| [1] |
ADLEMAN L M. Molecular computation of solutions to combinatorial problems[J]. Science, 1994, 266(5187): 1021–1024. doi: 10.1126/science.7973651
|
| [2] |
LI Wei, YANG Yang, YAN Hao, et al. Three-input majority logic gate and multiple input logic circuit based on DNA strand displacement[J]. Nano Letters, 2013, 13(6): 2980–2988. doi: 10.1021/nl4016107
|
| [3] |
THUBAGERE A J, THACHUK C, BERLEANT J, et al. Compiler-aided systematic construction of large-scale DNA strand displacement circuits using unpurified components[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 14373. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14373
|
| [4] |
GREEN S J, LUBRICH D, and TURBERFIELD A J. DNA hairpins: fuel for autonomous DNA devices[J]. Biophysical Journal, 2006, 91(8): 2966–2975. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.106.084681
|
| [5] |
ZHAO Yunbin, LIU Yuan, ZHENG Xuedong, et al. Half adder and half subtractor logic gates based on nicking enzymes[J]. Molecular Systems Design & Engineering, 2019, 4(6): 1103–1113. doi: 10.1039/C9ME00090A
|
| [6] |
殷志祥, 唐震, 张强, 等. 基于DNA折纸基底的与非门计算模型[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(6): 1355–1364. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190825YIN Zhixiang, TANG Zhen, ZHANG Qiang, et al. NAND gate computational model based on the DNA origami template[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(6): 1355–1364. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190825
|
| [7] |
孙军伟, 李智, 王延峰. 基于DNA链置换的三级联组合分子逻辑电路设计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(6): 1401–1409. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190847SUN Junwei, LI Zhi, and WANG Yanfeng. Design of three-cascade combinatorial molecular logic circuit based on DNA strand displacement[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(6): 1401–1409. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190847
|
| [8] |
LILIENTHAL S, KLEIN M, ORBACH R, et al. Continuous variables logic via coupled automata using a DNAzyme cascade with feedback[J]. Chemical Science, 2017, 8(3): 2161–2168. doi: 10.1039/C6SC03892A
|
| [9] |
WANG Bin, XIE Yingjie, ZHOU Shihua, et al. Correcting errors in image encryption based on DNA coding[J]. Molecules, 2018, 23(8): 1878. doi: 10.3390/molecules23081878
|
| [10] |
WANG Bin, ZHANG Qiang, and WEI Xiaopeng. Tabu variable neighborhood search for designing DNA barcodes[J]. IEEE Transactions on NanoBioscience, 2020, 19(1): 127–131. doi: 10.1109/TNB.2019.2942036
|
| [11] |
SONG Tianqi, GOPALKRISHNAN N, ESHRA A, et al. Improving the performance of DNA strand displacement circuits by shadow cancellation[J]. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(11): 11689–11697. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b07394
|
| [12] |
许鹏, 方刚, 石晓龙, 等. DNA存储及其研究进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(6): 1326–1331. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190863XU Peng, FANG Gang, SHI Xiaolong, et al. DNA storage and its research progress[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(6): 1326–1331. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190863
|
| [13] |
SEELIG G, SOLOVEICHIK D, ZHANG D Y, et al. Enzyme-free nucleic acid logic circuits[J]. Science, 2006, 314(5805): 1585–1588. doi: 10.1126/science.1132493
|
| [14] |
ZHANG D Y, TURBERFIELD A J, YURKE B, et al. Engineering entropy-driven reactions and networks catalyzed by DNA[J]. Science, 2007, 318(5853): 1121–1125. doi: 10.1126/science.1148532
|
| [15] |
LAKIN M R and STEFANOVIC D. Supervised learning in adaptive DNA strand displacement networks[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2016, 5(8): 885–897. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.6b00009
|
| [16] |
SONG Tianqi, GARG S, MOKHTAR R, et al. Analog computation by DNA strand displacement circuits[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2016, 5(8): 898–912. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.6b00144
|
| [17] |
QIAN Lulu, WINFREE E, and BRUCK J. Neural network computation with DNA strand displacement cascades[J]. Nature, 2011, 475(7356): 368–372. doi: 10.1038/nature10262
|
| [18] |
GENOT A J, FUJII T, and RONDELEZ Y. Scaling down DNA circuits with competitive neural networks[J]. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 2013, 10(85): 20130212. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2013.0212
|
| [19] |
SHI Xiaolong, WANG Zhiyu, DENG Chenyan, et al. A novel bio-sensor based on DNA strand displacement[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(10): e108856. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108856
|
| [20] |
CHERRY K M and QIAN Lulu. Scaling up molecular pattern recognition with DNA-based winner-take-all neural networks[J]. Nature, 2018, 559(7714): 370–376. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0289-6
|
| [21] |
LAKIN M R, YOUSSEF S, POLO F, et al. Visual DSD: A design and analysis tool for DNA strand displacement systems[J]. Bioinformatics, 2011, 27(22): 3211–3213. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr543
