Bayesian Variational Inference Algorithm Based on Expectation-Maximization and Simulated Annealing
-
摘要: 针对贝叶斯变分推理收敛精度低和搜索过程中易陷入局部最优的问题,该文基于模拟退火理论(SA)和最大期望理论(EM),考虑变分推理过程中初始先验对最终结果的影响和变分自由能的优化效率问题,构建了双重EM模型学习变分参数的初始先验,以降低初始先验的敏感性,同时构建逆温度参数改进变分自由能函数,使变分自由能在优化过程得到有效控制,并提出一种基于最大期望模拟退火的贝叶斯变分推理算法。该文使用收敛性准则理论分析算法的收敛性,利用所提算法对一个混合高斯分布实例进行实验仿真,实验结果表明该算法具有较优的收敛结果。Abstract: For the problem that Bayesian variational inference with low convergence precision is easy to fall into local optimum during search process, a Bayesian variational inference algorithm based on Expectation-Maximization (EM) and Simulated Annealing (SA) is proposed. The influence of the initial prior on the final result and the optimization efficiency of the variational free energy in the process of variational inference can not be ignored. The double EM is introduced to construct the initial prior of the variational parameter to reduce the sensitivity of the initial prior. And the inverse temperature parameter is introducted to improve the free energy function, which makes the energy be effectively controlled in the optimization process. This paper uses convergence criterion theory to analyze the convergence of the algorithm. The proposed algorithm is used for experiments with an Gaussian mixture model and the experimental results show that the proposed algorithm has better convergence results.
-
表 1 ES-VBI算法
(1)根据式(12)—式(18)方式构建基于最大似然估计的双重EM模型计算出初始先验${\omega ^ * }$,${z^ * }$; (2)设置模拟退火的初始逆温度参数$\phi $,$0 < \phi < 1$, $t = 0$,构建基于逆温参数变分自由能的目标函数; (3)根据拉格朗日算法子求得$z$和$\omega $的迭代公式; (4)执行以下迭代步骤直至收敛: 执行迭代式(26)更新$q\left( z \right)$; 执行迭代式(27)更新$q\left( \omega \right)$; 执行$t = t + 1$; (5)$\phi \leftarrow \phi \times {\rm{const}} $; (6)如果$\phi < 1$,则跳转第(4)步,否则终止算法。 表 2 各算法ELOB和时间对比
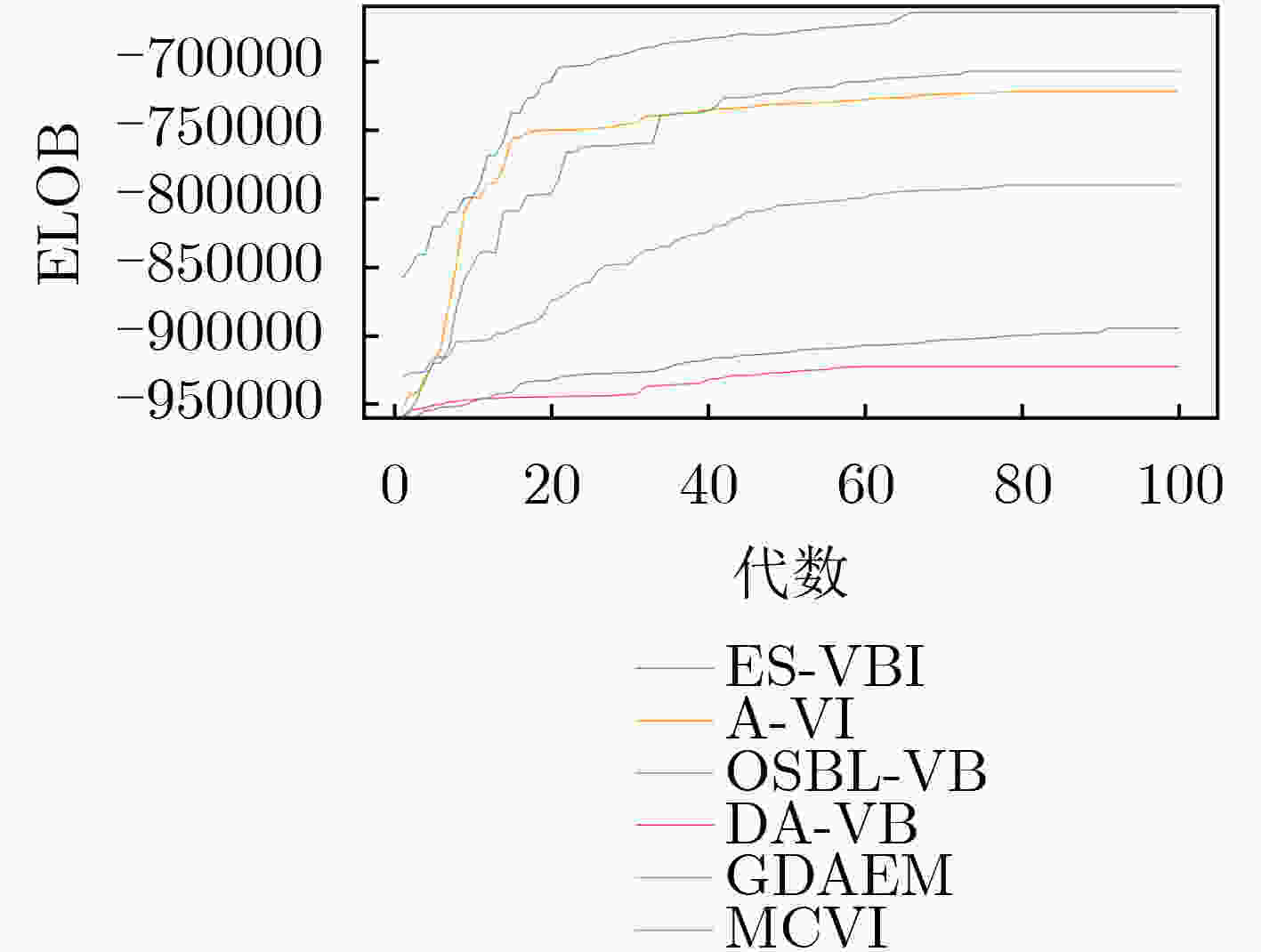
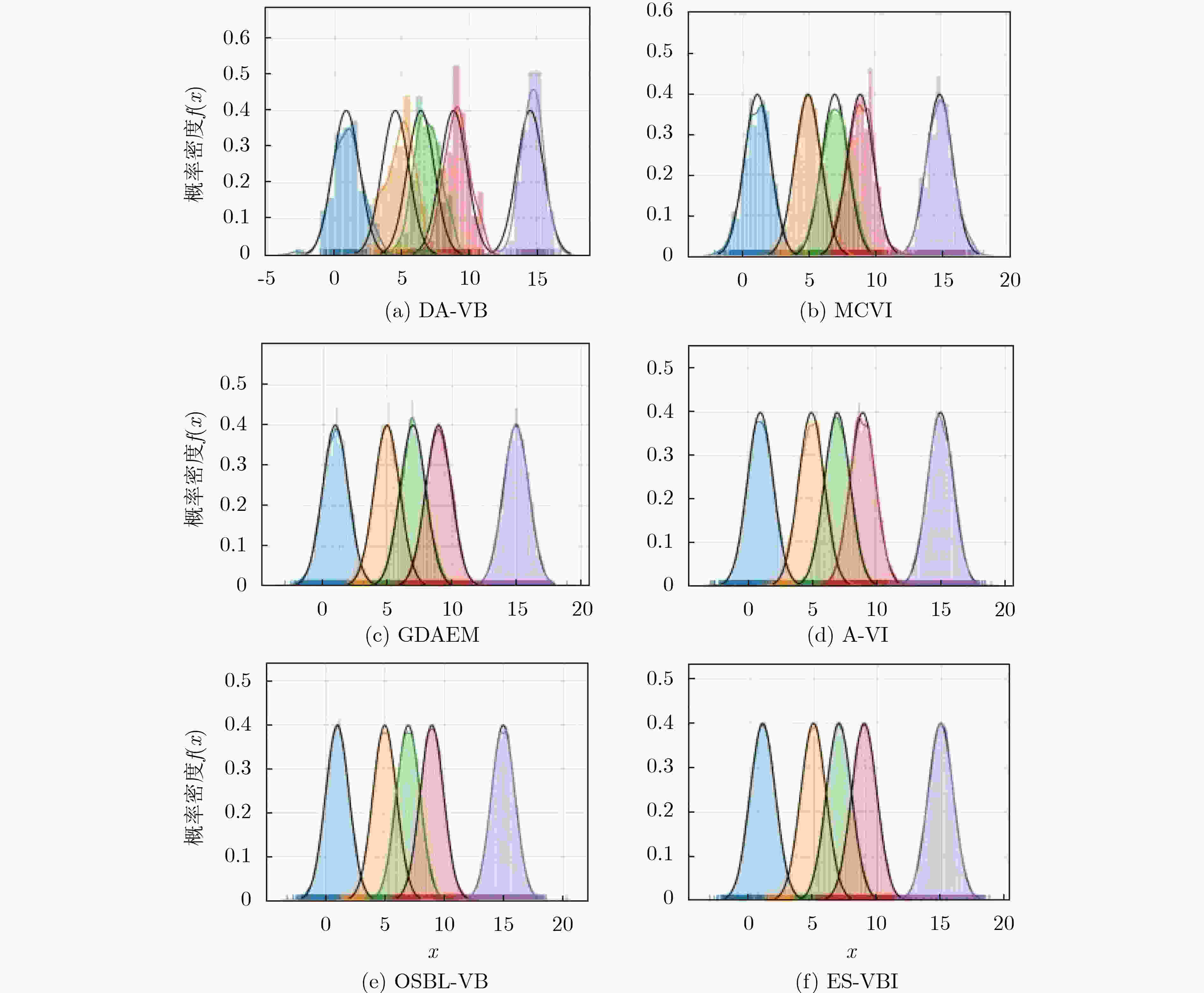
算法名称 ELOB t(s) ES-VBI –664428.51 9.28 A-VI –721994.83 15.44 OSBL-VB −707239.90 27.97 DA-VB –922489.46 12.83 GDAEM –790262.55 5.62 MCVI –894487.22 30.25 -
[1] SEEGER M W and WIPF D P. Variational Bayesian inference techniques[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2010, 27(6): 81–91. doi: 10.1109/msp.2010.938082 [2] MA Yanjun, ZHAO Shunyi, and HUANG Biao. Multiple-model state estimation based on variational Bayesian inference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019, 64(4): 1679–1685. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2018.2854897 [3] JORDAN M I, GHAHRAMANI Z, JAAKKOLA T S, et al. An introduction to variational methods for graphical models[J]. Machine Learning, 1999, 37(2): 183–233. doi: 10.1023/a:1007665907178 [4] LATOUCHE P and ROBIN S. Variational Bayes model averaging for graphon functions and motif frequencies inference in W-graph models[J]. Statistics and Computing, 2016, 26(6): 1173–1185. doi: 10.1007/s11222-015-9607-0 [5] WALTER J C and BARKEMA G T. An introduction to Monte Carlo methods[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2015, 418: 78–87. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2014.06.014 [6] 孙海英, 李锋, 商慧亮. 改进的变分自适应中值滤波算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2011, 33(7): 1743–1747. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.01295SUN Haiying, LI Feng, and SHANG Huiliang. Salt-and-pepper noise removal by variational method based on improved adaptive median filter[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2011, 33(7): 1743–1747. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.01295 [7] GUINDANI M and JOHNSON W O. More nonparametric Bayesian inference in applications[J]. Statistical Methods & Applications, 2018, 27(2): 239–251. doi: 10.1007/s10260-017-0399-6 [8] 王瑞, 芮国胜, 张洋. 基于变分贝叶斯推断的半盲信道估计[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2018, 50(5): 192–198. doi: 10.11918/j.issn.0367-6234.201708062WANG Rui, RUI Guosheng, and ZHANG Yang. Semi-blind channel estimation based on variational Bayesian inference[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2018, 50(5): 192–198. doi: 10.11918/j.issn.0367-6234.201708062 [9] DE CASTRO M and VIDAL I. Bayesian inference in measurement error models from objective priors for the bivariate normal distribution[J]. Statistical Papers, 2019, 60(4): 1059–1078. doi: 10.1007/s00362-016-0863-7 [10] GIANNIOTIS N, SCHNÖRR C, MOLKENTHIN C, et al. Approximate variational inference based on a finite sample of Gaussian latent variables[J]. Pattern Analysis and Applications, 2016, 19(2): 475–485. doi: 10.1007/s10044-015-0496-9 [11] SHEKARAMIZ M, MOON T K, and GUNTHER J H. Sparse Bayesian learning using variational Bayes inference based on a greedy criterion[C]. 2017 51st Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers, Pacific Grove, USA, 2017: 858–862. doi: 10.1109/ACSSC.2017.8335470. [12] KATAHIRA K, WATANABE K, and OKADA M. Deterministic annealing variant of variational Bayes method[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2008, 95(1): 012015. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/95/1/012015 [13] TABUSHI K and INOUE J. Improvement of EM algorithm by means of non-extensive statistical mechanics[C]. Neural Networks for Signal Processing XI: Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Signal Processing Society Workshop, North Falmouth, USA, 2001: 133–142. doi: 10.1109/NNSP.2001.943118. [14] SALIMANS T, KINGMA D P, and WELLING M. Markov Chain Monte Carlo and variational inference: Bridging the gap[C]. The 32nd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 2015: 1218–1226. doi: arxiv.org/pdf/1410.6460. [15] GHODHBANI E, KAANICHE M, and BENAZZA-BENYAHIA A. Close approximation of kullback–leibler divergence for sparse source retrieval[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2019, 26(5): 745–749. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2019.2907374 [16] HE Xingyu, TONG Ningning, and HU Xiaowei. Superresolution radar imaging based on fast inverse-free sparse Bayesian learning for multiple measurement vectors[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2018, 12(1): 015013. doi: 10.1117/1.JRS.12.015013 [17] LALAZISSIS G A, KÖNIG J, and RING P. New parametrization for the Lagrangian density of relativistic mean field theory[J]. Physical Review C, 1997, 55(1): 540–543. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevC.55.540 [18] FORTUNATO S. Community detection in graphs[J]. Physics Reports, 2010, 486(3/5): 75–174. doi: 10.1016/j.physrep.2009.11.002 [19] HUI Zhenyang, LI Dajun, JIN Shuanggen, et al. Automatic DTM extraction from airborne LiDAR based on expectation-maximization[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2019, 112: 43–55. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2018.10.051 [20] 胡磊, 周剑雄, 石志广, 等. 利用期望-最大化算法实现基于动态词典的压缩感知[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2012, 34(11): 2554–2560. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00347HU Lei, ZHOU Jianxiong, SHI Zhiguang, et al. An EM-based approach for compressed sensing using dynamic dictionaries[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2012, 34(11): 2554–2560. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00347 [21] LALAOUI M, EL AFIA A, and CHIHEB R. A self-tuned simulated annealing algorithm using hidden Markov model[J]. International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering, 2018, 8(1): 291–298. doi: 10.11591/ijece.v8i1.pp291-298 [22] HUANG Longbo and NEELY M J. Delay reduction via Lagrange multipliers in stochastic network optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2011, 56(4): 842–857. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2010.2067371 [23] 陈志敏, 田梦楚, 吴盘龙, 等. 基于蝙蝠算法的粒子滤波法研究[J]. 物理学报, 2017, 66(5): 050502. doi: 10.7498/aps.66.050502CHEN Zhimin, TIAN Mengchu, WU Panlong, et al. Intelligent particle filter based on bat algorithm[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2017, 66(5): 050502. doi: 10.7498/aps.66.050502 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
