Design of Large-scale UAV-assisted Multi-tier Heterogeneous Networks and Performance Research
-
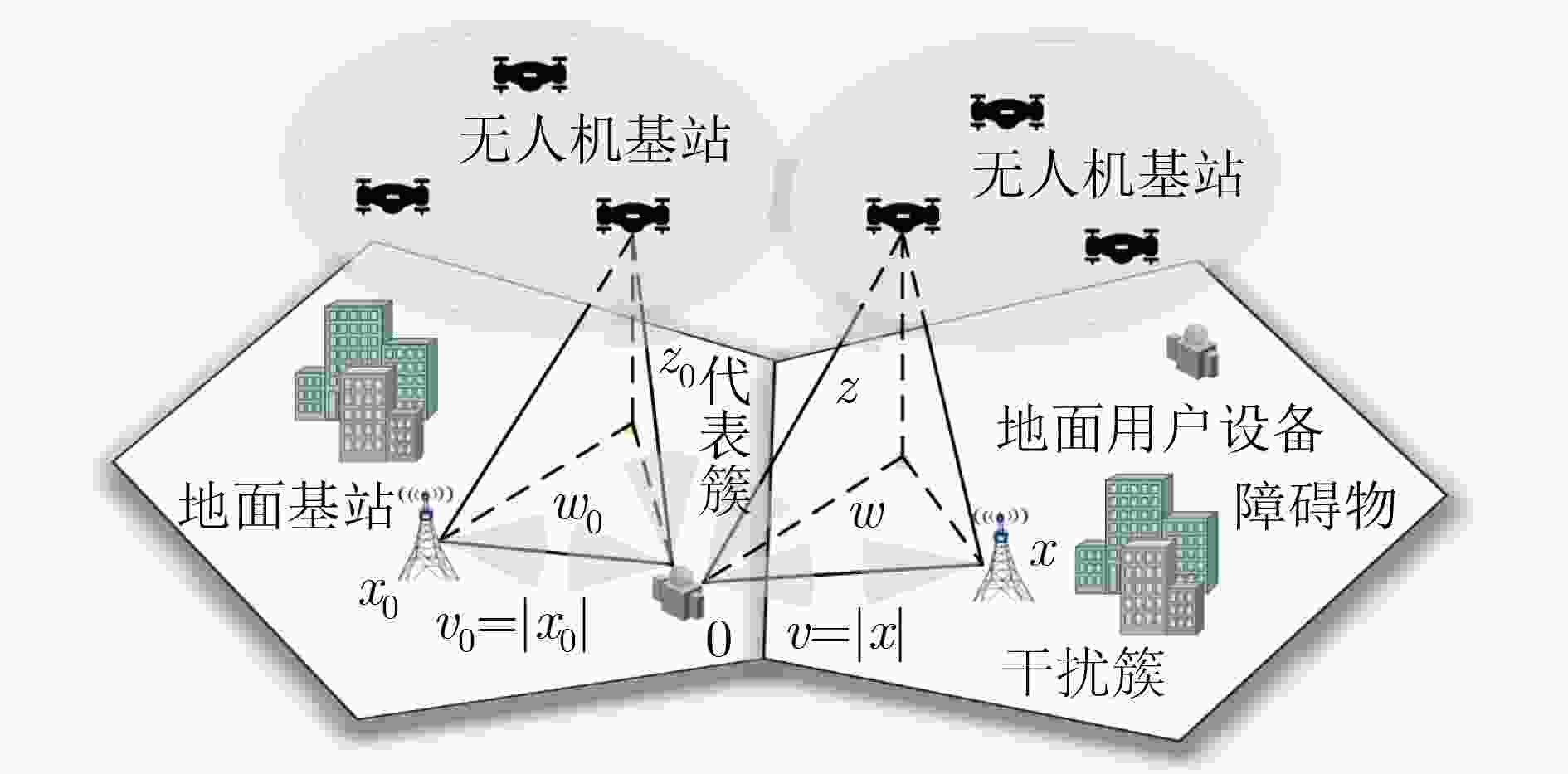
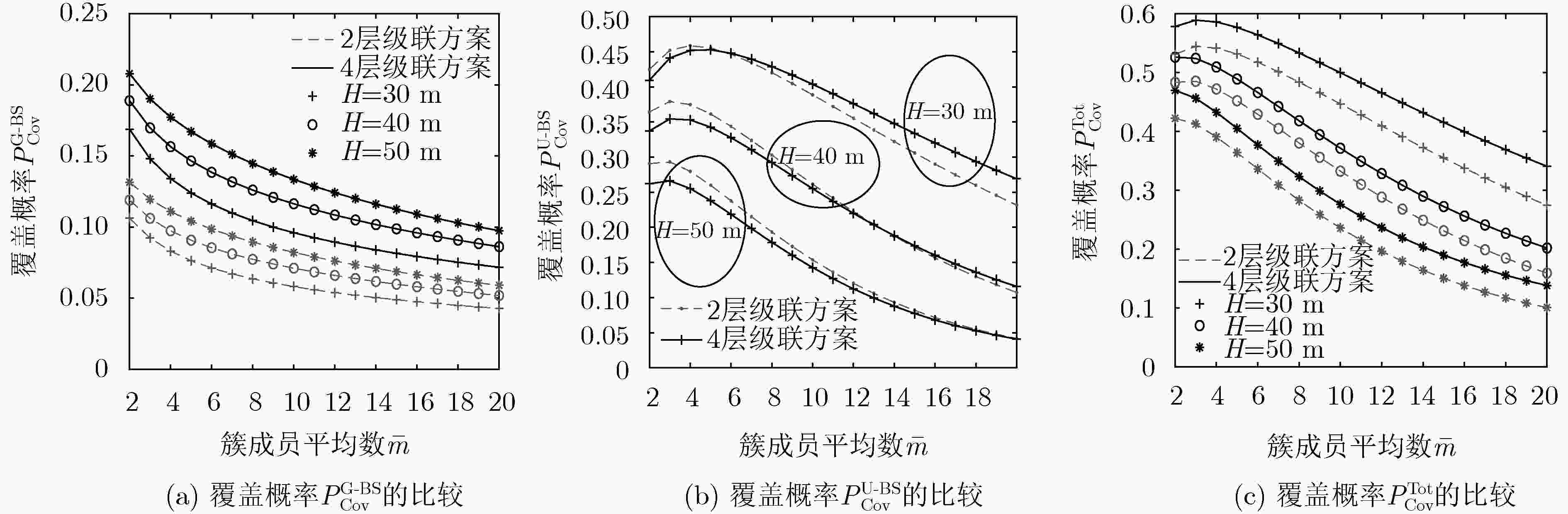
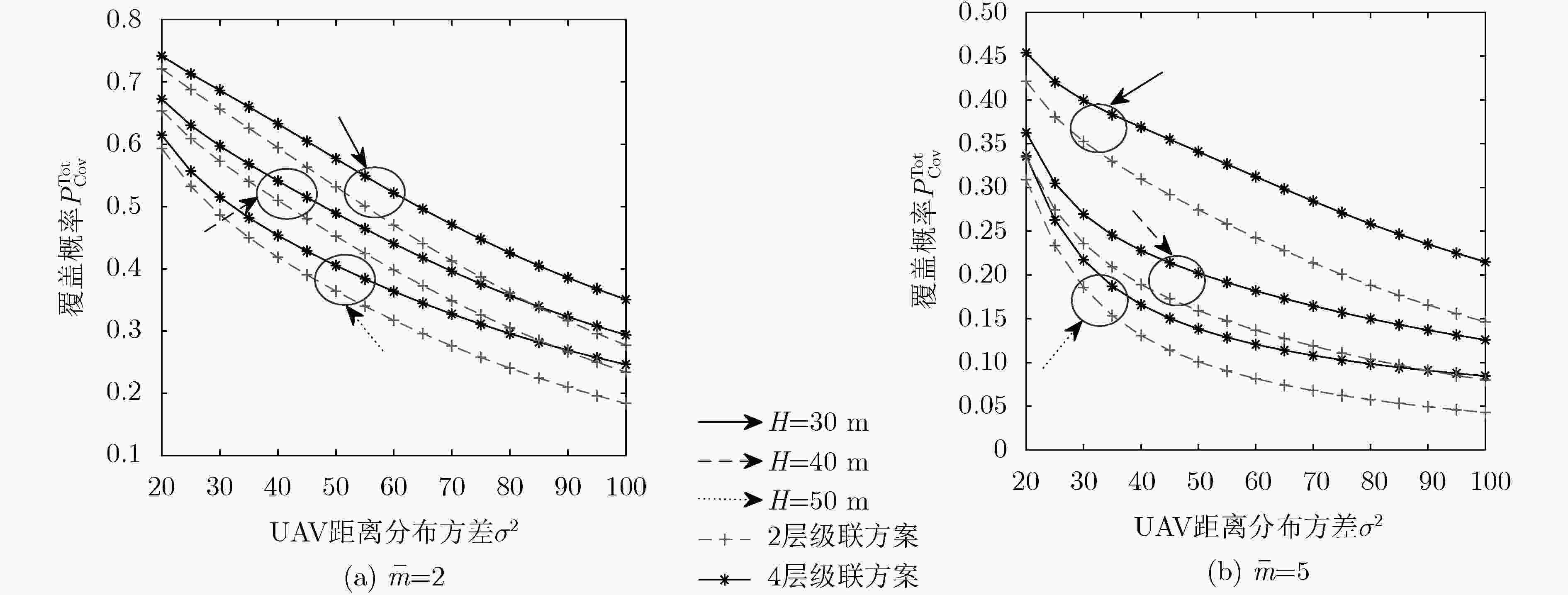
摘要: 针对B5G/6G中的热点场景,为满足其超大网络容量的需求,该文构建了多无人机(UAV)协助的毫米波异构网络模型,将地面基站(G-BS)的分布建模为泊松点过程,UAV的分布建模为泊松簇过程,且UAV在地面上的投影以及地面用户设备(GUE)分布在G-BS的周围。为了探讨簇间级联的贡献和簇间干扰的影响,将该2层网络模型扩展为由簇间和簇内基站(BS)共同构成的4层网络模型,并提出了GUE同时与簇内(间)BS级联的4层级联方案。首先,通过传播模型分析了各层级联距离的路径损耗。其次,采用随机几何的方法,结合GUE在下行链路中受到的干扰,推导出GUE可实现的信号与干扰加噪声比(SINR)覆盖概率表达式。最后,仿真结果表明,UAV的高度和簇成员平均数对SINR覆盖概率会产生非单调的影响。同时,当UAV高度较小时,该文所提出的4层级联方案可实现的SINR覆盖概率性能优于仅考虑GUE与簇内BS级联的2层级联方案。Abstract: In view of the hotspot scenarios in B5G/6G, in order to meet the needs of its ultra-large network capacity, a multi-Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) assisted millimeter wave heterogeneous network model is constructed. In this network model, the distribution of Ground Base Station (G-BS) is modeled as Poisson point process, the distribution of UAV is modeled as Poisson cluster process, and the projection of the UAV on ground and the Ground User Equipment (GUE) are distributed around the G-BS. For the sake of exploring the contribution of inter-cluster association and the impact of inter-cluster interference, the 2-tier network model is extended to 4-tier network model composed of inter-cluster and intra-cluster Base Station (BS). And the 4-tier association scheme in which the GUE is associated with intra-cluster BS and inter-cluster BS at the same time is proposed. Initially, the path loss of each tier’s association distance is analyzed through the propagation model. Furthermore, using stochastic geometry method, combined with the interference of GUE in the downlink, the Signal-to-Interference plus Noise Ratio (SINR) coverage probability expression of GUE is derived. Finally, the simulation results show that the height of UAV and the average number of cluster members have non-monotonic effect on SINR coverage probability. When UAV height is low, compared with the 2-tier association scheme that GUE is only associated with the intra-cluster BS, the 4-tier association scheme proposed in this paper can improve the SINR coverage probability significantly.
-
表 1 系统参数值
参数 数值 参数 数值 ${N_{0,t'}}$ 3 ${\alpha _{0,{\rm{L}}}}$ 2.1 ${N_1}$ 2 ${\alpha _{0,{\rm{N}}}}$ 3.4 ${N_{2,t'}}$ 3 ${\alpha _1}$ 3.4 ${N_3}$ 2 ${\alpha _{2,{\rm{L}}}}$ 2.5 ${R_0}$ 50~150 m ${\alpha _{2,{\rm{N}}}}$ 3.6 ${R_2}$ 30 m ${\alpha _3}$ 3.6 ${B_i}$ 1 ${\tau _{}}$ 1.5 -
[1] KIM D, LEE J, and QUEK T Q S. Multi-layer unmanned aerial vehicle networks: Modeling and performance analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(1): 325–339. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2944378 [2] 徐常志, 靳一, 李立, 等. 面向6G的星地融合无线传输技术[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(1): 28–36. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200363XU Changzhi, JIN Yi, LI Li, et al. Wireless transmission technology of satellite-terrestrial integration for 6G mobile communication[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(1): 28–36. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200363 [3] 黄天宇, 马林华, 胡星, 等. 一种实用的毫米波大规模MIMO混合预编码算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(8): 1788–1795. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161211HUANG Tianyu, MA Linhua, HU Xing, et al. Practical hybrid precoding algorithm for millimeter wave massive MIMO[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(8): 1788–1795. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161211 [4] 贾向东, 纪珊珊, 范巧玲, 等. 基于非正交多接入的多层全双工异构网回程方案及性能研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(4): 945–951. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180463JIA Xiangdong, JI Shanshan, FAN Qiaoling, et al. Backhaul scheme and performance study of full-duplex multi-tier heterogeneous networks based on non-orthogonal multiple access[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(4): 945–951. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180463 [5] ZHU Yongxu, ZHENG Gan, and FITCH M. Secrecy rate analysis of UAV-enabled mmWave networks using matérn hardcore point processes[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2018, 36(7): 1397–1409. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2018.2825158 [6] TURGUT E and GURSOY M C. Uplink performance analysis in D2D-enabled millimeter-wave cellular networks with clustered users[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(2): 1085–1100. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2018.2889755 [7] TURGUT E and GURSOY M C. Downlink analysis in unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) assisted cellular networks with clustered users[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 36313–36324. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2841655 [8] WANG Xueyuan and GURSOY M C. Simultaneous information and energy transfer in mmWave UAV-assisted cellular networks[C]. 2019 IEEE 20th International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications, Cannes, France, 2019: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/SPAWC.2019.8815566. [9] YI Wenqiang, LIU Yuanwei, BODANESE E, et al. A unified spatial framework for UAV-aided mmWave networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2019, 67(12): 8801–8817. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2019.2945332 [10] SAHA C and DHILLON H S. Downlink coverage probability of K-tier HetNets with general non-uniform user distributions[C]. 2016 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2016: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICC.2016.7511509. [11] HAENGGI M. Stochastic Geometry For Wireless Networks[M]. New York: Cambridge University Press, 2013: 13–16. [12] JO H S, SANG Y J, XIA Ping, et al. Heterogeneous cellular networks with flexible cell association: A comprehensive downlink SINR analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2012, 11(10): 3484–3495. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2012.081612.111361 [13] BAI Tianyang and HEATH R. Coverage and rate analysis for millimeter-wave cellular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2015, 14(2): 1100–1114. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2014.2364267 [14] WANG Xueyuan, TURGUT E, and GURSOY M C. Coverage in downlink heterogeneous mmWave cellular networks with user-centric small cell deployment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(4): 3513–3533. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2895816 [15] AI-HOURANI A, KANDEEPAN S, and LARDNER S. Optimal LAP altitude for maximum coverage[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2014, 3(6): 569–572. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2014.2342736 [16] WANG Xueyuan and GURSOY M C. Uplink coverage in heterogeneous mmWave cellular networks with user-centric small cell deployments[C]. 2018 IEEE 88th Vehicular Technology Conference, Chicago, USA, 2018: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/VTCFall.2018.8690884. [17] DAVID H A and NAGARAJA H N. Order Statistics[M]. 3rd ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2003: 18–27. [18] YI Wenqiang, LIU Yuanwei, and NALLANATHAN A. Modeling and analysis of D2D millimeter-wave networks with Poisson cluster processes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2017, 65(12): 5574–5588. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2017.2744644 [19] AFSHANG M, DHILLON H S, and CHONG P H J. Modeling and performance analysis of clustered device-to-device networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2016, 15(7): 4957–4972. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2016.2550024 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
