A Discriminative Feature Representation Method Based on Dual Attention Mechanism for Remote Sensing Image Scene Classification
-
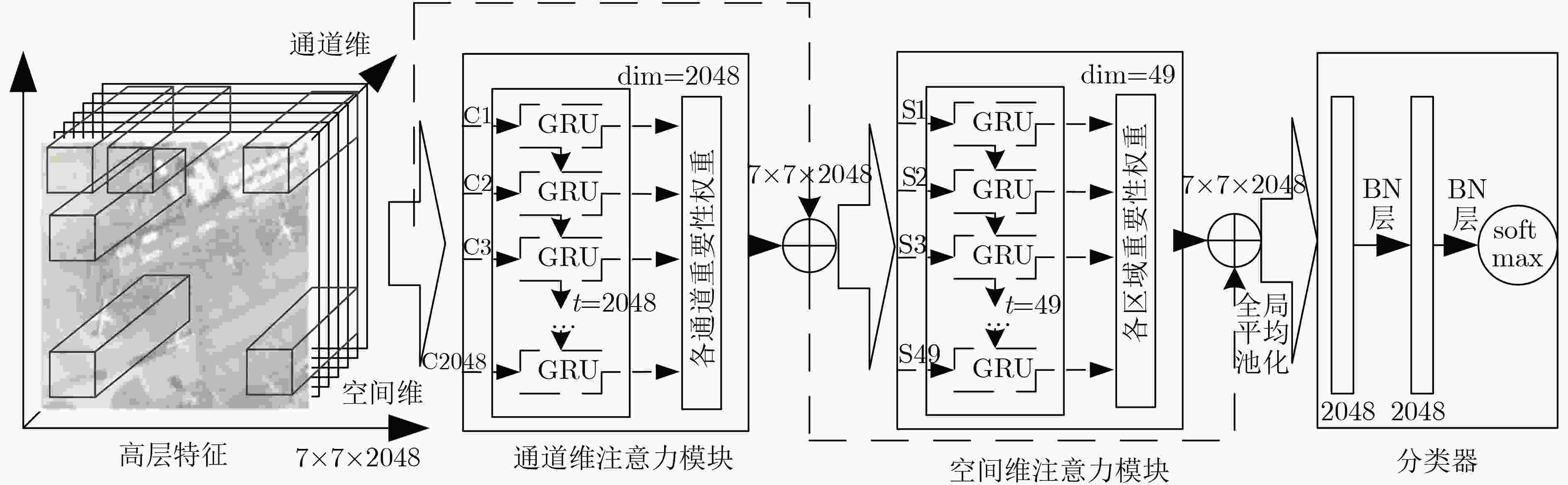
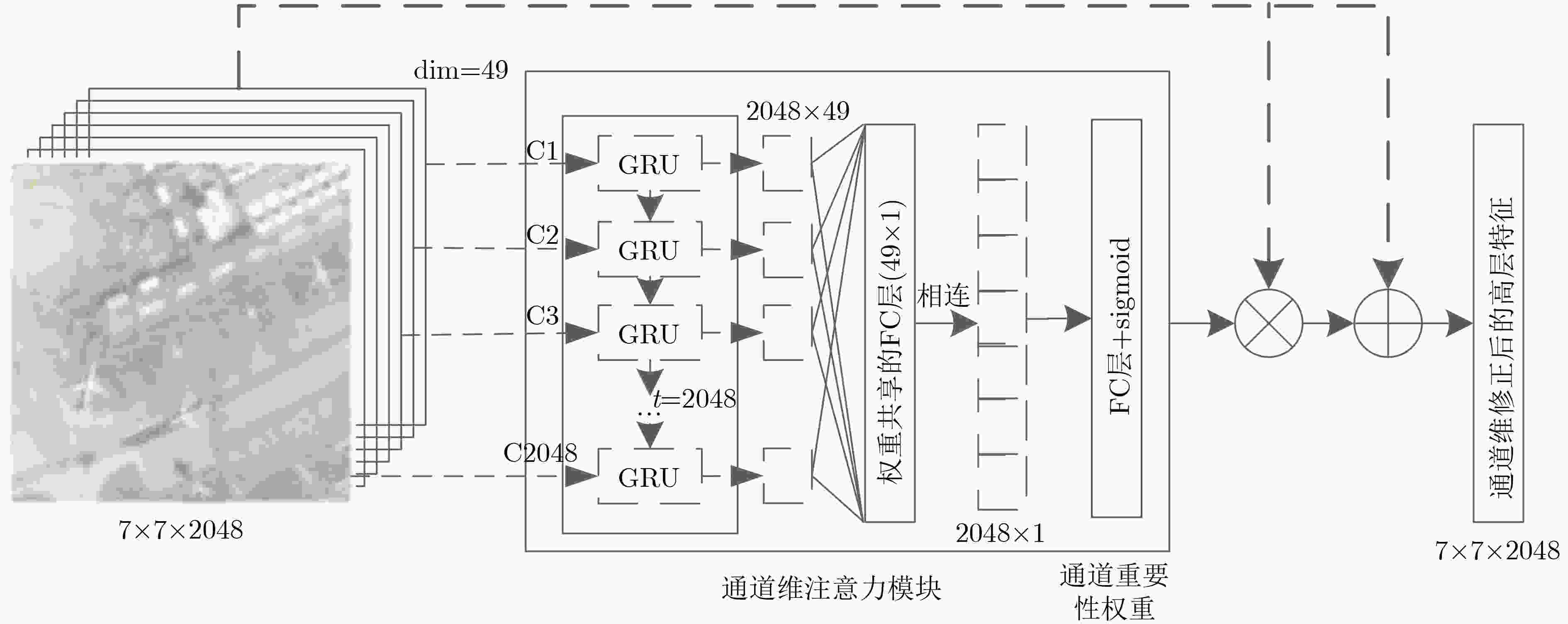
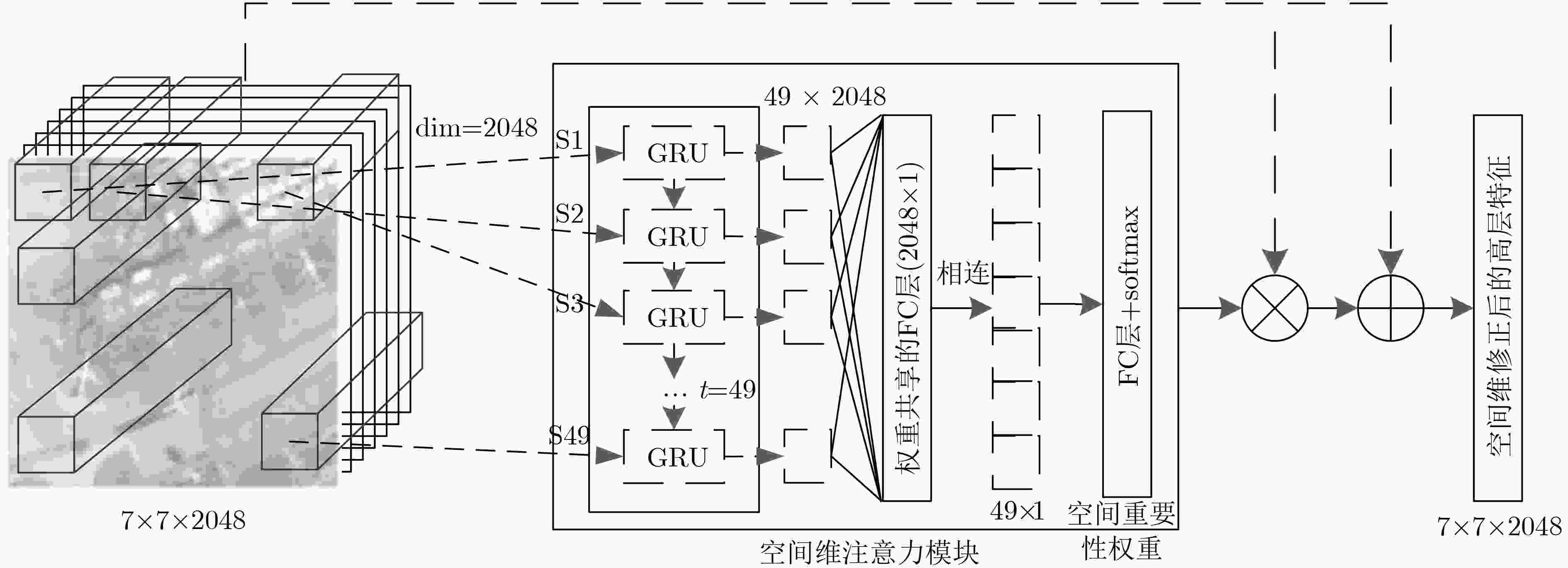
摘要: 针对遥感图像场景分类面临的类内差异性大、类间相似性高导致的部分场景出现分类混淆的问题,该文提出了一种基于双重注意力机制的强鉴别性特征表示方法。针对不同通道所代表特征的重要性程度以及不同局部区域的显著性程度不同,在卷积神经网络提取的高层特征基础上,分别设计了一个通道维和空间维注意力模块,利用循环神经网络的上下文信息提取能力,依次学习、输出不同通道和不同局部区域的重要性权重,更加关注图像中的显著性特征和显著性区域,而忽略非显著性特征和区域,以提高特征表示的鉴别能力。所提双重注意力模块可以与任意卷积神经网络相连,整个网络结构可以端到端训练。通过在两个公开数据集AID和NWPU45上进行大量的对比实验,验证了所提方法的有效性,与现有方法对比,分类准确率取得了明显的提升。Abstract: Considering the problem of low classification accuracy caused by large intra-class differences and high inter-class similarity in remote sensing image scene classification, a discriminative feature representation method based on dual attention mechanism is proposed. Due to the difference in the importance of the features contained in different channels and the significance of different local regions, the channel-wise and spatial-wise attention module are designed, based on the high-level features extracted by the Convolutional Neural Networks. Relying on the ability to extract contextual information, the Recurrent Neural Network is adopted to learn and output the importance weights of different channels and different local regions, paying more attention to the salient features and salient regions, while ignoring non-salience features and regions, to enhance the discriminative ability of feature representation. The proposed dual attention module can be connected to the last convolutional layer of any convolutional neural network, and the network structure can be trained end-to-end. Comparative experiments are conducted on the two public data sets AID and NWPU45. Compared with the existing methods, the classification accuracy has been significantly improved, and the effectiveness of the proposed method can be verified.
-
表 1 数据集AID和NWPU45下的模型简化测试OA(%)结果对比表
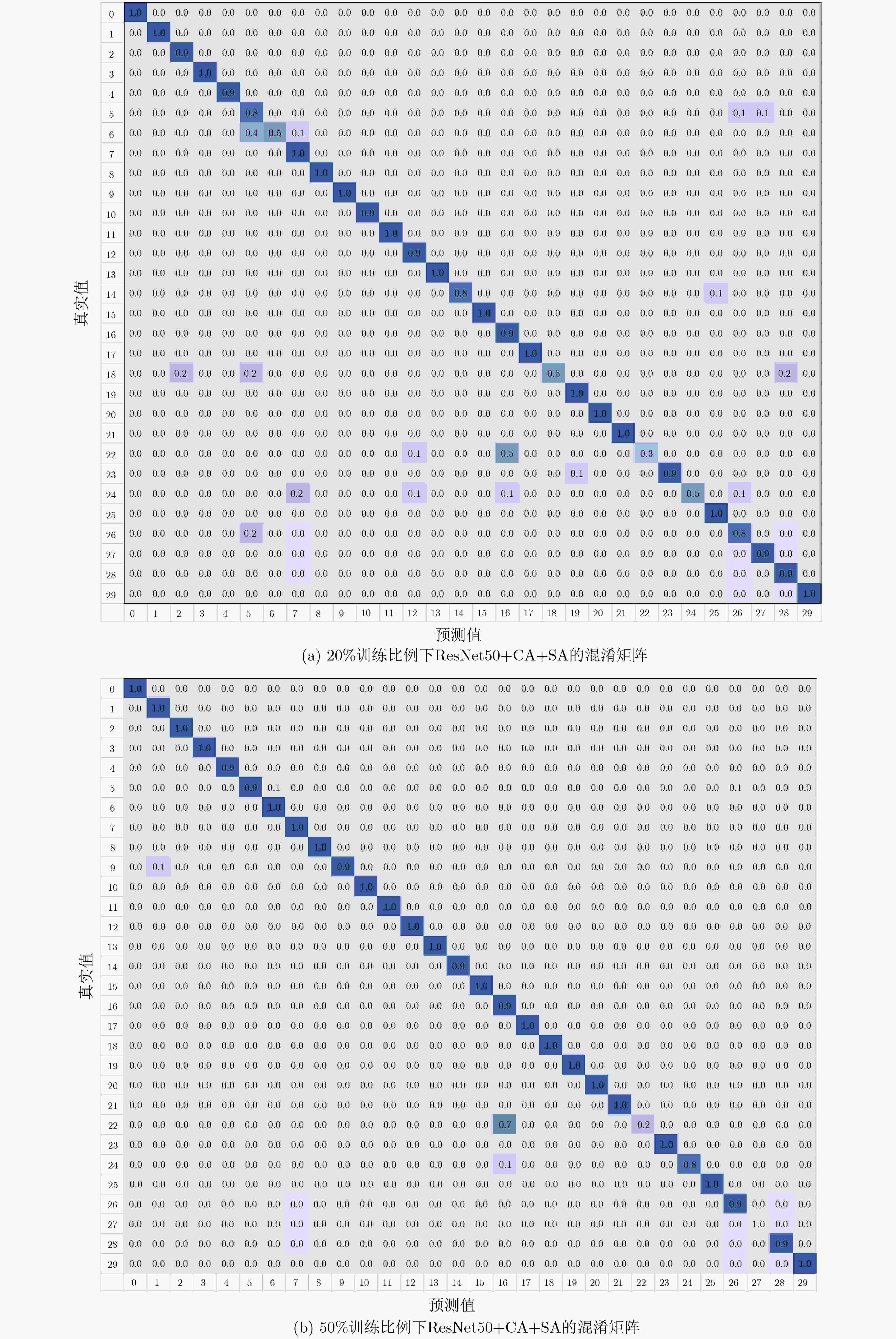
方法 AID NWPU45 20% 50% 10% 20% VGG16 86.59±0.29 89.64±0.30 87.15±0.45 90.36±0.18 VGG16+CA 87.73±0.19 89.98±0.25 88.54±0.39 90.89±0.23 VGG16+SA 89.36±0.21 94.06±0.19 93.23±0.21 95.05±0.18 VGG16+CA+SA 89.87±0.30 94.58±0.23 97.89±0.12 98.82±0.20 ResNet50 86.48±0.49 89.22±0.34 89.88±0.26 92.35±0.19 ResNet50+CA 88.23±0.34 91.45±0.30 91.52±0.19 93.48±0.21 ResNet50+SA 90.83±0.55 94.46±0.48 97.56±0.08 98.79±0.04 ResNet50+CA+SA 91.34±0.38 95.22±0.36 98.55±0.11 99.07±0.23 表 2 数据集AID下所提方法与其他基准方法的OA(%)结果对比表
方法 年份 AID 20% 50% VGG16 [16] 2017 86.59±0.29 89.64±0.30 CaffeNet [16] 2017 86.86±0.47 89.53±0.31 GoogLeNet [16] 2017 83.44±0.40 86.39±0.55 Fusion-by-add [19] 2017 91.87±0.36 MCNN [11] 2018 91.80±0.22 ARCNet [12] 2019 88.75±0.40 93.10±0.55 Finetune_ResNet50[14] 2019 86.48±0.49 89.22±0.34 ResNet_LGFFE [14] 2019 90.83±0.55 94.46±0.48 VGG16+CA+SA 本文方法 89.87±0.30 94.58±0.23 ResNet50+CA+SA 本文方法 91.34±0.38 95.22±0.36 表 3 数据集NWPU45下所提方法与其他基准方法的OA(%)结果对比表
方法 年份 NWPU45 10% 20% AlexNet [17] 2017 81.22±0.19 85.16±0.18 VGG_16 [17] 2017 87.15±0.45 90.36±0.18 GoogleNet [17] 2017 86.02±0.18 86.02±0.18 D_CNN [11] 2018 89.22±0.5 91.89±0.22 LGFF [20] 2018 93.61±0.1 96.37±0.05 文献[21] 2019 91.73±0.21 93.47±0.30 Finetune_ResNet50[14] 2019 89.88±0.26 92.35±0.19 ResNet_LGFFE[14] 2019 97.56±0.08 98.79±0.04 VGG16+CA+SA 本文方法 97.89±0.12 98.82±0.20 ResNet50+CA+SA 本文方法 98.55±0.11 99.07±0.23 -
CHI Mingmin, PLAZA A, BENEDIKTSSON J A, et al. Big data for remote sensing: Challenges and opportunities[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2016, 104(11): 2207–2219. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2016.2598228 ZHANG Liangpei, ZHANG Lefei, and DU Bo. Deep learning for remote sensing data: A technical tutorial on the state of the art[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2016, 6(4): 22–40. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2016.2540798 CHENG Gong, MA Chengcheng, ZHOU Peicheng, et al. Scene classification of high resolution remote sensing images using convolutional neural networks[C]. 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Beijing, China, 2016: 767–770. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2016.7729193. SZEGEDY C, LIU Wei, JIA Yangqing, et al. Going deeper with convolutions[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 1–9. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298594. HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. The 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2012: 1097–1105. HU Fan, XIA Guisong, YANG Wen, et al. Recent advances and opportunities in scene classification of aerial images with deep models[C]. 2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 2018: 4371–4374. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2018.8518336. CHENG Gong, YANG Ceyuan, YAO Xiwen, et al. When deep learning meets metric learning: Remote sensing image scene classification via learning discriminative CNNs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(5): 2811–2821. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2783902 LI Peng, REN Peng, ZHANG Xiaoyu, et al. Region-wise deep feature representation for remote sensing images[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(6): 871. doi: 10.3390/rs10060871 LIU Yanfei, ZHONG Yanfei, and QIN Qianqing. Scene classification based on multiscale convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(12): 7109–7121. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2848473 YUAN Yuan, FANG Jie, LU Xiaoqiang, et al. Remote sensing image scene classification using rearranged local features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(3): 1779–1792. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2869101 WANG Qi, LIU Shaoteng, CHANUSSOT J, et al. Scene classification with recurrent attention of VHR remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(2): 1155–1167. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2864987 XIONG Wei, LV Yafei, CUI Yaqi, et al. A discriminative feature learning approach for remote sensing image retrieval[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(3): 281. doi: 10.3390/rs11030281 LV Yafei, ZHANG Xiaohan, XIONG Wei, et al. An end-to-end local-global-fusion feature extraction network for remote sensing image scene classification[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(24): 3006. doi: 10.3390/rs11243006 CHO K, VAN MERRIËNBOER B, GULCEHRE C, et al. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder–decoder for statistical machine translation[C]. 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Doha, Qatar, 2014: 1724–1734. doi: 10.3115/v1/D14-1179. XIA Guisong, HU Jingwen, HU Fan, et al. AID: A benchmark data set for performance evaluation of aerial scene classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(7): 3965–3981. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2685945 CHENG Gong, HAN Junwei, and LU Xiaoqiang. Remote sensing image scene classification: Benchmark and state of the art[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2017, 105(10): 1865–1883. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2017.2675998 SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2015: 7–12. CHAIB S, LIU Huan, GU Yanfeng, et al. Deep feature fusion for VHR remote sensing scene classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(8): 4775–4784. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2700322 ZHU Qiqi, ZHONG Yanfei, LIU Yanfei, et al. A deep-local-global feature fusion framework for high spatial resolution imagery scene classification[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(4): 568. doi: 10.3390/rs10040568 叶利华, 王磊, 张文文, 等. 高分辨率光学遥感场景分类的深度度量学习方法[J]. 测绘学报, 2019, 48(6): 698–707. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2019.20180434YE Lihua, WANG Lei, ZHANG Wenwen, et al. Deep metric learning method for high resolution remote sensing image scene classification[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2019, 48(6): 698–707. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2019.20180434 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