|
| [22] |
WANG Yanfeng, ZHANG Wenwen, LI Xing, et al. Molecular logic gates based on localized DNA strand displacement[J]. Journal of Computational and Theoretical Nanoscience, 2016, 13(6): 3948–3952. doi: 10.1166/jctn.2016.5231
|
| [23] |
SONG Tianqi, GARG S, MOKHTAR R, et al. Design and analysis of compact DNA strand displacement circuits for analog computation using autocatalytic amplifiers[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(1): 46–53. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.6b00390
|
| [24] |
YANG Jing, WU Ranfeng, LI Yifan, et al. Entropy-driven DNA logic circuits regulated by DNAzyme[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2018, 46(16): 8532–8541. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky663
|
| [25] |
ESHRA A, SHAH S, SONG Tianqi, et al. Renewable DNA hairpin-based logic circuits[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nanotechnology, 2019, 18: 252–259. doi: 10.1109/TNANO.2019.2896189
|





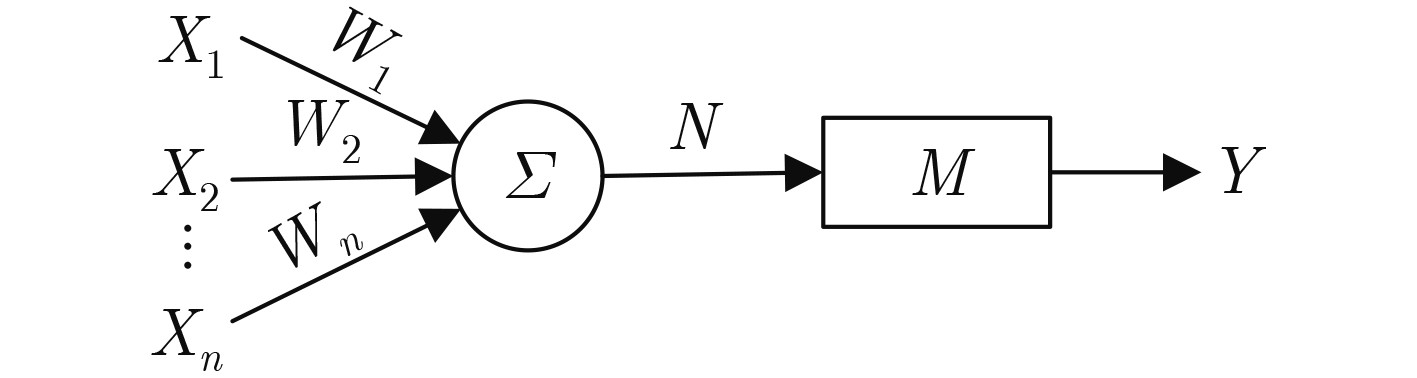
 下载:
下载:
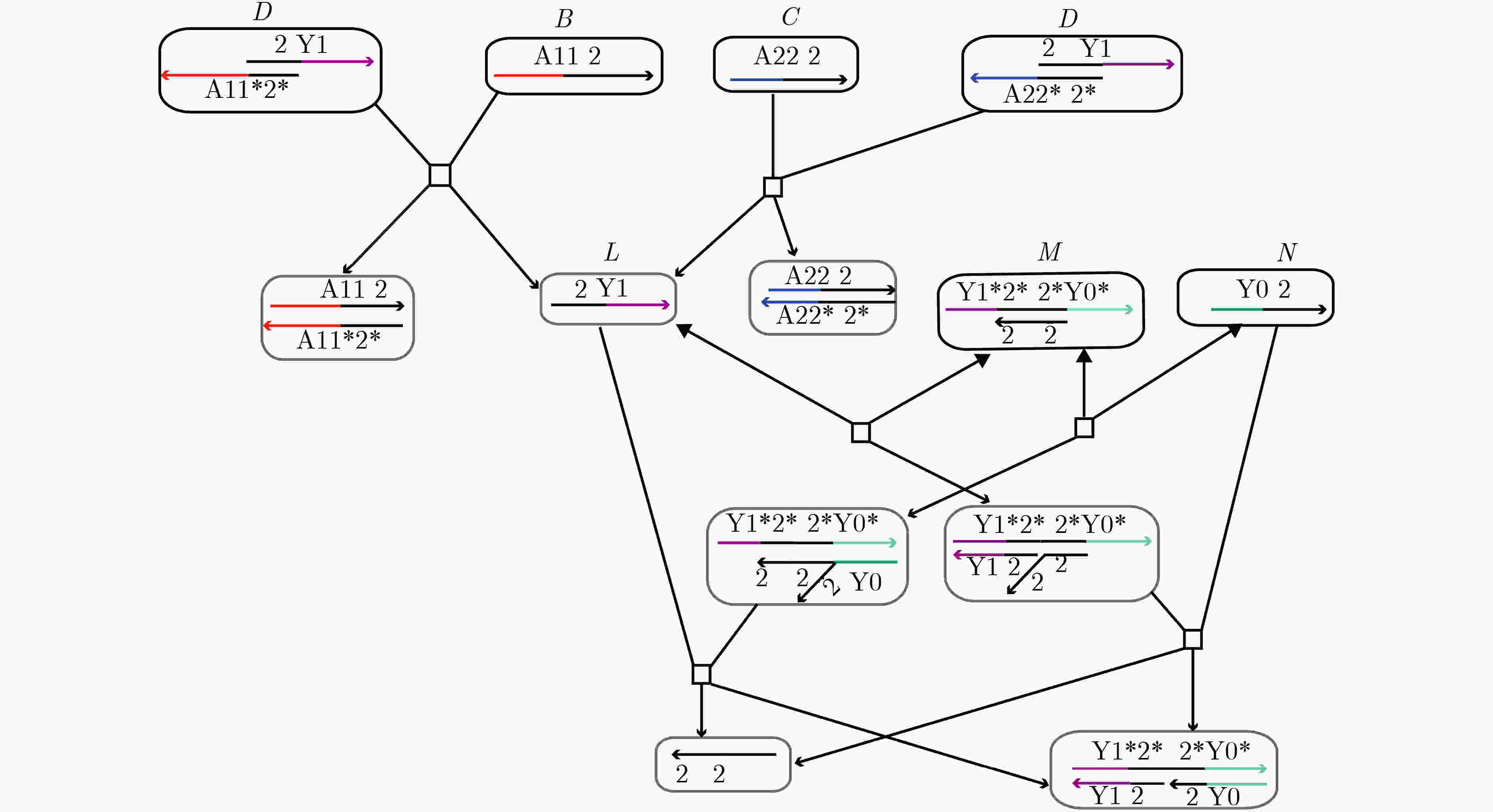
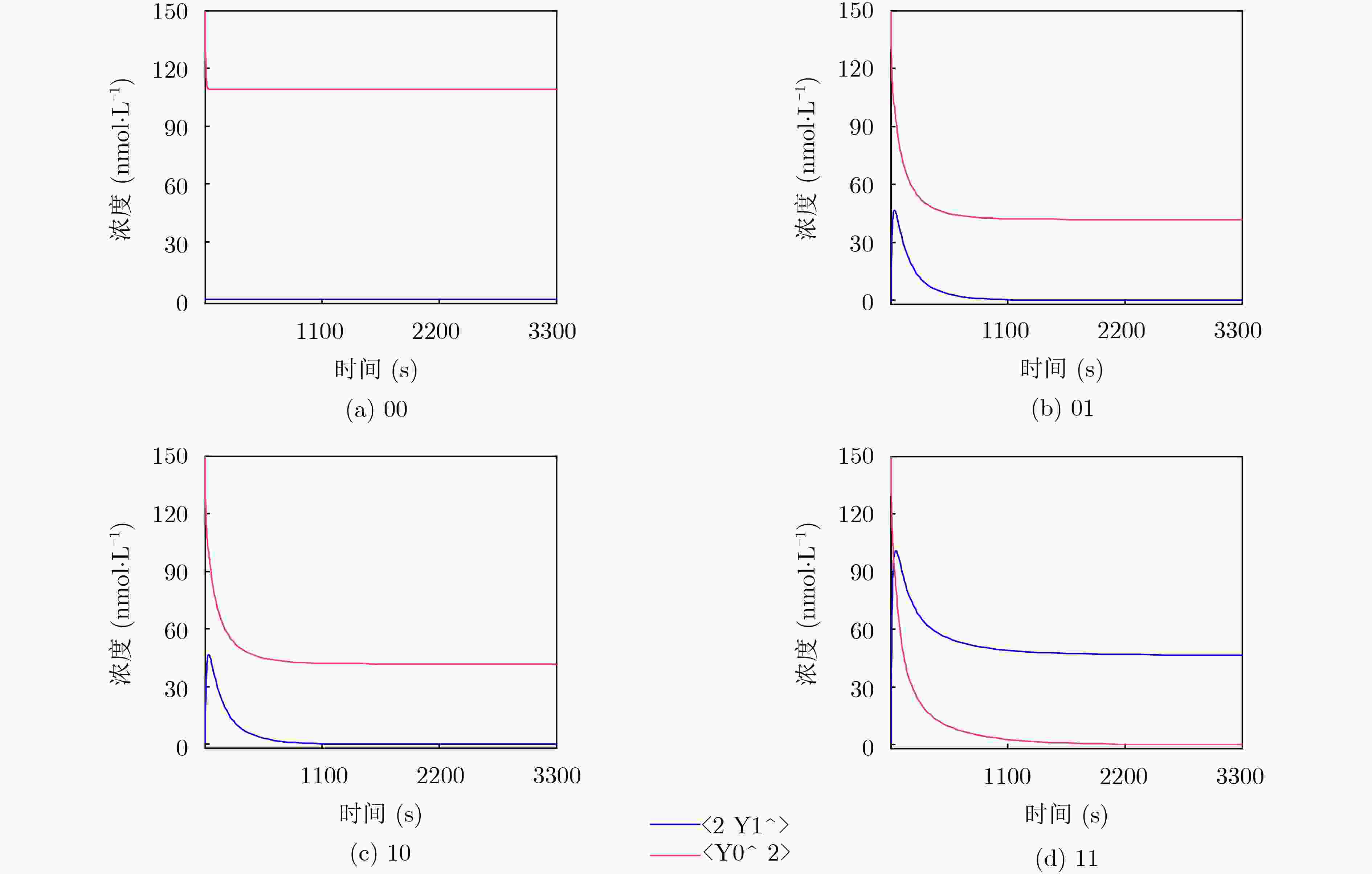
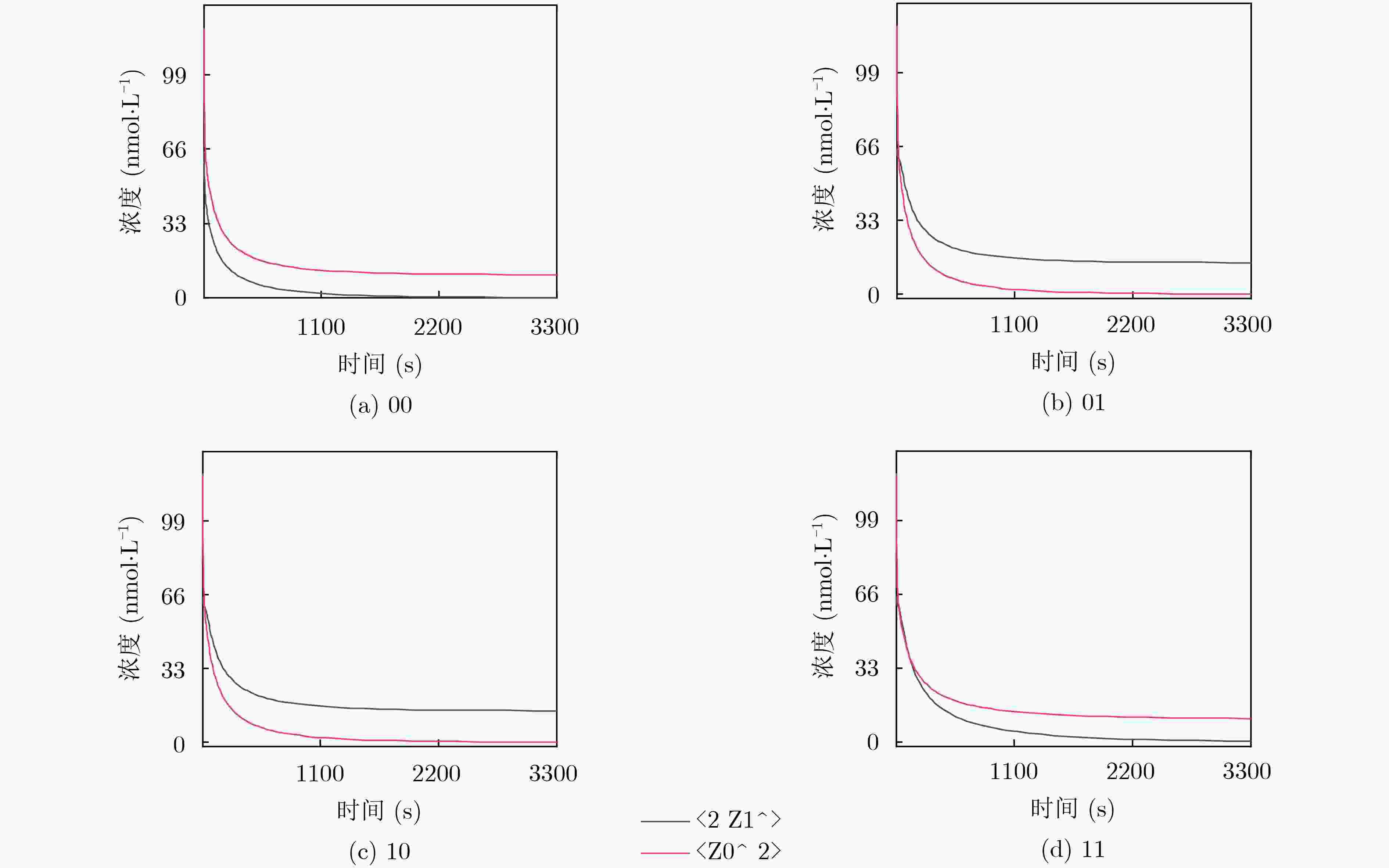


 下载:
下载:
