Action Recognition Model Based on 3D Graph Convolution and Attention Enhanced
-
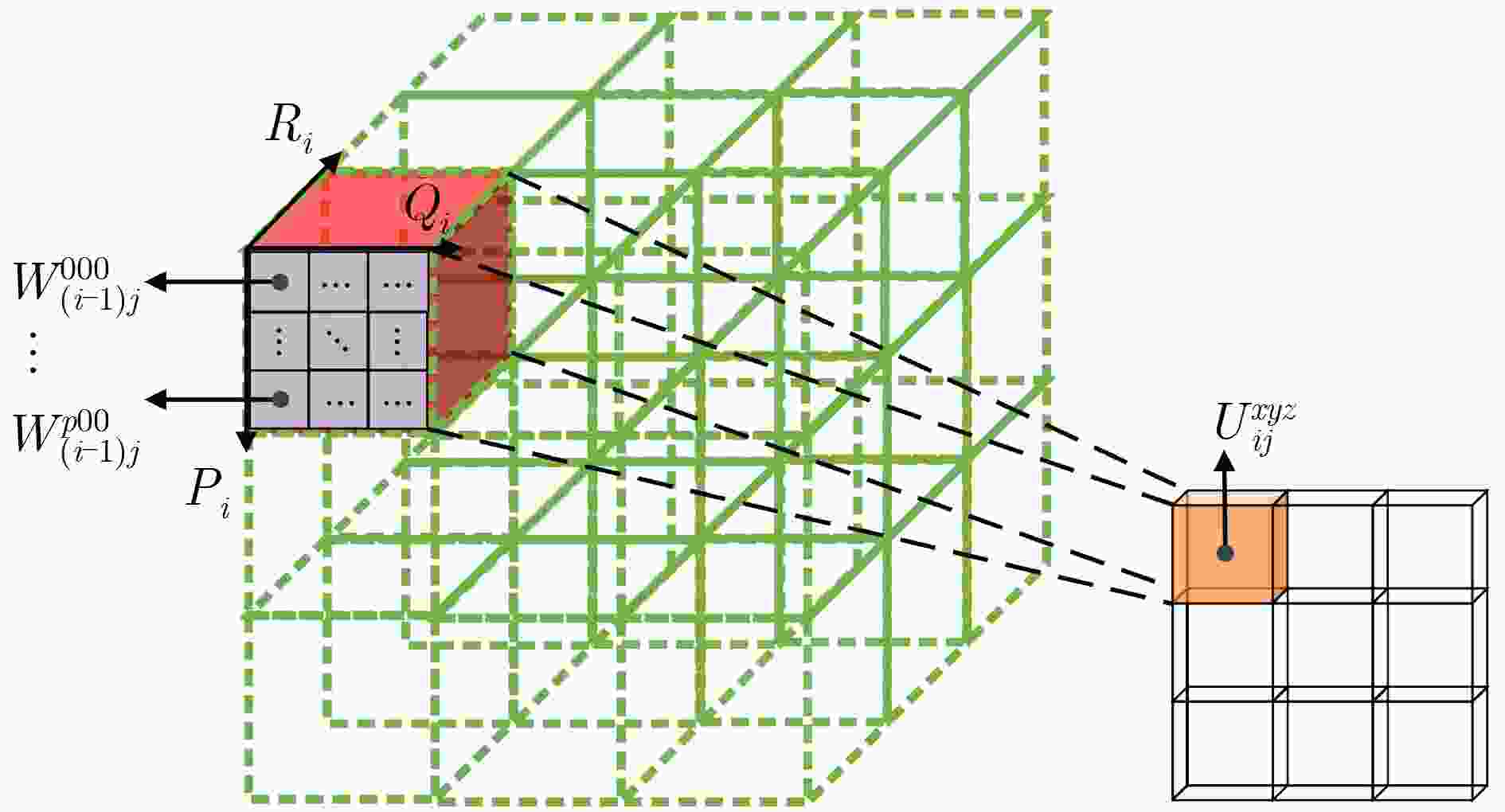
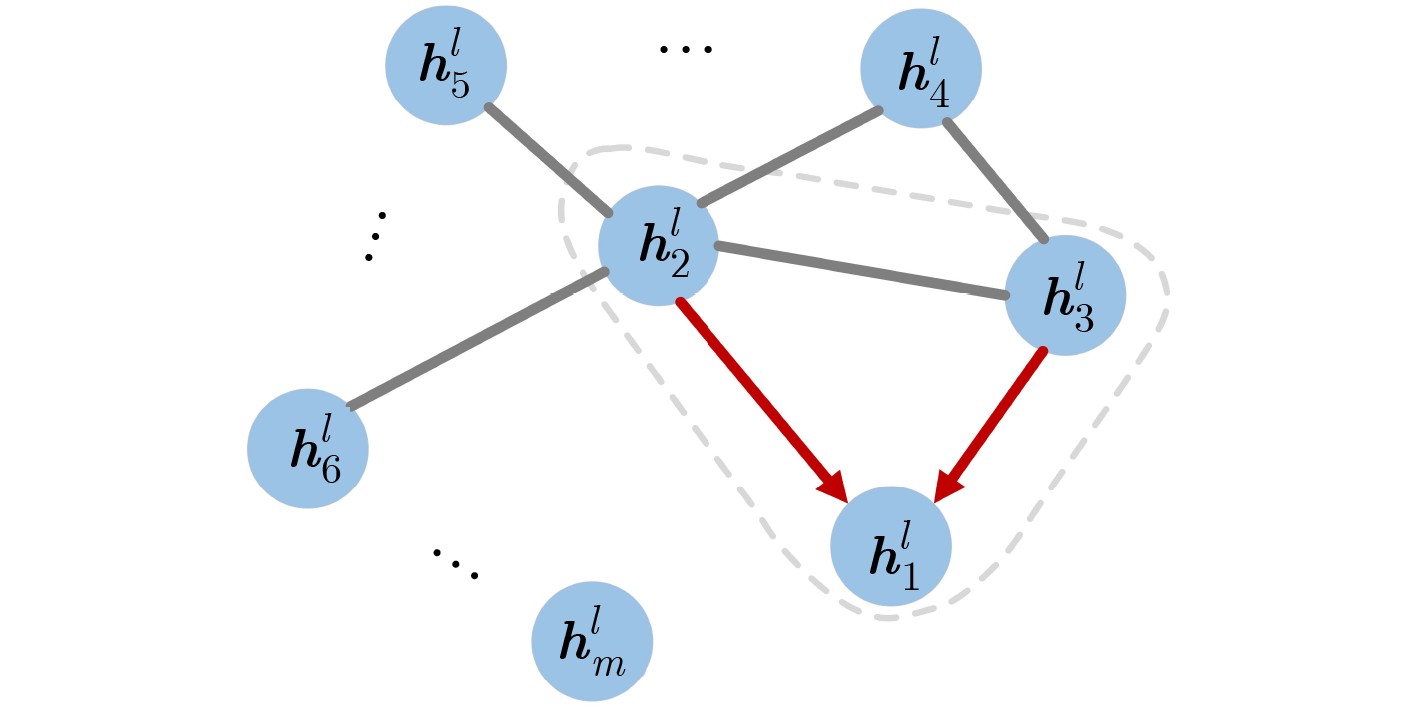
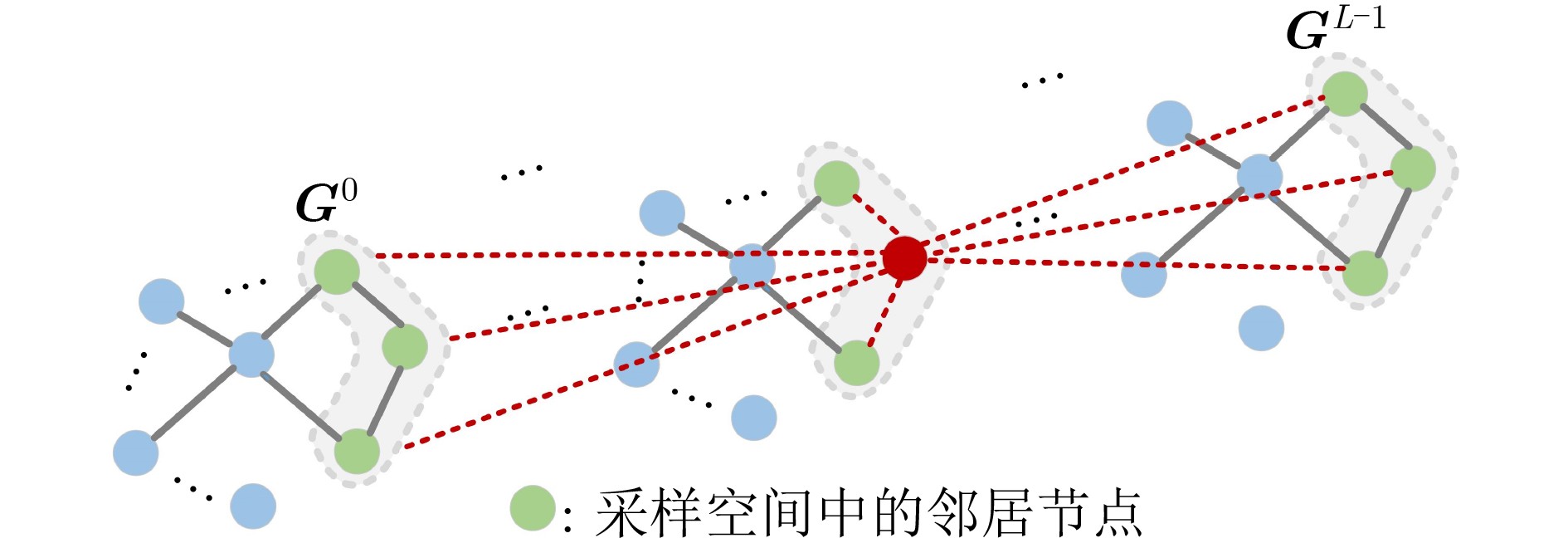
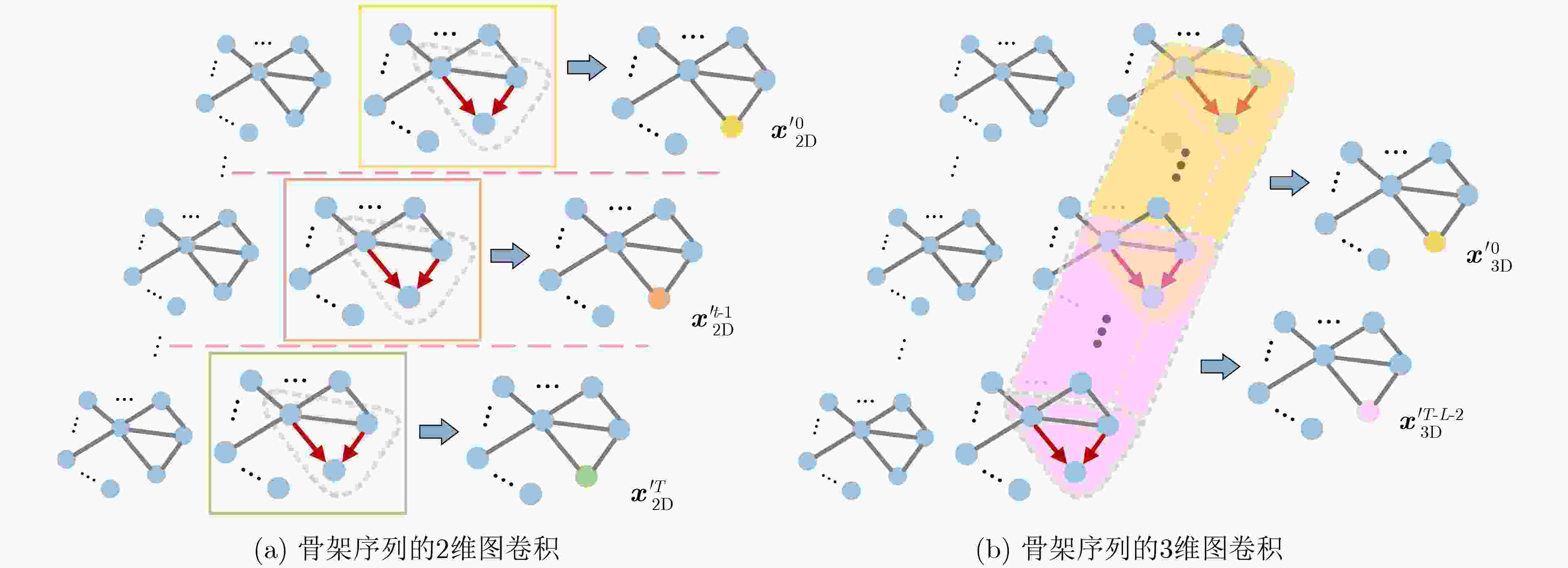
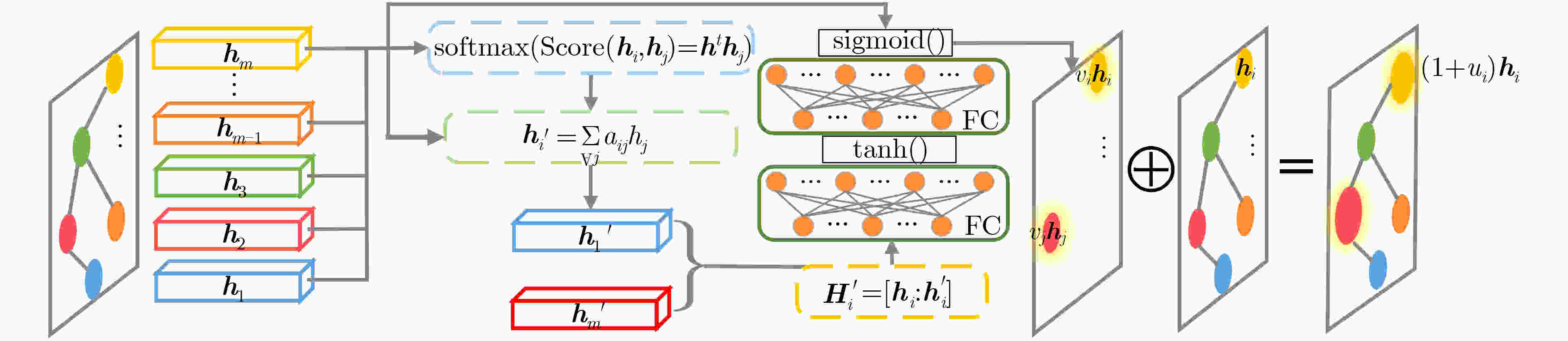
摘要: 针对当前行为识别方法无法有效提取非欧式3维骨架序列的时空信息与缺乏针对特定关节关注的问题,该文提出了一种基于3维图卷积与注意力增强的行为识别模型。首先,介绍了3维卷积与图卷积的具体工作原理;其次,基于图卷积中可处理变长邻居节点的图卷积核,引入3维卷积的3维采样空间将2维图卷积核改进为具有3维采样空间的3维图卷积核,提出一种3维图卷积方法。针对3维采样空间内的邻居节点,通过3维图卷积核,实现了对骨架序列中时空信息的有效提取;然后,为增强对于特定关节的关注,聚焦重要的动作信息,设计了一种注意力增强结构;再者,结合3维图卷积方法与注意力增强结构,构建了基于3维图卷积与注意力增强的行为识别模型;最后,基于NTU-RGBD和MSR Action 3D骨架动作数据集开展了骨架行为识别的研究。研究结果进一步验证了基于3维图卷积与注意力增强的行为识别模型针对时空信息的有效提取能力及识别准确率。Abstract: To solve the problems that current behavior recognition methods can not effectively extract the spatial-temporal information in non-European 3D skeleton sequence and lack attention for specific joints, an action recognition model based on 3D graph convolution and attention enhanced is proposed in this paper. Firstly, the specific working principles of the 3D convolution and graph convolution are introduced; Secondly, a 3D graph convolution method is proposed. It is based on the graph convolution kernel that can handle variable-length neighbor nodes in graph and 3D sampling space of 3D convolution is introduced to improve 2D graph convolution kernel to 3D graph convolution kernel with 3D sampling space. For neighbor nodes in 3D sampling space, this method realizes effective extraction of spatial-temporal information with a 3D graph convolution kernel; Thirdly, in order to enhance attention to specific joints and focus important action information, an attention enhanced structure is designed. Besides, through combining 3D graph convolution with attention enhanced structure, action recognition model based on 3D graph convolution and attention enhanced is proposed. Finally, the researches are carried on NTU-RGBD and MSR Action 3D skeleton action dataset. The results further verify the ability to extract spatial-temporal information of this model and its classification accuracy.
-
表 1 基于3维图卷积与注意力增强的行为识别模型的网络结构
结构层 输入 $ \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{\text{注意力增强结构}}}\\ {3{\text{维图卷积}}} \end{array}} \right]$ ··· $ \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{\text{注意力增强结构}}}\\ {3{\text{维图卷积}}} \end{array}} \right]$ ··· $ \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{\text{注意力增强结构}}}\\ {3{\text{维图卷积}}} \end{array}} \right]$ ··· Flatting FC Fusion 特征1 [3,300,25] [16,300,25] ··· [32,150,25] ··· [64,75,25] ··· [120000] [64] [60] 特征2 [3,300,25] [16,300,25] ··· [32,150,25] ··· [64,75,25] ··· [120000] [64] 表 2 不同模型深度的识别准确率对比(%)
模型深度 5层3DGCN 6层3DGCN 7层3DGCN 8层3DGCN 9层3DGCN 10层3DGCN 11层3DGCN Top-1 92.18 92.59 92.76 92.93 93.04 93.30 93.01 Top-5 99.05 99.07 99.07 99.10 99.07 99.49 99.17 表 3 不同邻居采样范围的识别准确率对比(%)
采样范围 3帧采样范围 5帧采样范围 7帧采样范围 9帧采样范围 11帧采样范围 Top-1 92.55 92.73 92.90 93.30 93.08 Top-5 99.11 99.40 99.00 99.49 99.10 表 4 注意力增强结构与多种注意力机制的识别准确率对比(%)
模型 3DGCN 3DGCN+Hard Attention 3DGCN+Soft Attention 3DGCN+Self Attention 3DGCN+注意力增强结构 Top-1 92.90 92.87 93.04 92.98 93.30 Top-5 99.14 99.02 99.04 99.12 99.09 表 5 NTU数据集上不同模型的识别准确率对比(%)
-
[1] 周风余, 尹建芹, 杨阳, 等. 基于时序深度置信网络的在线人体动作识别[J]. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(7): 1030–1039. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150629ZHOU Fengyu, YIN Jianqin, YANG Yang, et al. Online recognition of human actions based on temporal deep belief neural network[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(7): 1030–1039. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150629 [2] 刘天亮, 谯庆伟, 万俊伟, 等. 融合空间-时间双网络流和视觉注意的人体行为识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(10): 2395–2401. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171116LIU Tianliang, QIAO Qingwei, WAN Junwei, et al. Human action recognition via spatio-temporal dual network flow and visual attention fusion[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(10): 2395–2401. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171116 [3] 吴培良, 杨霄, 毛秉毅, 等. 一种视角无关的时空关联深度视频行为识别方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(4): 904–910. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180477WU Peiliang, YANG Xiao, MAO Bingyi, et al. A perspective-independent method for behavior recognition in depth video via temporal-spatial correlating[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(4): 904–910. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180477 [4] HOU Yonghong, LI Zhaoyang, WANG Pichao, et al. Skeleton optical spectra-based action recognition using convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2018, 28(3): 807–811. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2016.2628339 [5] LIU Zhi, ZHANG Chenyang, and TIAN Yingli. 3D-based deep convolutional neural network for action recognition with depth sequences[J]. Image and Vision Computing, 2016, 55: 93–100. doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2016.04.004 [6] TU Juanhui, LIU Mengyuan, and LIU Hong. Skeleton-based human action recognition using spatial temporal 3D convolutional neural networks[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), San Diego, USA, 2018: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICME.2018.8486566. [7] YAN Sijie, XIONG Yuanjun, and LIN Dahua. Spatial temporal graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition[C]. Proceedings of the 32nd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, (AAAI-18), the 30th innovative Applications of Artificial Intelligence (IAAI-18), and the 8th AAAI Symposium on Educational Advances in Artificial Intelligence (EAAI-18), New Orleans, USA, 2018: 7444–7452. [8] SI Chenyang, CHEN Wentao, WANG Wei, et al. An attention enhanced graph convolutional LSTM network for skeleton-based action recognition[C]. Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 1227–1236. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00132. [9] LI Maosen, CHEN Siheng, CHEN Xu, et al. Actional-structural graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition[C]. Proceedings of 2019 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 3590–3598. [10] KIM T S and REITER A. Interpretable 3D human action analysis with temporal convolutional networks[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 1623–1631. doi: 10.1109/CVPRW.2017.207. [11] JI Shuiwang, XU Wei, YANG Ming, et al. 3D convolutional neural networks for human action recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(1): 221–231. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.59 [12] 徐冰冰, 岑科廷, 黄俊杰, 等. 图卷积神经网络综述[J]. 计算机学报, 2020, 43(5): 755–780. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2020.00755XU Bingbing, CEN Keting, HUANG Junjie, et al. A survey on graph convolutional neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2020, 43(5): 755–780. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2020.00755 [13] CAI Yujun, GE Liuhao, LIU Jun, et al. Exploiting spatial-temporal relationships for 3D pose estimation via graph convolutional networks[C]. Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 2272–2281. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00236. [14] CHO S, MAQBOOL M H, LIU Fei, et al. Self-attention network for skeleton-based human action recognition[C]. Proceedings of 2020 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Snowmass, USA, 2020: 624–633. doi: 10.1109/WACV45572.2020.9093639. [15] SHAHROUDY A, LIU Jun, NG T T, et al. NTU RGB+D: A large scale dataset for 3D human activity analysis[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1010–1019. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.115. [16] LI Wanqing, ZHANG Zhengyou, and LIU Zicheng. Action recognition based on a bag of 3D points[C]. Proceedings of 2010 Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition-Workshops, San Francisco, USA, 2010: 9–14. doi: 10.1109/CVPRW.2010.5543273. [17] 冉宪宇, 刘凯, 李光, 等. 自适应骨骼中心的人体行为识别算法[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2018, 23(4): 519–525. doi: 10.11834/jig.170420RAN Xianyu, LIU Kai, LI Guang, et al. Human action recognition algorithm based on adaptive skeleton center[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2018, 23(4): 519–525. doi: 10.11834/jig.170420 [18] LIU Hong, TU Juanhui, and LIU Mengyuan. Two-stream 3D convolutional neural network for skeleton-based action recognition[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1705.08106, 2017. [19] GAO Xuesong, LI Keqiu, ZHANG Yu, et al. 3D skeleton-based video action recognition by graph convolution network[C]. Proceedings of 2019 IEEE International Conference on Smart Internet of Things (SmartIoT), Tianjin, China, 2019: 500–501. doi: 10.1109/SmartIoT.2019.00093. [20] PHAM H H, KHOUDOUR L, CROUZIL A, et al. Skeletal movement to color map: A novel representation for 3D action recognition with inception residual networks[C]. Proceedings of the 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Athens, Greece, 2018: 3483–3487. doi: 10.1109/ICIP.2018.8451404. [21] BATTISTONE F and PETROSINO A. TGLSTM: A time based graph deep learning approach to gait recognition[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2019, 126: 132–138. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2018.05.004 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
