分配: 博弈模型与性能分析[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2013.XU Youyun, LI Dapeng, ZHONG Wei, et al. Resource Management of Cognitive Radio Networks: Game Theoretic Modeling and Performance Analysis[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2013.
|
| [31] |
MITOLA J and MAGUIRE G Q. Cognitive radio: Making software radios more personal[J]. IEEE Personal Communications, 1999, 6(4): 13–18. doi: 10.1109/98.788210
|
| [32] |
BACHMANN D J, EVANS R J, and MORAN B. Game theoretic analysis of adaptive radar jamming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(2): 1081–1100. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2011.5751244
|
| [33] |
冯明月, 何明浩, 郁春来, 等. 相控阵雷达噪声干扰博弈分析[J]. 现代雷达, 2014, 36(5): 10–14, 30. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2014.05.010FENG Mingyue, HE Minghao, YU Chunlai, et al. Game theory analysis of noise jamming for phased array radar[J]. Modern Radar, 2014, 36(5): 10–14, 30. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2014.05.010
|
| [34] |
PANOUI A, LAMBOTHARAN S, and CHAMBERS J A. Game theoretic power allocation technique for a MIMO radar network[C]. The 2014 6th International Symposium on Communications, Control and Signal Processing, Athens, Greece, 2014: 509–512.
|
| [35] |
BACCI G, SANGUINETTI L, GRECO M S, et al. A game-theoretic approach for energy-efficient detection in radar sensor networks[C]. The 2012 IEEE 7th Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal Processing Workshop, Hoboken, USA, 2012: 157–160.
|
| [36] |
GODRICH H, PETROPULU A P, and POOR H V. Power allocation strategies for target localization in distributed multiple-radar architectures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(7): 3226–3240. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2144976
|
| [37] |
SLIMENI F, LE NIR V, SCHEERS B, et al. Optimal power allocation over parallel Gaussian channels in cognitive radio and jammer games[J]. IET Communications, 2016, 10(8): 980–986. doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2015.0976
|
| [38] |
PANOUI A, LAMBOTHARAN S, and CHAMBERS J A. Game theoretic power allocation for a multistatic radar network in the presence of estimation error[C]. 2014 Sensor Signal Processing for Defence, Edinburgh, UK, 2014: 1–5.
|
| [39] |
DELIGIANNIS A, PANOUI A, LAMBOTHARAN S, et al. Game-theoretic power allocation and the nash equilibrium analysis for a multistatic MIMO radar network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(24): 6397–6408. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2755591
|
| [40] |
DELIGIANNIS A and LAMBOTHARAN S. A Bayesian game theoretic framework for resource allocation in multistatic radar networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Radar Conference, Seattle, USA, 2017: 546–551.
|
| [41] |
WAN Kaifang, GAO Xiaoguang, LI Bo, et al. Optimal power management for antagonizing between radar and jamming based on continuous game theory[J]. Transactions of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2014, 31(4): 386–393. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-1120.2014.04.005
|
| [42] |
SUN Bin, CHEN Haowen, WEI Xizhang, et al. Power allocation for range-only localisation in distributed multiple-input multiple-output radar networks - a cooperative game approach[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2014, 8(7): 708–718. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2013.0260
|
| [43] |
CHEN Haowen, TA Shiying, and SUN Bin. Cooperative game approach to power allocation for target tracking in distributed MIMO radar sensor networks[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2015, 15(10): 5423–5432. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2015.2431261
|
| [44] |
SHI C G, SALOUS S, ZHOU J J, et al. Cooperative game-theoretic power allocation algorithm for target detection in radar network[C]. The 32nd General Assembly and Scientific Symposium of the International Union of Radio Science, Montreal, Canada, 2017: 1–4.
|
| [45] |
SHI Chenguang, SALOUS S, WANG Fei, et al. Power allocation for target detection in radar networks based on low probability of intercept: A cooperative game theoretical strategy[J]. Radio Science, 2017, 52(8): 1030–1045. doi: 10.1002/2017RS006332
|
| [46] |
LIU Yanqing and DONG Liang. Spectrum sharing in MIMO cognitive radio networks based on cooperative game theory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2014, 13(9): 4807–4820. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2014.2331287
|
| [47] |
GAO Hai, WANG Jian, JIANG Chunxiao, et al. Equilibrium between a statistical MIMO radar and a jammer[C]. IEEE Radar Conference, Arlington, USA, 2015: 461–466.
|
| [48] |
WONDERLEY D, SELEE T, and CHAKRAVARTHY V. Game theoretic decision support framework for electronic warfare applications[C]. 2016 IEEE Radar Conference, Philadelphia, USA, 2016: 1–5.
|
| [49] |
WANG Lulu, WANG Liandong, ZENG Yonghu, et al. Radar and jammer power allocation strategy based on matrix game[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2017, 107: 478–483. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2017.03.093
|
| [50] |
DELIGIANNIS A, ROSSETTI G, PANOUI A, et al. Power allocation game between a radar network and multiple jammers[C]. 2016 IEEE Radar Conference, Philadelphia, USA, 2016: 1–5.
|
| [51] |
HENAREH N and NOROUZI Y. Game theory modeling of MIMO radar and ARM missile engagement[C]. The 2016 8th International Symposium on Telecommunications, Tehran, Iran, 2016: 515–520.
|
| [52] |
SONG Xiufeng, WILLETT P, ZHOU Shengli, et al. The power game between a MIMO radar and jammer[C]. 2012 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Kyoto, Japan, 2012: 5185–5188.
|
| [53] |
SONG Xiufeng, WILLETT P, ZHOU Shengli, et al. The MIMO radar and jammer games[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 60(2): 687–699. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.216925
|
| [54] |
ZHANG Xinxun, MA Hui, WANG Jianlai, et al. Game theory design for deceptive jamming suppression in polarization MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 114191–114202. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2931604
|
| [55] |
SONG Xiufeng, WILLETT P, and ZHOU Shengli. Jammer detection and estimation with MIMO radar[C]. 2012 Conference Record of the Forty Sixth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, USA, 2012: 1312–1316.
|
| [56] |
LI Kang, JIU Bo, and LIU Hongwei. Game theoretic strategies design for monostatic radar and jammer based on mutual information[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 72257–72266. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2920398
|
| [57] |
NOROUZI T and NOROUZI Y. Scheduling the usage of radar and jammer during peace and war time[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2012, 6(9): 929–936. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2012.0049
|
| [58] |
LIU Xiaowen, ZHANG Qun, LUO Ying, et al. ISAR imaging task allocation for multi-target in radar network based on potential game[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(23): 11192–11204. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2936423
|
| [59] |
PIEZZO M, AUBRY A, and BUZZI S, et al. Non-cooperative code design in radar networks: A game-theoretic approach[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2013, 2013: 63. doi: 10.1186/1687-6180-2013-63
|
| [60] |
GOGINENI S and NEHORAI A. Game theoretic design for polarimetric MIMO radar target detection[J]. Signal Processing, 2012, 92(5): 1281–1289. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2011.11.024
|
| [61] |
DELIGIANNIS A, LAMBOTHARAN S, and CHAMBERS J A. Game theoretic analysis for MIMO radars with multiple targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2016, 52(6): 2760–2774. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2016.150699
|
| [62] |
LAN Xing, LI Wei, WANG Xingliang, et al. MIMO radar and target stackelberg game in the presence of clutter[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2015, 15(12): 6912–6920. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2015.2466812
|
| [63] |
DANIYAN A, GONG Yu, and LAMBOTHARAN S. Game theoretic data association for multi-target tracking with varying number of targets[C]. 2016 IEEE Radar Conference, Philadelphia, USA, 2016: 1–4.
|
| [64] |
DANIYAN A, ALDOWESH A, GONG Yu, et al.. Data association using game theory for multi-target tracking in passive bistatic radar[C]. 2017 IEEE Radar Conference, Seattle, USA, 2017: 42–46.
|
| [65] |
CHAVALI P and NEHORAI A. Concurrent particle filtering and data association using game theory for tracking multiple maneuvering targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(20): 4934–4948. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2272923
|
| [66] |
CHAVALI P and NEHORAI A. Distributed data association for multiple-target tracking using game theory[C]. 2013 IEEE Radar Conference, Ottawa, Canada, 2013: 1–6.
|
| [67] |
BOGDANOVIĆ N, DRIESSEN H, and YAROVOY A. Track selection in multifunction radars for multi-target tracking: An anti-coordination game[C]. 2016 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Shanghai, China, 2016: 3131–3135.
|
| [68] |
BOGDANOVIĆ N, DRIESSEN H, and YAROVOY A G. Target selection for tracking in multifunction radar networks: Nash and correlated equilibria[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(5): 2448–2462. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2819798
|
| [69] |
LEE S J, PARK S S, and CHOI H L. Potential game-based non-myopic sensor network planning for multi-target tracking[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 79245–79257. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2885027
|
| [70] |
XIE Mingchi, YI Wei, and KONG Lingjiang. Joint selection and power allocation strategy for target tracking in decentralized multiple radar systems[C]. 2016 IEEE Radar Conference, Philadelphia, USA, 2016: 1–6.
|
| [71] |
XIE Mingchi, YI Wei, and KONG Lingjiang. Joint node selection and power allocation for multitarget tracking in decentralized radar networks[C]. The 2016 19th International Conference on Information Fusion, Heidelberg, Germany, 2016: 45–52.
|
| [72] |
XIE Mingchi, YI Wei, KIRUBARAJAN T, et al. Joint node selection and power allocation strategy for multitarget tracking in decentralized radar networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(3): 729–743. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2777394
|
| [73] |
CHAVALI P and NEHORAI A. Scheduling and power allocation in a cognitive radar network for multiple-target tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 60(2): 715–729. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2174989
|
| [74] |
HAN Keyong and NEHORAI A. Joint frequency-hopping waveform design for MIMO radar estimation using game theory[C]. 2013 IEEE Radar Conference, Ottawa, Canada, 2013: 1–4.
|
| [75] |
HAN Keyong and NEHORAI A. Jointly optimal design for MIMO radar frequency-hopping waveforms using game theory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2016, 52(2): 809–820. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2015.140408
|
| [76] |
PANOUI A, LAMBOTHARAN S, and CHAMBERS J A. Game theoretic distributed waveform design for multistatic radar networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2016, 52(4): 1855–1865. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2016.150378
|
| [77] |
SHI Chenguang, WANG Fei, SALOUS S, et al. Distributed power allocation for spectral coexisting multistatic radar and communication systems based on stackelberg game[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Brighton, UK, 2019: 4265–4269.
|
| [78] |
SHI Chenguang, WANG Fei, SALOUS S, et al. A robust stackelberg game-based power allocation scheme for spectral coexisting multistatic radar and communication systems[C]. 2019 IEEE Radar Conference, Boston, USA, 2019: 1–5.
|
| [79] |
SHI Chenguang, DING Lintao, WANG Fei, et al. Low probability of intercept-based collaborative power and bandwidth allocation strategy for multi-target tracking in distributed radar network system[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(12): 6367–6377. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.2977328
|
| [80] |
SHI Chenguang, QIU Wei, SALOUS S, et al. Power control scheme for spectral coexisting multistatic radar and massive MIMO communication systems under uncertainties: A robust Stackelberg game model[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2019, 94: 146–155. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2019.05.007
|
| [81] |
MISHRA K V, MARTONE A, and ZAGHLOUL A I. Power allocation games for overlaid radar and communications[C]. 2019 URSI Asia-Pacific Radio Science Conference, New Delhi, India, 2019: 1–4.
|





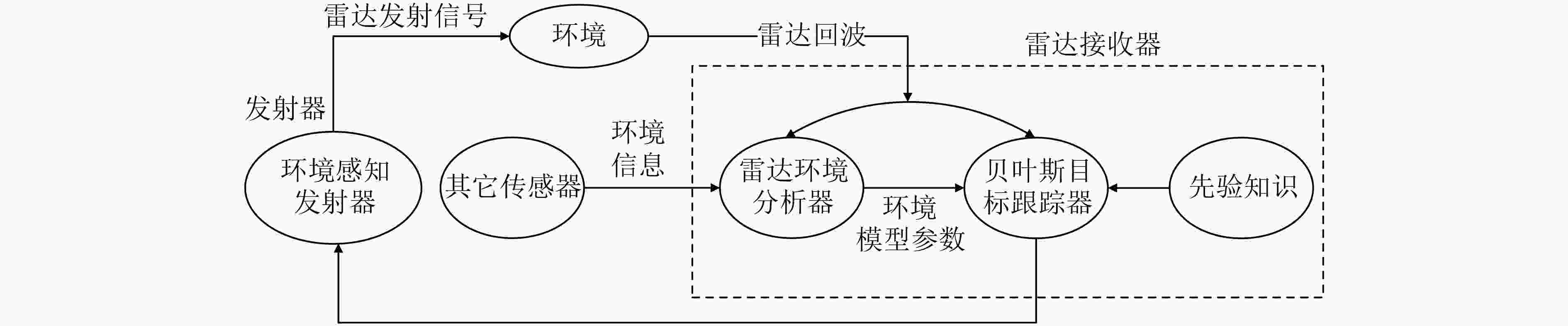
 下载:
下载:
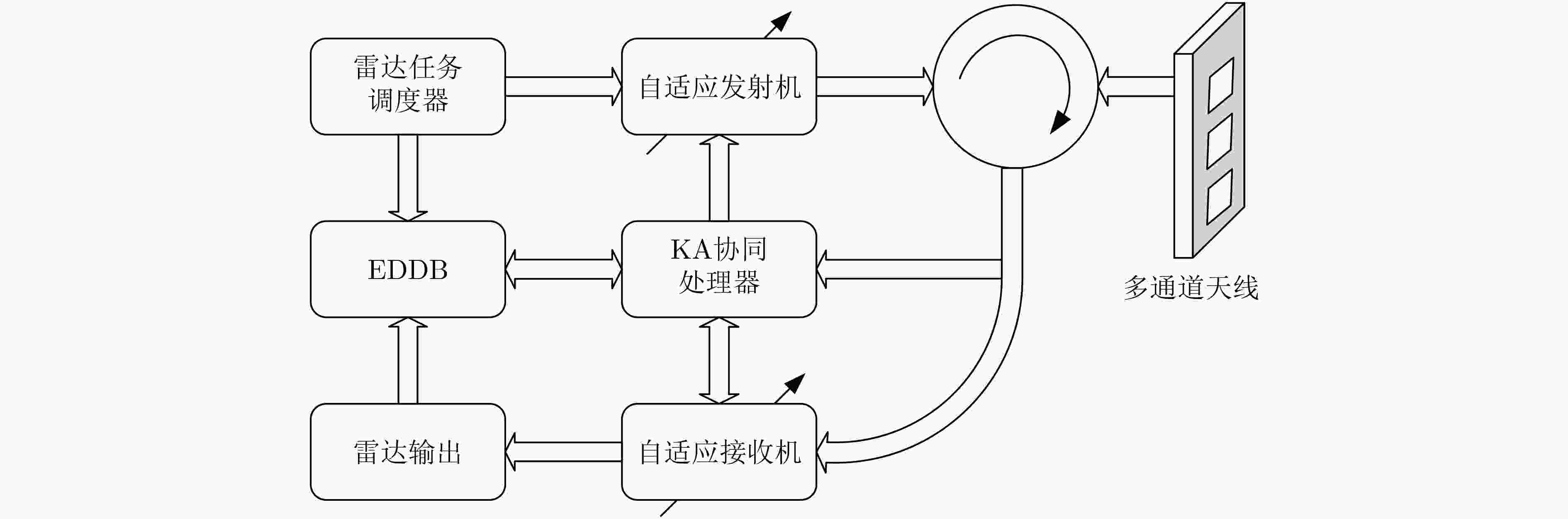




 下载:
下载:
