Error Analysis in SAR Imaging Due to Fluctuation of Atmospheric Refractive Index
-
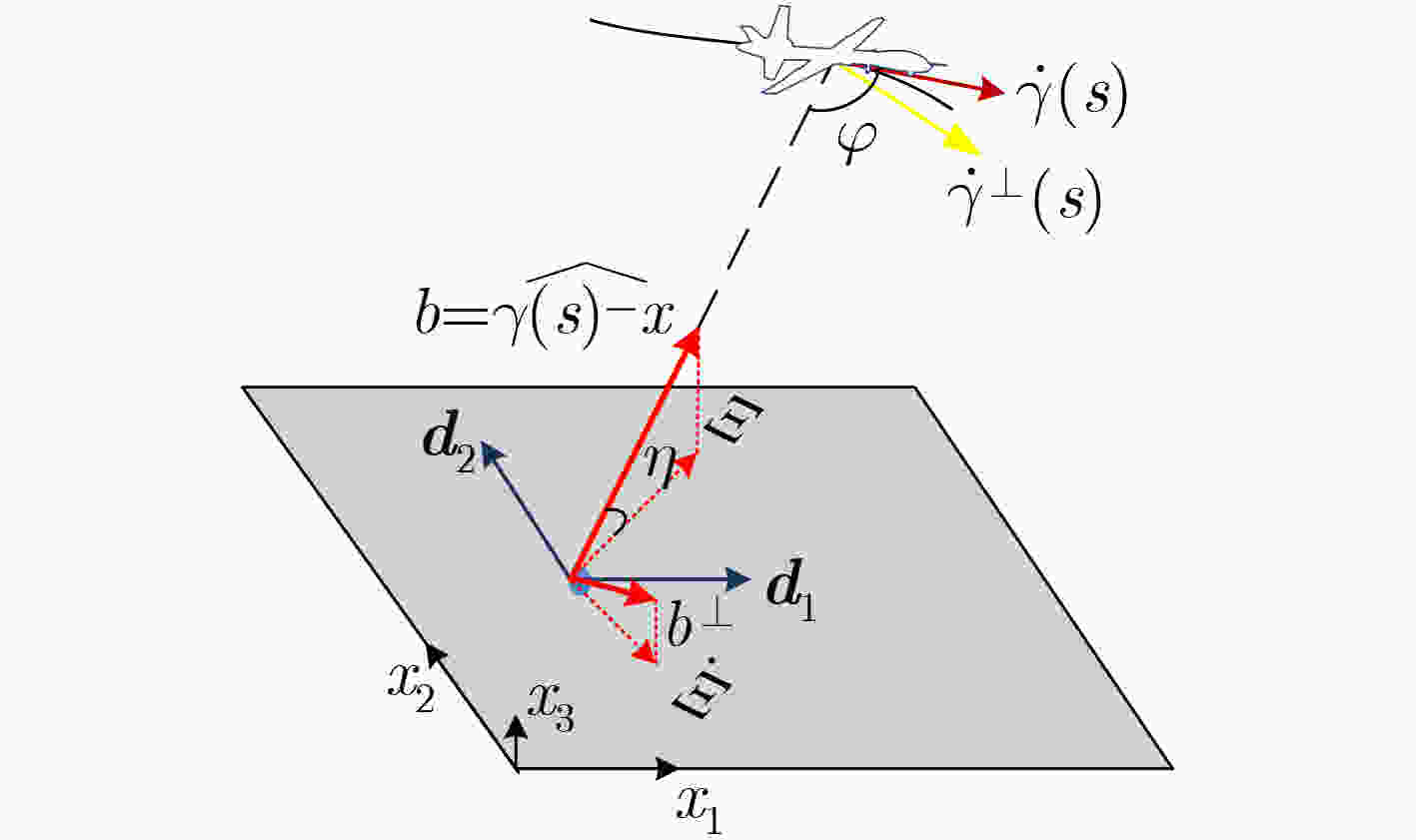
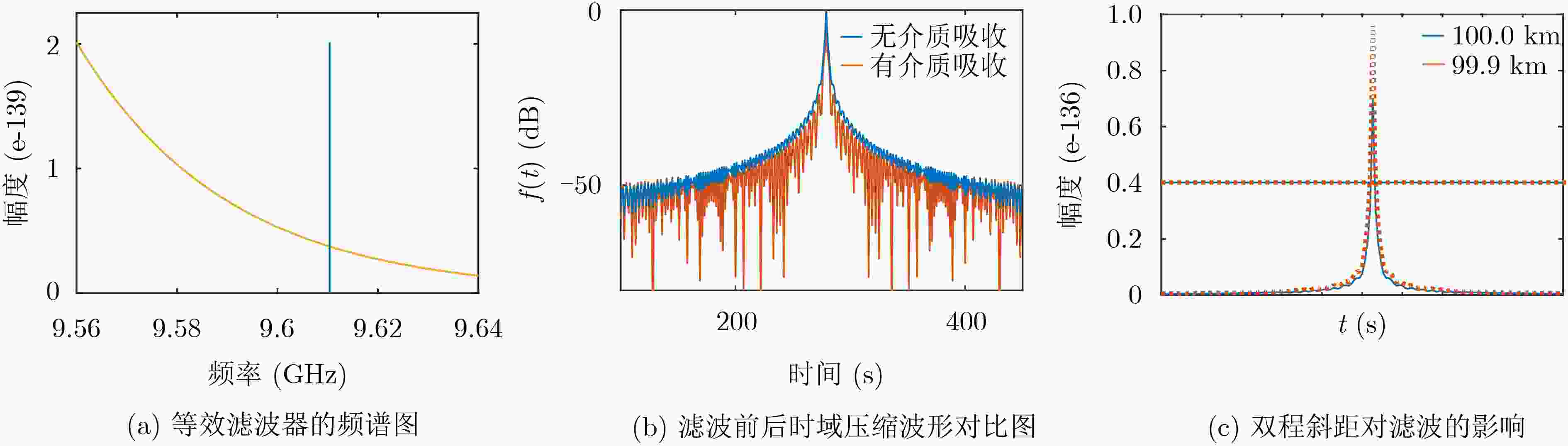
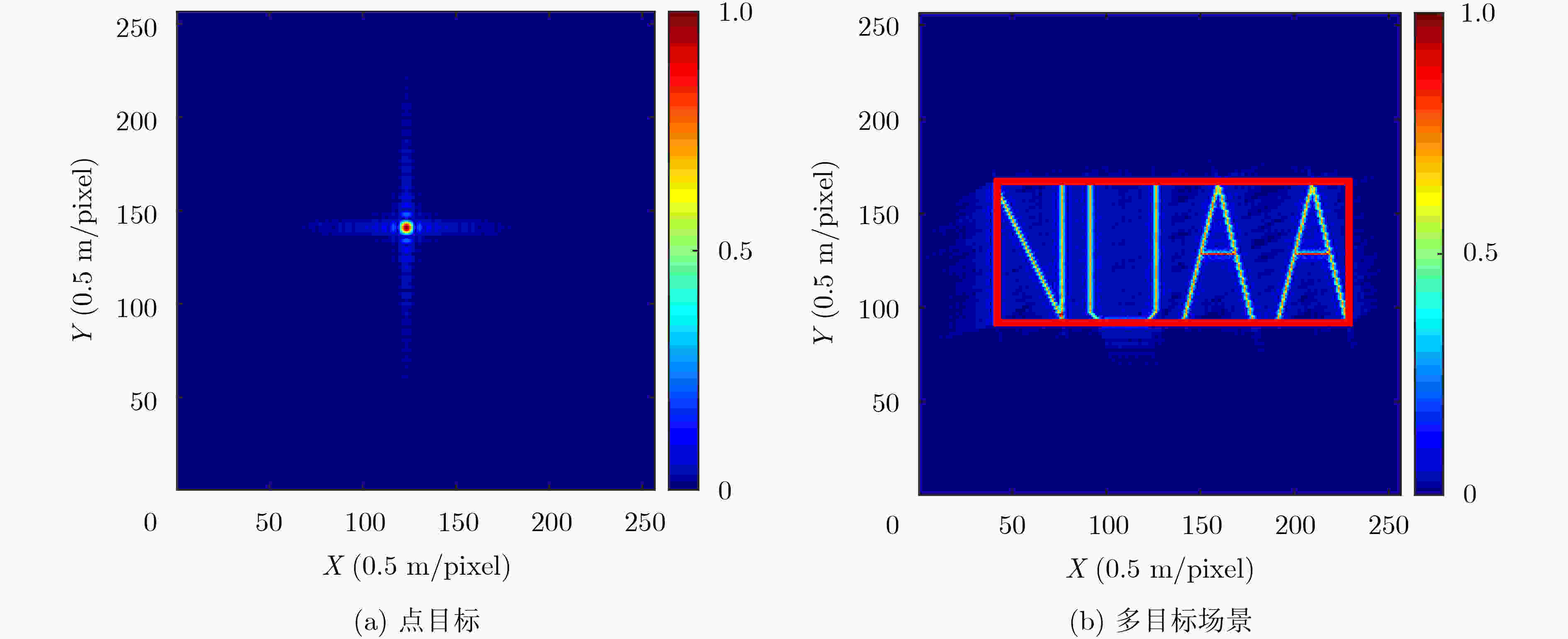
摘要: 合成孔径雷达(SAR)成像中通常默认大气折射率为1,即电磁(EM)波速率等于自由空间光速且忽略大气吸收特性,但实际存在的吸收会减弱入射功率,电磁波速率的变化会引起相位误差,从而影响图像重建。该文定量分析电磁波速率波动和大气吸收对雷达图像的影响,理论推导得出大气吸收会导致振幅误差,表现为散射点在图像中的重建幅度误差;电磁波速率波动会导致相位误差,表现为散射点在图像中的重建位置误差。仿真实验验证了误差分析的正确性。该分析进一步完备了SAR成像误差分析,有助于SAR图像正确解译。Abstract: Generally, the refractive index of atmosphere is simply 1 by default in Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) imaging, that is, the ElectroMagnetic (EM) wave velocity is equal to the speed of light in free-space and the atmospheric absorption is ignored. However, the actual absorption may weaken the incident power and variations in the speed of EM waves may cause phase error, thus affecting image reconstruction. In this paper, the influence of wave velocity fluctuation and atmospheric absorption in SAR imagery is analyzed quantitatively. It is theoretically deduced that the atmospheric absorption will lead to amplitude error, which is shown as strength error of the scatterer in the reconstructed image; EM velocity fluctuation will lead to phase error, which is shown as positioning error of the scatterer in the reconstructed image. The correctness of error analysis is verified by simulation experiments. The work in this paper completes further the SAR imaging error analysis, which is beneficial to SAR image interpretation.
-
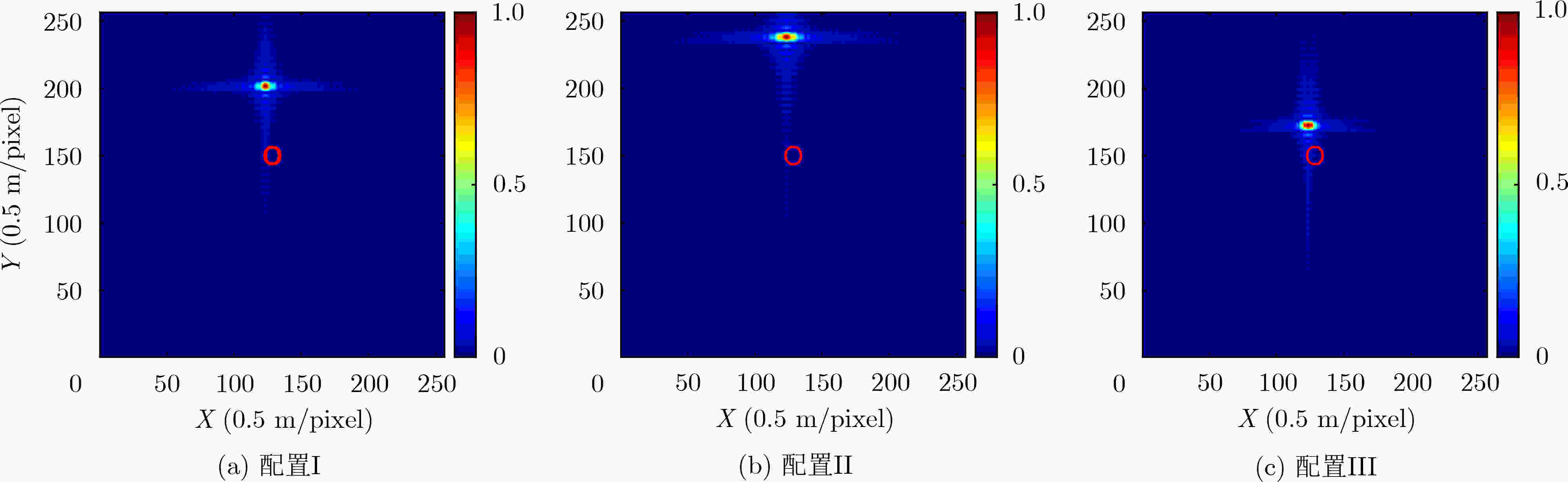
表 1 电磁波速率误差仿真参数设置
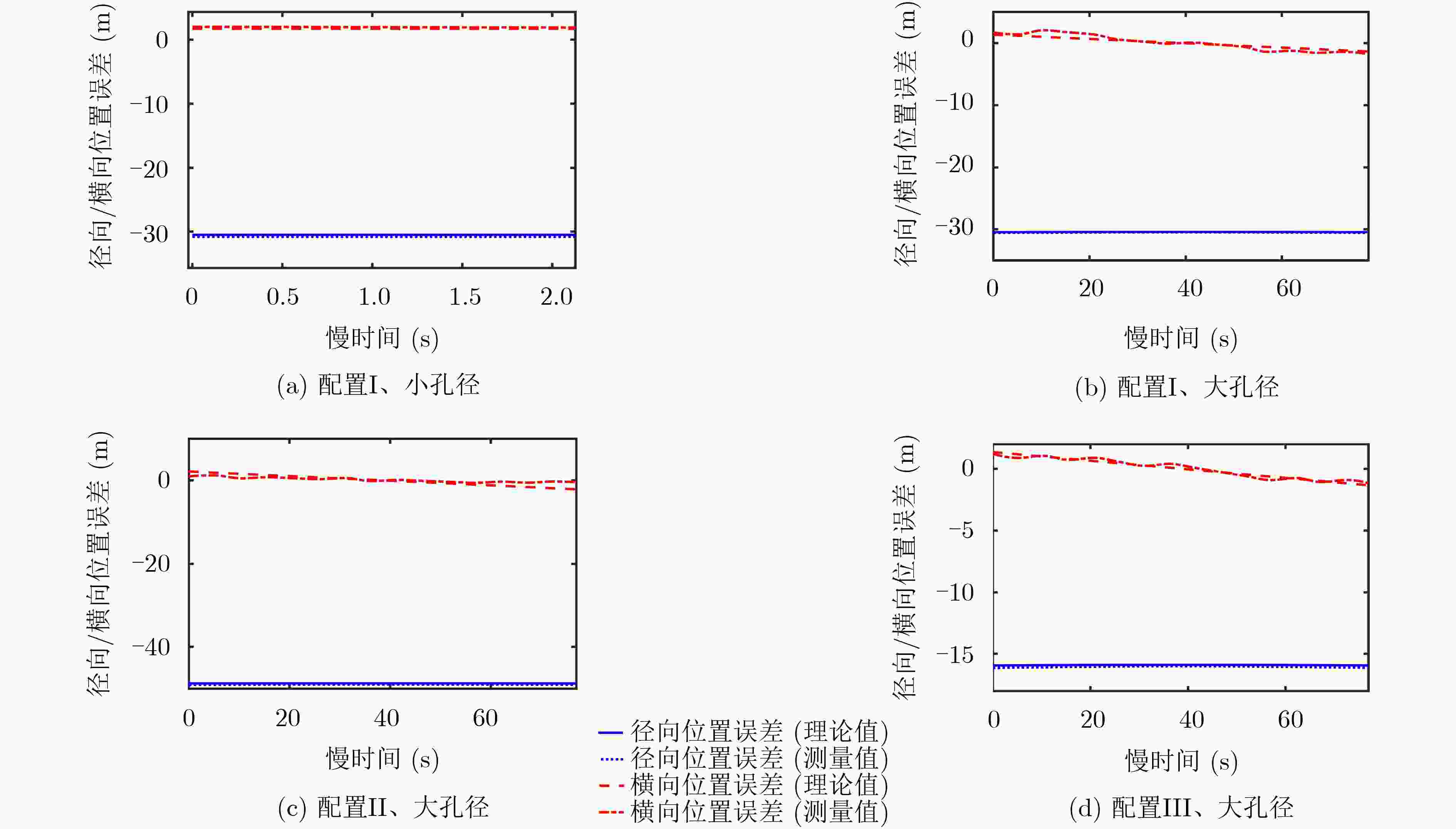
配置 天线到目标距离${R_c}$(km) 大气折射率$n$ 电磁波速率误差$\varDelta {\rm{c}}$(m/s) I 60 $1 + 5 \times 1{0^{ - 4}}$ $1.5 \times 1{0^5}$ II 60 $1 + 8 \times 1{0^{ - 4}}$ $2.4 \times 1{0^5}$ III 30 $1 + 5 \times 1{0^{ - 4}}$ $1.5 \times 1{0^5}$ -
PORCELLO L J. Turbulence-induced phase errors in synthetic-aperture radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1970, AES-6(5): 636–644. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1970.310064 DANKLMAYER A, DORING B J, SCHWERDT M, et al. Assessment of atmospheric propagation effects in SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(10): 3507–3518. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2022271 DANKLMAYER A. On the influence of the atmosphere on wideband space-borne SAR signal propagation and imaging[C]. The IEEE 5th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR), Singapore, 2015: 470–473. doi: 10.1109/APSAR.2015.7306251. DICKEY F M, DELAURENTIS J M, and DOERRY A W. A SAR imaging model for large-scale atmospheric inhomogeneities[C]. SPIE 5410, Radar Sensor Technology VIII and Passive Millimeter-Wave Imaging Technology VII, Orlando, United States, 2004: 1–9. doi: 10.1117/12.541560. MUSCHINSKI A, DICKEY F M, and DOERRY A W. Possible effects of clear-air refractive-index perturbations on SAR images[C]. SPIE 5788, Radar Sensor Technology IX, Orlando, United States, 2005: 25–33. doi: 10.1117/12.605651. SHAGAM R N, DICKEY F M, and DOERRY A W. Geometrical optics analysis of clear-air refractive-index perturbations on SAR images[C]. SPIE 6210, Radar Sensor Technology X, Orlando (Kissimmee), United States, 2006: 1–12. doi: 10.1117/12.668326. DICKEY F M, DOERRY A W, and ROMERO L A. Degrading effects of the lower atmosphere on long-range airborne synthetic aperture radar imaging[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2007, 1(5): 329–339. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn:20060134 LAWRENCE M, HANSEN C, DESHMUKH S, et al. Characterization of the effects of atmospheric lensing in SAR images[C]. SPIE 7308, Radar Sensor Technology XIII, Orlando, United States, 2009. doi: 10.1117/12.819027. 寇蕾蕾, 向茂生. 大气折射率时间变化对地球同步轨道圆迹SAR聚焦性能的影响[J]. 测绘学报, 2014, 43(9): 917–923. doi: 10.13485/j.cnki.11-2089.2014.0124KOU Leilei and XIANG Maosheng. Effect of temporal variation of atmospheric refraction on geosynchronous circular SAR focusing performance[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2014, 43(9): 917–923. doi: 10.13485/j.cnki.11-2089.2014.0124 YAZICI B and WANG Ling. Analysis of artifacts in SAR imagery due to fluctuation in refractive index[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2019, 5(3): 450–464. doi: 10.1109/TCI.2019.2895203 NOLAN C J and CHENEY M. Synthetic aperture inversion[J]. Inverse Problems, 2002, 18(1): 221–235. doi: 10.1088/0266-5611/18/1/315 NOLAN C J and CHENEY M. Synthetic aperture inversion for arbitrary flight paths and nonflat topography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2003, 12(9): 1035–1043. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.814243 CHENEY M. Synthetic-aperture assessment of a dispersive surface[J]. International Journal of Imaging Systems and Technology, 2004, 14(1): 28–34. doi: 10.1002/ima.20004 YARMAN C E, YAZICI B, and CHENEY M. Bistatic synthetic aperture radar imaging for arbitrary flight trajectories[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2008, 17(1): 84–93. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2007.911812 YAZICI B, CHENEY M, and YARMAN C E. Synthetic-aperture inversion in the presence of noise and clutter[J]. Inverse Problems, 2006, 22(5): 1705–1729. doi: 10.1088/0266-5611/22/5/011 YANIK H C, LI Zhengmin, and YAZICI B. Computationally efficient FBP-type direct segmentation of synthetic aperture radar images[C]. SPIE 8051, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XVIII, Orlando, United States, 2014: 361–372. doi: 10.1117/12.883762. GRIGIS A and SJÖSTRAND J. Microlocal Analysis for Differential Operators: An Introduction[M]. Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge University Press, 1994. BLEISTEIN N and HANDELSMAN R A. Asymptotic Expansions of Integrals[M]. New York: Dover, 1986: 113–140. GUILLEMIN V and STERNBERG S. Geometric Asymptotics[M]. Providence, RI: American Mathematical Society, 1977: 211–286. 闫贺, 王珏, 黄佳, 等. 基于二维速度搜索的星载SAR运动目标聚焦算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(6): 1287–1293. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180663YAN He, WANG Jue, HUANG Jia, et al. Moving-targets detection algorithm for spaceborne SAR system based on two-dimensional velocity search method[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(6): 1287–1293. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180663 王沛, 徐伟, 李宁, 等. 星载大斜视聚束SAR变PRI成像技术研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(10): 2470–2477. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180049WANG Pei, XU Wei, LI Ning, et al. Investigation on PRI variation for high squint spaceborn spotlight SAR[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(10): 2470–2477. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180049 -





 下载:
下载:
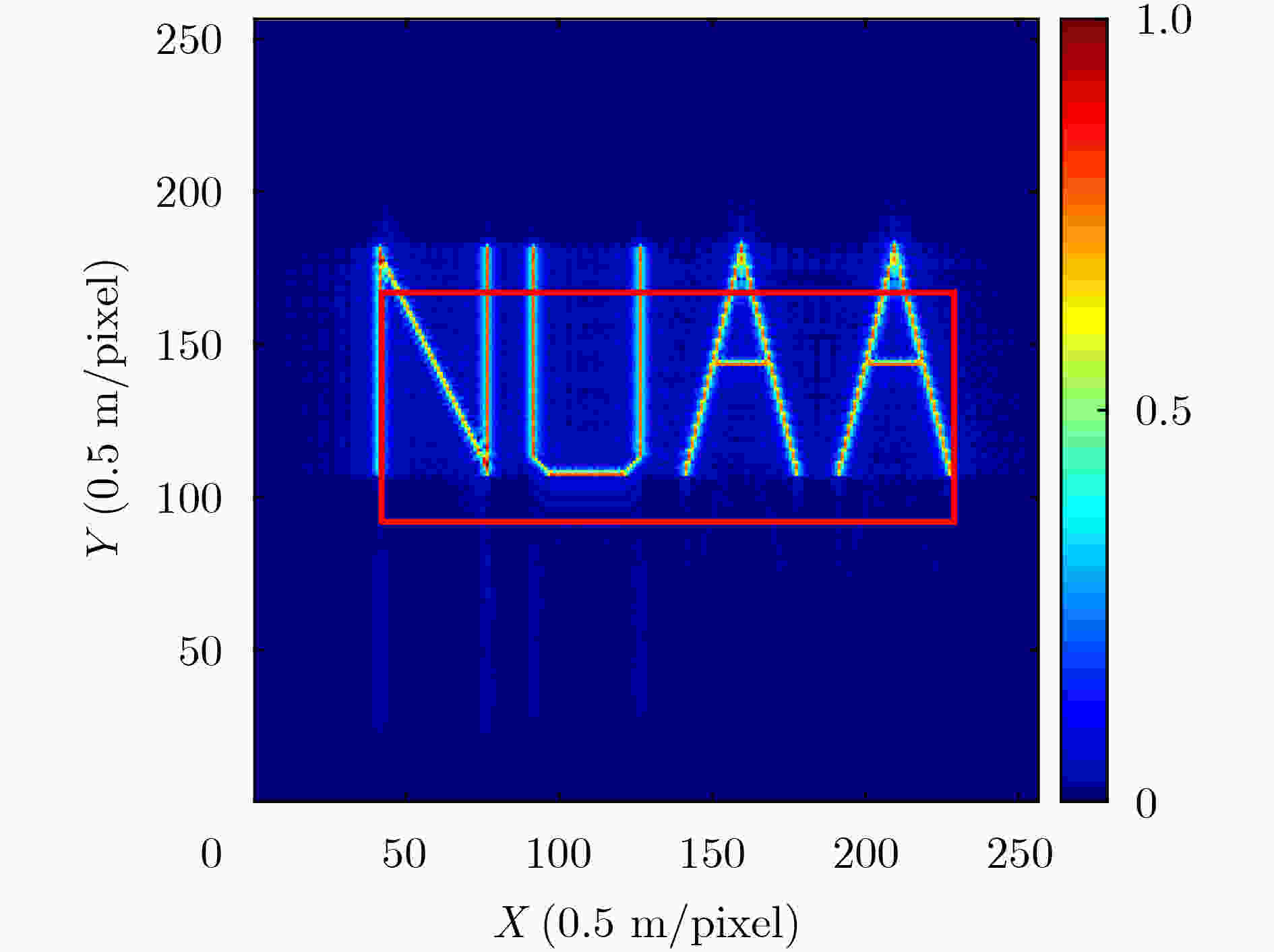
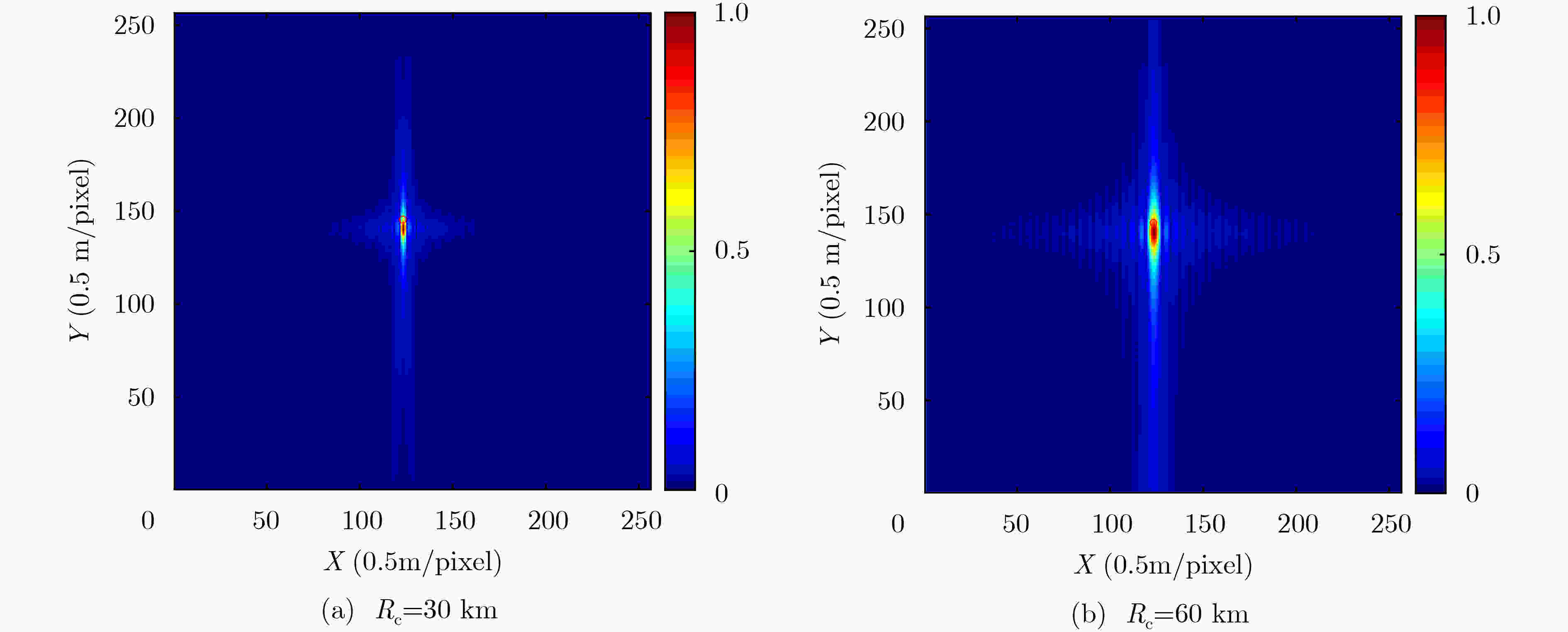
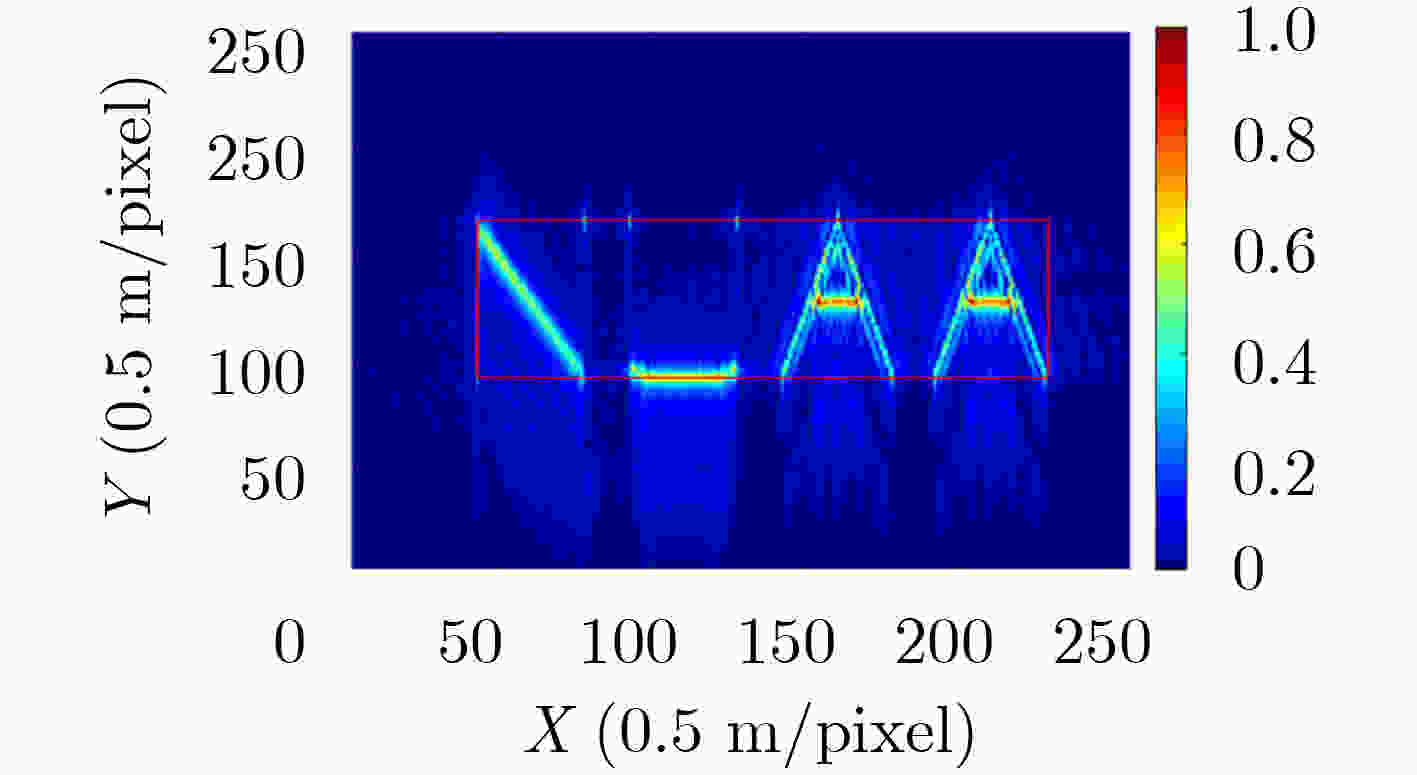


 下载:
下载:
