Image Saliency Detection Based on Background Constraint of Low Rank and Multi-cue Propagation
-
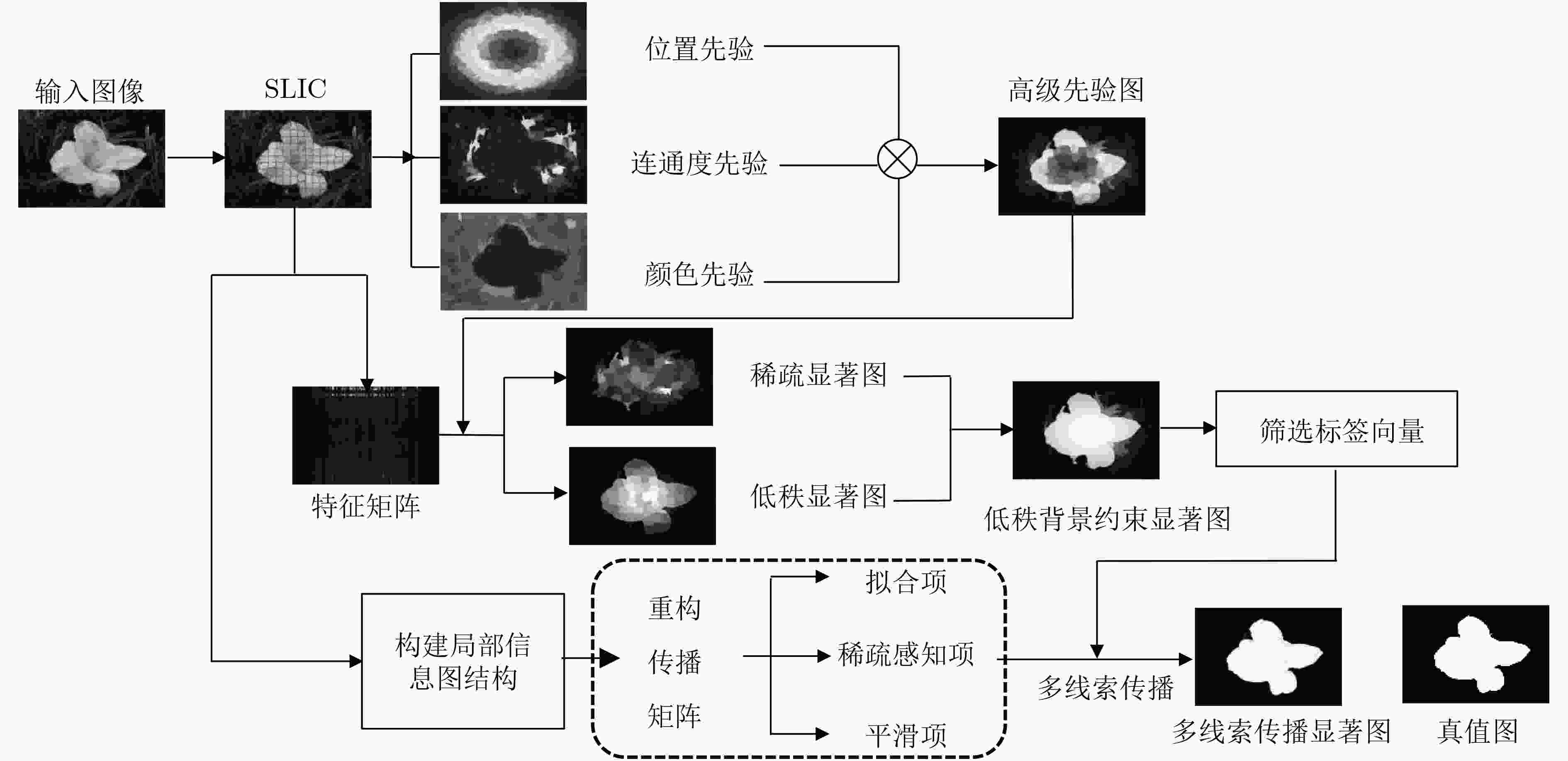
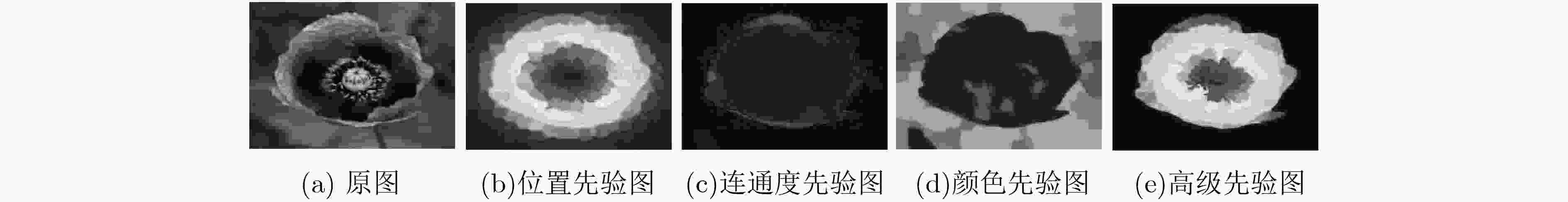
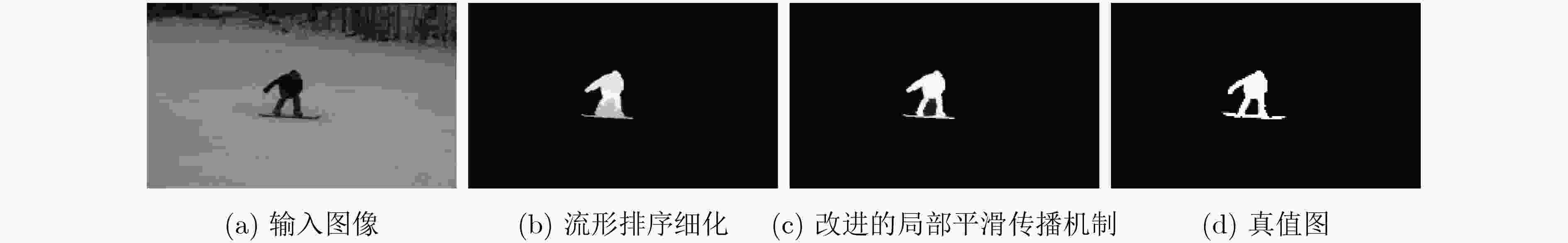
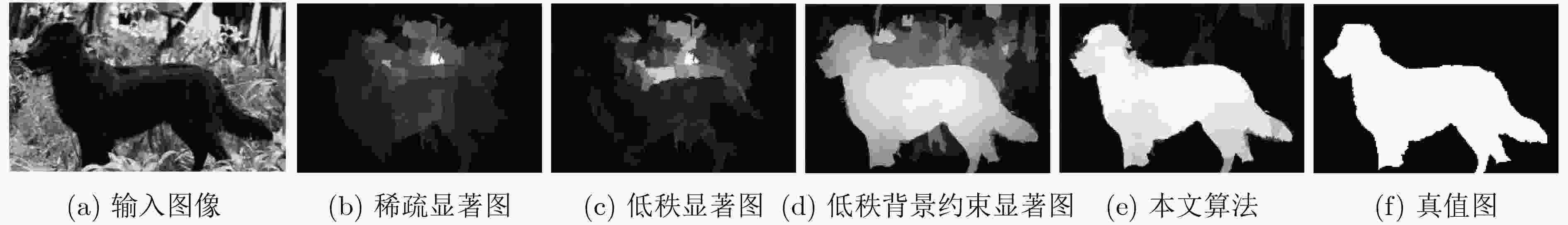
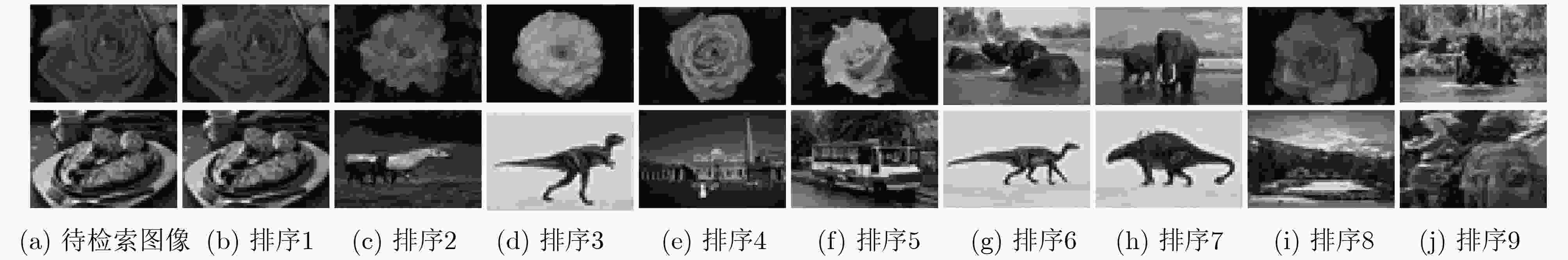
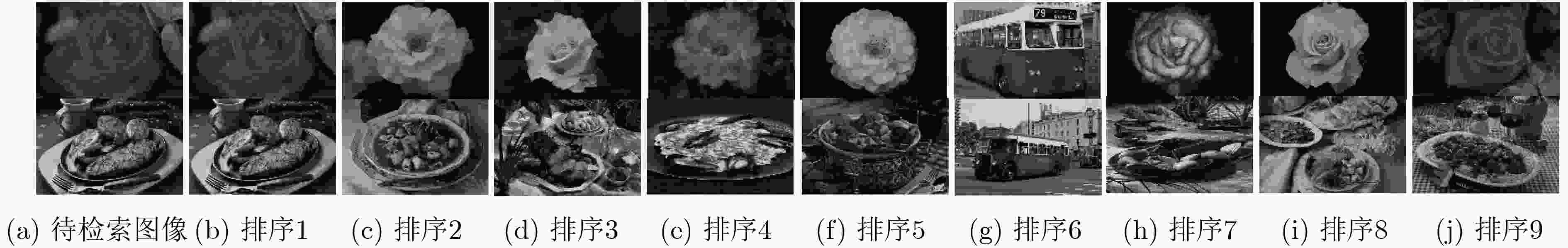
摘要: 针对当前基于流形排序的显著性检测算法缺乏子空间信息的挖掘和节点间传播不准确的问题,该文提出一种基于低秩背景约束与多线索传播的图像显著性检测算法。融合颜色、位置和边界连通度等初级视觉先验形成背景高级先验,约束图像特征矩阵的分解,强化低秩矩阵与稀疏矩阵的差异,充分描述子空间结构信息,从而有效地将前景与背景分离;引入稀疏感知和局部平滑等线索改进传播矩阵的构建,增强颜色特征出现概率低的节点的传播能力,加强局部区域内节点的关联性,准确凸显节点的属性,得到紧密且连续的显著区域。在3个基准数据集上的实验结果与图像检索领域的应用证明了该文算法的有效性和鲁棒性。Abstract: Considering the lack of subspace information digging and inaccurate propagation between nodes in existing saliency detection algorithm based on manifold ranking, an image saliency detection algorithm based on background constraint of low rank and multi-cue propagation is proposed. Primary visual priors such as color, location and boundary connectivity prior are fused to form a background high-level prior, which restrains the low rank decomposition of feature matrix and strengths the difference between low rank matrix and spares matrix, describes structural information of subspace fully to separate foreground and background efficiently. Cues of rareness perception and local smoothing are introduced for improving the reconstruction of propagation matrix, which improves the node’s propagation capacity that has low probability of color feature occurrence, enhances the relevance of local region, strengthens the properties of nodes accurately to obtain the compact and continuous salient regions. The experimental results on three benchmark datasets and the application to image retrieval demonstrate the efficiency and robustness of the proposed algorithm.
-
表 1 不同算法运行时间对比
方法 GS GBMR MPD TLLT WLRR 本文算法 时间(s) 0.24 0.33 3.29 2.73 1.98 2.18 表 2 两种图像检索方法的平均运行时间(s)
类别 基于整体图像的检索运行时间 基于显著图的检索运行时间 花朵 167.59 92.68 美食 140.15 83.42 -
[1] DENG Cheng, YANG Xu, NIE Feiping, et al. Saliency detection via a multiple self-weighted graph-based manifold ranking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2020, 22(4): 885–896. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2019.2934833 [2] JAEMSIRI J, TITIJAROONROJ T, and RUNGRATTANAUBOL J. Modified scale-space analysis in frequency domain based on adaptive multiscale Gaussian filter for saliency detection[C]. The 2019 16th International Joint Conference on Computer Science and Software Engineering, Chonburi, Thailand, 2019: 218–223. doi: 10.1109/JCSSE.2019.8864211. [3] WANG Chengjia, DONG Shizhou, ZHAO Xiaofeng, et al. SaliencyGAN: Deep learning semisupervised salient object detection in the fog of IoT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(4): 2667–2676. doi: 10.1109/TII.2019.2945362 [4] SRIVASTAVA G and SRIVASTAVA R. An efficient modification of generalized gradient vector flow using directional contrast for salient object detection and intelligent scene analysis[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2020, 79(19): 13599–13619. doi: 10.1007/s11042-020-08609-y [5] HUO Shuwei, ZHOU Yuan, XIANG Wei, et al. Semisupervised learning based on a novel iterative optimization model for saliency detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2019, 30(1): 225–241. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2809702 [6] 李炜, 李全龙, 刘政怡. 基于加权的K近邻线性混合显著性目标检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(10): 2442–2449. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190093LI Wei, LI Quanlong, LIU Zhengyi, et al. Salient object detection using weighted k-nearest neighbor linear blending[J]. Journal of Electronics and Information Technology, 2019, 41(10): 2442–2449. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190093 [7] WEI Yichen, WEN Fang, ZHU Wangjiang, et al. Geodesic saliency using background priors[C]. The 12th European Conference on Computer Vision, Florence, Italy, 2012: 29–42. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-33712-3_3. [8] TANG Chang, WANG Pichao, ZHANG Changqing, et al. Salient object detection via weighted low rank matrix recovery[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2017, 24(4): 490–494. doi: 10.1109/lsp.2016.2620162 [9] 张文明, 姚振飞, 高雅昆, 等. 一种平衡准确性以及高效性的显著性目标检测深度卷积网络模型[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(5): 1201–1208. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190229ZHANG Wenming, YAO Zhenfei, GAO Yakun, et al. A deep convolutional network for saliency object detection with balanced accuracy and high efficiency[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(5): 1201–1208. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190229 [10] YANG Chuan, ZHANG Lihe, LU Huchuan, et al. Saliency detection via graph-based manifold ranking[C]. 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, USA, 2013: 3166–3173. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2013.407. [11] FU Keren, GU I Y H, GONG Chen, et al. Robust manifold-preserving diffusion-based saliency detection by adaptive weight construction[J]. Neurocomputing, 2016, 175: 336–347. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.10.066 [12] TAO Dapeng, CHENG Jun, SONG Mingli, et al. Manifold ranking-based matrix factorization for saliency detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2016, 27(6): 1122–1134. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2015.2461554 [13] GONG Chen, TAO Dacheng, LIU Wei, et al. Saliency propagation from simple to difficult[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 2531–2539. doi: 10.1109/cvpr.2015.7298868. [14] ACHANTA R, SHAJI A, SMITH K, et al. SLIC superpixels compared to state-of-the-art superpixel methods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(11): 2274–2282. doi: 10.1109/tpami.2012.120 [15] ZHANG Jun, WANG Meng, ZHANG Shengping, et al. Spatiochromatic context modeling for color saliency analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2016, 27(6): 1177–1189. doi: 10.1109/tnnls.2015.2464316 -





 下载:
下载:
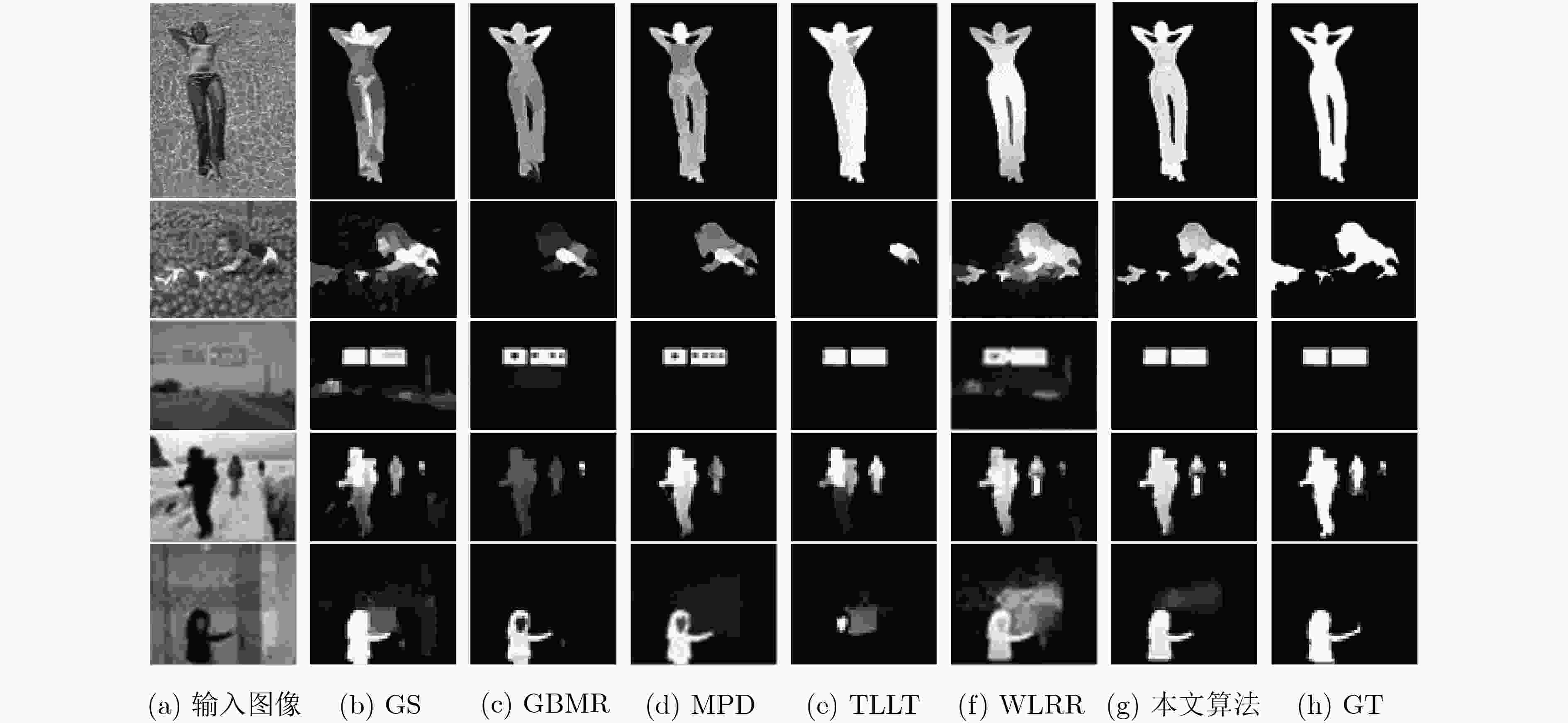
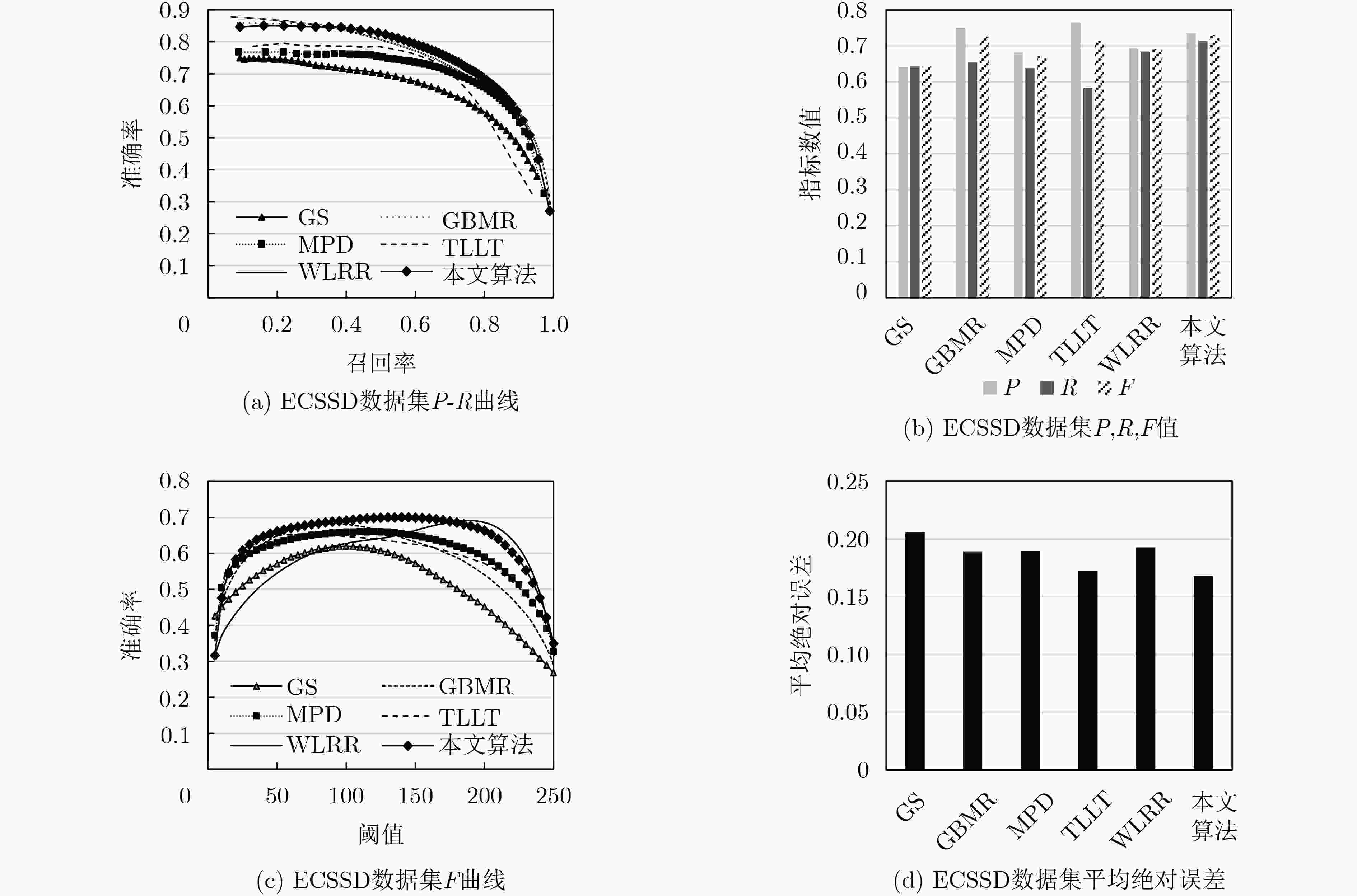
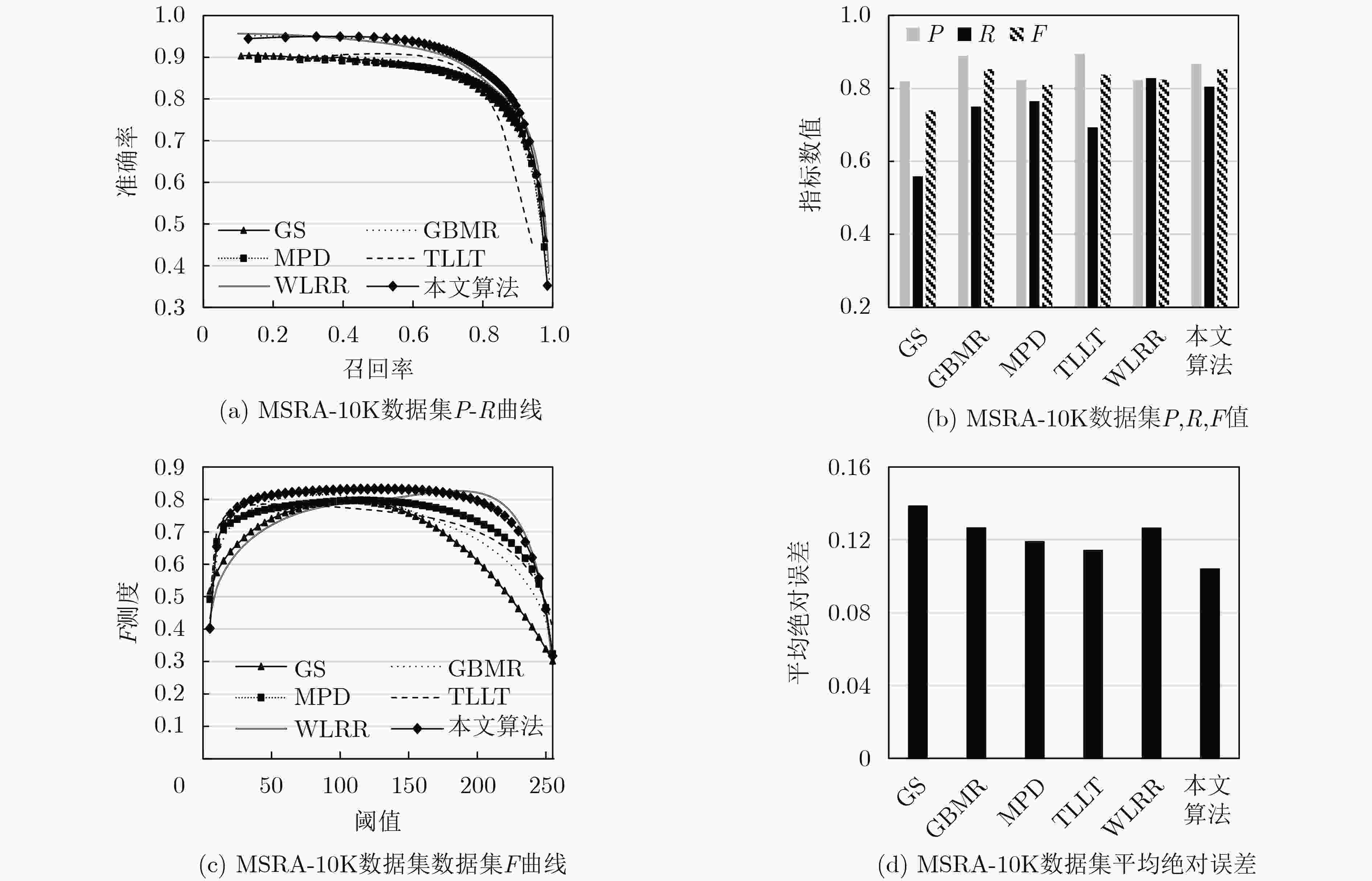

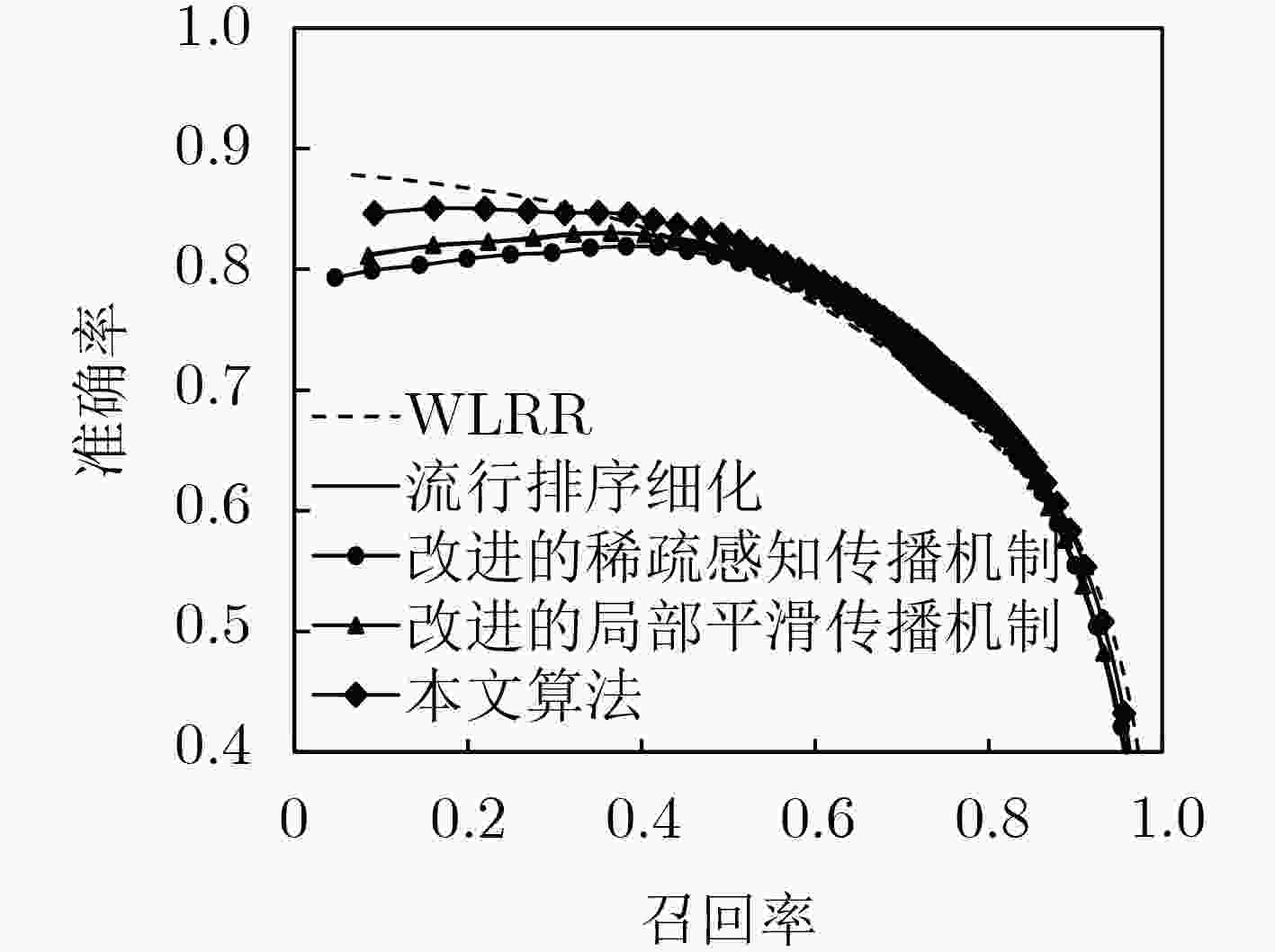


 下载:
下载:
