Zero-shot Learning by Semantic Autoencoder Based on Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm for Attribute Correlation
-
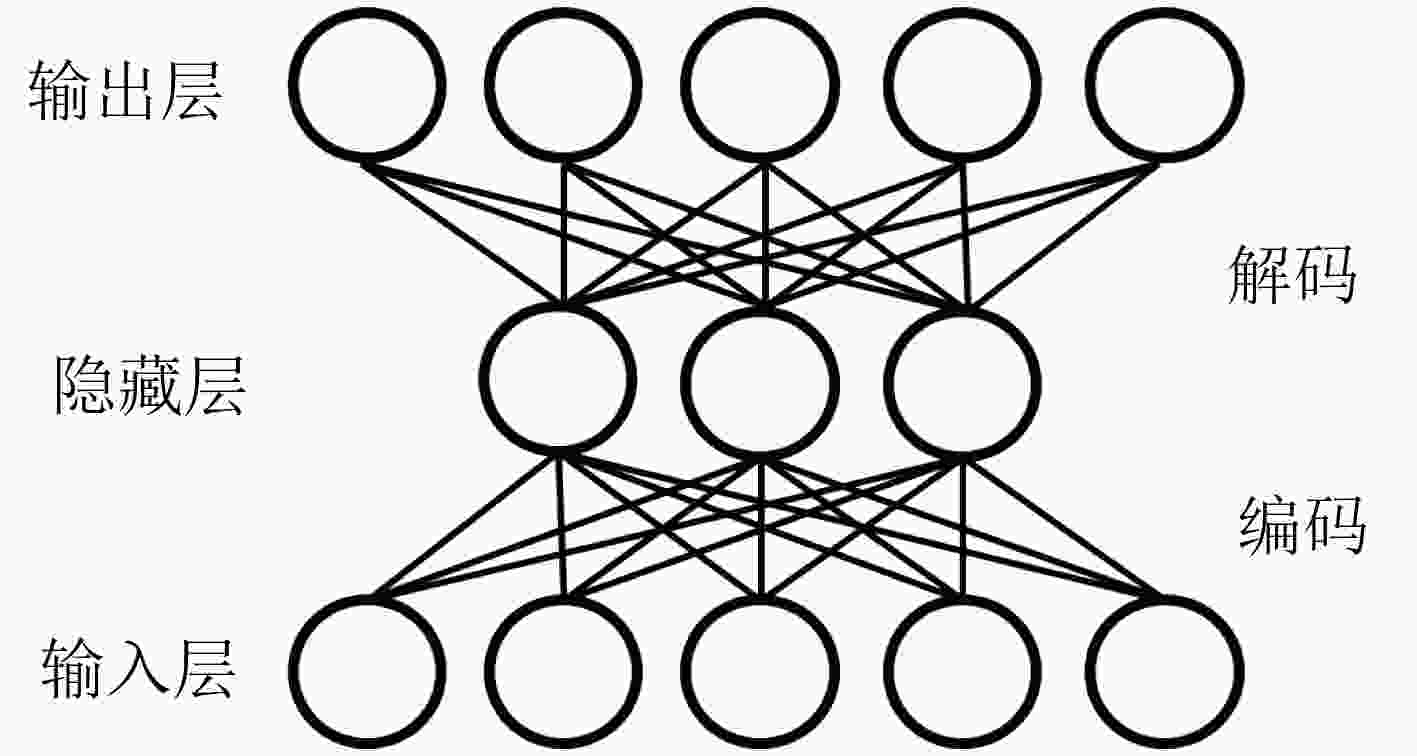
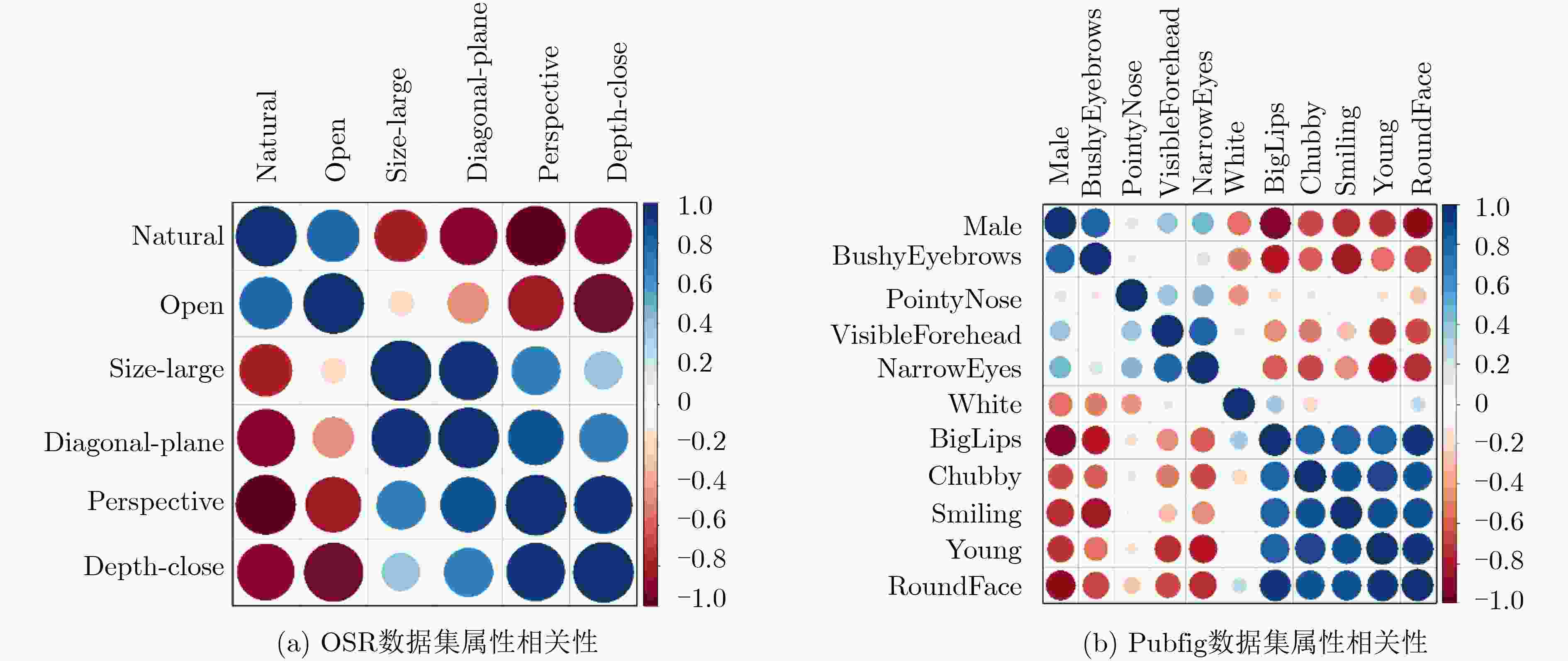
摘要: 针对零样本图像分类构建共享属性层时造成的信息缺失问题,该文提出一种嵌入属性关联性的补偿方法。通过语义自编码器构建特征到属性的映射,然后以最大后验概率估计在类高斯模型构建的基础上实现零样本图像分类。为弥补SAE对属性关系学习的不足,引入加性因子与乘性因子对属性相关性进行嵌入,并利用粒子群算法搜寻最优的因子参数,实现属性相关性信息的补偿。实验结果表明采取相同映射方法的情况下,基于属性相关性嵌入的零样本图像分类在Pubfig数据集和OSR数据集上的分类效果较之其他方法得到了显著提升。Abstract: To deal with the problem of missing information caused by zero-shot image classification during building a shared attribute layer, a compensation method is proposed to embed the attribute correlation. The proposed zero-shot classification utilizes Semantic AautoEncoder (SAE) to realize the feature-to-attribute mapping, and the invisible images are classified using maximum posterior probability estimation based on the class Gaussian distribution model. In order to make up for the lack of attribute relationships in SAE learning, the additive and multiplicative factors are introduced to embed the attribute correlation. The particle swarm algorithm is used to search for the optimal factor parameters to achieve the compensation of attribute correlation information. Experimental results show that when the same mapping method is adopted, the classification performance of zero-shot image classification based on attribute correlation on Pubfig and OSR data sets is significantly improved compared with other methods.
-
表 1 PSA算法伪代码
输入:${\bf{Score}}$, X, Y, Z(其中,底层特征X分为测试部分${{{X}}_{{\bf{te}}}}$(标签数为m)和训练部分${{{X}}_{{\bf{tr}}}}$(标签数为n), Y为训练集标签集合,Z为测试集标
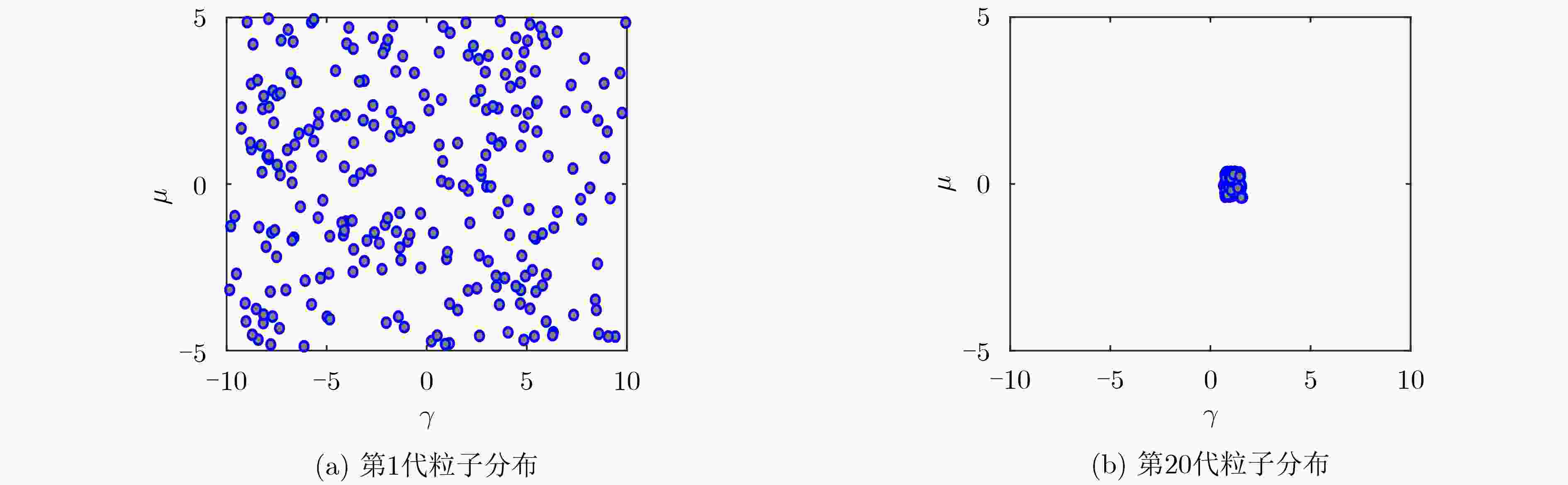
签集合)输出:Acc(测试准确率) PSO: 初始化设定n, m, ${{{G}}_{\max }}$, ${{{G}}_{\min }}$, ${{{V}}_{\max }}$, ${{{V}}_{\min }}$,Fitness 求得${{{P}}_{{{g}} - {\rm{best}}}}$, ${\rm{Fitnes}}{{\rm{s}}_{\min }}$解下的G For t in $\left[ {1,C_n^m} \right]$ do (交叉验证) For i in $ \left[ {1,n} \right]$ do 确定${{{P}}_{{{g}} - {\rm{best}}}}$以及此解下的G AR:用G更新${\bf{Scor}}{{\bf{e}}^*}$与属性值排序矩阵O SAE:用${{{X}}_{{\bf{tr}}}}$, ${\bf{Scor}}{{\bf{e}}^*}$, ${{{X}}_{{\bf{tr}}}}$, Y, O;求得W, ${\rm{Fitness}} = \mathop {\min }\limits_{{W}} \left\| {{{X}} - {{{W}}^{\rm{T}}}{{S}}} \right\|_{\rm{F}}^2 + \kappa \left\| {{{X}} - {{{W}}^{\rm{T}}}{{S}}} \right\|_{\rm{F}}^2$ 用Fitness确定是否更新${{{P}}_{{{g}} - {\rm{best}}}}$以及该解下的粒子解G End DAP:用映射矩阵W,粒子群最优解G,属性值排序矩阵O,测试集${{{X}}_{{\bf{te}}}}$及标签Z 计算每一组交叉验证的测试集精度ACUt End Acc = mean(ACUt) 表 2 PSO的参数设置
规模 代数 参数 速度 位置 250 20 λ [–2 2] [–10 10] µ [–1 1] [–5 5] 表 3 PSO寻优参数及测试精度(Pubfig数据集 测试类别数:2)
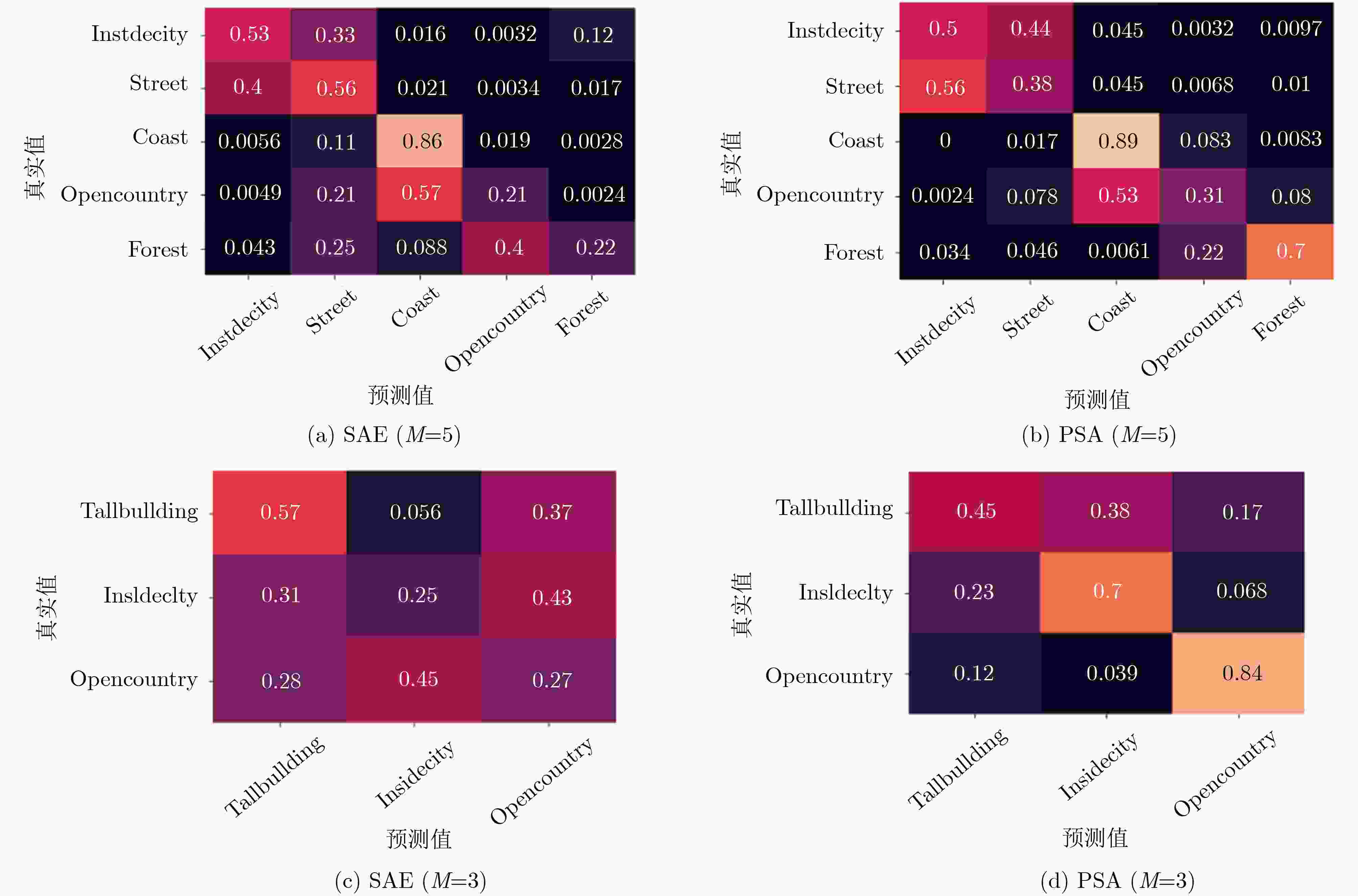
序号 测试精度 $\lambda $ $\mu $ 序号 测试精度 $\lambda $ $\mu $ 1 89.7959 1.7132 –0.0039 15 83.9378 1.4155 0.1333 2 82.0513 1.9473 –0.4259 16 82.3834 2.0000 0.1245 3 92.8205 1.0834 –0.3664 17 80.5263 1.4407 –0.0169 4 75.3846 1.6065 –0.4163 18 68.9119 1.7021 0.1057 5 89.7436 1.2878 –0.0714 19 88.0829 1.3892 0.0619 6 69.5876 1.1262 –0.3859 20 87.0466 1.4444 –0.0670 7 71.3542 1.6406 –0.4989 21 87.5000 1.0901 –0.0366 8 75.5208 1.3301 –0.4631 22 88.5417 1.0043 –0.0176 9 92.1466 1.0432 –0.0615 23 85.7143 1.4594 –0.4434 10 91.6230 1.5004 –0.1000 24 89.0625 1.0434 –0.3854 11 89.7436 1.5019 –0.4517 25 76.4398 1.2033 0.0182 12 82.5641 1.3095 –0.4647 26 73.2984 1.3058 –0.4541 13 94.3299 1.2792 –0.4621 27 87.6289 1.2718 0.0168 14 92.2680 1.6835 0.1445 28 80.4124 1.2860 0.1277 表 4 OSR数据集的分类精度和AUC值
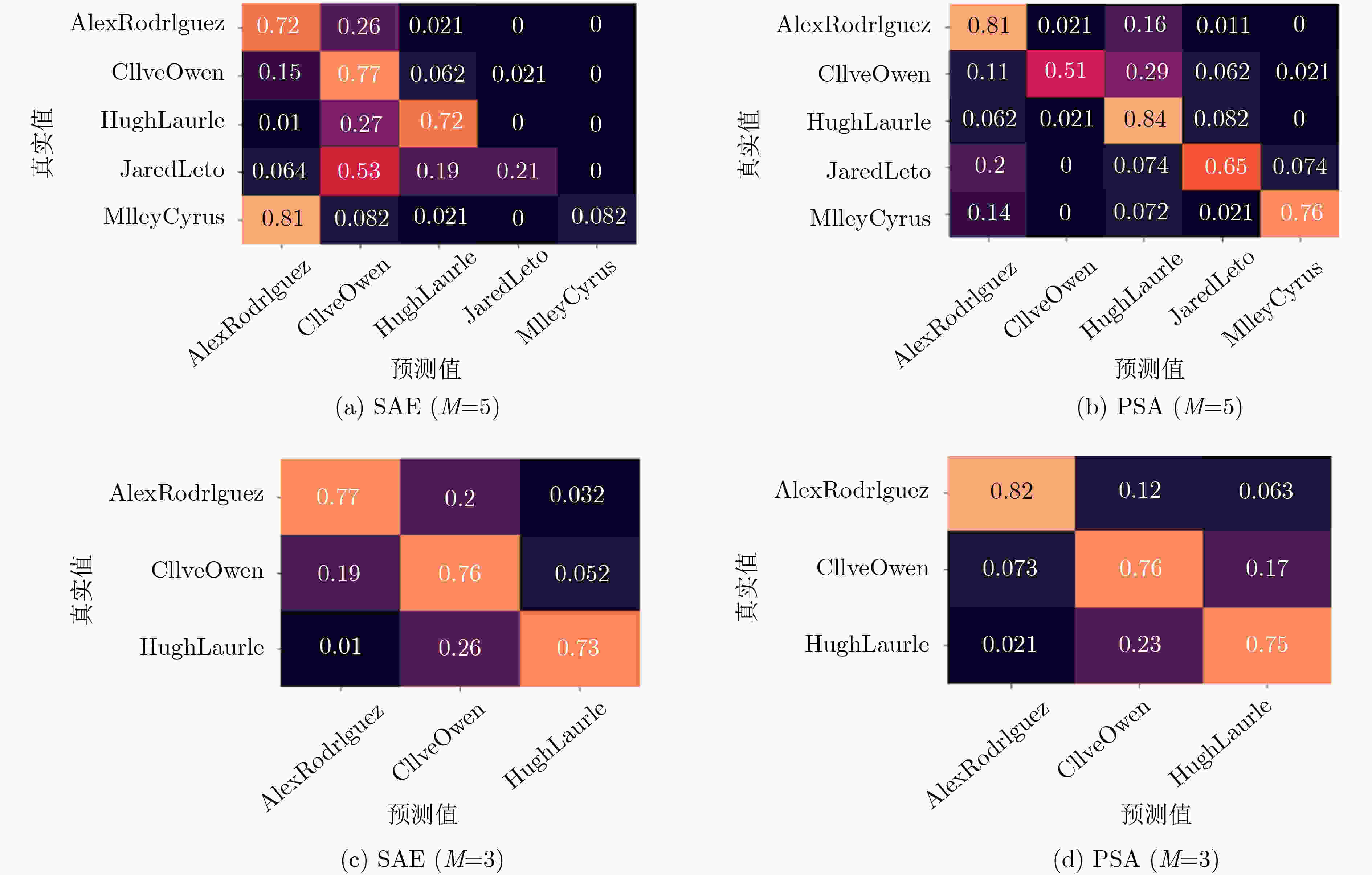
