Subspace Projection Based Track-Before-Detect Scheme for Small Moving Target in Complex Underwater Environment
-
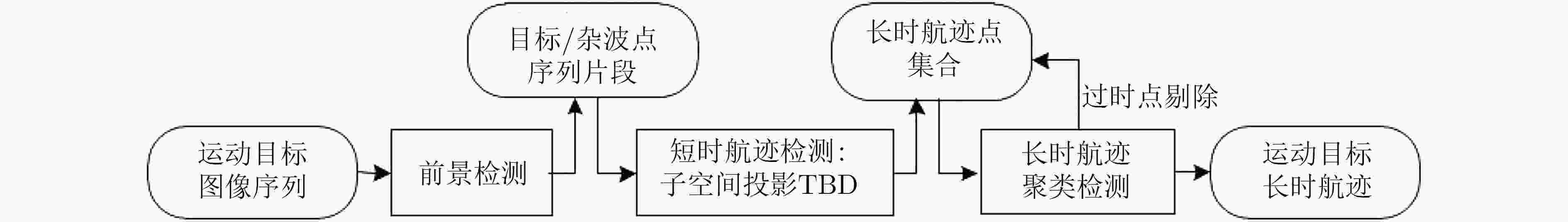
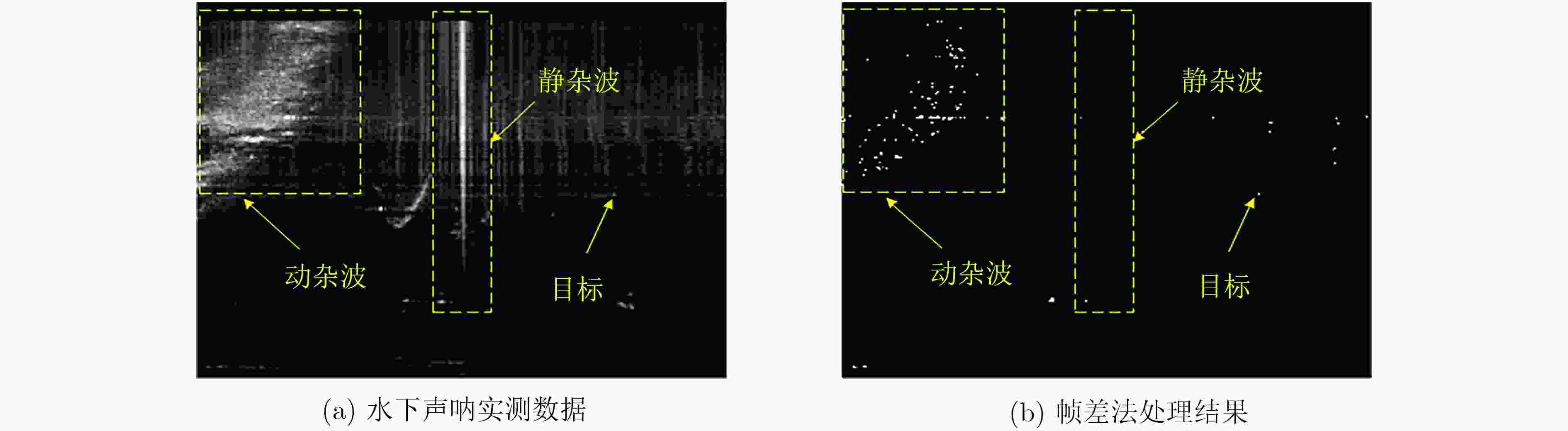
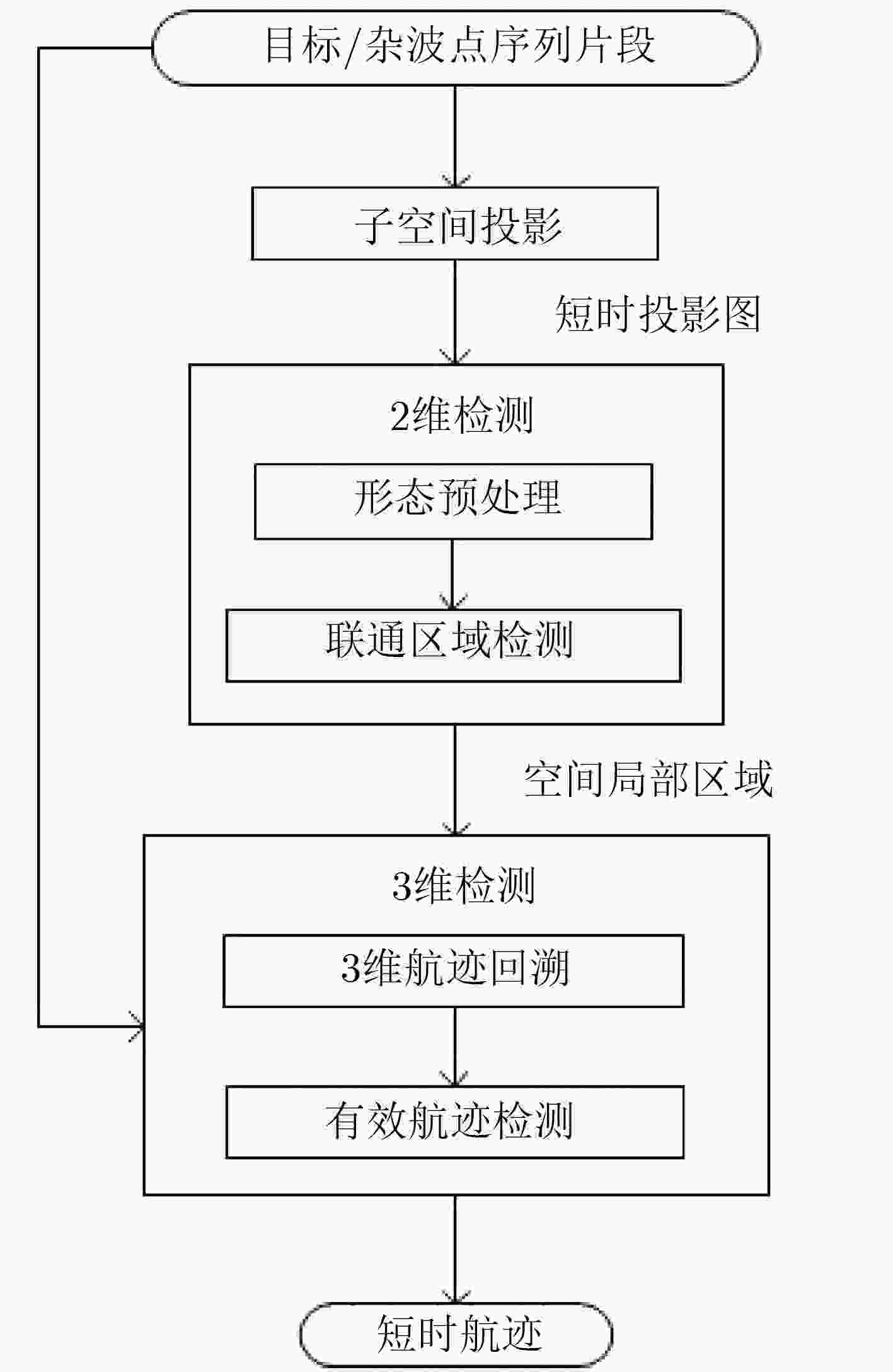
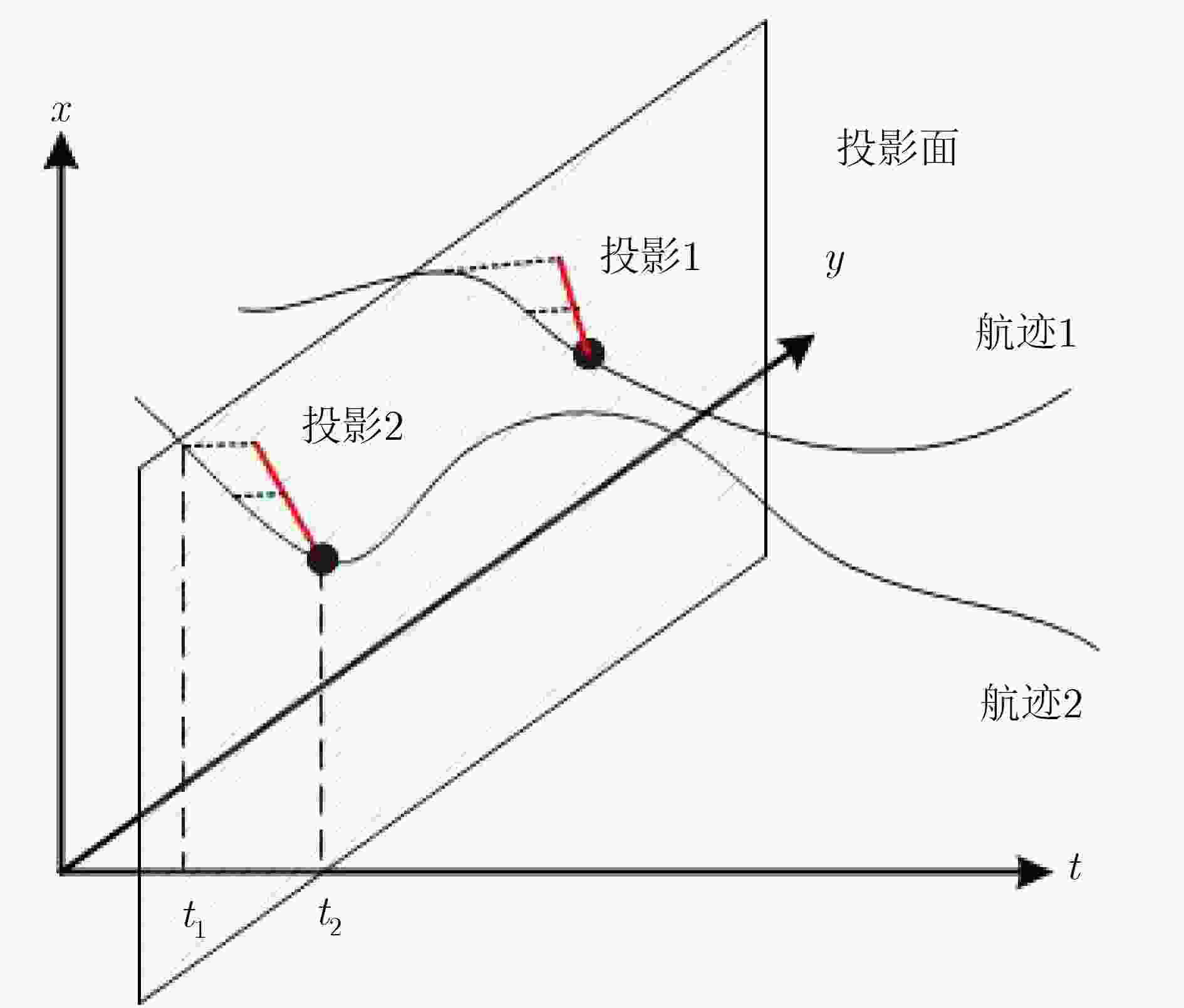
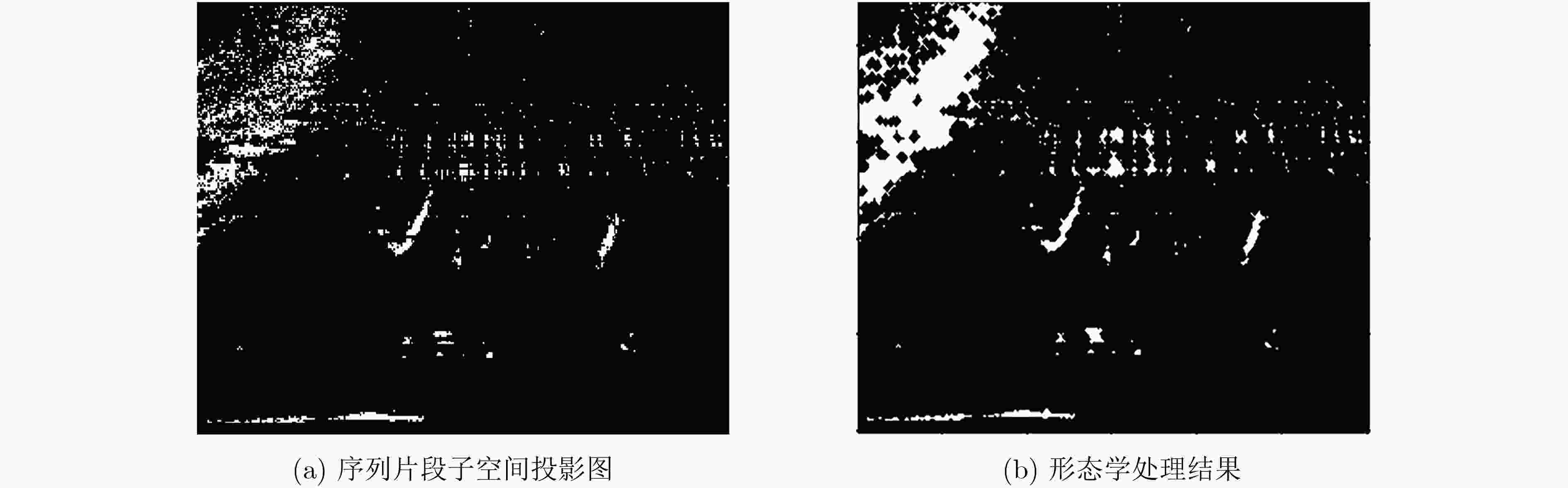
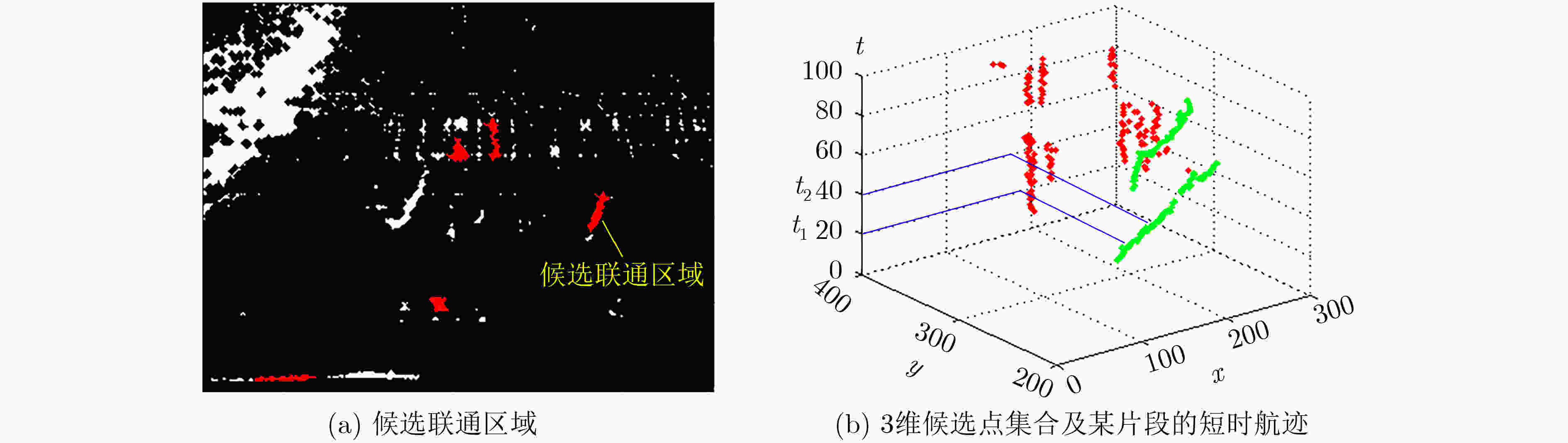
摘要: 针对复杂水下环境运动小目标检测中存在的目标信号强度弱、信杂比低等问题,该文提出基于子空间投影的检测前跟踪(TBD)算法:对原始图像数据截取序列片段,将3维时空片段中的短时运动航迹投影到2维子空间平面;利用2维投影图中平面航迹的形态特征进行初步筛选,提取目标的有效运动区域;将2维平面中的目标短时航迹在局部区域重建3维时序,在3维航迹回溯过程中利用目标运动特征再次筛选目标短时航迹。通过上述分级检测机制,可实现快速高精度的目标短时航迹检测。结合前景检测以及基于层次凝聚聚类(HAC)的长时航迹检测算法,构建了针对运动小目标的完整检测前跟踪方法。最后使用实测声呐图像数据验证了算法的检测精度和检测速度。Abstract: The small moving target detection in complex underwater environment is complicated due to the weak target signal strength and low signal-to-clutter ratio. A Track-Before-Detect (TBD) algorithm based on subspace projection is proposed to solve these problems. A sequence motion track fragment is extracted from the original data, and then projected from the 3D space-time onto the 2D subspace. The morphological features in 2D subspace are applied to preliminary screening to remove most of the clutters and locate the local motion areas of the target. The 3D space-time track is reconstructed from 2D subspace in these local motion areas. During the above 3D track backtracking process, the motion continuity characteristics are also extracted to further remove the clutters and select the effective target track fragments. Through the above-mentioned hierarchical processing, a fast and high-precision target track fragment detection algorithm is achieved. By combing this track fragment detection algorithm with the foreground detection and Hierarchical Agglomerative Clustering (HAC) based long-time track detection algorithms, a complete TBD scheme for small moving targets detection is constructed. The accuracy and speed of this detection scheme are verified on the real sonar image data.
-
表 1 基于DP-TBD的检测结果
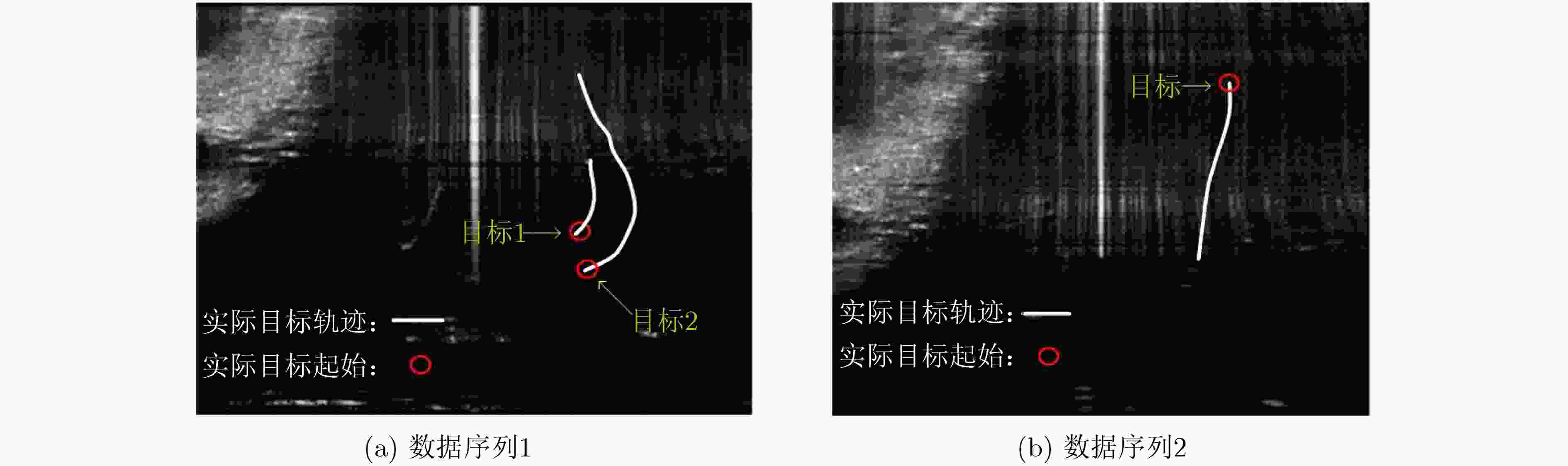
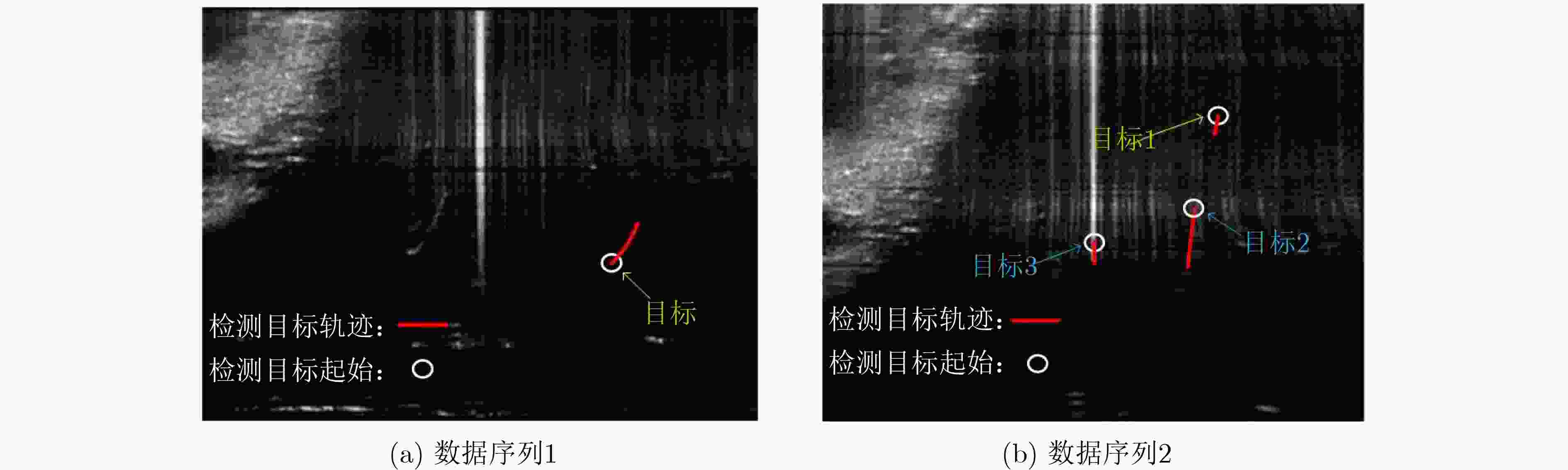
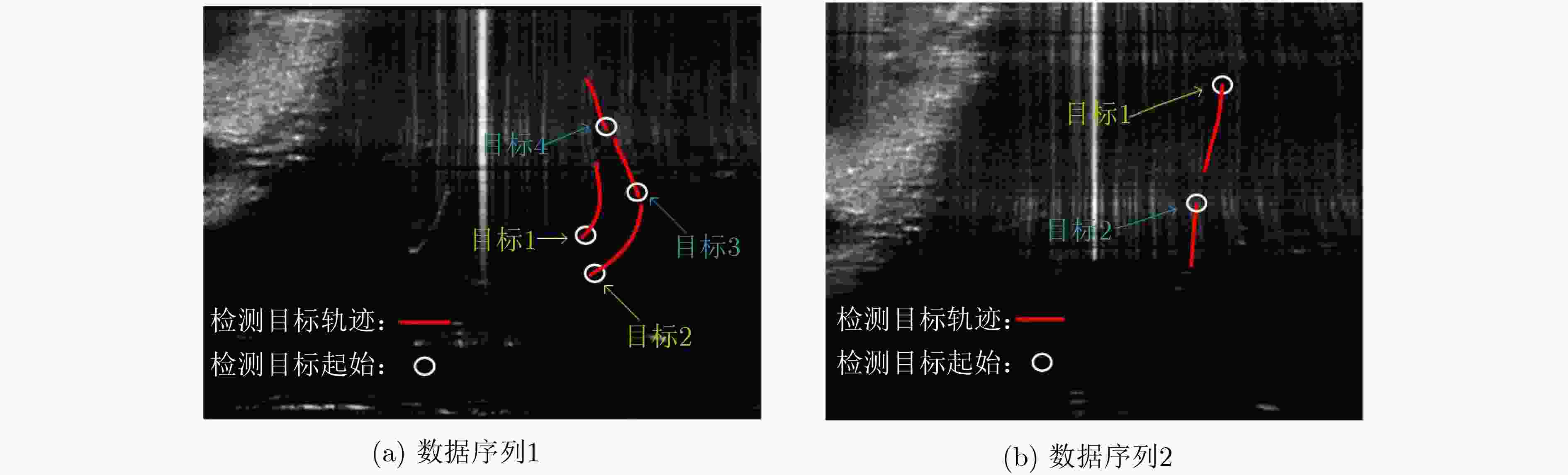
数据 实际目标数量 检测目标数量 跟踪精度(%) 虚警率(%) 数据序列1 2 1 20.06 0 数据序列2 1 3 42.22 31.57 表 2 基于子空间投影TBD的检测结果
数据 实际目标数量 检测目标数量 跟踪精度(%) 虚警率(%) 数据序列1 2 4 95.84 0 数据序列2 1 2 88.15 0 表 3 处理单帧数据的平均用时(帧/s)
数据 基于子空间投影TBD 基于DP-TBD 数据序列1 0.010 0.025 数据序列2 0.030 0.126 -
钟雷, 李勇, 牟之英, 等. 未知强杂波下基于DP-TBD的雷达弱目标检测[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41(1): 43–49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.01.07ZHONG Lei, LI Yong, MOU Zhiying, et al. Detection method for weak target under unknown strong clutter based on DP-TBD[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(1): 43–49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.01.07 WANG Hui, YI Jianxin, and WAN Xianrong. Greedy algorithm-based track-before-detect in radar systems[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(17): 7158–7165. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2853188 BARNIV Y. Dynamic programming solution for detecting dim moving targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1985, AES-21(1): 144–156. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1985.310548 BARNIV Y, and KELLA O. Dynamic programming solution for detecting dim moving targets part II: Analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1987, AES-23(6): 776–788. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1987.310914 CARLSON B D, EVANS E D, and WILSON S L. Search radar detection and track with the Hough transform. I. system concept[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1994, 30(1): 102–108. doi: 10.1109/7.250410 HART P E. How the Hough transform was invented [DSP History][J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2009, 26(6): 18–22. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2009.934181 GUSTAFSSON F, GUNNARSSON F, BERGMAN N, et al. Particle filters for positioning, navigation, and tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2002, 50(2): 425–437. doi: 10.1109/78.978396 ORTON M and FITZGERALD W. A Bayesian approach to tracking multiple targets using sensor arrays and particle filters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2002, 50(2): 216–223. doi: 10.1109/78.978377 YAN Bo, XU Luping, LI Muqing, et al. Track-before-detect algorithm based on dynamic programming for multi-extended-targets detection[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2017, 11(6): 674–686. doi: 10.1049/iet-spr.2016.0582 GUO Qiang, LI Zhenwu, SONG Wenming, et al. Parallel computing based dynamic programming algorithm of track-before-detect[J]. Symmetry, 2019, 11(1): 29. doi: 10.3390/sym11010029 GAO Jie, DU Jinsong, and WANG Wei. Radar detection of fluctuating targets under heavy- tailed clutter using Track-before-detect[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(7): 2241. doi: 10.3390/s18072241 LI Yuansheng, WEI Ping, GAO Lin, et al. Micro-doppler aided track-before-detect for UAV detection[C]. 2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019: 9086–9089. CAO Chenghu, ZHAO Yongbo, PANG Xiaojiao, et al. Sequential Monte Carlo Cardinalized probability hypothesized density filter based on Track-Before-Detect for fluctuating targets in heavy-tailed clutter[J]. Signal Processing, 2020, 169: 107367. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2019.107367 HAN Yulan and HAN Chongzhao. Two measurement set partitioning algorithms for the extended target probability hypothesis density filter[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(12): 2665. doi: 10.3390/s19122665 陈一梅. 基于随机有限集的杂波估计与多扩展目标跟踪问题研究[D]. [硕士论文], 杭州电子科技大学, 2019.CHEN Yimei. Clutter estimation and multiple extended target tracking based on random finite set[D]. [Master dissertation], Hangzhou Dianzi University, 2019. WANG Jinghe, YI Wei, KIRUBARAJAN T, et al. An efficient recursive multiframe track-before-detect algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(1): 190–204. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2741898 熊伟, 顾祥岐, 徐从安, 等. 多编队目标先后出现时的无先验信息跟踪方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(7): 1619–1626. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190508XIONG Wei, GU Xiangqi, XU Cong’an, et al. Tracking method without prior information when multi-group targets appear successively[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(7): 1619–1626. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190508 QIN Xiaoyu, TING Kaiming, ZHU Ye, et al. Nearest-neighbour-induced isolation similarity and its impact on density-based clustering[C]. The 33rd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, USA, 2019: 4755–4762. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
