A Real-time Detection Method for Multi-scale Pedestrians in Complex Environment
-
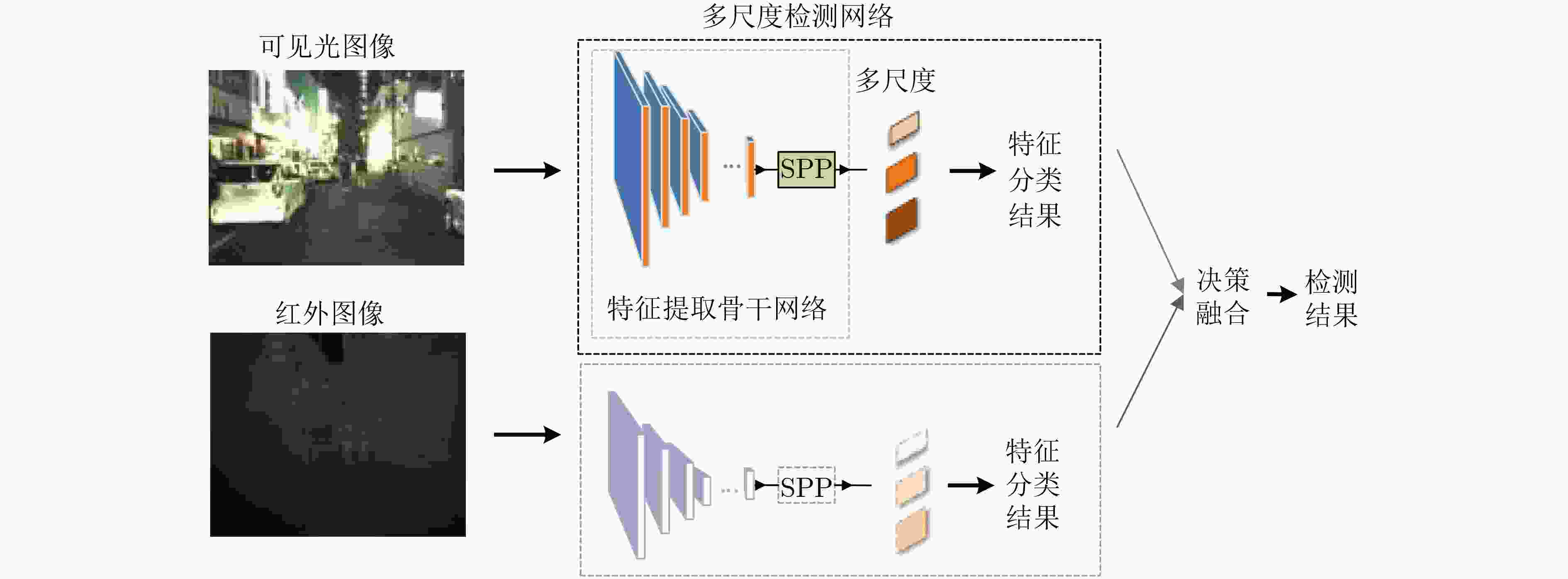
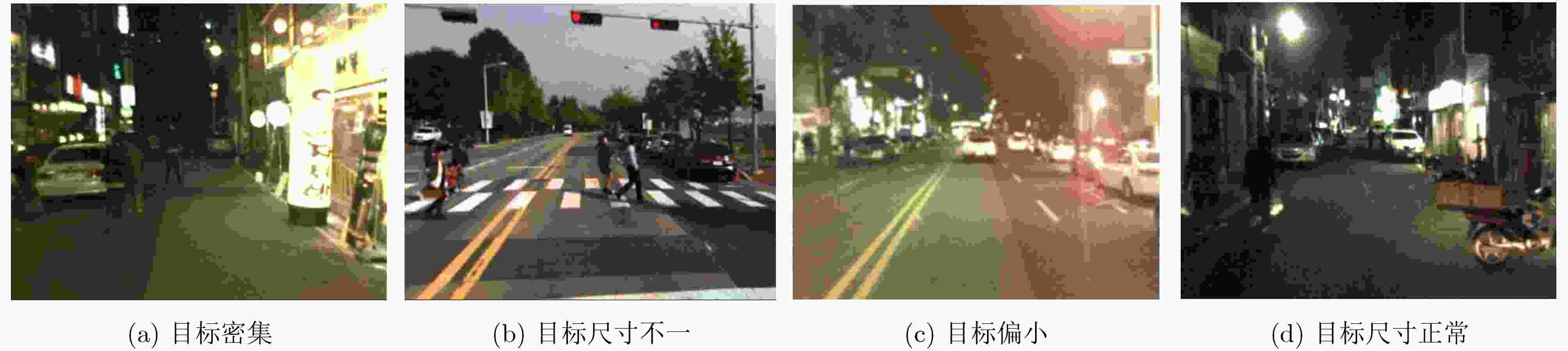
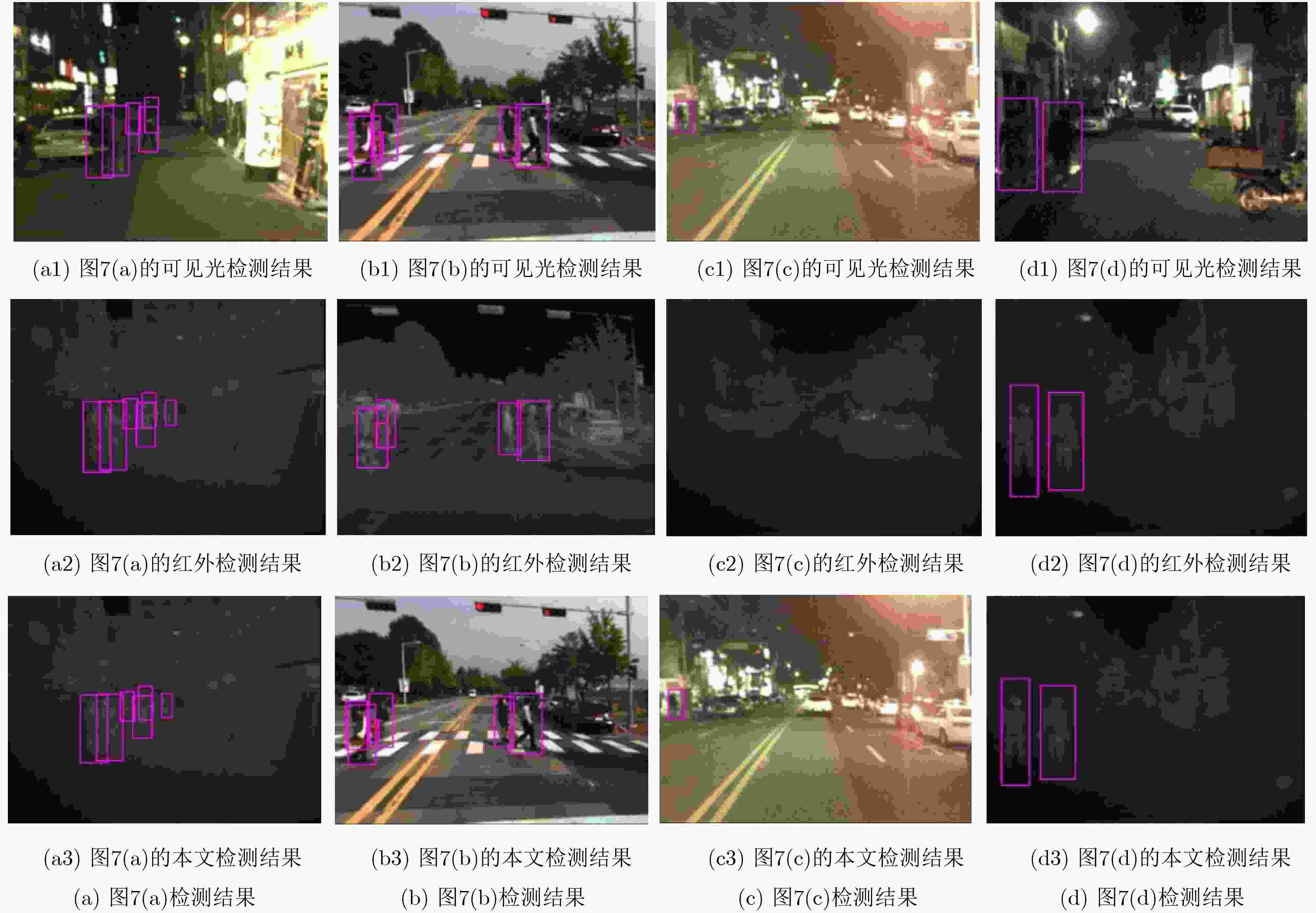
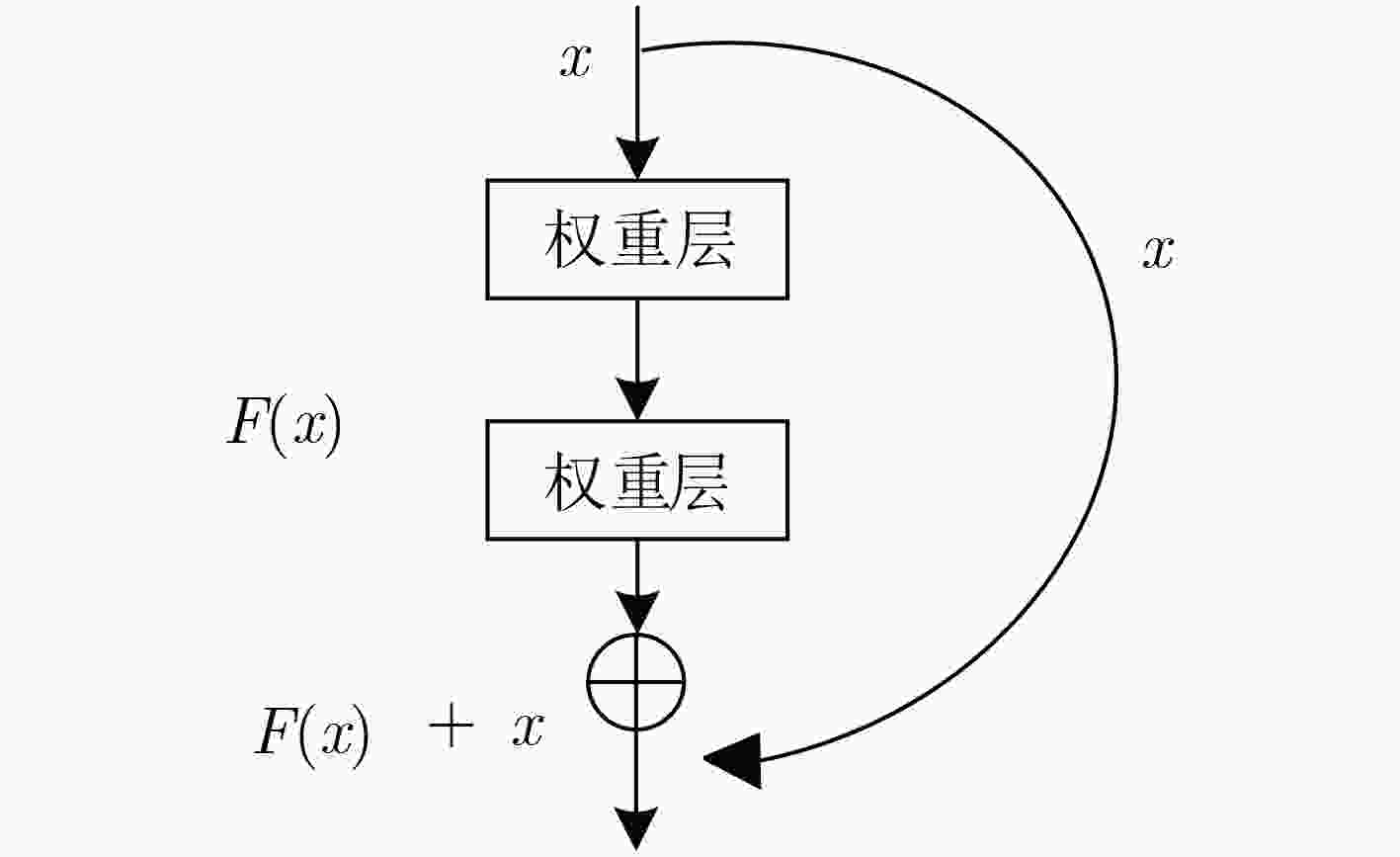
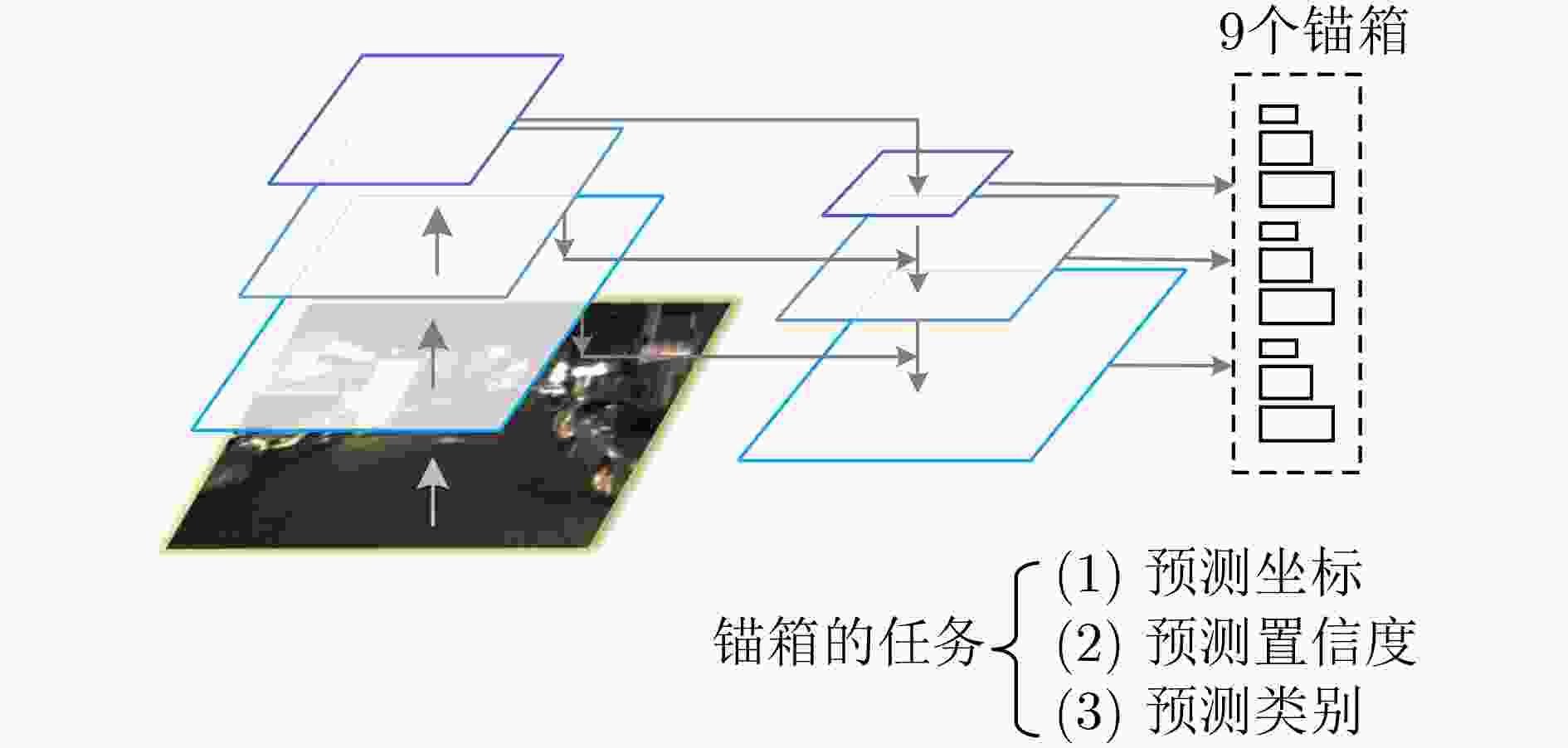
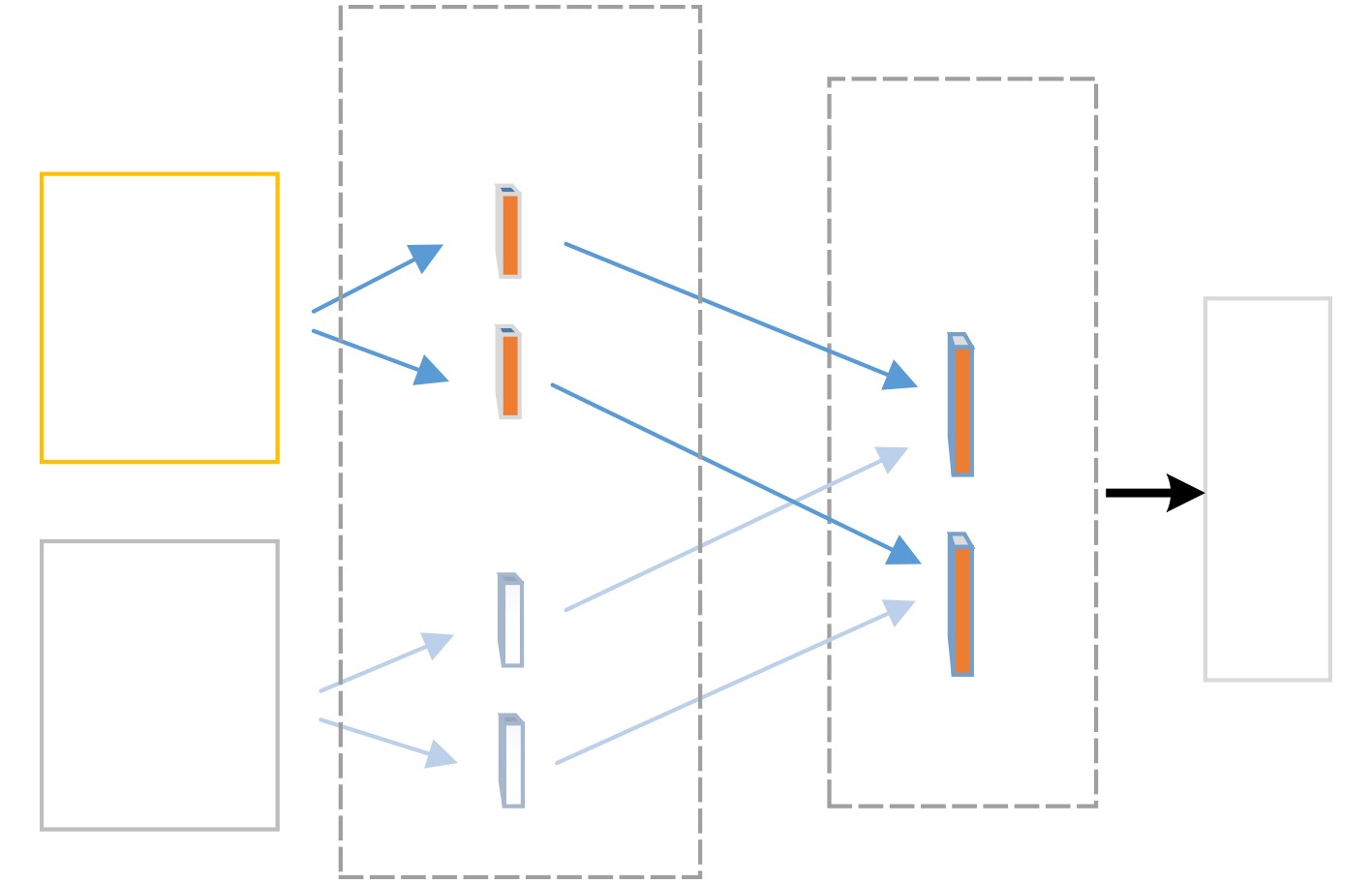
摘要: 作为计算机视觉和图像处理研究领域中的经典课题,行人检测技术在智能驾驶、视频监控等领域中具有广泛的应用空间。然而,面对一些复杂的环境和情况,如阴雨、雾霾、被遮挡、照明度变化、目标尺度差异大等,常见的基于可见光或红外图像的行人检测方法的效果尚不尽如人意,无论是在检测准确率还是检测速度上。该文分析并抓住可见光和红外检测系统中行人特征差异较大,但在不同环境中又各有优势的特点,并结合多尺度特征提取方法,提出一种适用于多样复杂环境下多尺度行人实时检测的方法——融合行人检测网络(FPDNet)。该网络主要由特征提取骨干网络、多尺度检测和信息决策融合3个部分构成,可自适应提取可见光或红外背景下的多尺度行人。实验结果证明,该检测网络在多种复杂视觉环境下都具有较好的适应能力,在检测准确性和检测速度上均能满足实际应用的需求。Abstract: As a classic subject in computer vision and image processing, pedestrian detection has a wide range of applications to intelligence driving and video monitoring fields. However, most of pedestrian detection methods based on visible or infrared images have no satisfying result in some complex environments or situations, such as rain, smog, occlusion, variation of illuminance and target scales, no matter in terms of detection accuracy or speed. This paper analyzes and finds out that, pedestrians usually have quite different characteristics in visible and infrared image, and which have their own advantages in different environments. Therefore, combining fusion and multi-scale technology, a real-time multi-scale pedestrian detection algorithm suitable for complex environment named FPDNet (Fusion Pedestrian Detection Network) is proposed. The detection framework is consisted by three main modules: feature extraction backbone network, multi-scale detection network and decision-level fusion network. The proposed method is able to extract multi-scale pedestrian characteristics under visible or infrared background adaptively. Experimental results prove that the detection network has good adaptability in complex visual environments, and can meet the demands of practical applications to detection accuracy and speed.
-
Key words:
- Pedestrian detection /
- Complex environment /
- Adaptive extracting /
- Multi-scale /
- Decision-level fusion
-
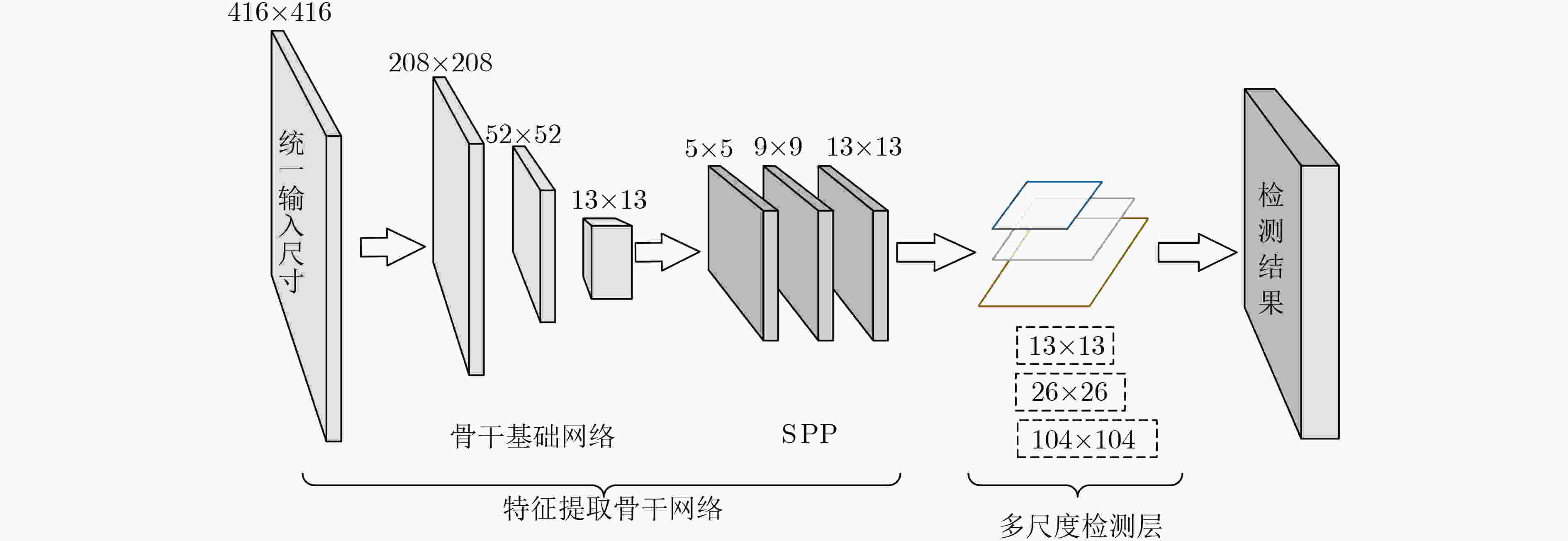
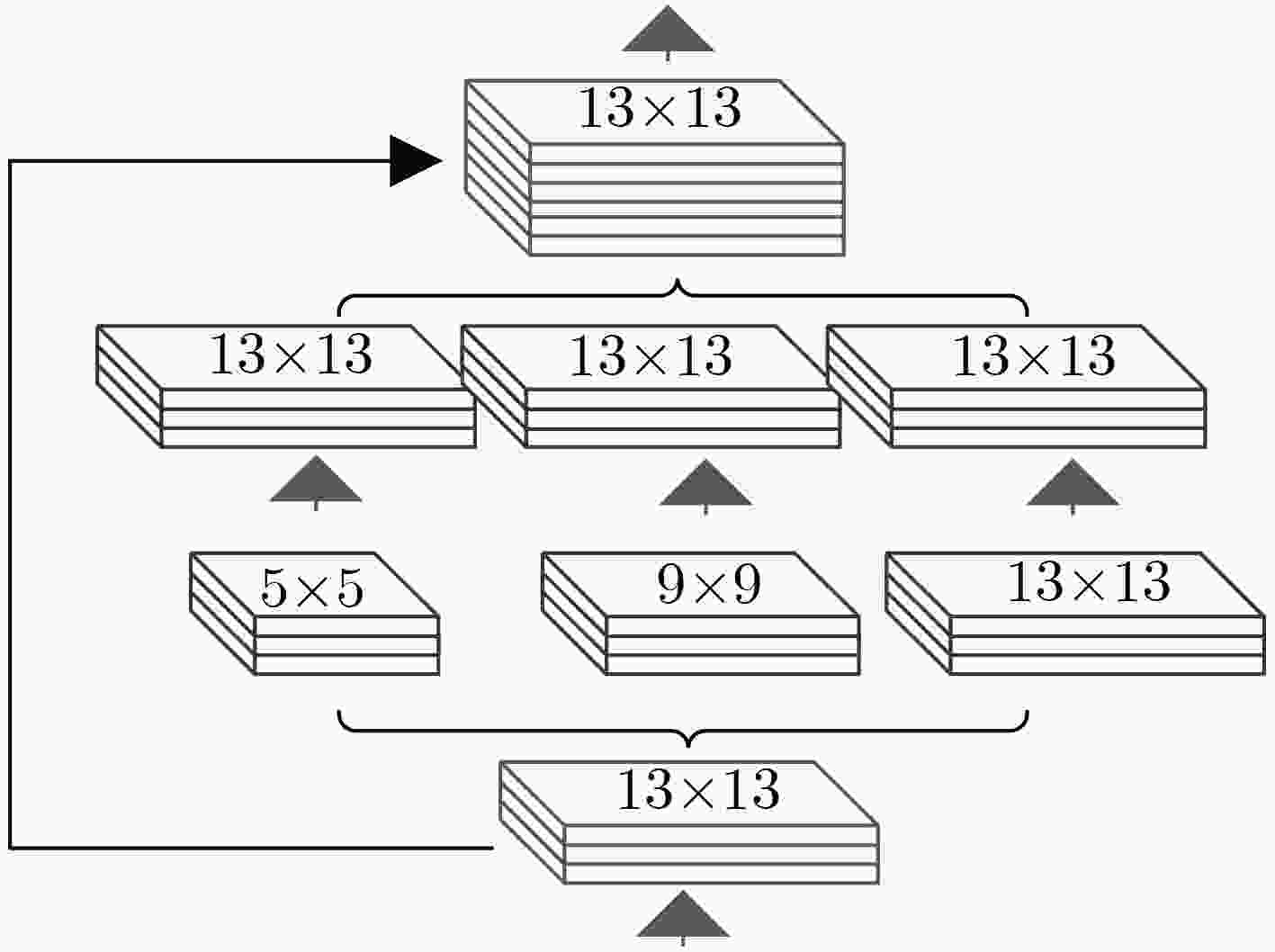
表 1 骨干基础网络结构表
重复次数 类别 卷积核 卷积核尺寸 输出特征图大小 Conv 64 7×7/2 208×208 Max 2×2/2 104×104 3 Conv 64 3×3/1 Conv 64 3×3/1 Res 104×104 Conv 128 3×3/2 Conv 128 3×3/1 Res 52×52 3 Conv 128 3×3/1 Conv 128 3×3/1 Res 52×52 Conv 256 3×3/2 Conv 256 3×3/1 Res 26×26 4 Conv 256 3×3/1 Conv 256 3×3/1 Res 26×26 Conv 512 3×3/2 Conv 512 3×3/1 Res 13×13 2 Conv 512 3×3/1 Conv 512 3×3/1 Res 13×13 表 2 候选框的宽度和高度表
检测层尺寸(像素) (宽度,高度) (宽度,高度) (宽度,高度) 13×13 (41,103) (53,138) (77,205) 26×26 (30,74) (30,94) (35,84) 104×104 (20,30) (20,51) (27,61) 表 3 网络模型的对比结果表
模型 mAP(%) FPS ACF+T+THOG 71.49 32 HalFus+TSDCNN 88.24 2.5 TSDCNN+Ada 89.03 1.3 SSD 88.01 42 YOLOv3 91.35 45 YOLOv3-tiny 80.57 155 FPDNet 91.29 68 -
[1] SAGAR U, RAJA R, and SHEKHAR H. Deep learning for pedestrian detection[J]. International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, 2019, 9(8): 66–69. doi: 10.29322/IJSRP.9.08.2019.p9212 [2] PRISCILLA C V and SHEILA S P A. Pedestrian detection - A survey[C]. Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Innovative Computing and Cutting-edge Technologies, Istanbul, Turkey, 2020: 349–358. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-38501-9_35. [3] CHEN Runxing, WANG Xiaofei, LIU Yong, et al. A survey of pedestrian detection based on deep learning[C]. Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Communications, Signal Processing, and Systems, Singapore, 2020: 1511–1516. [4] LOWE D G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 60(2): 91–110. doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94 [5] 孙锐, 陈军, 高隽. 基于显著性检测与HOG-NMF特征的快速行人检测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2013, 35(8): 1921–1926. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01700SUN Rui, CHEN Jun, and GAO Jun. Fast pedestrian detection based on saliency detection and HOG-NMF features[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2013, 35(8): 1921–1926. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01700 [6] FELZENSZWALB P F, GIRSHICK R B, MCALLESTER D, et al. Object detection with discriminatively trained part- based models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2010, 32(9): 1627–1645. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2009.167 [7] HASTIE T, ROSSET S, ZHU Ji, et al. Multi-class AdaBoost[J]. Statistics and its Interface, 2009, 2(3): 349–360. doi: 10.4310/SII.2009.v2.n3.a8 [8] BREIMAN L. Random forests[J]. Machine Learning, 2001, 45(1): 5–32. doi: 10.1023/A:1010933404324 [9] 陈勇, 刘曦, 刘焕淋. 基于特征通道和空间联合注意机制的遮挡行人检测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(6): 1486–1493. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190606CHEN Yong, LIU Xi, and LIU Huanlin. Occluded pedestrian detection based on joint attention mechanism of channel-wise and spatial information[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(6): 1486–1493. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190606 [10] REN Jing, REN Rui, GREEN M, et al. Defect detection from X-ray images using a three-stage deep learning algorithm[C]. Proceedings of 2019 IEEE Canadian Conference of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Edmonton, Canada, 2019: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/CCECE.2019.8861944. [11] PAN Meiyan, CHEN Jianjun, WANG Shengli, et al. A novel approach for marine small target detection based on deep learning[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE 4th International Conference on Signal and Image Processing, Wuxi, China, 2019: 395–399. doi: 10.1109/SIPROCESS.2019.8868862. [12] GIRSHICK R, DONAHUE J, DARRELL T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]. Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 580–587. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2014.81. [13] GIRSHICK R. Fast R-CNN[C]. Proceedings of 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1440–1448. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.169. [14] REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137–1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [15] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 779–788. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.91. [16] REDMON J and FARHADI A. YOLO9000: Better, faster, stronger[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6517–6525. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.690. [17] REDMON J and FARHADI A. YOLOv3: An incremental improvement[J]. arXiv: 1804.02767, 2018. [18] LIU Wei, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot multibox detector[C]. Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 21–37. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_2. [19] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1904–1916. doi: 10.1109/tpami.2015.2389824 [20] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. [21] LIU Weiyang, WEN Yandong, YU Zhiding, et al. Large-margin Softmax loss for convolutional neural networks[C]. Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, USA, 2016: 507–516. [22] HWANG S, PARK J, KIM N, et al. Multispectral pedestrian detection: Benchmark dataset and baseline[C]. Proceedings of 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 1037–1045. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298706. [23] KANUNGO T, MOUNT D M, NETANYAHU N S, et al. An efficient K-means clustering algorithm: Analysis and implementation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2002, 24(7): 881–892. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2002.1017616 [24] BOTTOU L. Stochastic gradient descent tricks[M]. Neural Networks: Tricks of the Trade. 2nd ed. Berlin Germany: Springer, 2012: 421–436. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-35289-8_25. [25] RAHMAN M A and WANG Yang. Optimizing intersection-over-union in deep neural networks for image segmentation[C]. Proceedings of the 12th International Symposium on Advances in Visual Computing, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 234–244. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-50835-1_22. [26] KROTOSKY S J and TRIVEDI M M. On color-, infrared-, and multimodal-stereo approaches to pedestrian detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2007, 8(4): 619–629. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2007.908722 [27] LIU Jingjing, ZHANG Shaoting, WANG Shu, et al. Multispectral deep neural networks for pedestrian detection[C]. Proceedings of 2016 British Machine Vision Conference, York, UK, 2016: 73.1–73.13. doi: 10.5244/C.30.73. [28] KÖNIG D, ADAM M, JARVERS C, et al. Fully convolutional region proposal networks for multispectral person detection[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 243–250. doi: 10.1109/CVPRW.2017.36. -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