m/M 2/6 3/5 4/4 5/3 6/2 交叉验证组数 28 56 70 56 28 Measures Acc AUC Acc AUC Acc AUC Acc AUC Acc AUC DAP 20.80 0.578 24.48 0.588 27.37 0.586 37.64 0.595 54.15 0.645 Relative 26.79 0.695 31.76 0.694 43.99 0.717 50.71 0.732 60.50 0.759 SAE 37.01 0.705 48.58 0.736 60.90 0.729 58.15 0.736 64.62 0.775 PSA 49.88 0.731 54.75 0.744 60.30 0.720 66.77 0.752 75.95 0.780 表 5 Pubfig数据集的分类精度和AUC值
$m/M$ 2/6 3/5 4/4 5/3 6/2 交叉验证组数 28 56 70 56 28 Measures Acc AUC Acc AUC Acc AUC Acc AUC Acc AUC DAP 16.80 0.545 21.01 0.572 37.18 0.566 46.91 0.596 63.40 0.636 Relative 23.54 0.670 33.13 0.651 44.80 0.658 54.50 0.669 65.92 0.733 SAE 44.16 0.662 52.48 0.670 69.36 0.673 76.20 0.661 77.15 0.671 PSA 52.13 0.670 61.03 0.683 69.47 0.674 76.97 0.667 86.93 0.678 -
LAROCHELLE H, ERHAN D, and BENGIO Y. Zero-data learning of new tasks[C]. The 23rd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Chicago, USA, 2008: 646–651. LAMPERT C H, NICKISCH H, and HARMELING S. Attribute-based classification for zero-shot visual object categorization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2014, 36(3): 453–465. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2013.140 BANSAL A, SIKKA K, SHARMA G, et al. Zero-shot object detection[C]. The European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 397–414. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01246-5_24. FU Yanwei, XIANG Tao, JIANG Yugang, et al. Recent advances in zero-shot recognition: Toward data-efficient understanding of visual content[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2018, 35(1): 112–125. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2017.2763441 FARHADI A, ENDRES I, HOIEM D, et al. Describing objects by their attributes[C]. 2019 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, USA, 2009: 1778–1785. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2009.5206772. PARIKH D and GRAUMAN K. Relative attributes[C]. 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 2011: 6–13. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2011.6126281. CHENG Yuhu, QIAO Xue, WANG Xuesong, et al. Random forest classifier for zero-shot learning based on relative attribute[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(5): 1662–1674. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2677441 乔雪, 彭晨, 段贺, 等. 基于共享特征相对属性的零样本图像分类[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(7): 1563–1570. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161133QIAO Xue, PENG Chen, DUAN He, et al. Shared features based relative attributes for zero-shot image classification[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(7): 1563–1570. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161133 兰红, 方治屿. 零样本图像识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(5): 1188–1200. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190485LAN Hong and FANG Zhiyu. Recent advances in zero-shot learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(5): 1188–1200. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190485 KODIROV E, XIANG Tao, and GONG Shaogang. Semantic autoencoder for zero-shot learning[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 4447–4456. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.473. LAMPERT C H, NICKISCH H, and HARMELING S. Learning to detect unseen object classes by between-class attribute transfer[C]. 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, USA, 2009: 951–958. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2009.5206594. KANKUEKUL P, KAWEWONG A, TANGRUAMSUB S, et al. Online incremental attribute-based zero-shot learning[C]. 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, USA, 2012: 3657–3664. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2012.6248112. TAO Rentuo, LI Ziqiang, TAO Renshuai, et al. ResAttr-GAN: Unpaired deep residual attributes learning for multi-domain face image translation[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 132594–132608. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2941272 冀中, 汪浩然, 于云龙, 等. 零样本图像分类综述: 十年进展[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2019, 49(10): 1299–1320. doi: 10.1360/N112018-00312JI Zhong, WANG Haoran, YU Yunlong, et al. A decadal survey of zero-shot image classification[J]. Scientia Sinica:Informationis, 2019, 49(10): 1299–1320. doi: 10.1360/N112018-00312 张鲁宁, 左信, 刘建伟. 零样本学习研究进展[J]. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(1): 1–23.ZHANG Luning, ZUO Xin, and LIU Jianwei. Research and development on zero-shot learning[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(1): 1–23. WANG Wei, ZHENG V W, YU Han, et al. A survey of zero-shot learning: Settings, methods, and applications[J]. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology, 2019, 10(2): 13. doi: 10.1145/3293318 LIU Mingxia, ZHANG Daoqiang, and CHEN Songcan. Attribute relation learning for zero-shot classification[J]. Neurocomputing, 2014, 139: 34–46. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2013.09.056 WANG Yang and MORI G. A discriminative latent model of object classes and attributes[C]. European Conference on Computer Vision, Berlin, Germany, 2010: 155–168. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-15555-0_12. BISWAS S and ANNADANI Y. Preserving semantic relations for zero-shot learning[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7603–7612. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00793. QUERCIA D, O’HARE N K, and CRAMER H. Aesthetic capital: What makes London look beautiful, quiet, and happy?[C]. The 17th ACM Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work & Social Computing, New York, USA, 2014: 945–955. MIN Weiqing, MEI Shuhuan, LIU Linhu, et al. Multi-task deep relative attribute learning for visual urban perception[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 657–669. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2932502 QIAO Lingfeng, TUO Hongya, FANG Zheng, et al. Joint probability estimation of attribute chain for zero-shot learning[C]. 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Phoenix, USA, 2016: 1863–1867. doi: 10.1109/ICIP.2016.7532681. 巩萍, 程玉虎, 王雪松. 