Low-complexity Iterative Sparse Channel Estimation for Underwater Acoustic OFDM Systems Based on Generalized Path Identification Algorithm
-
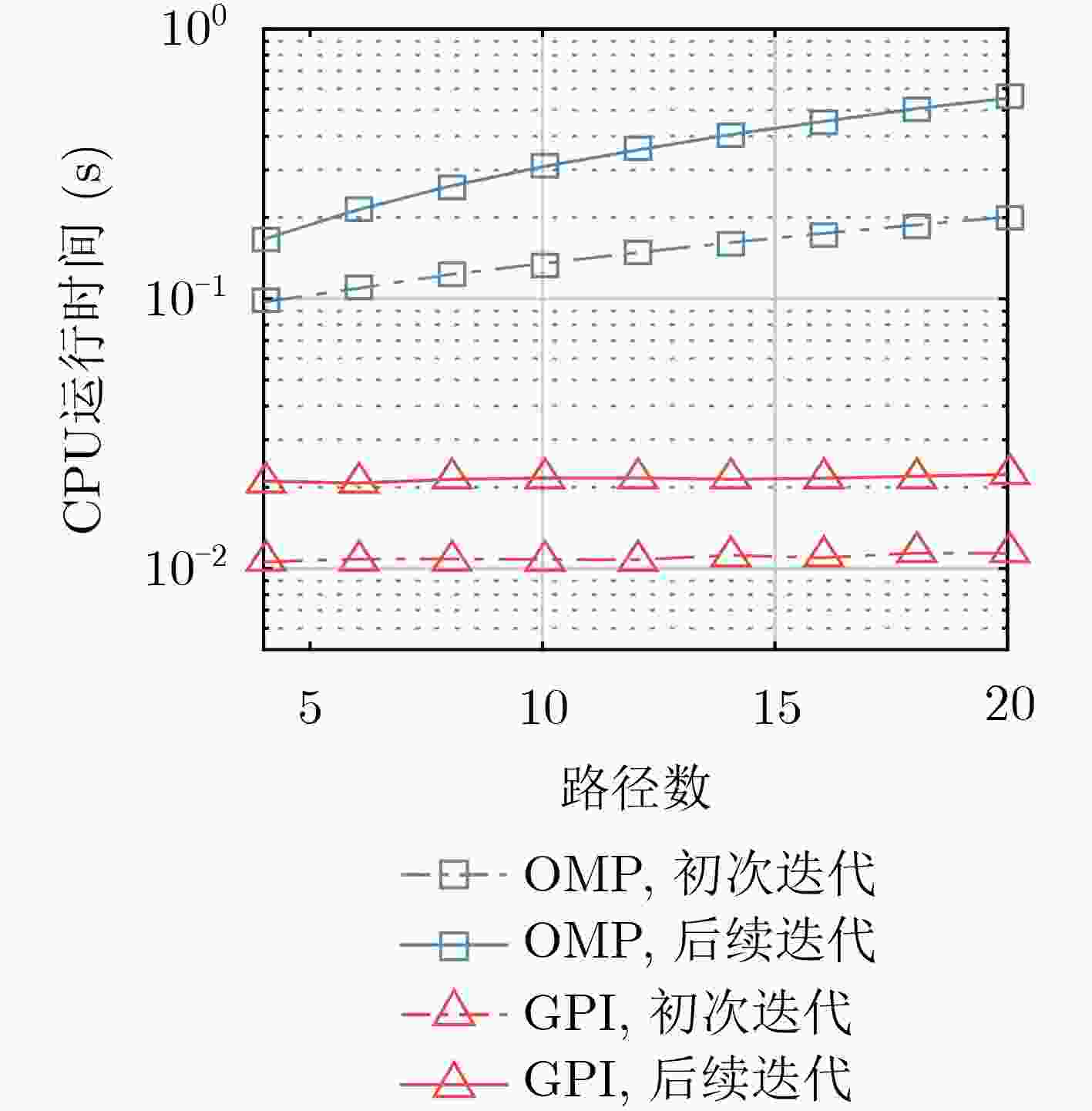
摘要: 移动OFDM水声通信系统中,基于压缩感知的稀疏信道估计方法计算量较大,不适用于实时通信。针对这一问题,该文基于一致多普勒信道模型提出一种扩展路径识别(GPI)算法。该方法首先使用信道多普勒扩展矩阵构造等效发射序列,将多普勒信道转化为等效线性时不变信道。然后使用GPI算法估计信道多普勒及各路径的时延及幅度参数,实现低复杂度稀疏信道估计。此外,该文将GPI算法扩展到Turbo接收机中,通过利用信道译码器反馈的数据符号先验信息迭代提高信道估计精度。仿真结果表明,所提方法的性能优于传统的路径识别算法,且与OMP算法接近,而其计算量远低于后者。Abstract: In mobile OFDM underwater acoustic communication systems, the compressed sensing-based sparse channel estimation methods suffer from high computational complexity, which is not suitable for real-time communication. To solve this problem, this paper proposes a Generalized Path Identification (GPI) algorithm for estimating uniform Doppler distorted channel. This scheme first constructs equivalent transmitted symbols using Doppler spread matrices, and thus the channel is converted into an equivalent linear time-invariant one. Then the GPI algorithm is utilized to estimate the channel parameters. Furthermore, the GPI algorithm is extended to Turbo receivers to iteratively improve the channel estimation accuracy. Simulation results show that the performance of the proposed method is better than that of the conventional path identification algorithm, and is close to the Orthogonal Matching Pursuit (OMP) algorithm. Its computational complexity, however, is much lower than OMP algorithm.
-
表 1 OFDM水声通信系统仿真参数
参数 符号 值 最低子载波频率 ${f_0}$ 9 kHz 带宽 $B$ 6 kHz 子载波数 $K$ 1024 OFDM符号周期 $T$ 170.65 ms 子载波间隔 $\Delta f$ 5.86 Hz ZP长度 ${T_{{\rm{ZP}}}}$ 15 ms -
LI Baosheng, ZHOU Shengli, STOJANOVIC M, et al. Multicarrier communication over underwater acoustic channels with nonuniform Doppler shifts[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2008, 33(2): 198–209. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2008.920471 LI Baosheng, HUANG Jie, ZHOU Shengli, et al. MIMO-OFDM for high-rate underwater acoustic communications[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2009, 34(4): 634–644. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2009.2032005 QIAO Gang, SONG Qingjun, MA Lu, et al. Sparse Bayesian learning for channel estimation in time-varying underwater acoustic OFDM communication[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 56675–56684. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2873406 WANG Shuche, HE Zhiqiang, NIU Kai, et al. New results on joint channel and impulsive noise estimation and tracking in underwater acoustic OFDM systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(4): 2601–2612. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.2966622 YERRAMALLI S, STOJANOVIC M, and MITRA U. Partial FFT demodulation: A detection method for highly Doppler distorted OFDM systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 60(11): 5906–5918. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2210547 王茜竹, 方冬, 吴广富. 基于改进稀疏度自适应匹配算法的免授权非正交多址接入上行传输多用户检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(9): 2216–2222. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190505WANG Qianzhu, FANG Dong, and WU Guangfu. Multi-user detection based on sparsity adaptive matching pursuit compressive sensing for uplink grant-free non-orthogonal multiple access[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(9): 2216–2222. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190505 BERGER C R, WANG Zhaohui, HUANG Jianzhong, et al. Application of compressive sensing to sparse channel estimation[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2010, 48(11): 164–174. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2010.5621984 BERGER C R, ZHOU Shengli, PREISIG J C, et al. Sparse channel estimation for multicarrier underwater acoustic communication: From subspace methods to compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2010, 58(3): 1708–1721. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2009.2038424 LI Chunguo, SONG Kang, and YANG Luxi. Low computational complexity design over sparse channel estimator in underwater acoustic OFDM communication system[J]. IET Communications, 2017, 11(7): 1143–1151. doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2016.1215 ARUNKUMAR K P and MURTHY C R. Iterative sparse channel estimation and data detection for underwater acoustic communications using partial interval demodulation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(19): 5041–5055. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2864599 TADAYON A and STOJANOVIC M. Iterative sparse channel estimation and spatial correlation learning for multichannel acoustic OFDM systems[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2019, 44(4): 820–836. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2019.2932662 HUANG Jianzhong, ZHOU Shengli, HUANG Jie, et al. Progressive inter-carrier interference equalization for OFDM transmission over time-varying underwater acoustic channels[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2011, 5(8): 1524–1536. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2011.2160040 ZHAO Shiduo, YAN Shefeng, and XU Lijun. Doppler estimation based on HFM signal for underwater acoustic time-varying multipath channel[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing, Dalian, China, 2019: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICSPCC46631.2019.8960810. STOJANOVIC M. Low complexity OFDM detector for underwater acoustic channels[C]. The OCEANS 2006, Boston, USA, 2006: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/OCEANS.2006.307057. LIU Yinsheng, TAN Zhenhui, HU Hongjie, et al. Channel estimation for OFDM[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2014, 16(4): 1891–1908. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2014.2320074 ZHAO Shiduo, YAN Shefeng, and XI Junyi. Bidirectional soft-decision feedback equalization for OFDM systems[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(8): 1283–1286. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.2988659 TUCHLER M, KOETTER R, and SINGER A C. Turbo equalization: Principles and new results[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2002, 50(5): 754–767. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2002.1006557 -





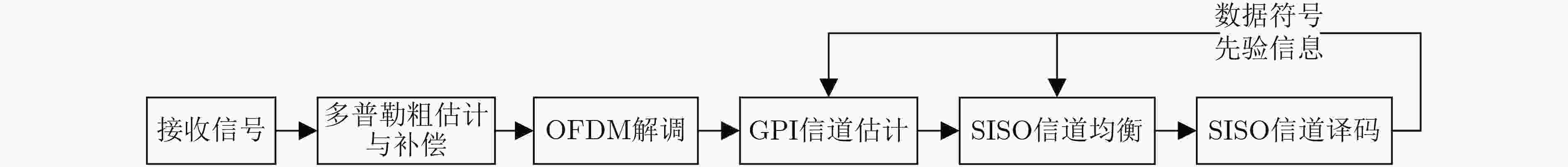
 下载:
下载:
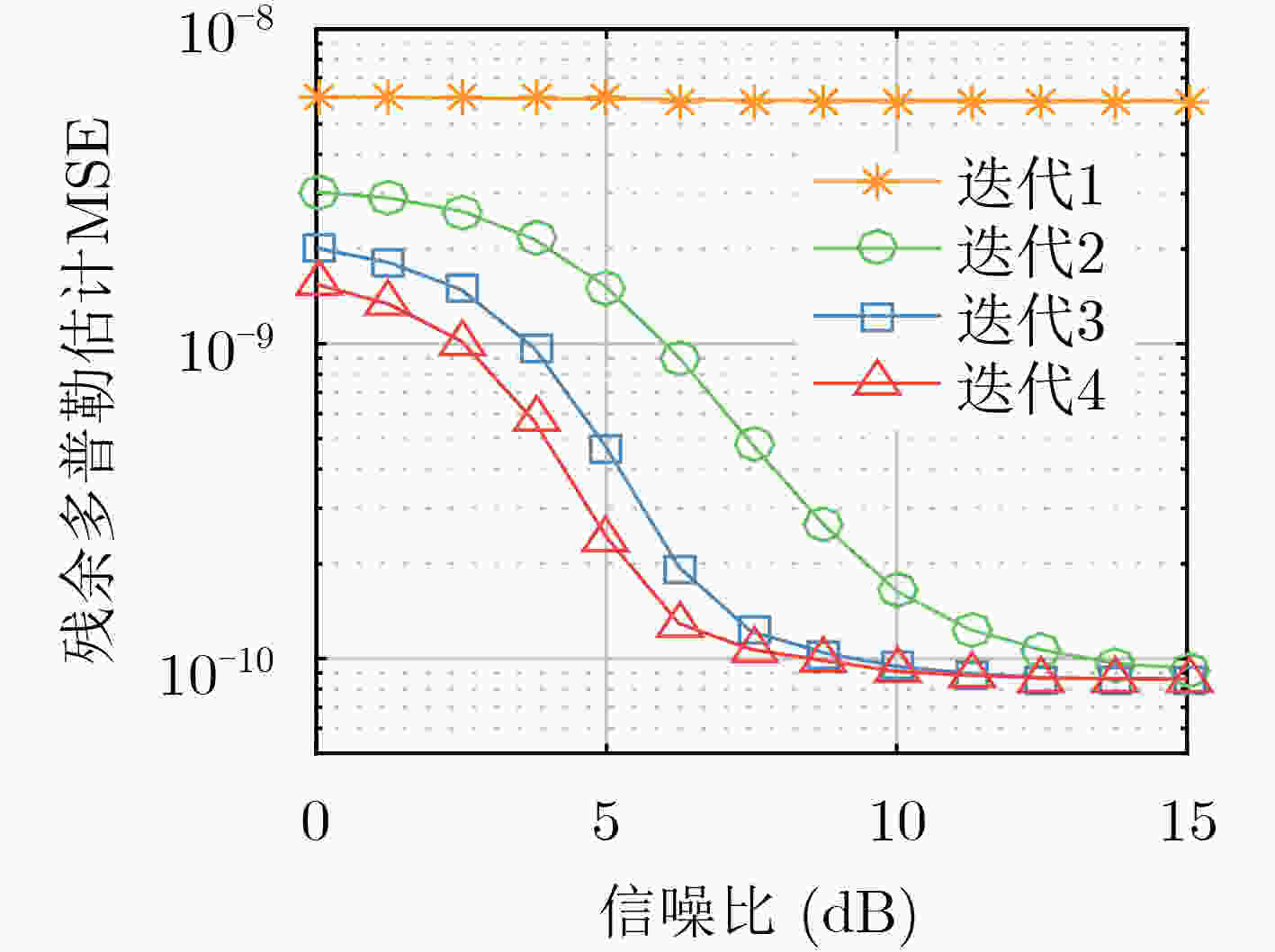

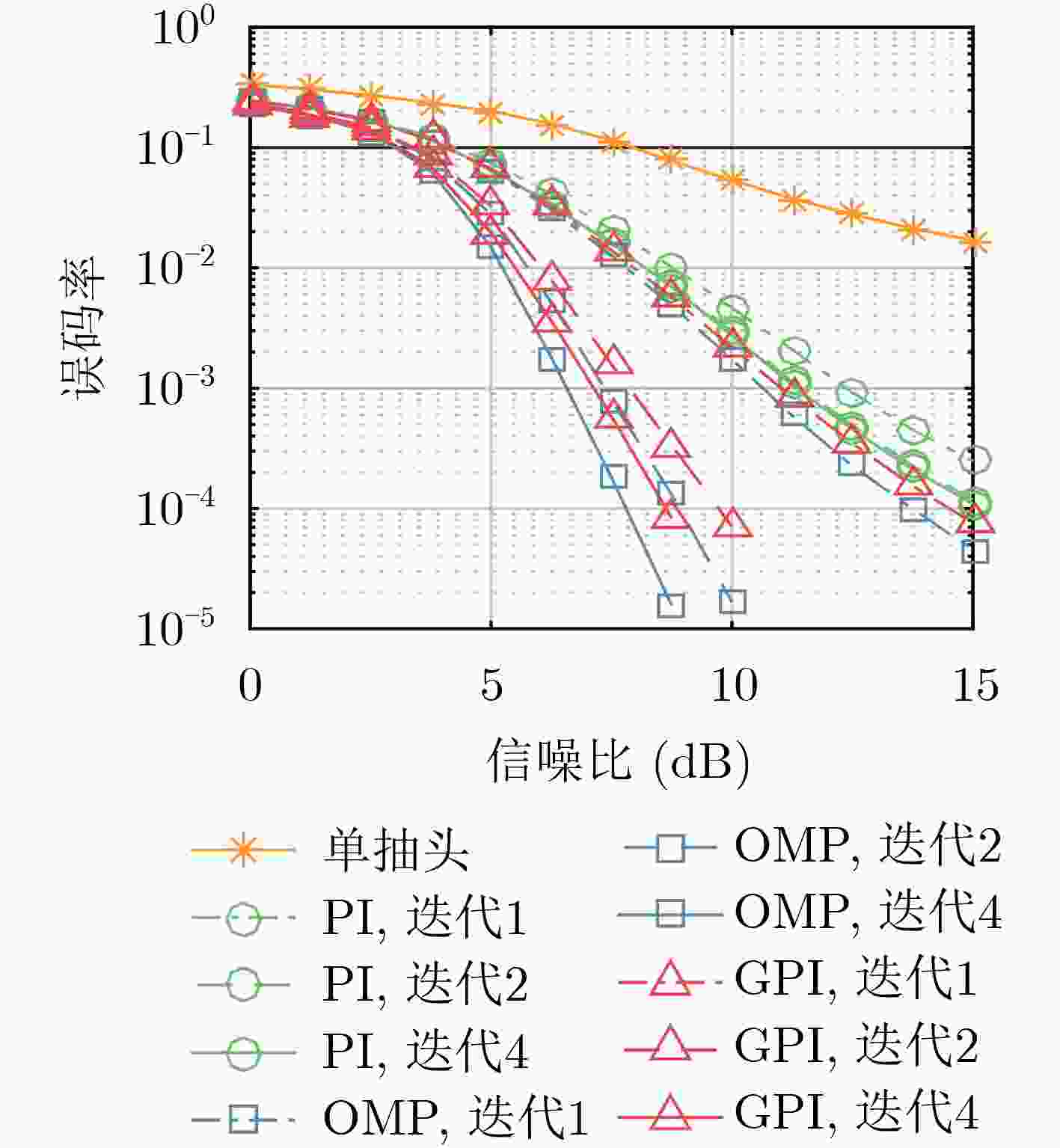

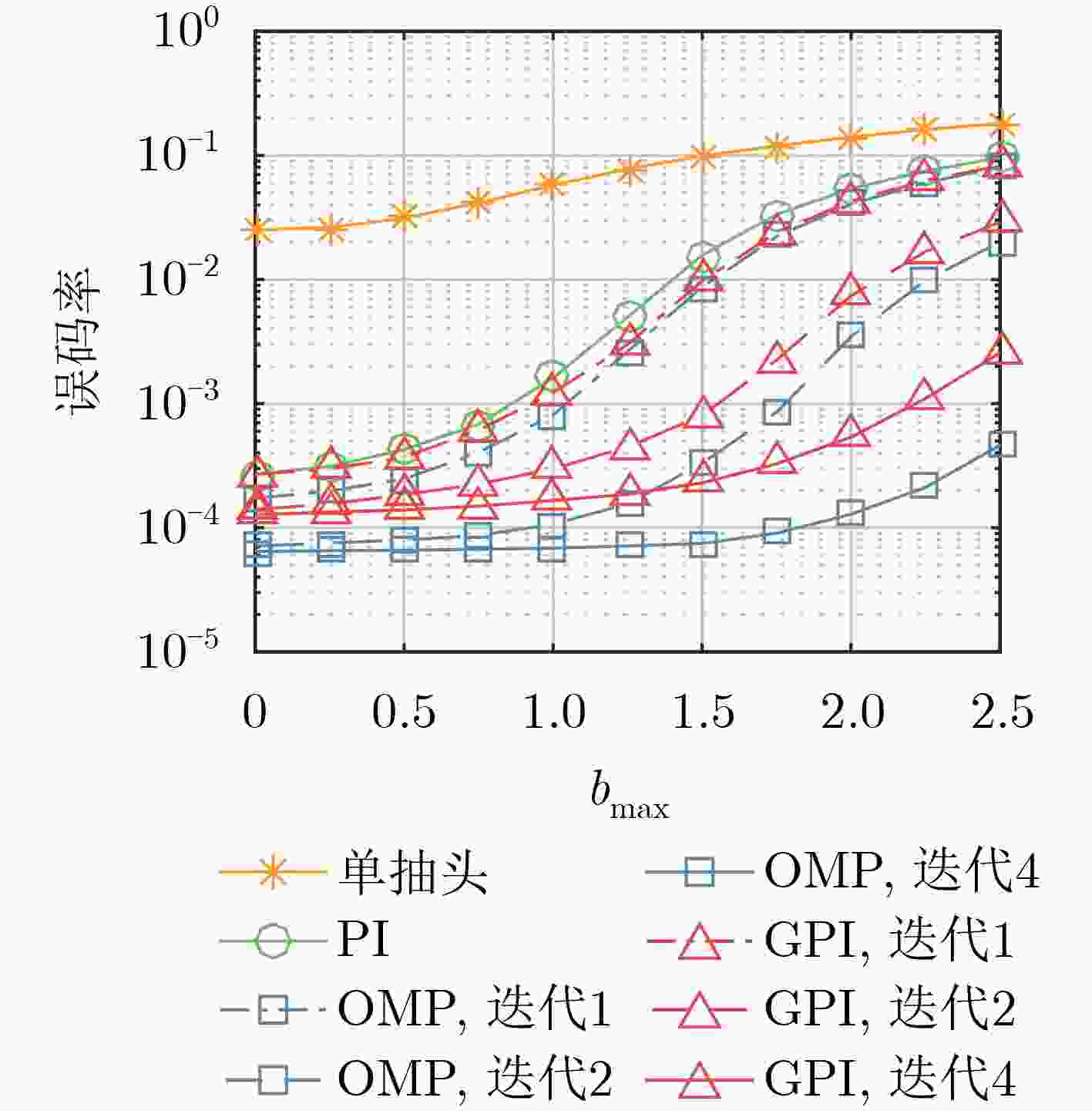




 下载:
下载:
