Sparse Bayesian Learning Based Algorithm for DOA Estimation of Closely Spaced Signals
-
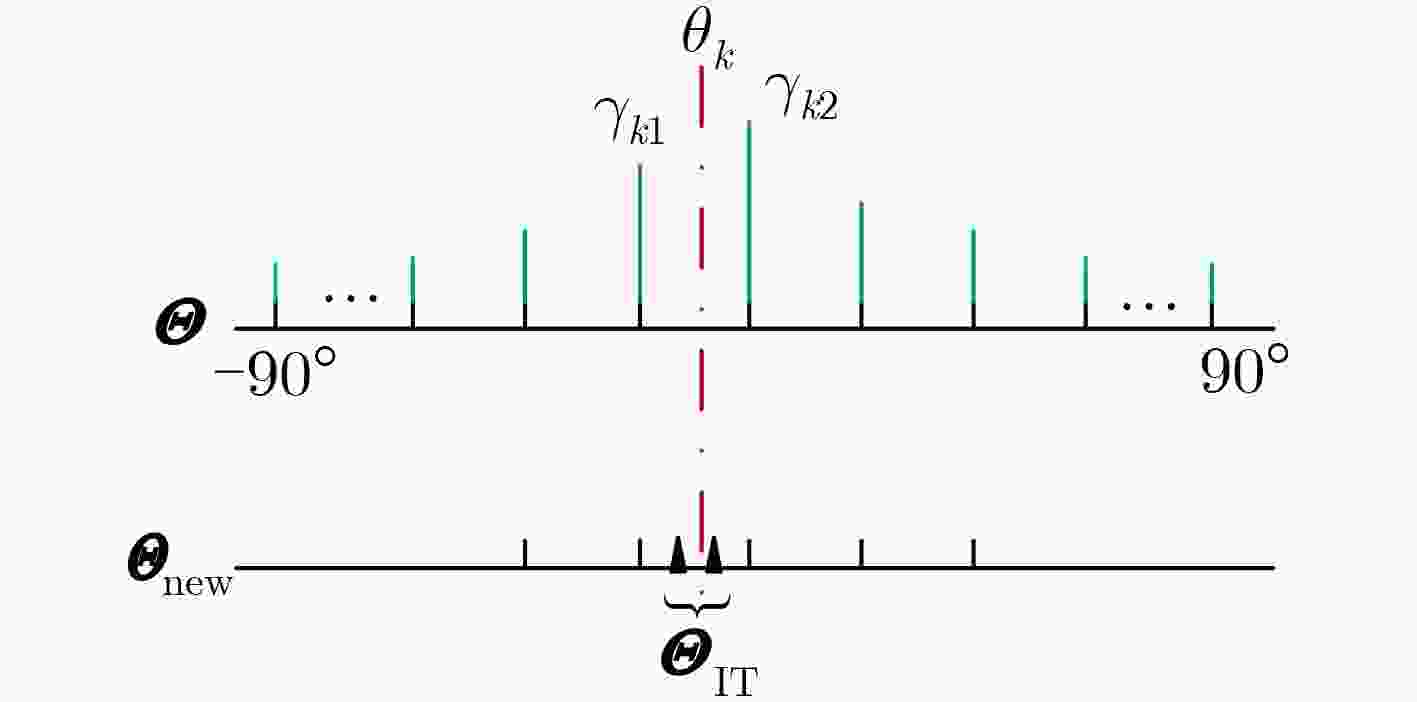
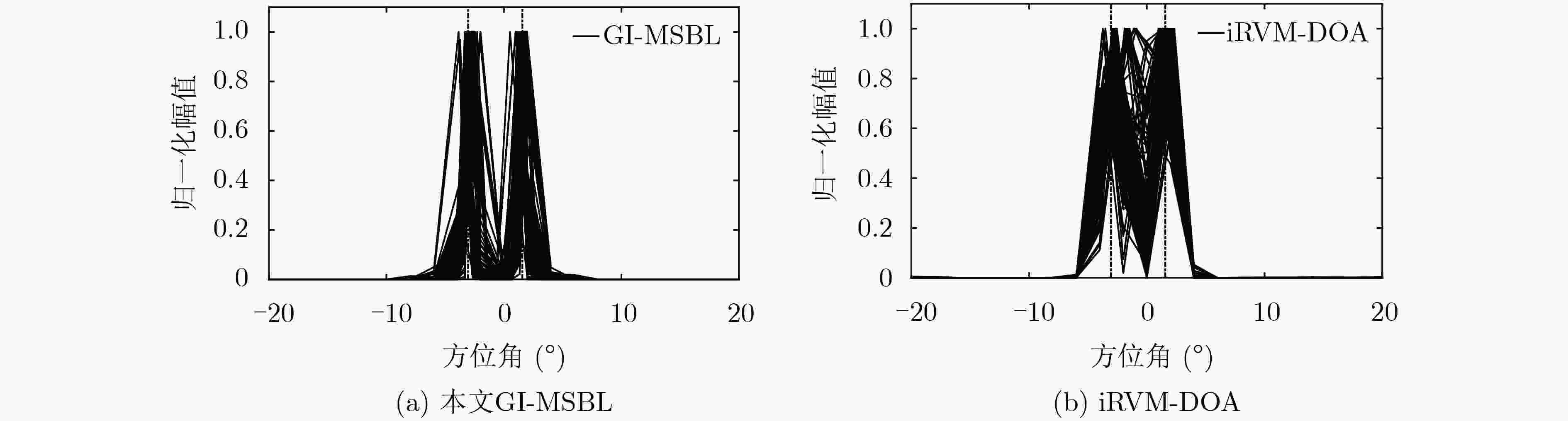
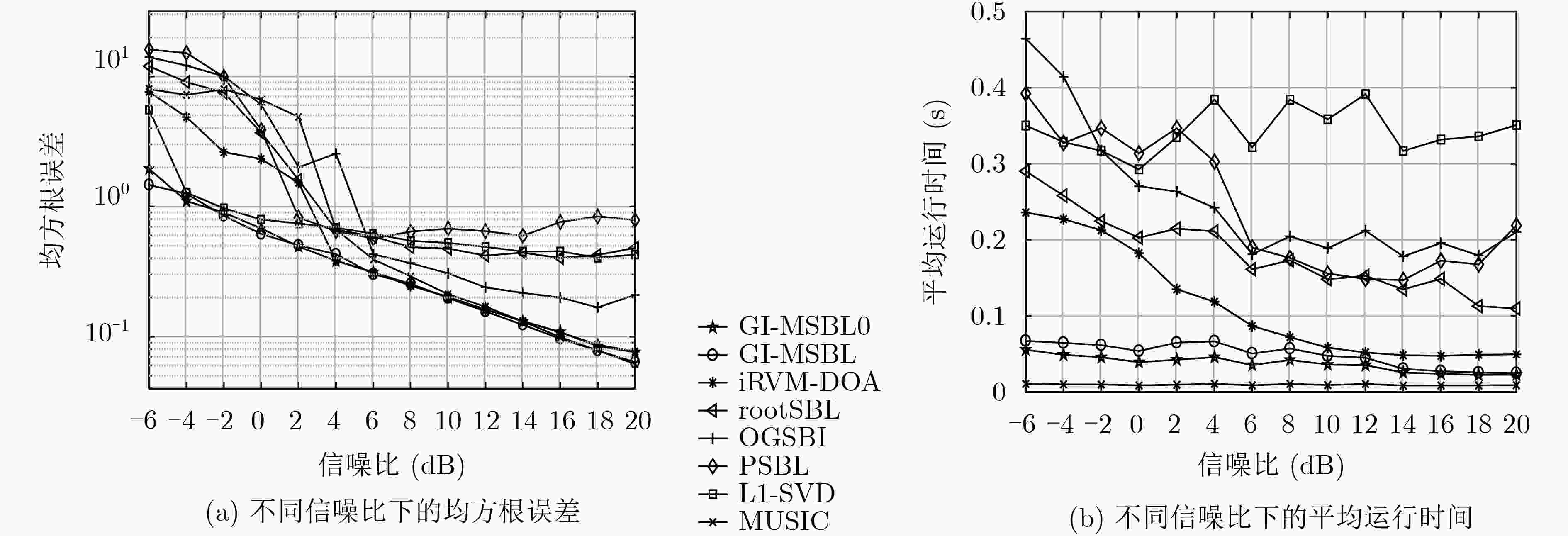
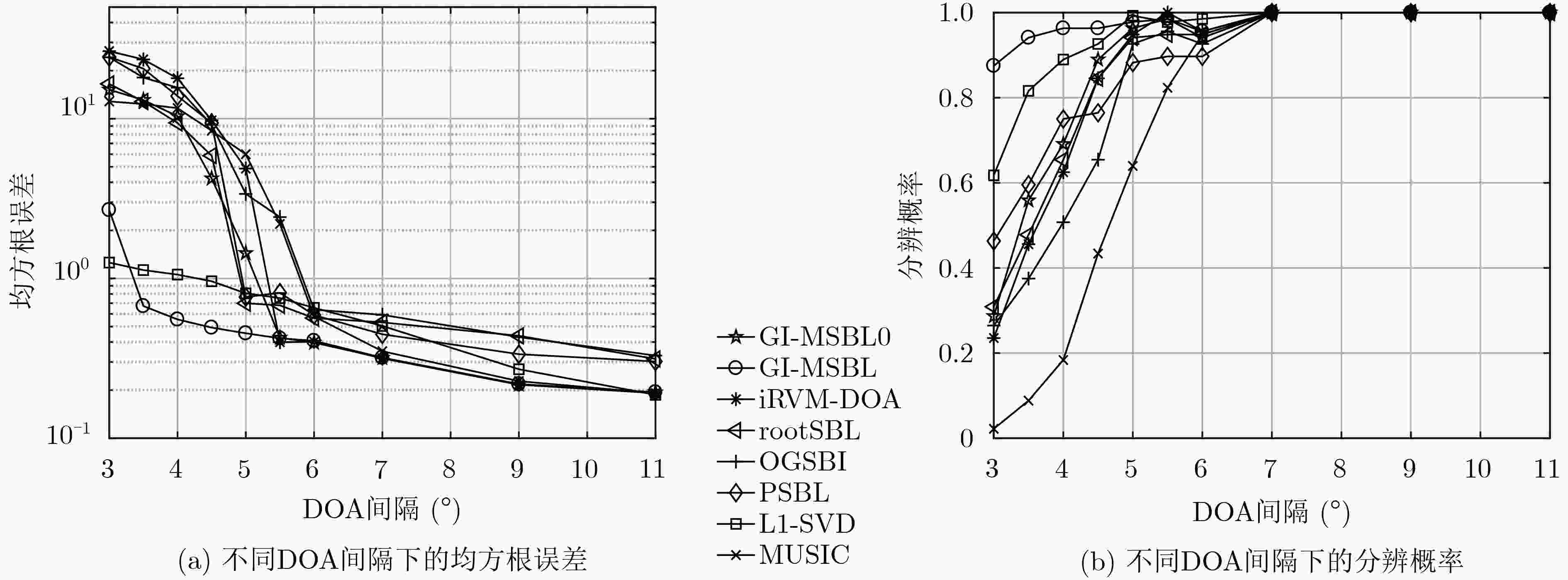
摘要: 离格(off-grid)波达方向(DOA)估计解决的是实际DOA和假设网格点的失配问题。对于空间紧邻信号的DOA,稀疏的网格点会导致精度和分辨率的下降,密集的网格点虽然可以提高估计精度却显著增加计算负担。针对此问题,该文提出基于稀疏贝叶斯学习(SBL)的空间紧邻信号DOA估计算法,主要包括3个步骤。首先,通过最大化阵列输出的边缘似然函数,推导了信号在拉普拉斯先验下的新不动点迭代方法,进行超参数的预估计,相比其他经典SBL算法提高了收敛速度;其次,利用新网格插值方法优化网格点集,并二次估计噪声方差和信号功率以分辨空间紧邻信号的DOA;最后,推导了似然函数关于角度的最大化公式以改进离格DOA搜索。仿真表明该算法比其他经典SBL类算法对空间紧邻信号的DOA具有更高的精度和分辨率,同时有计算效率的提升。Abstract: Off-grid Direction Of Arrival (DOA) estimation aims to handle the mismatch between the actual DOA and the presumed grid points. For DOAs of closely spaced signals, sparse grid points leads to degradation of accuracy and resolution, although dense grid points can improve the estimation accuracy, it significantly increases the computational burden. To solve this problem, this paper proposes a Sparse Bayesian Learning (SBL) based algorithm for DOA estimation of closely spaced signals, which consists of three steps. Firstly, a novel fixed point iterative method for signal of Laplace priori is derived to pre-estimate the hyper-parameters by maximizing the array’s marginal likelihood function, which results in faster convergence speed compared to other classical SBL algorithms. Secondly, a new grid interpolation method is implemented to optimize a set of grid points, and signal power and noise variance are estimated again to resolve closely spaced DOAs. Finally, an expression of maximum likelihood function with respect to angle is derived to improve the search of the off-grid DOA. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm has higher accuracy and resolution for closely spaced DOAs with higher computational efficiency compared with other classical algorithms based on SBL.
-
表 1 算法的计算复杂度
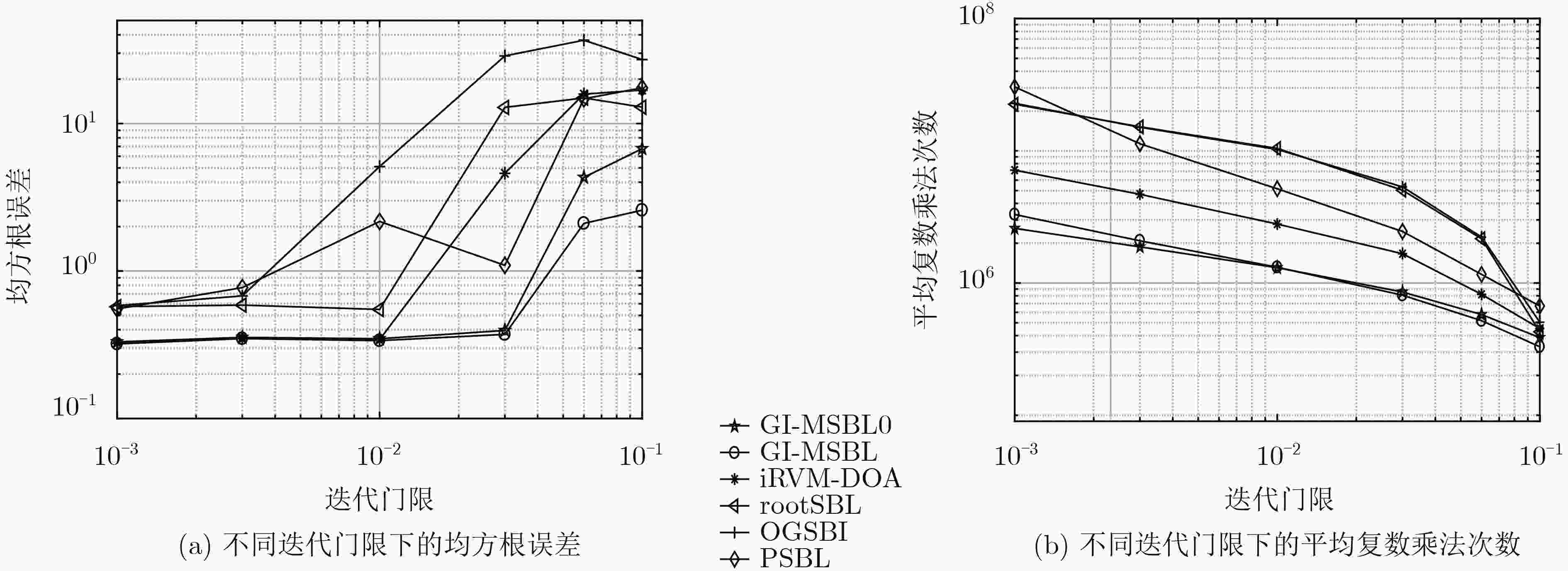
算法 计算复杂度 本文GI-MSBL $\begin{gathered} {l_1}\left( {2MNL + (M + 1)MN} \right) \\ + {l_2}\left( {M\bar NL + (M + 1)M\bar N} \right) + (2{M^2} + 2M)K{N_0} \\ \end{gathered} $ iRVM-DOA[7] $\begin{gathered} {l_{{\rm{iRVM - DOA}}}}\left( {MNL + M{N^2} + {M^2}N} \right) \\ + (2{M^2}{\rm{ + }}6M)K{N_1} \\ \end{gathered} $ OGSBI[8] ${l_{{\rm{OGSBI}}}}\left( {2MNL + M{N^2} + {M^2}N + MN(L + K)} \right)$ rootSBL[12] ${l_{{\rm{rootSBL}}}}\left( {2MNL + M{N^2} + {M^2}N{\rm{ + }}M(N - 1)L} \right)$ PSBL[9,10] $ \begin{array}{l}{l}_{\rm{PSBL}}\left(2MNL+M(N-1{)}^{2}+{M}^{2}(N-1)\right)\\ +{l}_{\rm{PSBL}}\left(L(N-1)(M+K)\right)\end{array}$ L1-SVD[3] $O({(KN)^3})$ MUSIC[2] $(M - K)ML{N_{{\rm{MUSIC}}}}$ -
鄢社锋, 马远良. 传感器阵列波束优化设计及应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009, 230–235.YAN Shefeng and MA Yuanliang. Sensor Array Beampattern Optimization: Theory with Applications[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009, 230–235. SCHMIDT R. Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1986, 34(3): 276–280. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1986.1143830 MALIOUTOV D, CETIN M, and WILLSKY A S. A sparse signal reconstruction perspective for source localization with sensor arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2005, 53(8): 3010–3022. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2005.850882 WIPF D P and RAO B D. An empirical Bayesian strategy for solving the simultaneous sparse approximation problem[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2007, 55(7): 3704–3716. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.894265 TIPPING M E and SMOLA A. Sparse Bayesian learning and the relevance vector machine[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2001, 1(3): 211–244. BABACAN S D, MOLINA R, and KATSAGGELOS A K. Bayesian compressive sensing using Laplace priors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2010, 19(1): 53–63. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2009.2032894 LIU Zhangmeng, HUANG Zhitao, and ZHOU Yiyu. An efficient maximum likelihood method for direction-of-arrival estimation via sparse Bayesian learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2012, 11(10): 1–11. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2012.090312.111912 YANG Zai, XIE Lihua, and ZHANG Cishen. Off-grid direction of arrival estimation using sparse Bayesian inference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(1): 38–43. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2222378 WU Xiaohuan, ZHU Weiping, and YAN Jun. Direction of arrival estimation for off-grid signals based on sparse Bayesian learning[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2016, 16(7): 2004–2016. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2015.2508059 郭英, 东润泽, 张坤峰, 等. 基于稀疏贝叶斯学习的多跳频信号DOA估计方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(3): 516–522. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180435GUO Ying, DONG Runze, ZHANG Kunfeng, et al. Direction of arrival estimation for multiple frequency hopping signals based on sparse Bayesian learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(3): 516–522. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180435 游康勇, 杨立山, 刘玥良, 等. 基于稀疏贝叶斯学习的网格自适应多源定位[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(9): 2150–2157. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171238YOU Kangyong, YANG Lishan, LIU Yueliang, et al. Adaptive grid multiple sources localization based on sparse Bayesian learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(9): 2150–2157. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171238 DAI Jisheng, BAO Xu, XU Weichao, et al. Root sparse Bayesian learning for off-grid DOA estimation[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2017, 24(1): 46–50. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2016.2636319 DAI Jisheng and SO H C. Sparse Bayesian learning approach for outlier-resistant direction-of-arrival estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(3): 744–756. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2773420 GEMBA K L, NANNURU S, and GERSTOFT P. Robust ocean acoustic localization with sparse Bayesian learning[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2019, 13(1): 49–60. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2019.2900912. DAI Jisheng, ZHOU Lei, CHANG Chunqi, et al. Robust Bayesian learning approach for massive MIMO channel estimation[J]. Signal Processing, 2020, 168: 107345. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2019.107345 ZHENG Rui, XU Xu, YE Zhongfu, et al. Sparse Bayesian learning for off-grid DOA estimation with Gaussian mixture priors when both circular and non-circular sources coexist[J]. Signal Processing, 2019, 161: 124–135. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2019.03.021 SHI Yunmei, MAO Xingpeng, ZHAO Chunlei, et al. Underdetermined DOA estimation for wideband signals via joint sparse signal reconstruction[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2019, 26(10): 1541–1545. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2019.2937381 ZHOU Changguo, HABER F, and JAGGARD D L. A resolution measure for the MUSIC algorithm and its application to plane wave arrivals contaminated by coherent interference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1991, 39(2): 454–463. doi: 10.1109/78.80829 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