基于属性关系图正则化特征选择的零样本分类[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2015, 44(6): 1097–1104.GONG Ping, CHENG Yuhu, and WANG Xuesong. Zero-shot classification based on attribute correlation graph regularized feature selection[J]. Journal of China University of Mining &Technology, 2015, 44(6): 1097–1104. XIAO Fanyi and LEE Y J. Discovering the spatial extent of relative attributes[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, USA, 2015: 1458–1466. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.171. SINGH K K and LEE Y J. End-to-end localization and ranking for relative attributes[C]. European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2016: 753–769. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46466-4_45. KENNEDY J and EBERHART R. Particle swarm optimization[C]. ICNN'95-International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, Australia, 1995. doi: 10.1109/ICNN.1995.488968. ANAMIKA, PEESAPATI R, and KUMAR N. Electricity price forecasting and classification through wavelet–dynamic weighted PSO–FFNN approach[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2018, 12(4): 3075–3084. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2017.2717446 KUMAR N, BERG A C, BELHUMEUR P N, et al. Attribute and simile classifiers for face verification[C]. The 12th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Kyoto, Japan, 2009: 365–372. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2009.5459250. OLIVA A and TORRALBA A. Modeling the shape of the scene: A holistic representation of the spatial envelope[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2001, 42(3): 145–175. doi: 10.1023/A:1011139631724 LEE W H, GADER P D, and WILSON J N. Optimizing the area under a receiver operating characteristic curve with application to landmine detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2007, 45(2): 389–397. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2006.887018 CASTRO C L and BRAGA A P. Novel cost-sensitive approach to improve the multilayer perceptron performance on imbalanced data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2013, 24(6): 888–899. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2013.2246188 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
