A Study on Resampling Strategy of Intelligent Particle Filter Based on Genetic Algorithm
-
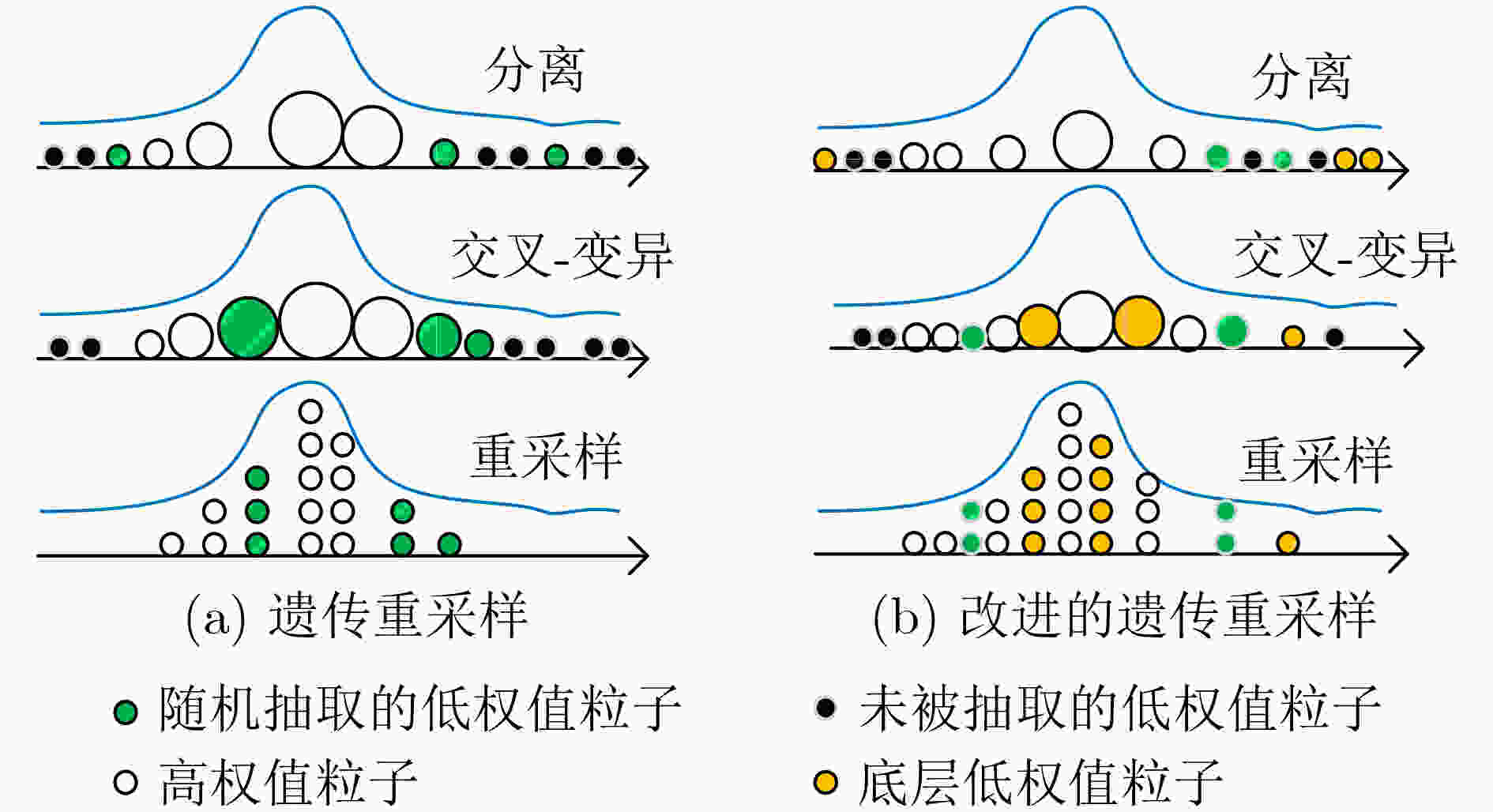
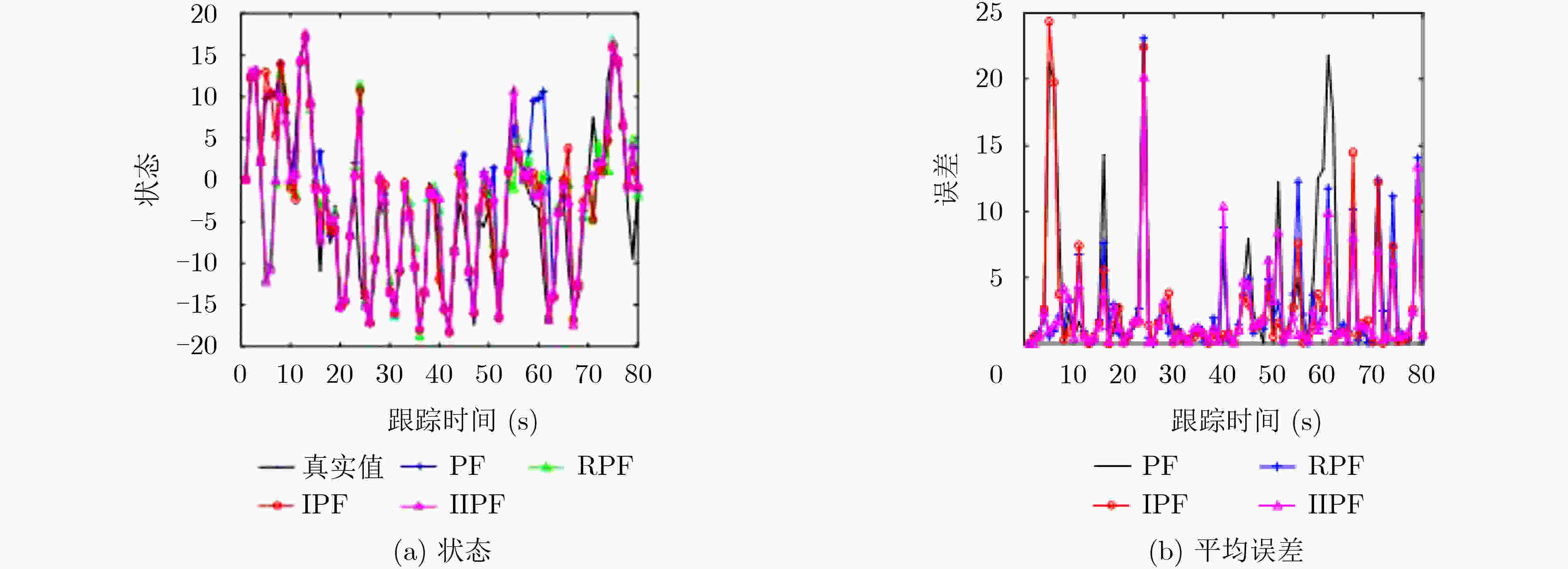
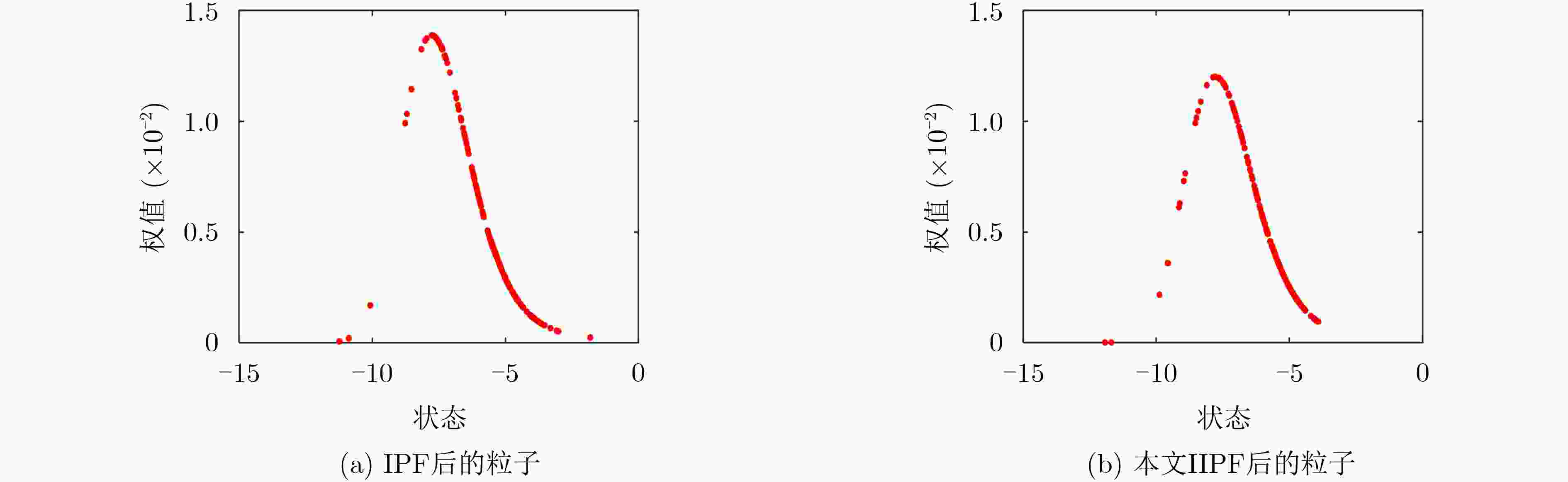
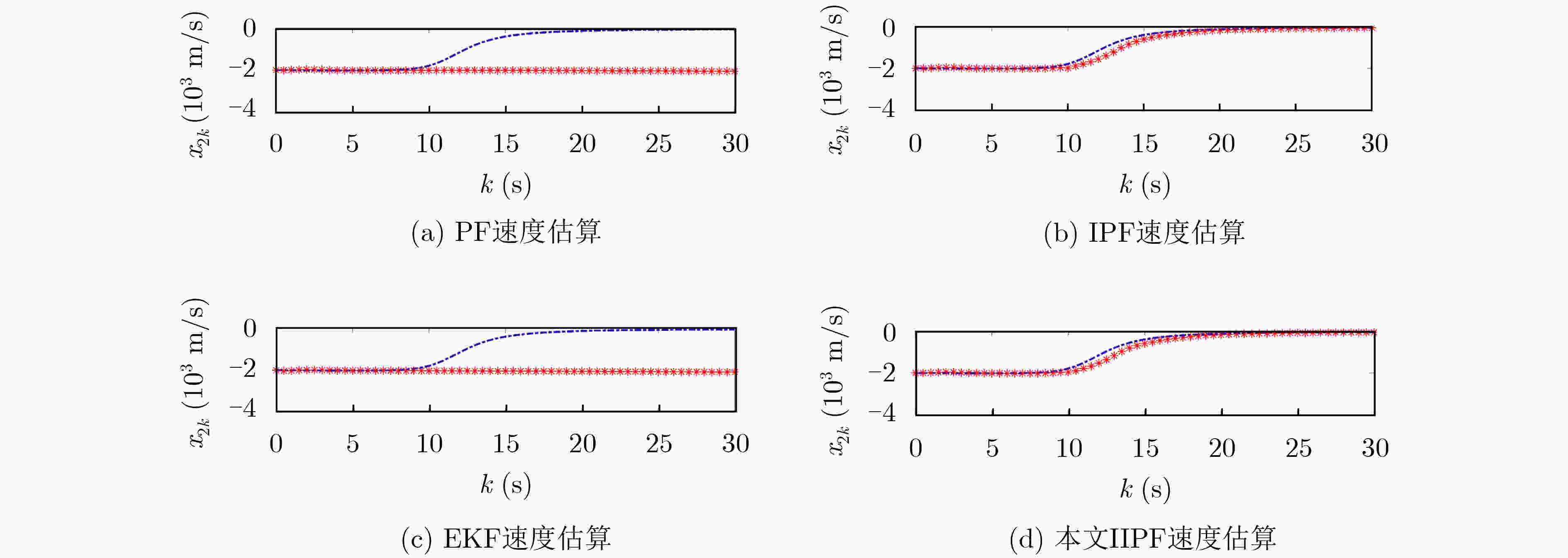
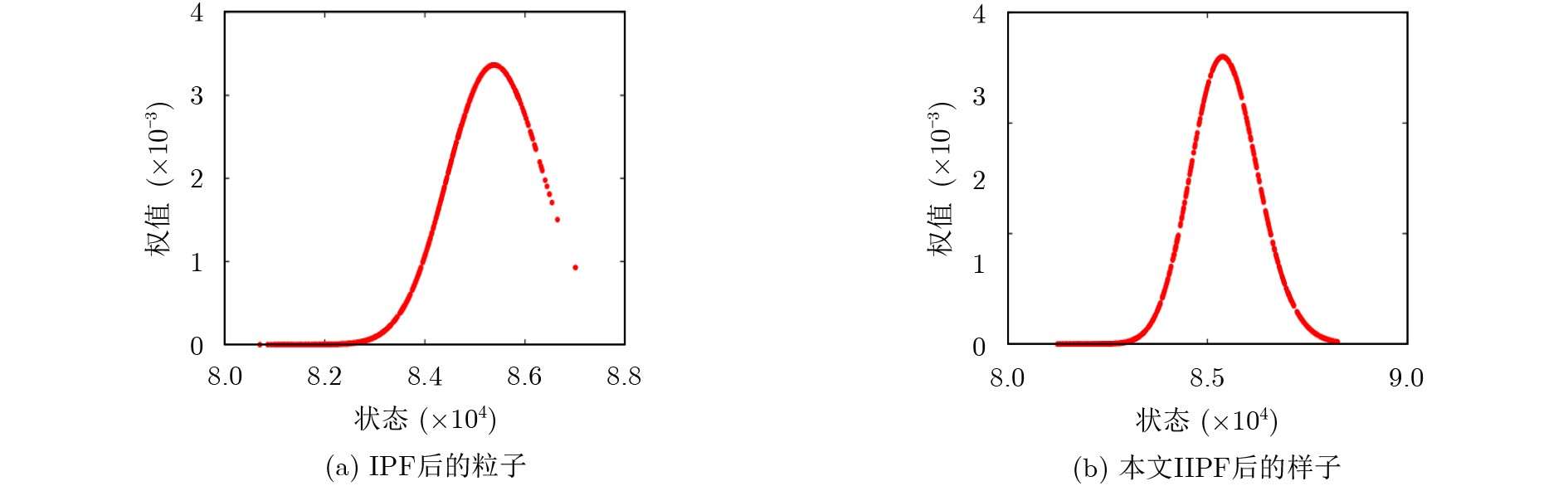
摘要: 智能粒子滤波通过借鉴遗传算法思想能够减轻粒子退化现象。在基于遗传算法的智能粒子滤波基础上,该文提出对低权值粒子的改进的智能粒子滤波(IIPF)处理策略。在对粒子进行分离、交叉后,优化遗传算子,对低权值粒子进行自适应处理。低权值粒子根据权值大小自行判断是否为底层粒子;底层粒子将直接进行变异,其余低权值粒子将根据变异概率随机变异。仿真结果表明,改进的智能粒子滤波(IIPF)性能优于智能粒子滤波、一般粒子滤波算法和拓展卡尔曼滤波。在1维仿真实验中,改进的智能粒子滤波误差较一般粒子滤波算法和智能粒子滤波分别降低了10.5%和8.5%,且具有更好的收敛性;在多维仿真实验中,改进的智能粒子滤波较智能粒子滤波在高度均方根误差和平均误差上分别降低了8.5%和7.5%,在速度均方根误差和平均误差上分别降低了11.5%和7.6%;在乘性噪声和非高斯随机噪声中,改进的智能粒子滤波依旧有10%以上的性能优势。Abstract: The intelligent Particle Filter (PF) based on the genetic algorithm can reduce particle degradation. An adaptive processing strategy for low weight particles is proposed for an Intelligent Particle Filter (IPF) based on the genetic algorithm. After the particles are separated and crossed, the genetic operators are optimized to deal with the low weight particles adaptively. Low weight particles determine whether they are the bottom particle according to the weight size. Then the bottom particles mutate directly, and the rest low-weight particles mutate randomly according to the mutation probability. Simulation results show that the performance of the Improved Intelligent Particle Filter (IIPF) is better than intelligent particle filter, general particle filter algorithms and extended Kalman filter. In the one-dimensional simulation experiment, the error of the improved intelligent particle filter is reduced by 10.5% and 8.5% compared with general particle filters and intelligent particle filter, and the improved intelligent particle filter has better convergence. In the multi-dimensional simulation experiment, the improved intelligent particle filter reduces the root-mean-square error and average error of the altitude by 8.5% and 7.5%, and the root-mean-square error and average error of the speed by 11.5% and 7.6%, respectively. Moreover, under the cases of multiplicative noise and non-Gaussian random noise, the improved intelligent particle filter still has more than 10% performance advantage.
-
Key words:
- Particle Filtering (PF) /
- Genetic algorithm /
- Particle degradation /
- Adaptive
-
表 1 改进的智能粒子滤波算法
(1) 获取$N$个初始粒子${\boldsymbol{x}}_0^i$,其中$i = 1,2, \cdots ,N$。 (2) For $k = 1,2, \cdots$。 (a) 抽取粒子样本${\boldsymbol{x}}_k^i$,计算权值$w_k^i$; (b) 将粒子按权值大小分为${\boldsymbol{x}}_{k{\rm{L}}}^l$和${\boldsymbol{x}}_{k{\rm{H}}}^j$; (c) 根据式(11)、式(12)及式(13)得到变异后的新粒子${\boldsymbol{x}}_{k{\rm{E}}}^l$; (d) 更新${\boldsymbol{x}}_{k{\rm{E}}}^l$和${\boldsymbol{x}}_{k{\rm{H}}}^j$权值; (e) 根据权值进行重采样过程。 end 表 2 1维模型仿真结果
PF RPF IPF 本文IIPF 平均耗时(s) 0.022 3.884 0.041 0.044 均方根误差 5.061 4.670 5.124 4.688 平均误差 2.805 2.705 2.757 2.549 平均有效粒子数 22.965 21.301 26.145 26.476 表 3 多维模型均方根误差与平均误差表
PF KPF IPF 本文IIPF 均方根误差 高度(m) 92496.7 336.7 289.0 255.8 速度(m/s) 8762.8 8872.8 919.8 857.3 平均误差 高度(m) 125065.4 548.8 320.9 296.4 速度(m/s) 14013.8 14205.1 1099.1 1051.1 表 4 非高斯随机噪声和乘性噪声下多维仿真模型的均方根误差
IPF IIPF 提升率(%) 非高斯随机噪声 高度(m) 232.6 207.3 10.9 速度(m/s) 856.5 799.1 6.7 乘性噪声 高度(m) 223.3 200.3 10.3 速度(m/s) 845.6 790.5 6.5 -
[1] ARULAMPALAM M S, MASKELL S, GORDON N, et al. A tutorial on particle filters for online nonlinear/non-Gaussian Bayesian tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2002, 50(2): 174–188. doi: 10.1109/78.978374 [2] KLEE U, GEHRIG T, and MCDONOUGH J. Kalman filters for time delay of arrival-based source localization[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2006, 2006: 012378. doi: 10.1155/ASP/2006/12378 [3] 鞠纯纯, 何波, 刘保龙, 等. 基于粒子滤波器的SLAM的仿真研究[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2007, 19(16): 3715–3718, 3723. doi: 10.1360/jos182740JU Chunchun, HE Bo, LIU Baolong, et al. Simulation research on simultaneous robot localization and mapping based on particle filter[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2007, 19(16): 3715–3718, 3723. doi: 10.1360/jos182740 [4] 程兰, 王志远, 陈杰, 等. 基于粒子滤波和滑动平均扩展Kalman滤波的多径估计算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(3): 709–716. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160587CHENG Lan, WANG Zhiyuan, CHEN Jie, et al. An improved multipath estimation algorithm using particle filter and sliding average extended Kalman filter[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(3): 709–716. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160587 [5] ZHANG Ke, ZHU Shibing, and LI Changqing. Blind separation of PCMA signals based on improved particle filter algorithm[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2019, 1176(6): 062004. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1176/6/062004 [6] 张颖, 高灵君. 基于格拉布斯准则和改进粒子滤波算法的水下传感网目标跟踪[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(10): 2294–2301. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190079ZHANG Ying and GAO Lingjun. Target tracking with underwater sensor networks based on Grubbs criterion and improved particle filter algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(10): 2294–2301. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190079 [7] WANG Fasheng, LIN Baowei, ZHANG Junxing, et al. Object tracking using Langevin Monte Carlo particle filter and locality sensitive histogram based likelihood model[J]. Computers & Graphics, 2018, 70: 214–223. doi: 10.1016/j.cag.2017.07.023 [8] GUSTAFSSON F. Particle filter theory and practice with positioning applications[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2010, 25(7): 53–82. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2010.5546308 [9] 张洪涛, 马培军, 崔平远. 一种用于解决粒子滤波粒子退化现象的重要性重采样算法的研究[J]. 飞行器测控学报, 2008, 27(4): 44–48.ZHANG Hongtao, MA Peijun, and CUI Pingyuan. Research on an importance resampling algorithm to solve particle degeneration of particle filter[J]. Journal of Spacecraft TT &C Technology, 2008, 27(4): 44–48. [10] MURRAY L M, LEE A, and JACOB P E. Parallel resampling in the particle filter[J]. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 2016, 25(3): 789–805. doi: 10.1080/10618600.2015.1062015 [11] BOLIC M, DJURIC P M, and HONG S. New resampling algorithms for particle filters[C]. 2003 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Hong Kong, China, 2003: II-589. [12] 冯驰, 赵娜, 王萌. 一种改进残差重采样算法的研究[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2010, 31(1): 120–124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7043.2010.01.021FENG Chi, ZHAO Na, and WANG Meng. Improving the residual resampling algorithm[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2010, 31(1): 120–124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7043.2010.01.021 [13] LI Tiancheng, BOLIC M, and DJURIC P M. Resampling methods for particle filtering: Classification, implementation, and strategies[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2015, 32(3): 70–86. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2014.2330626 [14] 叶龙, 王京玲, 张勤. 遗传重采样粒子滤波器[J]. 自动化学报, 2007, 33(8): 885–887. doi: 10.1360/aas-007-0885YE Long, WANG Jingling, and ZHANG Qin. Genetic resampling particle filter[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2007, 33(8): 885–887. doi: 10.1360/aas-007-0885 [15] BI Jun, GUAN Wei, and QI Longtao. A genetic resampling particle filter for freeway traffic-state estimation[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2012, 21(6): 068901. doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/21/6/068901 [16] BI Jun, ZHANG Ting, YU Haiyang, et al. State-of-health estimation of lithium-ion battery packs in electric vehicles based on genetic resampling particle filter[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 182: 558–568. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.08.138 [17] KHONG W L, KOW W Y, CHIN Y K, et al. Enhancement of particle filter resampling in vehicle tracking via genetic algorithm[C]. The 2012 6th UKSim/AMSS European Symposium on Computer Modeling and Simulation, Valetta, Malta, 2012: 243–248. doi: 10.1109/EMS.2012.72. [18] 张民, 贾海涛, 沈震. 基于遗传算法改进的粒子滤波重采样模型(英文)[J]. 电子科技大学学报, 2015, 44(3): 344–349. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2015.03.005ZHANG Min, JIA Haitao, and SHEN Zhen. Improved resampling procedure based on genetic algorithm in particle filter[J]. Journal of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2015, 44(3): 344–349. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2015.03.005 [19] YIN Shen and ZHU Xiangping. Intelligent particle filter and its application to fault detection of nonlinear system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(6): 3852–3861. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2015.2399396 [20] SIMON D. Optimal state estimation[J]. Ceylon Medical Journal, 2006, 5(3): 451–452. doi: 10.1002/0470045345 -





 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:
