Application of Manifold Learning to Shallow Water Acoustic Communication
-
摘要: 在复杂的浅海环境中,水声信道具有强烈的空变和时变特性,致使水声通信系统的鲁棒性很难得到保证。该文不同于依赖复杂信道编码和信道均衡手段的传统水声通信算法,将流形学习思想应用于高维海洋环境参数空间刻画及信号空间映射中,为水下数据传输提出创新方案。从声场角度出发,结合浅海实验数据,分析通信信号时空起伏特性,研究环境参数空间和声场信号空间的内在关系,提出了基于非线性流形学习算法增加合理的物理约束,结合信道稀疏特性,对于高维非线性水声信号系统的冗余维度信息进行维数约简,映射到稳定的低维目标空间,降低信道时空起伏对通信系统的影响。仿真和实验结果验证了算法的可靠性和有效性。Abstract: Sallow water acoustic channel is severely affected by time-space variation, which destroys the robustness of underwater acoustic communication system. By introducing manifold learning in the analysis of high dimensional underwater environment and channel equalization processing, a novel underwater acoustic communication algorithm is presented. By establishing the mapping between environment parameter space and signal space, several physical restrictions can be posed on non-linear manifold learning algorithm. Moreover, the sparse property can reduce the dimension of underwater acoustic channel in order to exclude high dimensional non-linear noise from channel time-space variation. Both sound field analysis and shallow water experimental data verify the validity and the robustness of the proposed algorithm.
-
表 1 实验参数设置
参数 参数值 参数 参数值 采样频率(kHz) 48 FFT点数 1024 频率范围(kHz) 8~16 码率 1/2 信道编码 LDPC 带宽(kHz) 8 映射方式 QPSK 符号时长(ms) 128 -
惠俊英. 水下声信道[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 1992: 179. LI Qihu, WANG Lei, WEI Chonghua, et al. Theoretical analysis and experimental results of interference striation pattern of underwater target radiated noise in shallow water waveguide[J]. Chinese Journal of Acoustics, 2011, 30(1): 73–80. doi: 10.15949/j.cnki.0217-9776.2011.01.002 WANG Huakui, ZHAO Ye, WU Bi, et al. Estimation of source parameters based on underwater acoustic interference pattern in shallow water[C]. 2011 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing, Xi'an, China, 2011: 1–4. 陈守虎, 赵连军, 曹建国, 等. 浅水近距离测量声场的干涉结构分析[J]. 声学学报, 2017, 42(2): 129–142. doi: 10.15949/j.cnki.0371-0025.2017.02.001CHEN Shouhu, ZHAO Lianjun, CAO Jianguo, et al. Analytical study on acoustic interference pattern in shallow water[J]. Acta Acustica, 2017, 42(2): 129–142. doi: 10.15949/j.cnki.0371-0025.2017.02.001 WOLD S, ESBENSEN K, and GELADI P. Principal component analysis[J]. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 1987, 2(1/3): 37–52. COX T F and COX M A A. Multidimensional Scaling[M]. 2nd ed. New York: Chapman & Hall/CRC, 2000. ROWEIS S T and SAUL L K. Nonlinear dimensionality reduction by locally linear embedding[J]. Science, 2000, 290(5500): 2323–2326. doi: 10.1126/science.290.5500.2323 BELKIN M and NIYOGI P. Laplacian eigenmaps for dimensionality reduction and data representation[J]. Neural Computation, 2003, 15(6): 1373–1396. doi: 10.1162/089976603321780317 DONOHO D L and GRIMES C. Hessian eigenmaps: Locally linear embedding techniques for high-dimensional data[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2003, 100(10): 5591–5596. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1031596100 ZHANG Zhenyue and ZHA Hongyuan. Principal manifolds and nonlinear dimensionality reduction via tangent space alignment[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 2004, 26(1): 313–338. doi: 10.1137/S1064827502419154 YANG Jian, LI Fuxin, and WANG Jue. A better scaled local tangent space alignment algorithm[C]. 2005 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Montreal, Canada, 2005: 1006–1011. doi: 10.1109/IJCNN.2005.1555990. BAQAR M and ZAIDI S S H. Performance evaluation of linear and multi-linear subspace learning techniques for object classification based on underwater acoustics[C]. The 14th International Bhurban Conference on Applied Sciences and Technology (IBCAST), Islamabad, Pakistan, 2017: 675–683. ZHUANG Honghai, LIU Guoguo, ZHANG Xuewu, et al. Dimensionality reduction based on feature points of underwater image mosaic algorithm[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2013, 462/463: 308–311. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.462-463.308 管鲁阳, 鲍明, 张鹏, 等. 基于流形学习的单类分类算法及其在不均衡声目标识别中的应用[J]. 声学学报, 2009, 34(1): 67–73. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-0025.2009.01.010GUAN Luyang, BAO Ming, ZHANG Peng, et al. One-class classification algorithm based on manifold learning and its application to imbalanced acoustic target recognition[J]. Acta Acustica, 2009, 34(1): 67–73. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-0025.2009.01.010 梁春燕, 袁文浩, 李艳玲, 等. 基于判别邻域嵌入算法的说话人识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(7): 1774–1778. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180761LIANG Chunyan, YUAN Wenhao, LI Yanling, et al. Speaker recognition using discriminant neighborhood embedding[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(7): 1774–1778. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180761 刘辉, 杨俊安, 王一. 基于流形学习的声目标特征提取方法研究[J]. 物理学报, 2011, 60(7): 437–443. doi: 10.7498/aps.60.074302LIU Hui, YANG Junan, and WANG Yi. A novel approach to research on feature extraction of acoustic targets based on manifold learning[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2011, 60(7): 437–443. doi: 10.7498/aps.60.074302 -





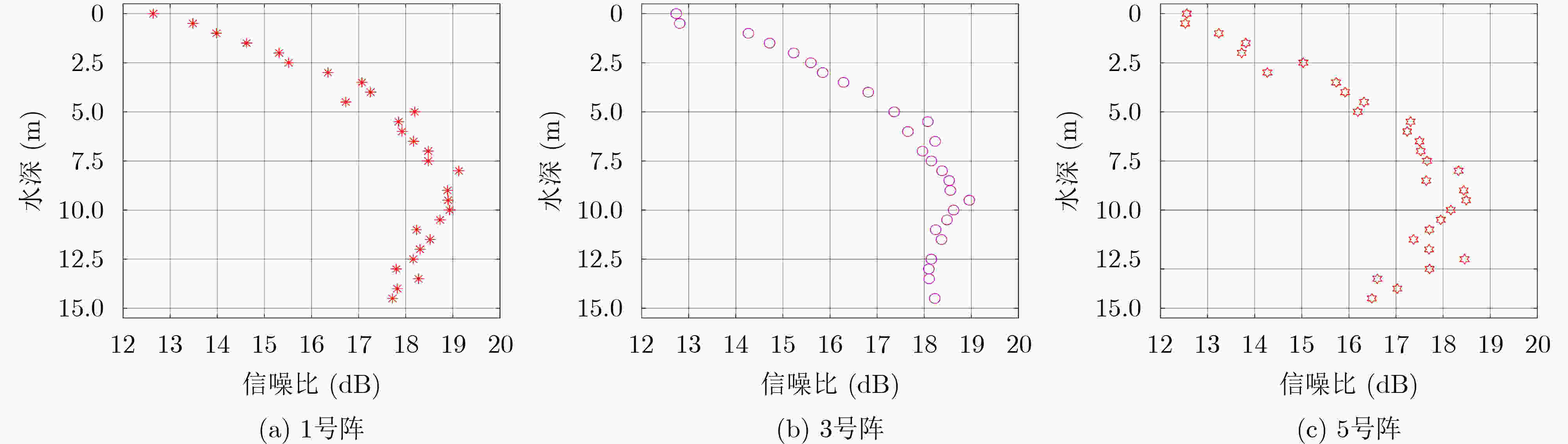
 下载:
下载:

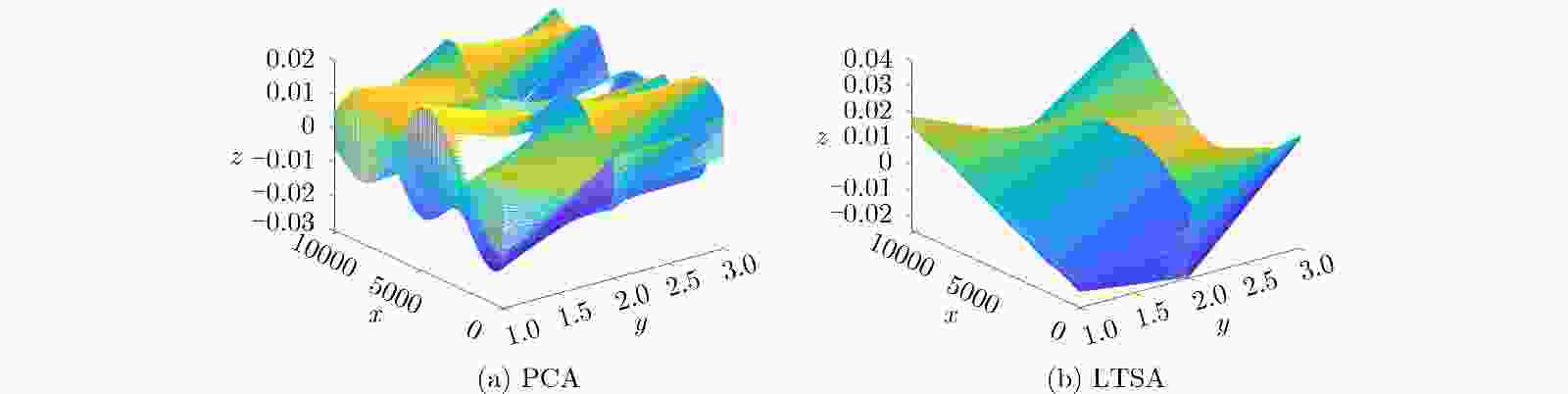

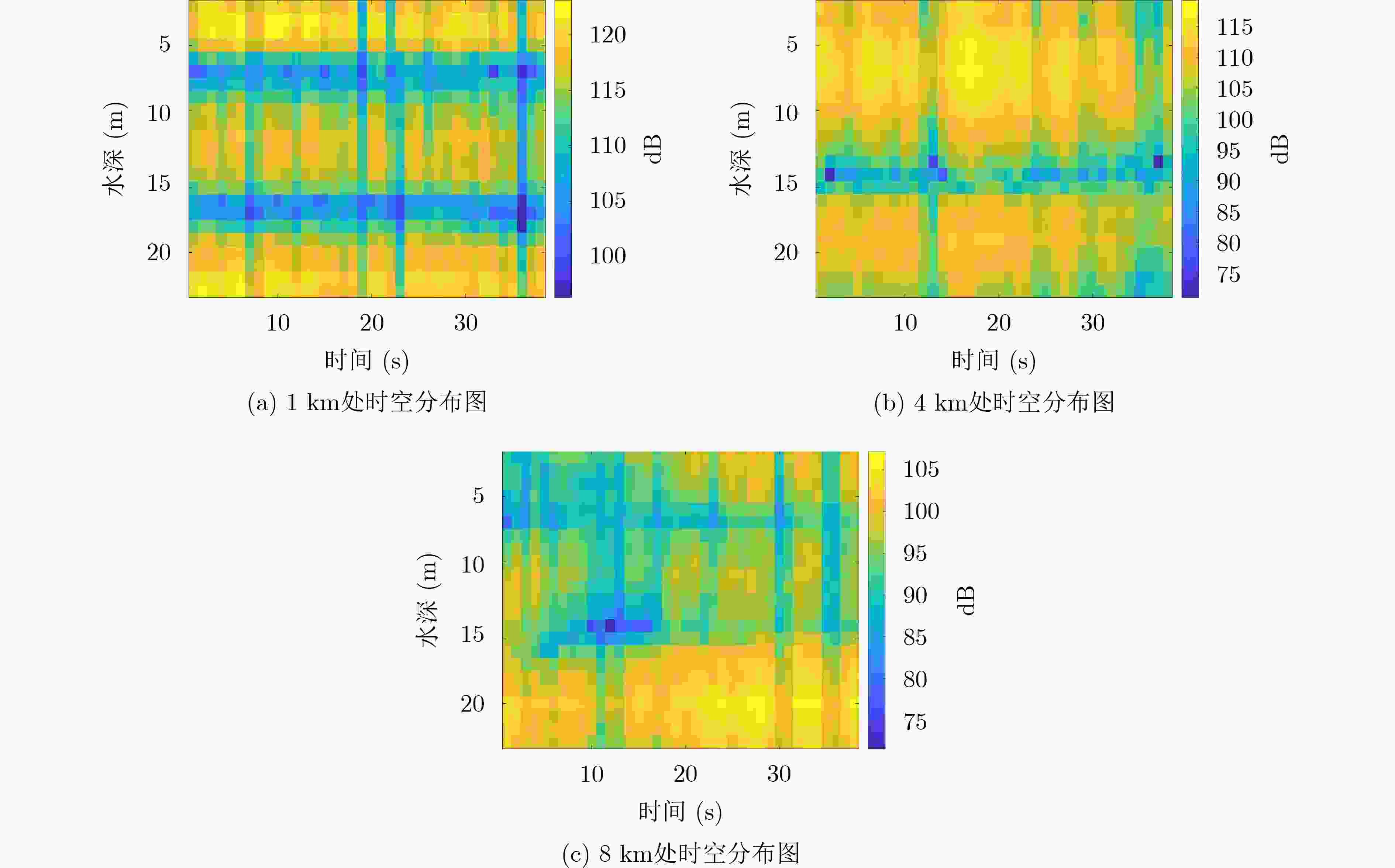
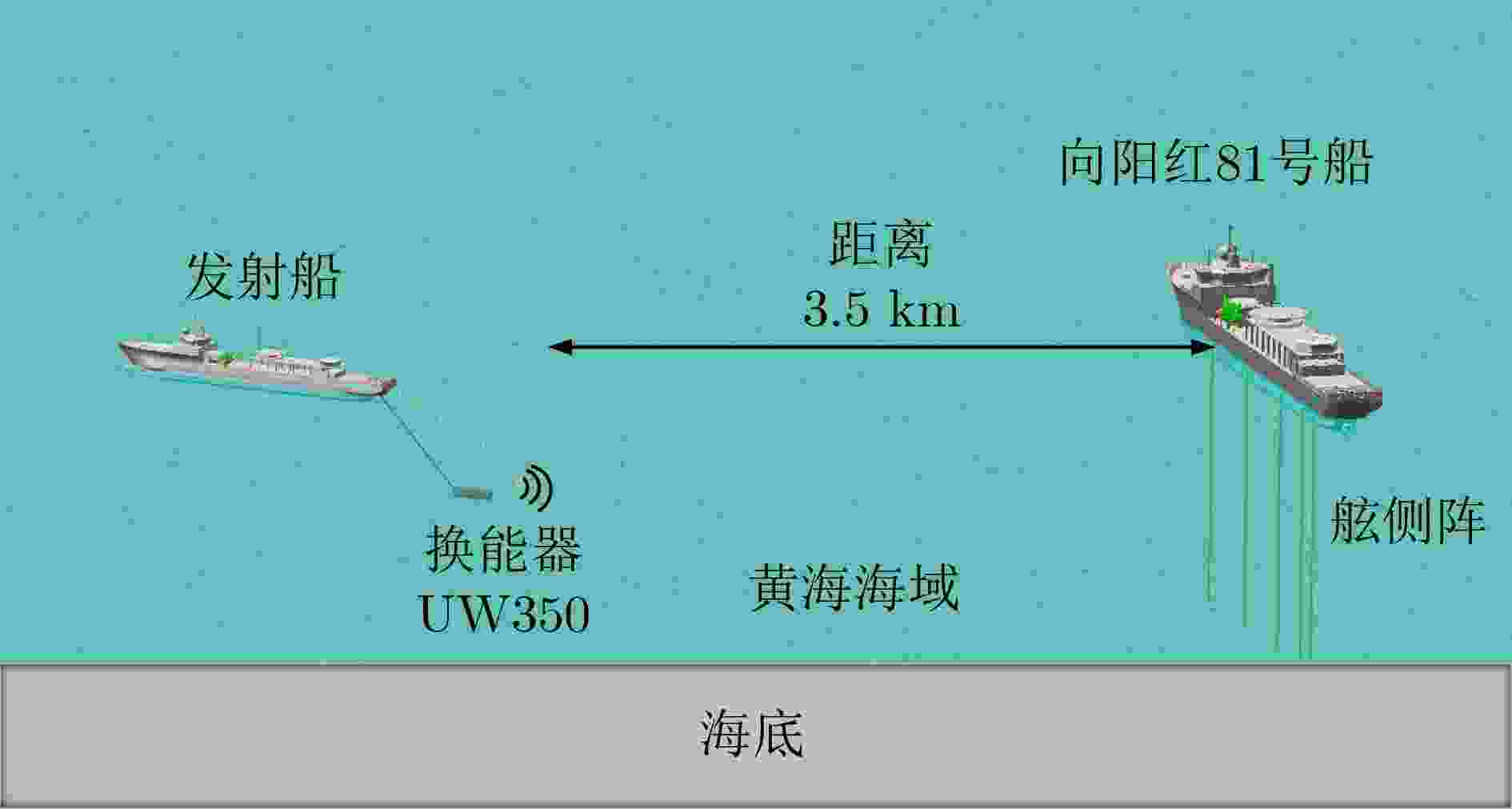
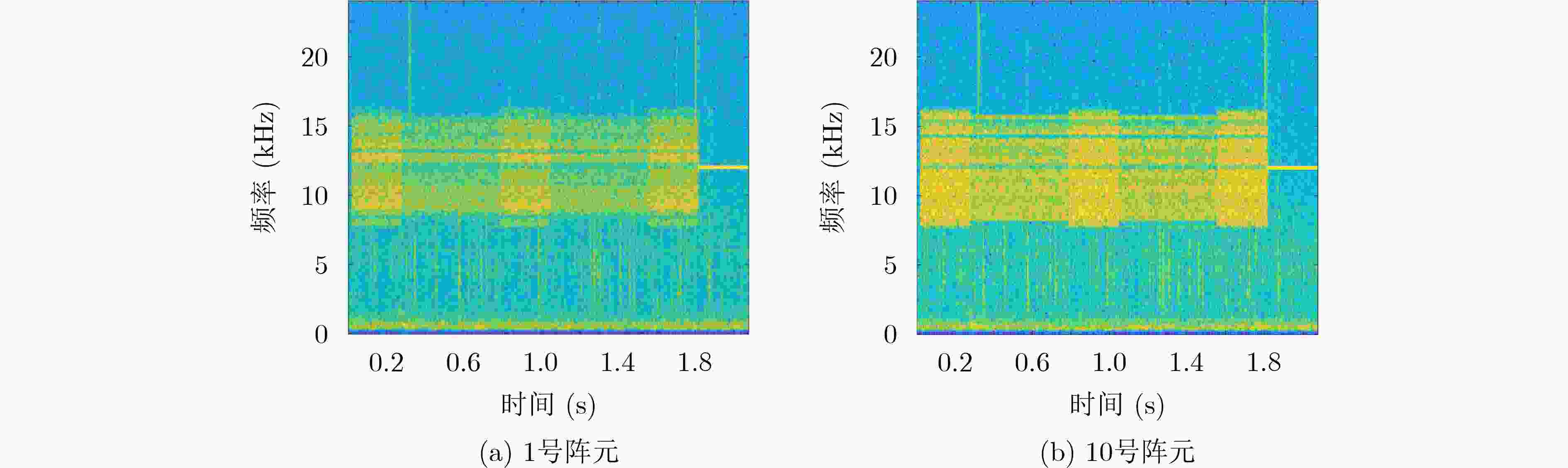
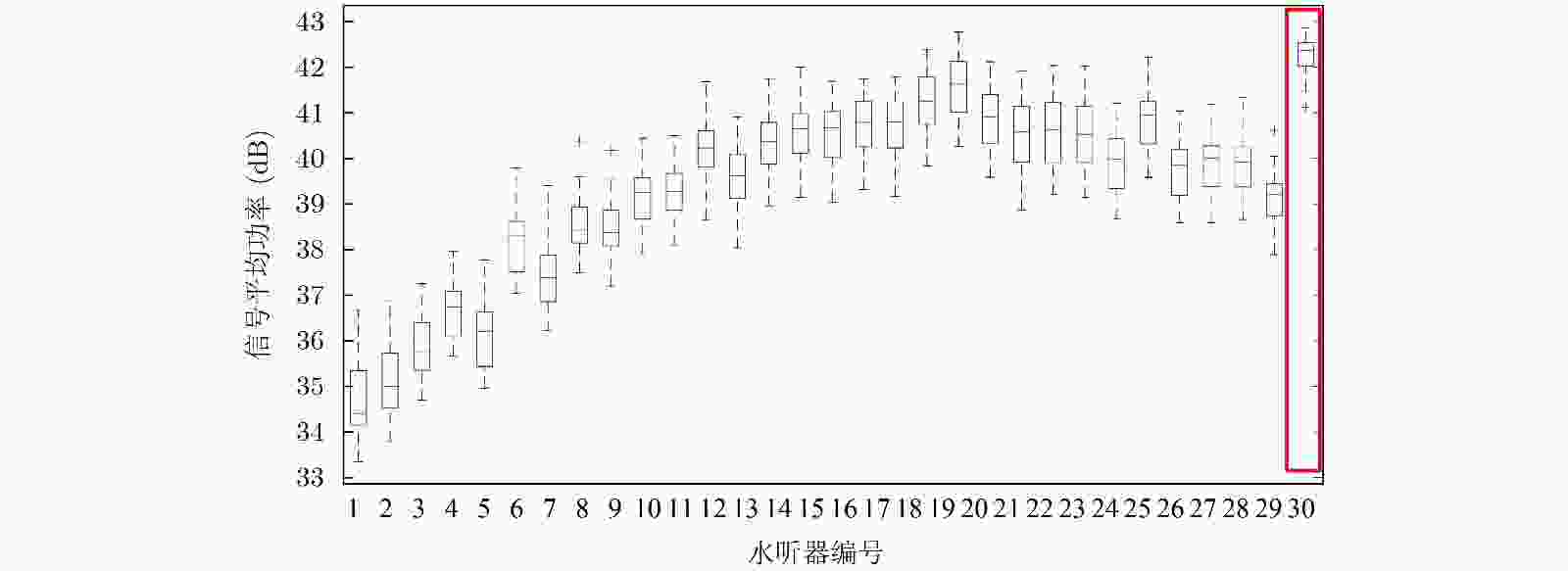


 下载:
下载:
