A Novel Discontinuous Reception Mechanism for 5G in Unlicensed Band
-
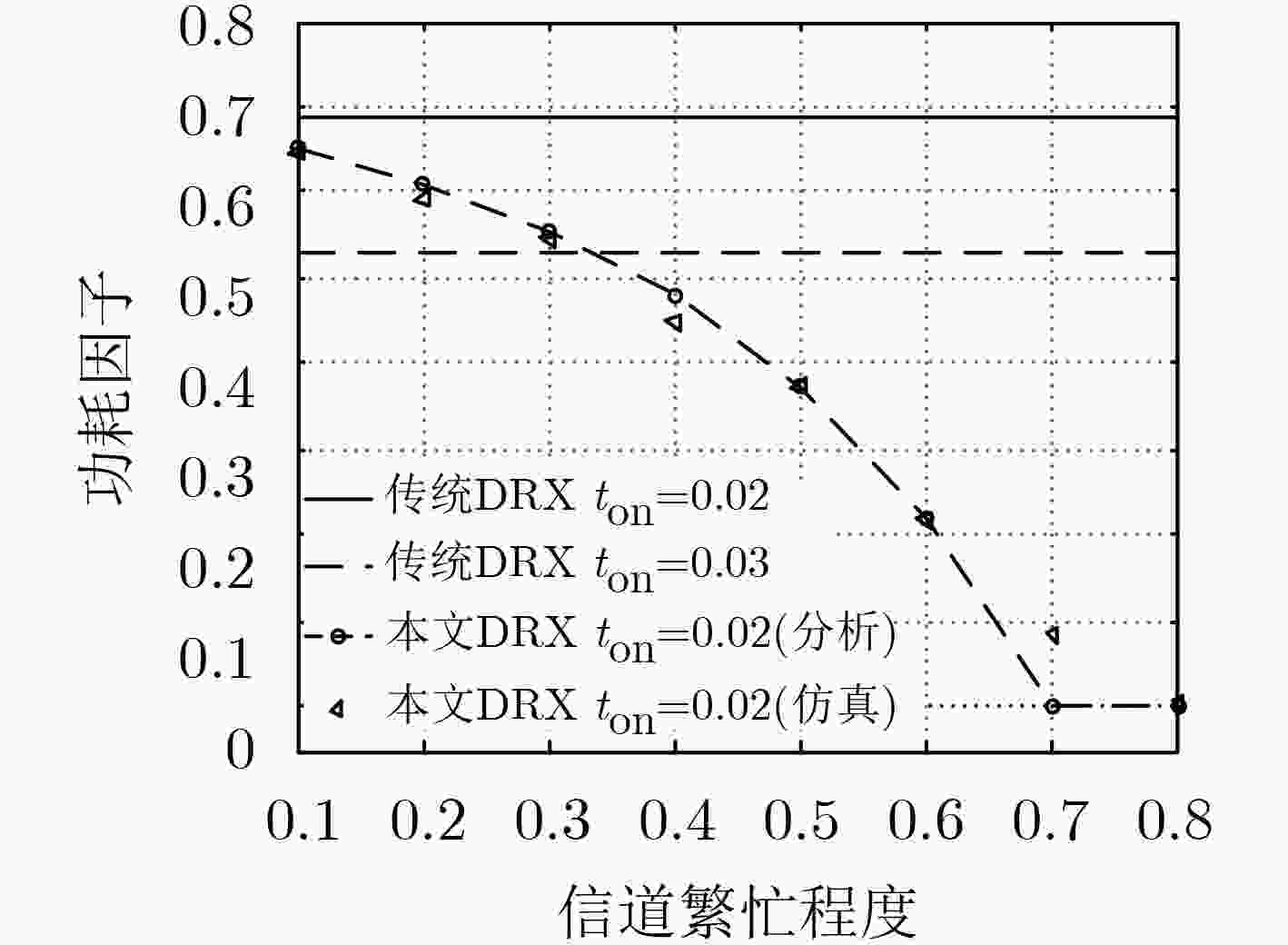
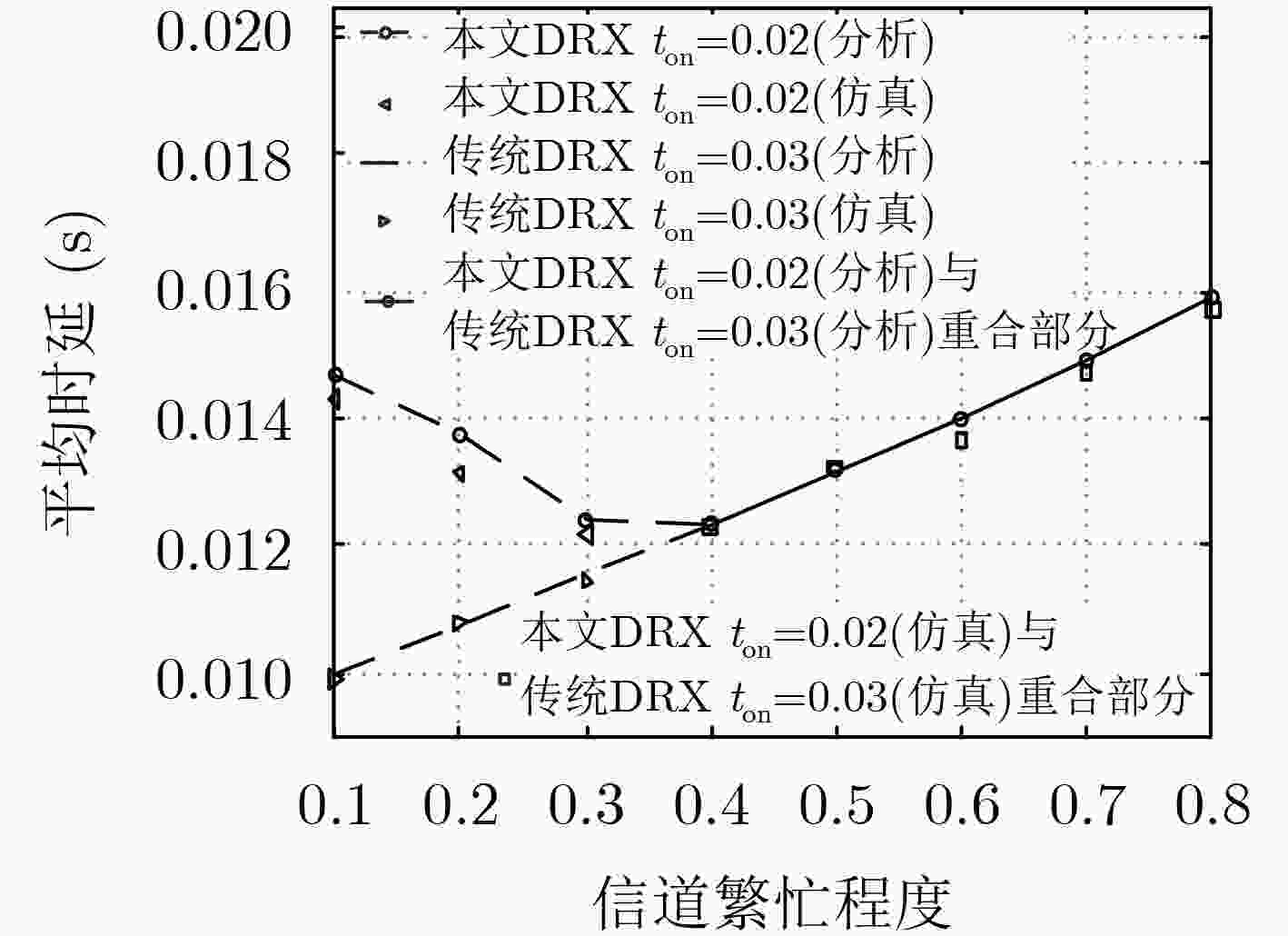
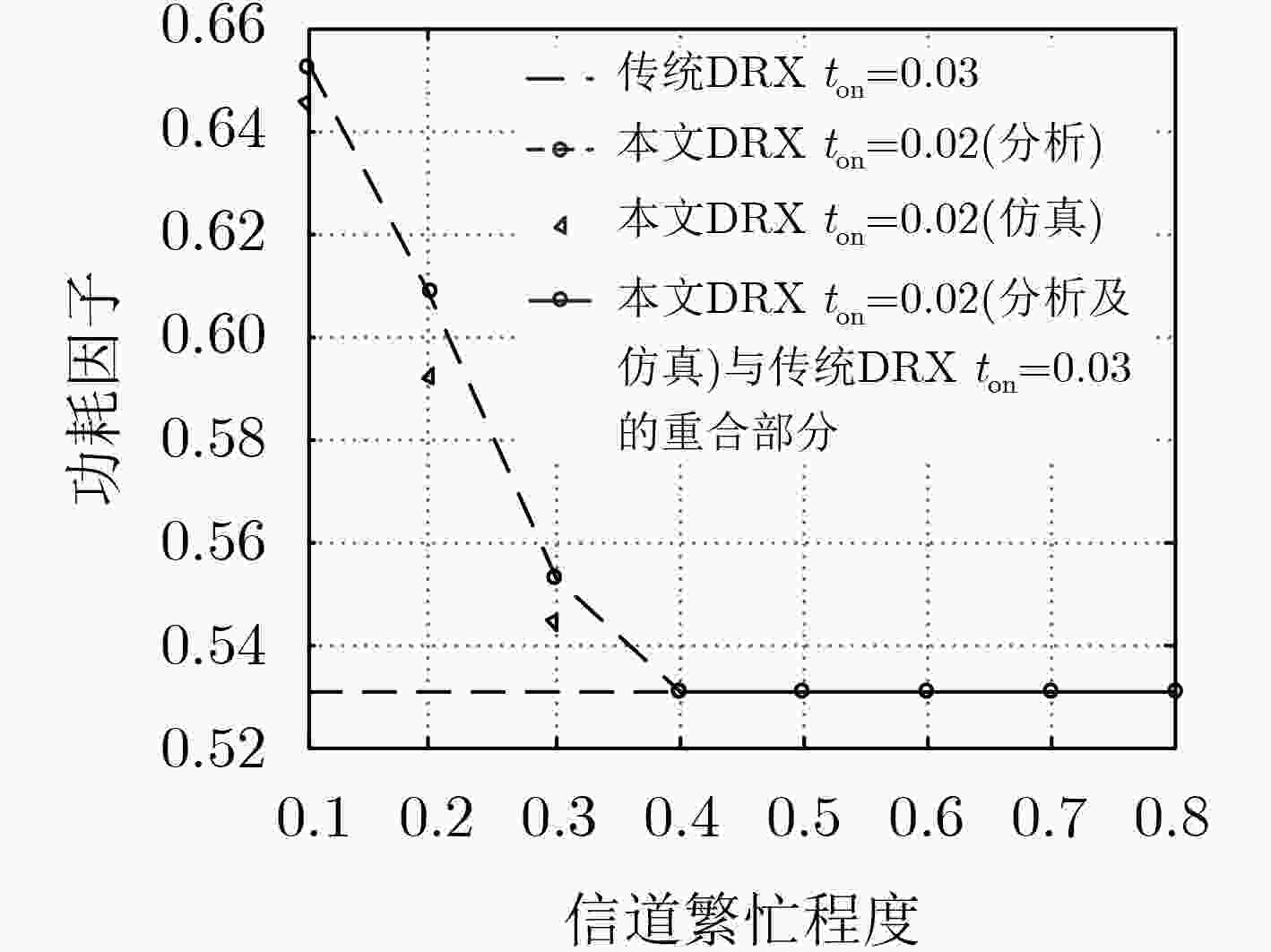
摘要: 非连续接收(DRX)是5G非授权频段部署中重要的节能机制。为授权频段设计的非连续接收机制,不能良好适配非授权频段,唤醒窗口长度固定而不能随信道繁忙程度调整,为保证传输时延性能则需要消耗更多能量。该文针对5G非授权频段新无线技术(5G NR-U),提出一种新型非连续接收机制。在新机制中,非授权频段新空口设备处于唤醒状态时不断对信道进行能量检测来判断信道的忙闲状态,并据此自适应调整唤醒窗口时间。相比唤醒窗口长度固定的原有机制,数学模型分析和仿真实验的结果表明,在保证业务传输时延要求的前提下,新机制可比原有机制节约更多的能量。在文中典型场景中,新机制比原有机制可多节约能量11%。
-
关键词:
- 非连续接收 /
- 能量效率 /
- 先听后说 /
- 5G非授权频段新无线技术
Abstract: Discontinuous Reception (DRX) is power-saving mechanism in 5G unlicensed band deployments. Legacy DRX scheme for licensed band does not work well in unlicensed band. Wakeup window size is fixed and can not adjust with channel busy level. Guaranteed transmission delay is at the cost of more power consumption. A novel DRX scheme of is proposed for the 5th Generation New Radio-Unlicensed (5G NR-U) standalone scenario. In the novel scheme, NR-U equipment runs energy detection continuously during its wakeup period to get channel state: busy or free and adjusts its wakeup window size adaptively according to energy detection results. Comparing to legacy method with wakeup window fixed, it is demonstrated by analysis and simulation that the novel method saves more power than traditional method while both of them meet the average delay requirement. In the analysis scenario of this paper, novel method saves 11% power more than legacy method. -
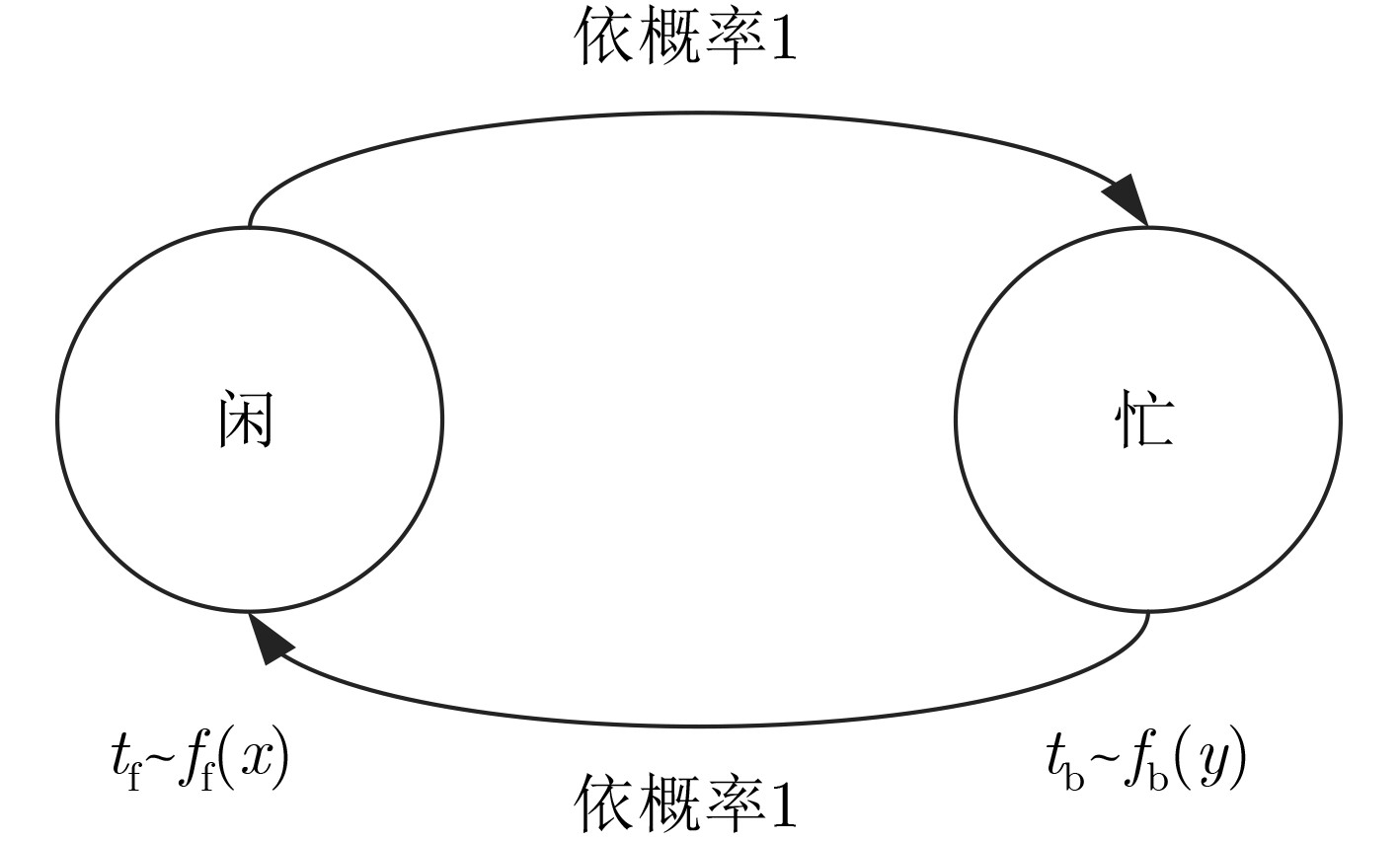
图 2 非授权频段信道忙闲模型[19]
-
[1] 3GPP. Technical specification group radio access network: Study on NR-based access to unlicensed spectrum TR 38.889 V16.0. 0[S]. 3GPP, 2018. [2] 徐振宇. 非授权频段接入关键技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 北京邮电大学, 2019.XU Zhenyu. Study on access technology of unlicensed bands[D]. [Master dissertation], Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2019. [3] 朱正航, 贾建鑫, 郦振红, 等. 一种应用于5G非授权频段通信的低时延随机接入机制[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(11): 2680–2688. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190515.ZHU Zhenghang, JIA Jianxin, LI Zhenhong, et al. A low latency random access mechanism for 5G new radio in unlicensed spectrum[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2020, 42(11): 2680–2688. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190515. [4] Panasonic. R2–1811920 DRX Procedure for NR-U[R]. 3GPP RAN2#103, 2018. [5] 蔡博文. 非连续传输机制下网络性能研究[D]. [硕士论文], 北京邮电大学, 2019.CAI Bowen. Research on network performance for discontinuous transmission[D]. [Master dissertation], Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2019. [6] FOWLER S A, MELLOUK A, and YAMADA N. LTE-Advanced DRX Mechanism for Power Saving[M]. London, UK: Wiley, 2013: 33–68. [7] RAMAZANALI H and VINEL A. Mean queuing delay in LTE DRX[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2016, 5(4): 444–447. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2016.2582694 [8] WANG Ke, LI Xi, and JI Hong. Modeling 3GPP LTE advanced DRX mechanism under multimedia traffic[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2014, 18(7): 1238–1241. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2014.2323231 [9] LIANG Jiaming, HSU C K, CHEN J J, et al. Three-stage DRX scheduling for joint downlink transmission in C-RAN[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(2): 129–133. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2019.2943471 [10] ROSTAMI S, HEISKA K, PUCHKO O, et al. Robust pre-grant signaling for energy-efficient 5G and beyond mobile devices[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Kansas City, USA, 2018: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICC.2018.8422523. [11] ROSTAMI S, HEISKA K, PUCHKO O, et al. Pre-grant signaling for energy-efficient 5G and beyond mobile devices: Method and analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 2019, 3(2): 418–432. doi: 10.1109/TGCN.2019.2893504 [12] MAHESHWARI M K, AGIWAL M, SAXENA N, et al. Directional discontinuous reception (DDRX) for mmWave enabled 5G communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2019, 18(10): 2330–2343. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2018.2872550 [13] MORADI F, FITZGERALD E, PIÓRO M, et al. Flexible DRX optimization for LTE and 5G[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(1): 607–621. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2952251 [14] MAHESHWARI M K, ROY A, and SAXENA N. DRX over LAA-LTE-A new design and analysis based on Semi-Markov model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2019, 18(2): 276–289. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2018.2835443 [15] InterDigital Inc. R2–1816780 TP for DRX in NR-U[R]. 3GPP RAN2#104, 2018. [16] Xiaomi Communications. R2–1915945 DRX enhancement for NR-U[R]. 3GPP RAN2#108, 2019. [17] 3GPP. Technical specification group radio access network: Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA) Medium Access Control (MAC) protocol specification TR 36.321 V16.0. 0[S]. 3GPP, 2020. [18] 3GPP. R2–2000009 Report of 3GPP TSG RAN2#108 meeting[R]. 3GPP RAN2#109-e, 2020. [19] KIM H and SHIN K G. Efficient discovery of spectrum opportunities with MAC-Layer sensing in cognitive radio networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2008, 7(5): 533–545. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2007.70751 [20] OGUNTUNDE P E, ODETUNMIBI O A, and ADEJUMO A O. On the sum of exponentially distributed random variables: A convolution approach[J]. European Journal of Statistics and Probability, 2014, 2(1): 1–8. [21] LARSEN R J and MARX M L. An Introduction to Mathematical Statistics and its Applications[M]. Boston, USA: Pearson Education, 2012: 273. [22] 张永利. 关于伽马分布及相关分布性质的一点研究[J]. 大学数学, 2012, 28(3): 135–140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1454.2012.03.030ZHANG Yongli. A research for character of gamma distribution and its relevant distribution[J]. College Mathematics, 2012, 28(3): 135–140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1454.2012.03.030 [23] 3GPP. Technical specification group radio access network: Study on licensed-assisted access to unlicensed spectrum TR 36.889 V13.0. 0[S]. 3GPP, 2015. [24] HOFFMAN J I E. Biostatistics for Medical and Biomedical Practitioners[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2015: 269–270. [25] 3GPP. TR 36.331 V16.0. 0 Technical specification group radio access network: Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA) Radio Resource Control (RRC), protocol specification[S]. 3GPP, 2020. -





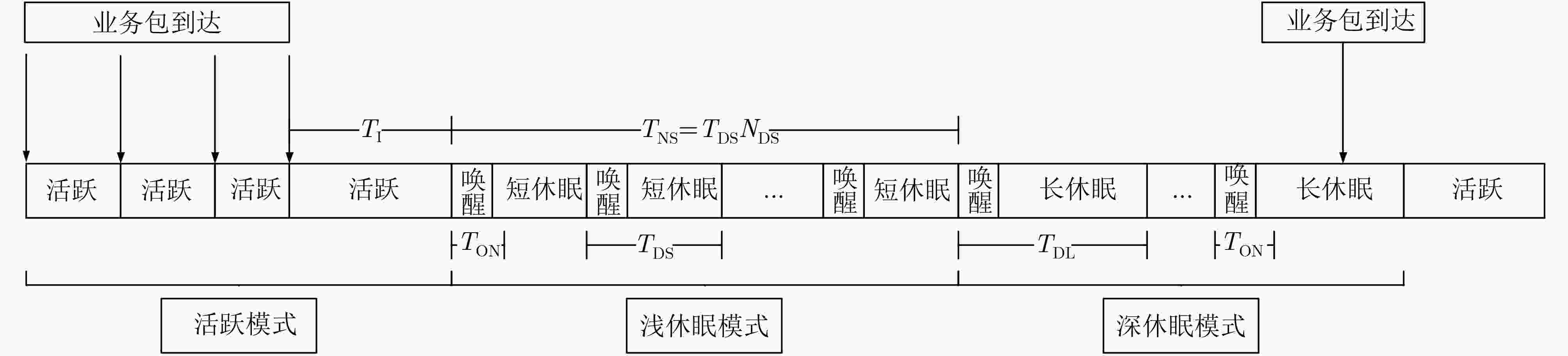
 下载:
下载:
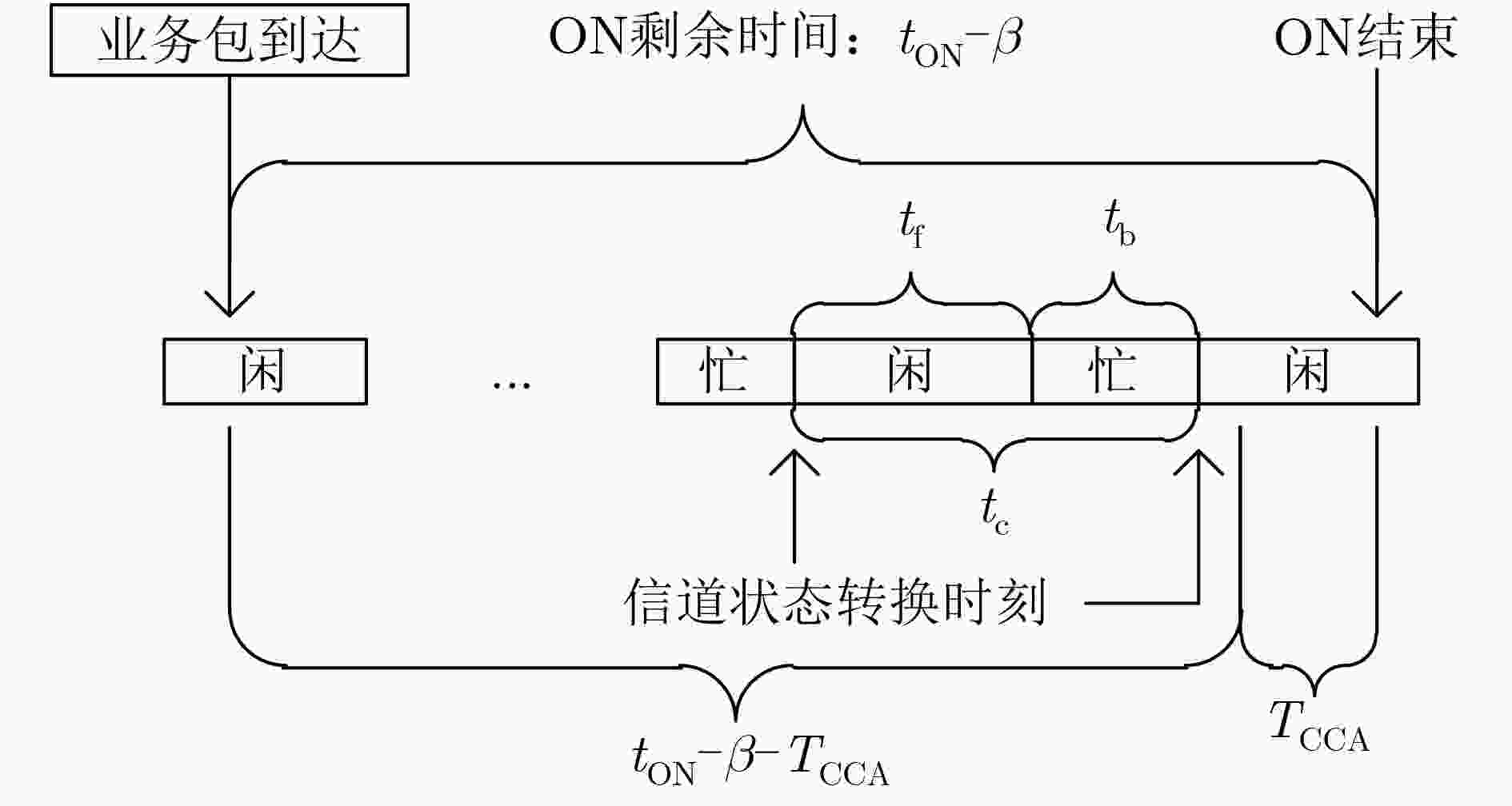
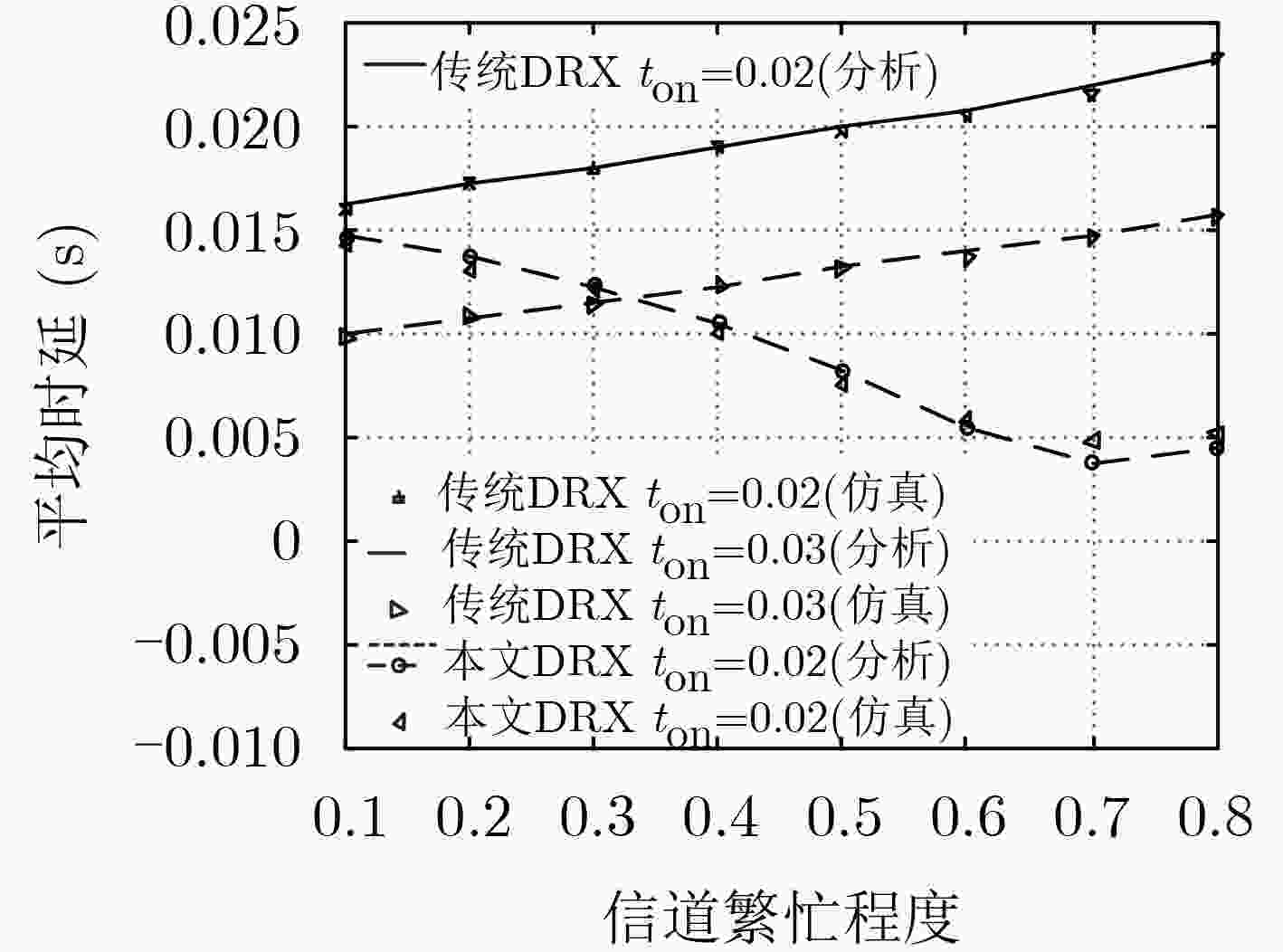


 下载:
下载:
