Arrhythmia Detection Based on Wavelet Decomposition and 1D-GoogLeNet
-
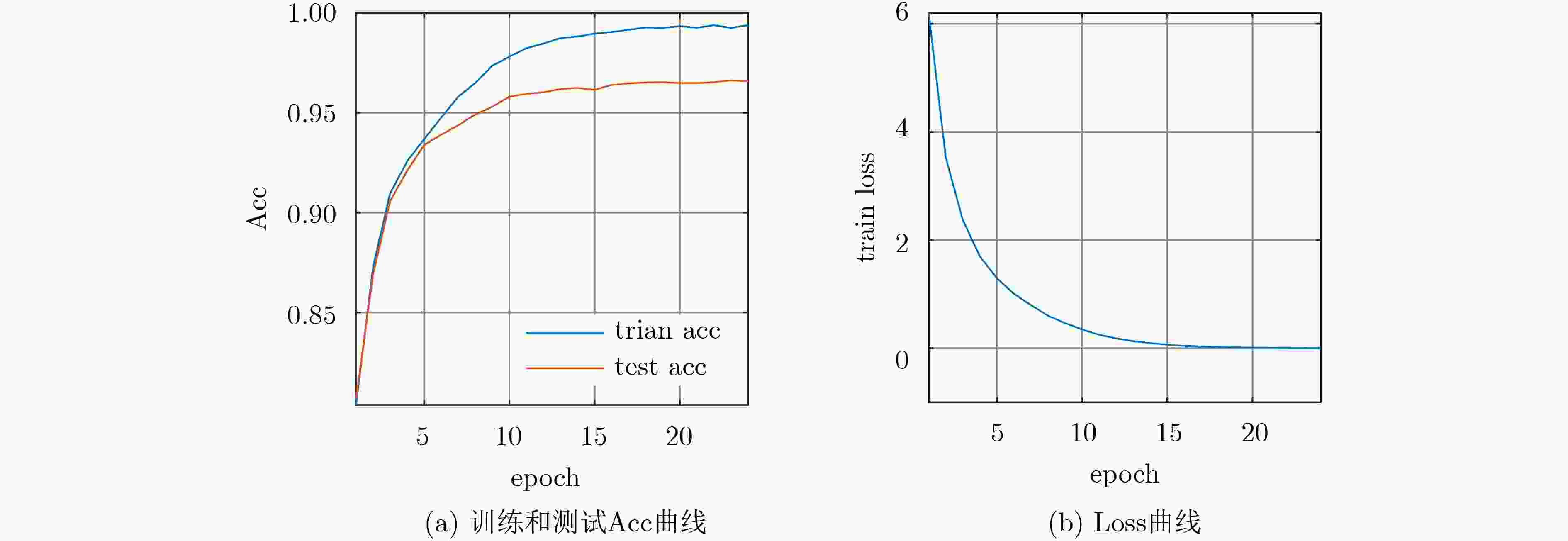
摘要: 心电图(ECG)信号的准确分类对于心脏病的自动诊断非常重要。为了实现对心律失常的智能分类,该文提出一种基于小波分解和1D-GoogLeNet的精确分类方法。在该方法中,利用Db6小波对ECG信号进行8级分解,得到既含时域信息又有频域信息的多维数据。随后,分解的样本用作1D-GoogLeNet的输入训练该模型。在提出的1D-GoogLeNet模型中,借鉴Inception在图像特征提取中的优异性能,将2维卷积变换为1维卷积学习ECG的特征,并且简化各个Inception的结构,降低模型参数。该文提出的神经网络分类器能够有效缓解计算效率低、收敛困难和模型退化的问题。在实验中,选用MIT-BIH心律失常数据集测试所提模型的性能,对比了信号的不同分解分量组合作为输入的检测结果,当输入数据由{d2-d7}组合时,所提1D-GoogLeNet模型可以达到96.58%的平均准确率。此外,还对比了该模型与未经结构优化的简单1维GoogLeNet在数据集上的表现,前者在准确率上比后者提高了4.7%,训练效率提高了118%。Abstract: The accurate classification of ElectroCardioGram (ECG) signals is essential for the automatic diagnosis of heart disease. In order to realize the intelligent classification of arrhythmia, an accurate classification method based on wavelet decomposition and 1D-GoogLeNet is proposed. In this method, Db6 wavelet is used to decompose the ECG signal in eight levels to obtain multi-dimensional data containing both time domain information and frequency domain information. Subsequently, Decomposed samples are used as input to 1D-GoogLeNet to train the model. In the proposed 1D-GoogLeNet model, using Inception's excellent performance in image feature extraction, the two-dimensional convolution is transformed into one-dimensional convolution to learn the features of ECG, and the structure of each Inception is simplified, and the model parameters are reduced. The deep learning classifier proposed in this paper can effectively alleviate the problems of low computational efficiency, difficulty in convergence and model degradation. In the experiment, the MIT-BIH arrhythmia dataset is used to test the performance of the proposed model. The experiment compares the detection results when different decomposition component combinations are used as input. When the input data is combined by {d2-d7}, the proposed 1D-GoogLeNet model can achieve an average accuracy of 96.58%. In addition, the performance of the model and the simple one-dimensional GoogLeNet without structural optimization on the data set is compared. The accuracy of the former is 4.7% higher than the latter, and the training efficiency is increased by 118%.
-
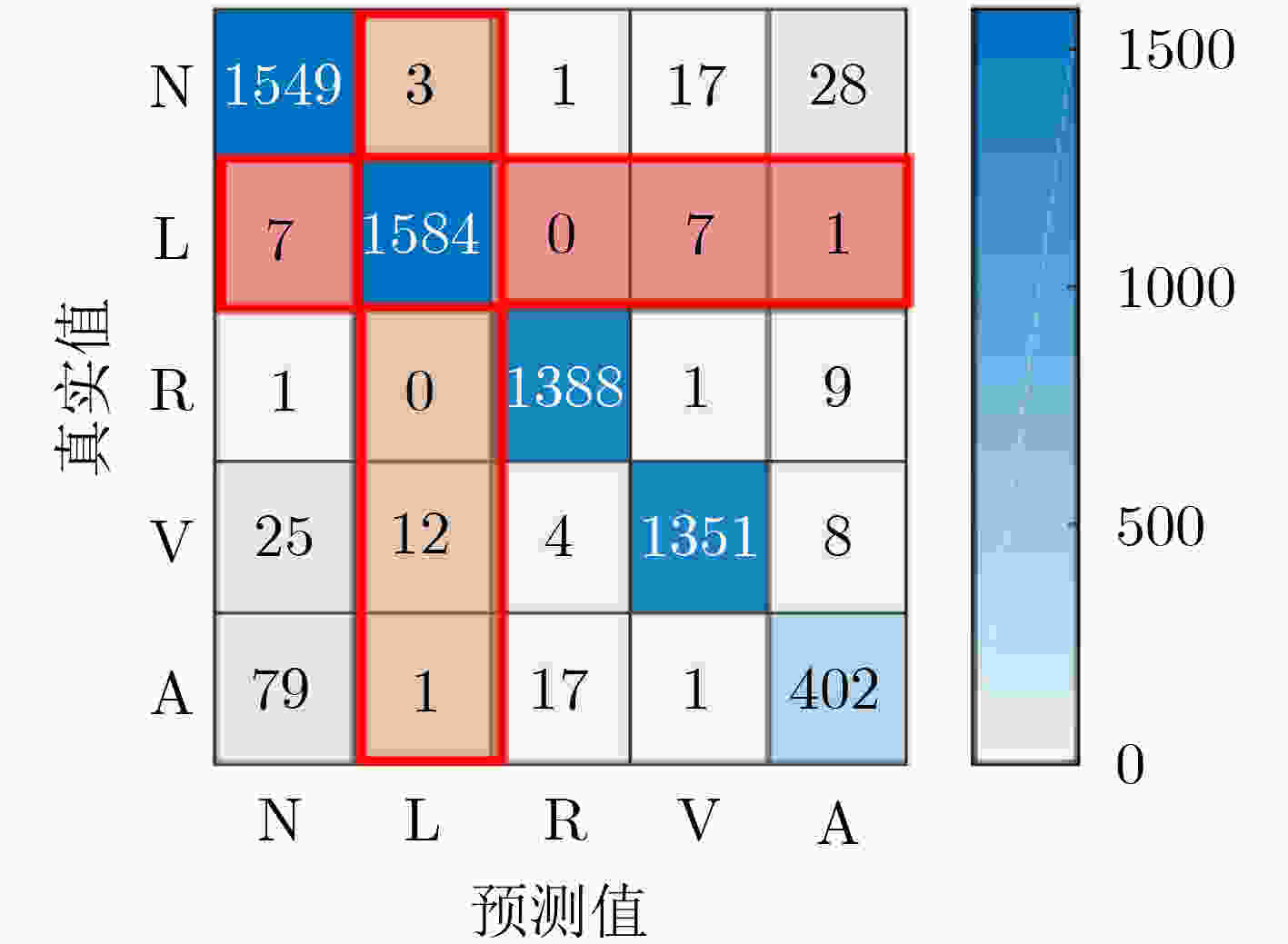
表 1 MI-BIH中L, R, V, A和N统计结果
标签 L R V A N 计数 8069 7250 7122 2544 74724 表 2 基于小波分解和1D-GoogLeNet的分类检测结果(%)
输入数据 多通道数据 原始数据 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 Acc 96.37 95.83 96.51 96.58 95.00 PM 95.37 95.28 96.37 95.71 93.61 RM 94.23 93.33 93.73 94.42 92.96 F1M 94.75 94.17 94.82 95.01 93.26 表 3 各预处理方法在心律失常检测任务中的比较
预处理 DFT EMD WD Acc 94.63 94.81 96.58 PM 93.74 93.31 95.71 RM 92.85 92.85 94.42 F1M 93.27 93.07 95.01 表 4
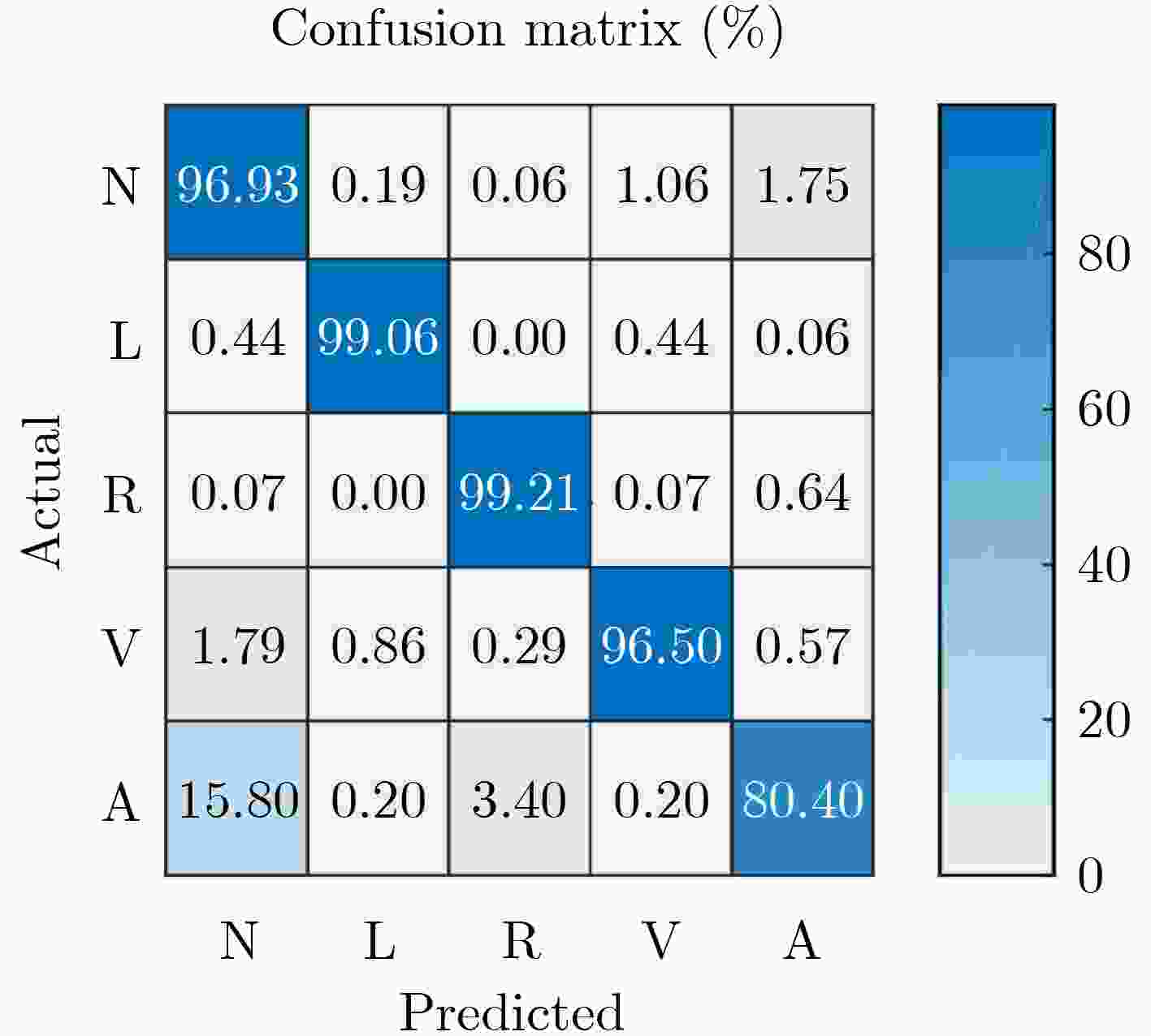
${D_4}$ 数据作为1D-GoogLeNet的输入,各类的测试结果(%)心律类型 N L R V A macro-average P 93.26 99.00 98.44 98.11 89.73 95.71 R 96.93 99.06 99.21 96.50 80.40 94.42 F1 95.06 99.03 98.83 97.30 84.81 95.01 表 5 1D-GoogLeNet与其他分类模型的实验比较
Model AccM(%) PM(%) RM(%) F1M(%) Time(s) Params 1D-GoogLeNet 96.58 95.71 94.42 95.01 4228 9111.0K 1维化GoogLeNet 92.18 90.54 89.27 89.83 9226 13145.4K LeNet 94.17 91.62 93.25 92.29 2545 4956.8 LSTM 93.04 90.02 91.02 90.44 2668 70.7 -
[1] 胡盛寿, 高润霖, 刘力生, 等. 《中国心血管病报告2018》概要[J]. 中国循环杂志, 2019, 34(3): 209–220. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2019.03.001HU Shengshou, GAO Runlin, LIU Lisheng, et al. Summary of the 2018 report on cardiovascular diseases in China[J]. Chinese Circulation Journal, 2019, 34(3): 209–220. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2019.03.001 [2] HUANG Jingshan, CHEN Binqing, ZENG Nianyin, et al. Accurate classification of ECG arrhythmia using MOWPT enhanced fast compression deep learning networks[J]. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, To be published. doi: 10.1007/s12652-020-02110-y [3] RANGAYYAN R M. Biomedical Signal Analysis: A Case Study Approach[M]. New York: IEEE Press, 2002. [4] VELAYUDHAN A and PETER S. Noise analysis and different denoising techniques of ECG signal - a survey[J]. IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering, 2016, 1(1): 40–44. [5] SLONIM T Y M, SLONIM M A, and OVSYSCHER E A. The use of simple FIR filters for filtering of ECG signals and a new method for post-filter signal reconstruction[C]. Computers in Cardiology Conference, London, UK, 1993: 871–873. doi: 10.1109/CIC.1993.378347. [6] THAKOR N V and ZHU Y S. Applications of adaptive filtering to ECG analysis: Noise cancellation and arrhythmia detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 1991, 38(8): 785–794. doi: 10.1109/10.83591 [7] KABIR M A and SHAHNAZ C. Denoising of ECG signals based on noise reduction algorithms in EMD and wavelet domains[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2012, 7(5): 481–489. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2011.11.003 [8] WANG Ze, WAN Feng, WONG C M, et al. Adaptive Fourier decomposition based ECG denoising[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2016, 77: 195–205. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2016.08.013 [9] WANG Ge, YANG Lin, LIU Ming, et al. ECG signal denoising based on deep factor analysis[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2020, 57: 101824. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2019.101824 [10] YÜCELBAŞ Ş, YÜCELBAŞ C, TEZEL G, et al. Pre-determination of OSA degree using morphological features of the ECG signal[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2017, 81: 79–87. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2017.03.049 [11] INAN O T, GIOVANGRANDI L, and KOVACS G T A. Robust neural-network-based classification of premature ventricular contractions using wavelet transform and timing interval features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2006, 53(12): 2507–2515. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2006.880879 [12] LINH T H, OSOWSKI S, and STODOLSKI M. On-line heart beat recognition using Hermite polynomials and neuro-fuzzy network[C]. The 19th IEEE Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference, Anchorage, USA, 2002: 165–170. doi: 10.1109/IMTC.2002.1006834. [13] MARTIS R J, ACHARYA U R, and MIN L C. ECG beat classification using PCA, LDA, ICA and discrete wavelet transform[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2013, 8(5): 437–448. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2013.01.005 [14] ALQURAN H, ALQUDAH A M, ABU-QASMIEH I, et al. ECG classification using higher order spectral estimation and deep learning techniques[J]. Neural Network World, 2019, 29: 207–219. doi: 10.14311/NNW.2019.29.014 [15] LYON A, MINCHOLÉ A, MARTÍNEZ J P, et al. Computational techniques for ECG analysis and interpretation in light of their contribution to medical advances[J]. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 2018, 15(138): 20170821. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2017.0821 [16] LLAMEDO M and MARTÍNEZ J P. Heartbeat classification using feature selection driven by database generalization criteria[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2011, 58(3): 616–625. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2010.2068048 [17] NASIRI J A, NAGHIBZADEH M, YAZDI H S, et al. ECG arrhythmia classification with support vector machines and genetic algorithm[C]. The 3rd UKSim European Symposium on Computer Modeling and Simulation, Athens, Greece, 2009: 187–192. doi: 10.1109/EMS.2009.39. [18] CASAS M M, AVITIA R L, GONZALEZ-NAVARRO F F, et al. Bayesian classification models for premature ventricular contraction detection on ECG traces[J]. Journal of Healthcare Engineering, 2018, 2018: 2694768. doi: 10.1155/2018/2694768 [19] KUMAR G R and KUMARASWAMY D Y S. Investigating cardiac arrhythmia in ECG using random forest classification[J]. International Journal of Computer Applications, 2012, 37(4): 31–34. doi: 10.5120/4599-6557 [20] RAJPURKAR P, HANNUN A Y, HAGHPANAHI M, et al. Cardiologist-level arrhythmia detection with convolutional neural networks[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1707.01836,2017. [21] MOSTAYED A, LUO Junye, SHU Xingliang, et al. Classification of 12-lead ECG signals with Bi-directional LSTM network[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1811.02090,2018. [22] SINGH S, PANDEY S K, PAWAR U, et al. Classification of ECG arrhythmia using recurrent neural networks[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2018, 132: 1290–1297. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2018.05.045 [23] MOODY G B and MARK R G. The impact of the MIT-BIH arrhythmia database[J]. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Magazine, 2001, 20(3): 45–50. doi: 10.1109/51.932724 [24] GOLDBERGER A L, AMARAL L A, GLASS L, et al. PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: Components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals[J]. Circulation, 2000, 101(23): e215–e220. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.101.23.e215 [25] MAHMOODABADI S Z, AHMADIAN A, and ABOLHASANI M D. ECG feature extraction using Daubechies wavelets[C]. Visualization, Imaging, and Image Processing, Benidorm, Spain, 2005. [26] SZEGEDY C, LIU Wei, JIA Yangqing, et al. Going deeper with convolutions[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, USA, 2015: 1–9. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298594. [27] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 3–19. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_1. [28] IOFFE S and SZEGEDY C. Batch Normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[C]. The 32nd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 2015: 448–456. [29] SZEGEDY C, VANHOUCKE V, IOFFE S, et al. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2818–2826. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.308. [30] SZEGEDY C, IOFFE S, VANHOUCKE V, et al. Inception-v4, Inception-ResNet and the impact of residual connections on learning[C]. The 31st AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, USA, 2017: 4278–4284. [31] KINGMA D P and BA J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), San Diego, USA, 2015. -





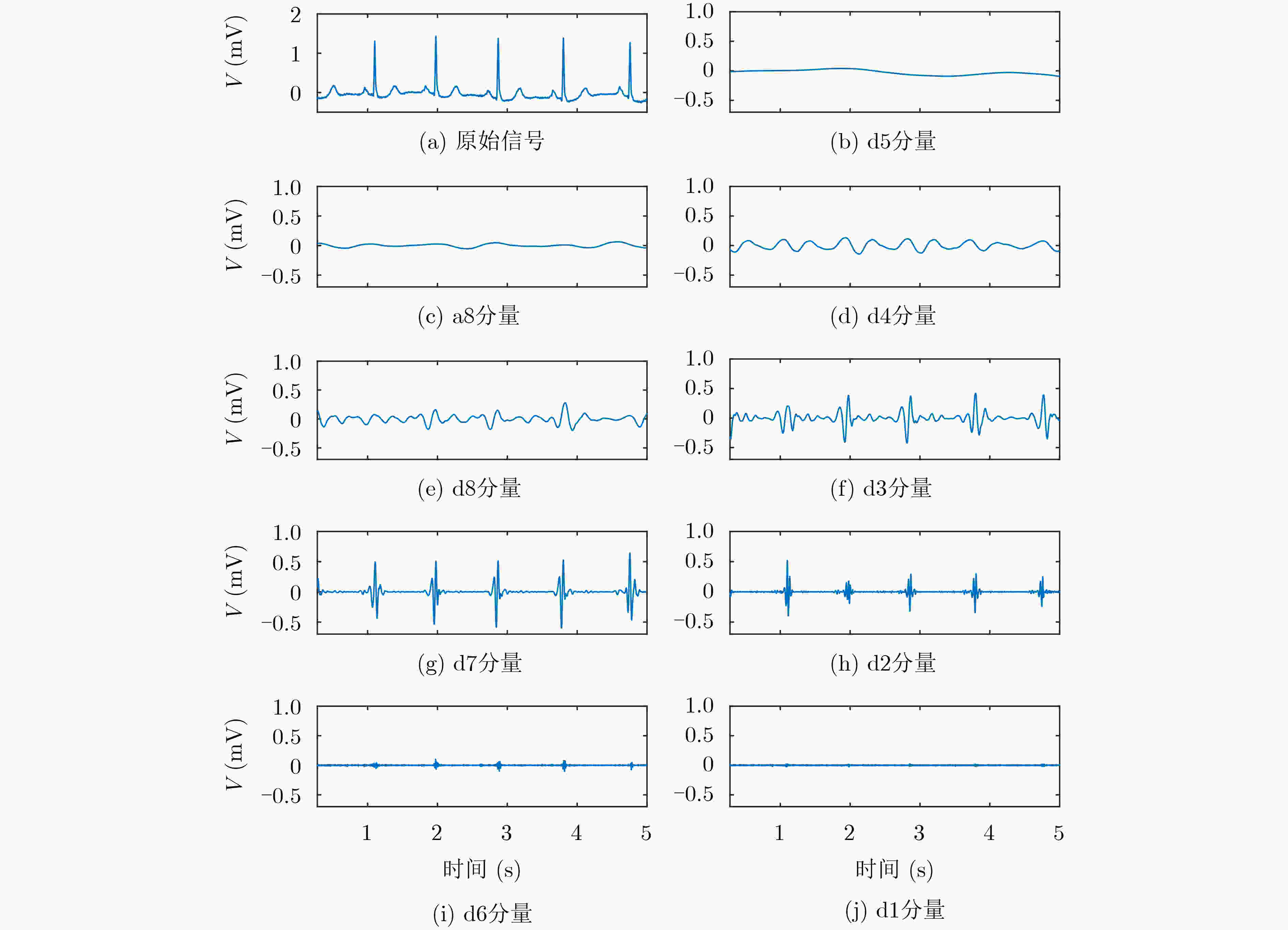
 下载:
下载:
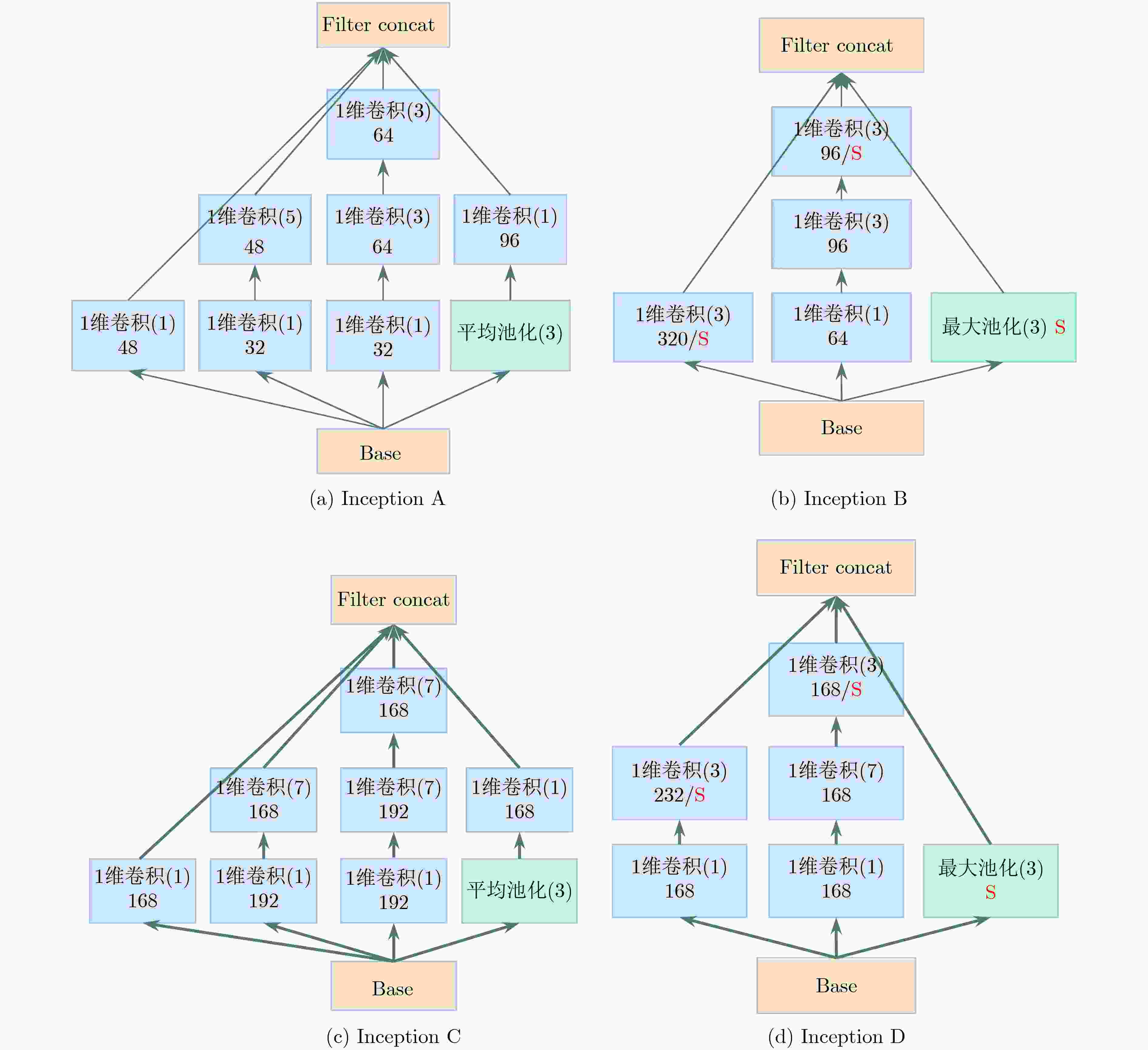
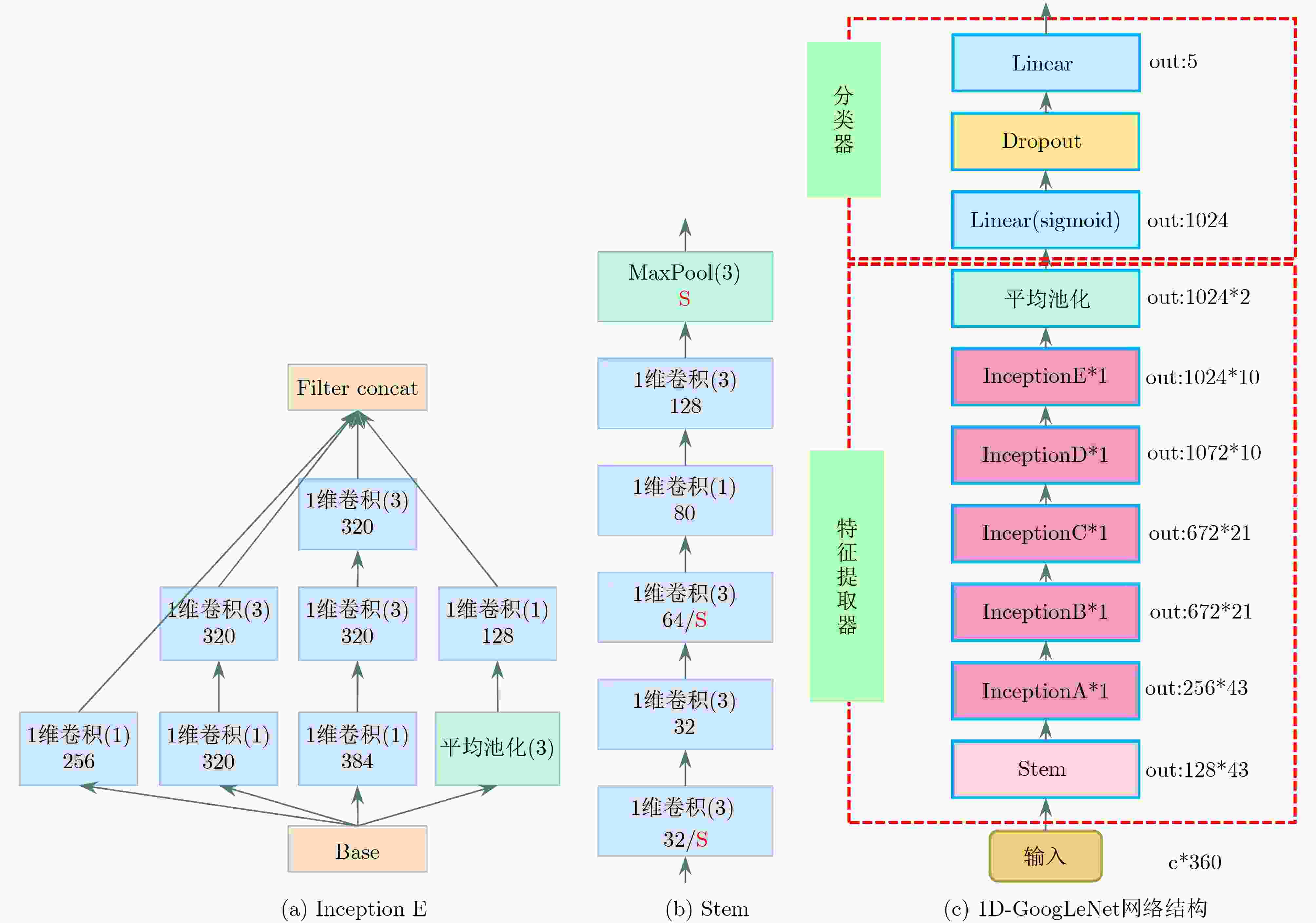




 下载:
下载:
