A Survey for Cloud Data Security
-
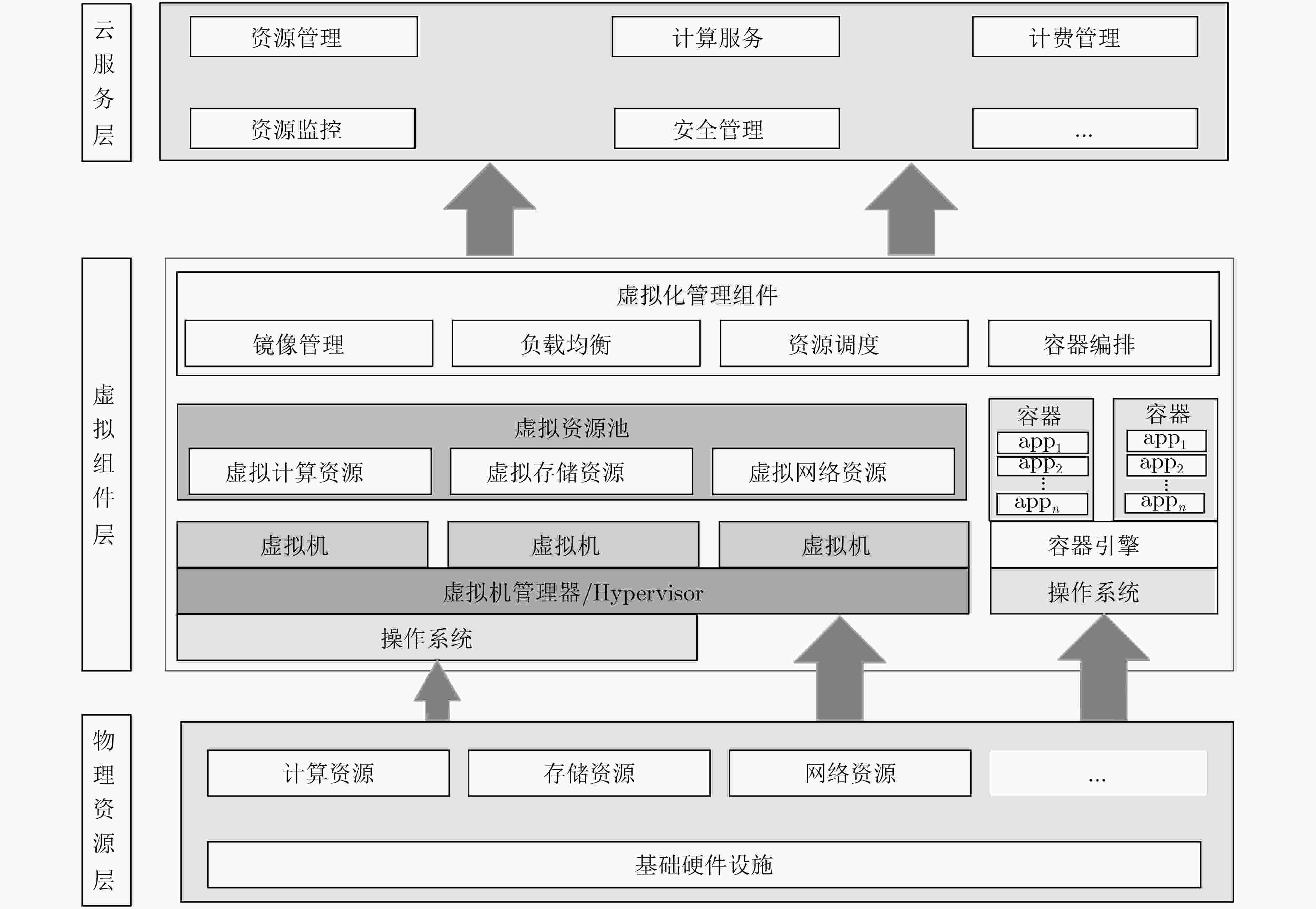
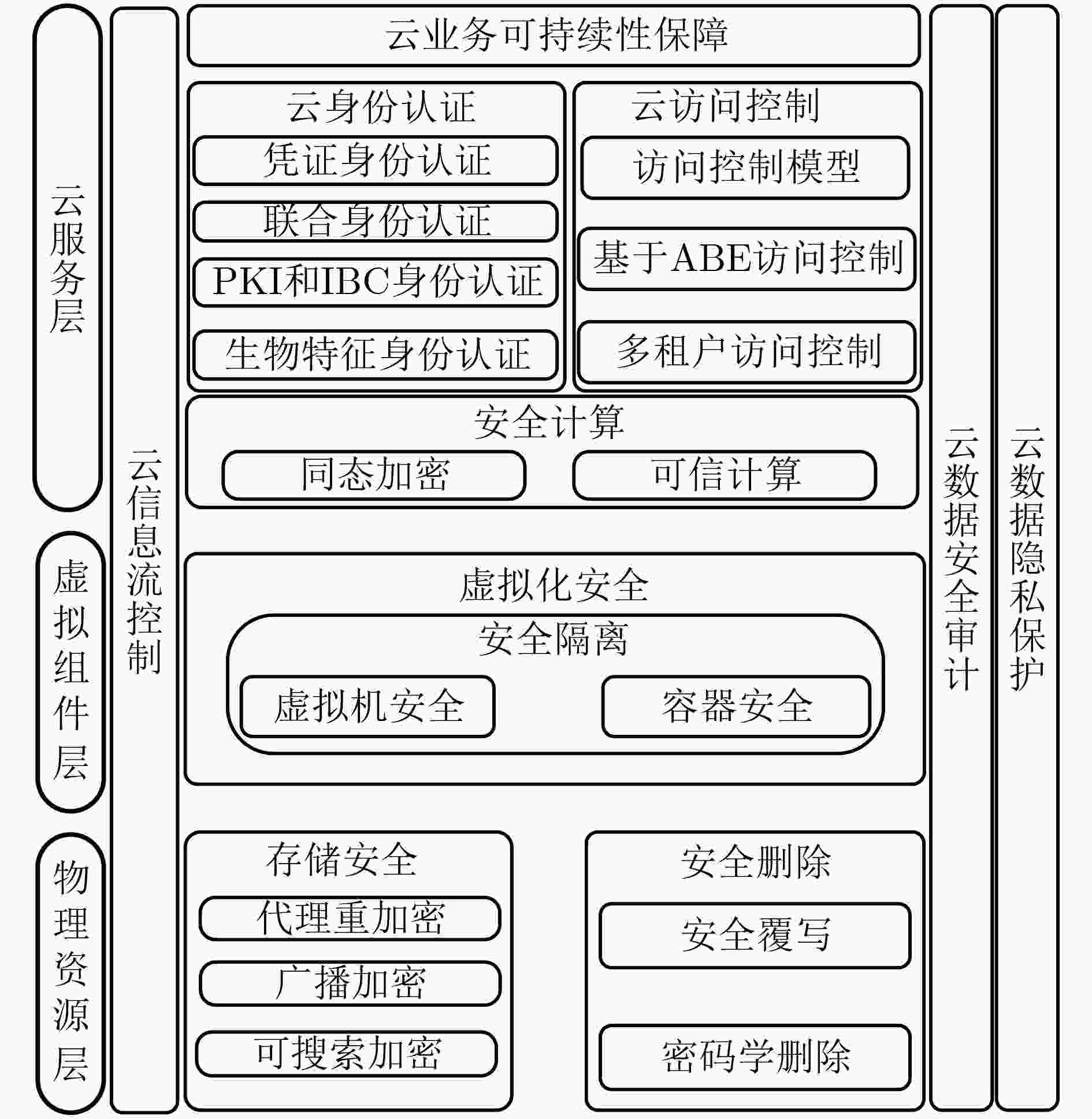
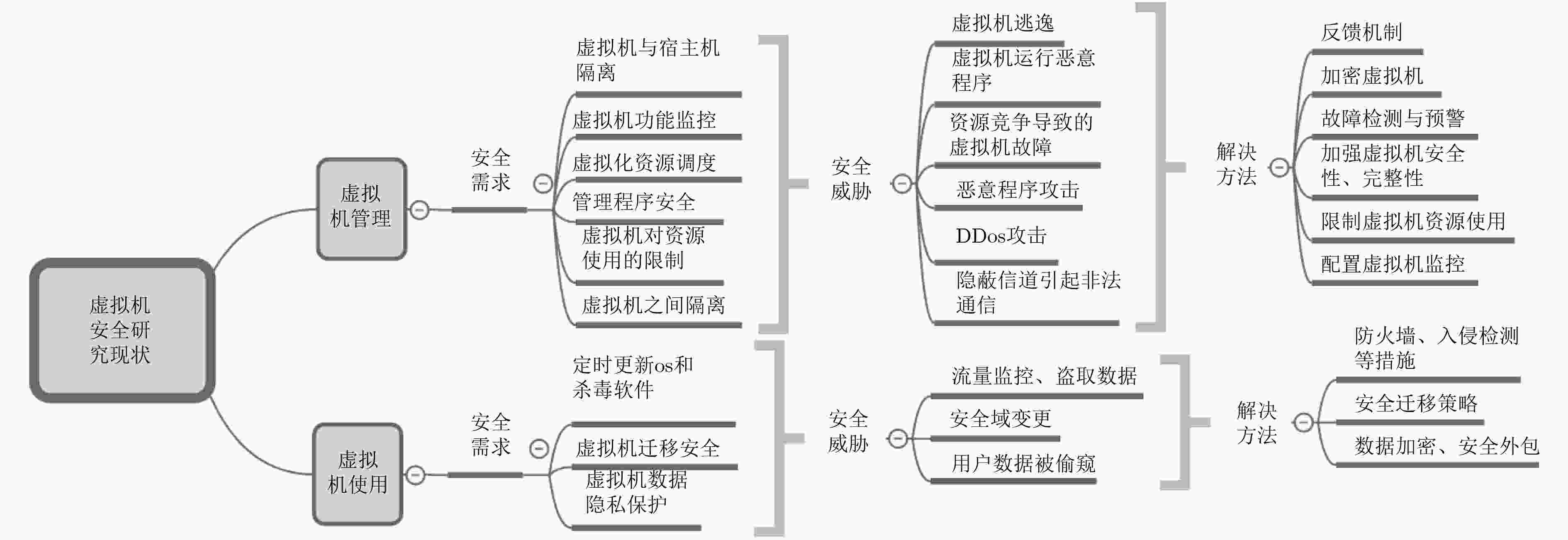
摘要: 云数据安全问题是制约云计算发展的重要因素之一。该文综述了云数据安全方面的研究进展,将云数据安全所涉及的云身份认证、云访问控制、云数据安全计算、虚拟化安全技术、云数据存储安全、云数据安全删除、云信息流控制、云数据安全审计、云数据隐私保护及云业务可持续性保障10方面相关研究工作纳入到物理资源层、虚拟组件层及云服务层所构成的云架构中进行总结和分析;并给出了相关技术的未来发展趋势。Abstract: The security of cloud data is one of the most important factors to obstruct the development of cloud computing. Therefore, on the basis of proposed three-tiers cloud architecture that consists of physical resources layer, virtual component layer, and cloud service layer, this paper makes a detail survey on existing works that focus on the security of cloud data, which involves in cloud identify authentication, cloud access control, cloud data secure computing, virtualization, cloud data security storage, cloud data secure deletion, information flow control, cloud data secure auditing, cloud data privacy preserving, and cloud business continuity, respectively. Finally, research trends in the field of cloud data security are presented.
-
表 1 云身份认证各类方法比较
技术 机制/方法 优点 缺点 适用场景 ACCESS Key 安全凭证 可靠 灵活性较差 安全需求高场景 OpenID 单点登录 方便 安全性较低 减轻租户负担 OpenID Connect 单点登录 互操作 安全性较低 减轻租户负担 OAuth 单点登录 方便 安全性较低 统一授权场景 基于SAML 单点登录 互操作 安全性较低 统一身份证认证 基于PKI&IBC PKI&IBC 跨云 复杂性较高 跨云的服务访问 基于生物特征 虹膜/静脉等 灵活 易攻击/复杂性高 小规模高效认证 表 2 云访问控制技术方法比较
表 3 云数据安全计算方法比较
表 4 基于代理重加密方法比较
表 5 可搜索加密相关方法比较
表 6 云数据审计隐私保护方法比较
技术 应用场景 可拓展性 同态线性认证器&随机伪装 第三方审计,分批的远程数据审计 较好 同态消息验证码 共享数据的审计 一般 线性映射 分块数据集跨云数据审计 较好 同态可验证群/环签名 共享数据分块第三方审计 较差 表 7 云数据隐私保护方法比较
隐私对象 方法 优点 缺点 访问模式 PIR 信息论PIR 通信开销低 计算开销高 可计算PIR 节省带宽,防止合谋 计算开销高 ORAM 局部ORAM 系统开销较高 清洗部分遗漏 多轮ORAM 系统开销可承受 效率较低 并行ORAM 系统开销低 系统性能要求高 单轮ORAM 系统开销较高 效率低 查询隐私 索引隐私 – – 关键字隐私和限门不可链接 非确定性限门 隐私性强 计算开销较高 用户身份隐私 环/群签名 环/群签名 攻击难度大/强隐私 可拓展性差 表 8 常见备份技术之间区别
技术模型 同步时间 恢复时间 备份特点 容错支持 热备份 几秒 几秒或几分钟 物理镜像 很高 改进的热备份 几分钟 约1 h 虚拟镜像 高 暖备份 几小时内 1~24 h 限制的物理镜像 一般 冷备份 几天内 超过24 h 从站点备份 低 -
[1] SAKIMURA N, NRI, BRADLEY J, et al. OpenID Authentication 2.0[OL]. https://openid.net/specs/openid-authentication-2_0-11.html, 2007. [2] SAKIMURA N, NRI, BRADLEY J, et al. OpenID Connect Core 1.0[OL]. https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-core-1_0.html#toc. 2014, 2014. [3] JIANG Qi, MA Jianfeng, and WEI Fushan. On the security of a privacy-aware authentication scheme for distributed mobile cloud computing services[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2018, 12(2): 2039–2042. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2016.2574719 [4] SERVOS D and OSBORN S L. Current research and open problems in attribute-based access control[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2017, 49(4): 65. doi: 10.1145/3007204 [5] LI Jiguo, YAO Wei, ZHANG Yichen, et al. Flexible and fine-grained attribute-based data storage in cloud computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, 2017, 10(5): 785–796. doi: 10.1109/TSC.2016.2520932 [6] ALAM Q, MALIK S U R, AKHUNZADA A, et al. A Cross Tenant Access Control (CTAC) model for cloud computing: Formal specification and verification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2017, 12(6): 1259–1268. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2016.2646639 [7] ALMUTAIRI A, SARFRAZ M I, and GHAFOOR A. Risk-aware management of virtual resources in access controlled service-oriented cloud datacenters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cloud Computing, 2018, 6(1): 168–181. doi: 10.1109/TCC.2015.2453981 [8] ACAR A, AKSU H, ULUAGAC A S, et al. A survey on homomorphic encryption schemes: Theory and Implementation[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2018, 51(4): 79. doi: 10.1145/3214303 [9] GENTRY C. Fully homomorphic encryption using ideal lattices[C]. The 41st Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, Bethesda, USA, 2009: 169–178. doi: 10.1145/1536414.1536440. [10] POTEY M M, DHOTE C A, and SHARMA D H. Homomorphic encryption for security of cloud data[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2016, 79: 175–181. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2016.03.023 [11] SHEN Changxiang. Constructing cloud security with trusted computing[J]. China Economic & Trade Herald, 2017(16): 56–57. [12] CONTRACTOR D and PATEL D. Accountability in cloud computing by means of chain of trust[J]. International Journal of Network Security, 2017, 19(2): 251–259. doi: 10.6633/IJNS.201703.19(2).10 [13] 拱长青, 肖芸, 李梦飞, 等. 云计算安全研究综述[J]. 沈阳航空航天大学学报, 2017, 34(4): 1–17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1248.2017.04.001GONG Changqing, XIAO Yun, LI Mengfei, et al. Summary of cloud computing security research[J]. Journal of Shenyang Aerospace University, 2017, 34(4): 1–17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1248.2017.04.001 [14] SIERRA-ARRIAGA F, BRANCO R, and LEE B. Security issues and challenges for virtualization technologies[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2020, 53(2): 45. doi: 10.1145/3382190 [15] KUMAR N, AUJLA G S, GARG S, et al. Renewable energy-based multi-indexed job classification and container management scheme for sustainability of cloud data centers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2019, 15(5): 2947–2957. doi: 10.1109/TII.2018.2800693 [16] AIKAT J, AKELLA A, CHASE J S, et al. Rethinking security in the era of cloud computing[J]. IEEE Security & Privacy, 2017, 15(3): 60–69. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2017.80 [17] LIANG Xiaohui, CAO Zhenfu, LIN Huang, et al. Attribute based proxy re-encryption with delegating capabilities[C]. The 4th International Symposium on Information, Computer, and Communications Security, Sydney, Australia, 2009: 276–286. doi: 10.1145/1533057.1533094. [18] LUO Song, HU Jianbin, and CHEN Zhong. Ciphertext policy attribute-based proxy re-encryption[C]. The 12th International Conference on Information and Communications Security, Barcelona, Spain, 2010: 401–415. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-17650-0_28. [19] 冯朝胜, 罗王平, 秦志光, 等. 支持多种特性的基于属性代理重加密方案[J]. 通信学报, 2019, 40(6): 177–189. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2019127FENG Chaosheng, LUO Wangping, QIN Zhiguang, et al. Attribute-based proxy re-encryption scheme with multiple features[J]. Journal on Communications, 2019, 40(6): 177–189. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2019127 [20] 苏铓, 史国振, 付安民, 等. 基于代理重加密的云端多要素访问控制方案[J]. 通信学报, 2018, 39(2): 96–104. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2018028SU Mang, SHI Guozhen, FU Anmin, et al. Proxy re-encryption based multi-factor access control scheme in cloud[J]. Journal on Communications, 2018, 39(2): 96–104. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2018028 [21] XIONG Hu, ZHAO Yanan, PENG Li, et al. Partially policy-hidden attribute-based broadcast encryption with secure delegation in edge computing[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2019, 97: 453–461. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2019.03.008 [22] 张玉磊, 文龙, 王浩浩, 等. 多用户环境下无证书认证可搜索加密方案[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(5): 1094–1101. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190437ZHANG Yulei, WEN Long, WANG Haohao, et al. Certificateless authentication searchable encryption scheme for multi-user[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(5): 1094–1101. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190437 [23] 牛淑芬, 谢亚亚, 杨平平, 等. 加密邮件系统中基于身份的可搜索加密方案[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(7): 1803–1810. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190578NIU Shufen, XIE Yaya, YANG Pingping, et al. Identity-based searchable encryption scheme for encrypted email system[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(7): 1803–1810. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190578 [24] BOST R, MINAUD B, and OHRIMENKO O. Forward and backward private searchable encryption from constrained cryptographic primitives[C]. 2017 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Dallas, USA, 2017: 1465–1482. doi: 10.1145/3133956.3133980. [25] CHAMANI J G, PAPADOPOULOS D, PAPAMANTHOU C, et al. New constructions for forward and backward private symmetric searchable encryption[C]. 2018 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Toronto, Canada, 2018: 1038–1055. doi: 10.1145/3243734.3243833. [26] SUN Shifeng, YUAN Xingliang, LIU J K, et al. Practical backward-secure searchable encryption from symmetric puncturable encryption[C]. 2018 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Toronto, Canada, 2018: 763–780. doi: 10.1145/3243734.3243782. [27] ZUO C, SUN Shifeng, LIU J K, et al. Dynamic searchable symmetric encryption with forward and stronger backward privacy[C]. The 24th European Symposium on Research in Computer Security, Luxembourg, 2019: 283–303. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-29962-0_14. [28] NAJAFI A, JAVADI H H S, and BAYAT M. Verifiable ranked search over encrypted data with forward and backward privacy[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2019, 101: 410–419. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2019.06.018 [29] PAUL M and SAXENA A. Proof of erasability for ensuring comprehensive data deletion in cloud computing[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Recent Trends in Network Security and Applications, Chennai, India, 2010: 340–348. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-14478-3_35. [30] LUO Yuchuan, XU Ming, FU Shaojing, et al. Enabling assured deletion in the cloud storage by overwriting[C]. The 4th ACM International Workshop on Security in Cloud Computing, Xi’an, China, 2016: 17–23. doi: 10.1145/2898445.2898447. [31] TANG Yang, LEE P P C, LUI J C S, et al. Secure overlay cloud storage with access control and assured deletion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2012, 9(6): 903–916. doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2012.49. [32] 杜瑞忠, 石朋亮, 何欣枫. 基于覆写验证的云数据确定性删除方案[J]. 通信学报, 2018, 40(1): 130–140. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2019012DU Ruizhong, SHI Pengliang, and HE Xinfeng. Cloud data assured deletion scheme based on overwrite verification[J]. Journal on Communications, 2018, 40(1): 130–140. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2019012 [33] XUE Liang, YU Yong, LI Yannan, et al. Efficient attribute-based encryption with attribute revocation for assured data deletion[J]. Information Sciences, 2019, 479: 640–650. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2018.02.015 [34] PAPPAS V, KEMERLIS V P, ZAVOU A, et al. CloudFence: Data flow tracking as a cloud service[C]. The 16th International Symposium on Research in Attacks, Intrusions, and Defenses, Rodney Bay, USA, 2013: 411–431. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-41284-4_21. [35] PASQUIER T F J M, SINGH J, EYERS D, et al. Camflow: Managed data-sharing for cloud services[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cloud Computing, 2017, 5(3): 472–484. doi: 10.1109/tcc.2015.2489211 [36] PRIEBE C, MUTHUKUMARAN D, KEEFFE D O, et al. CloudSafetyNet: Detecting data leakage between cloud tenants[C]. The 6th edition of the ACM Workshop on Cloud Computing Security, Scottsdale, USA, 2014: 117–128. doi: 10.1145/2664168.2664174. [37] ATENIESE G, BURNS R, CURTMOLA R, et al. Provable data possession at untrusted stores[C]. The 14th ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Alexandria, USA, 2007: 598–609. doi: 10.1145/1315245.1315318. [38] ERWAY C C, KÜPÇÜ A, PAPAMANTHOU C, et al. Dynamic provable data possession[J]. ACM Transactions on Information and System Security, 2015, 17(4): 15. doi: 10.1145/2699909 [39] WANG Yujue, WU Qianhong, QIN Bo, et al. Online/offline provable data possession[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2017, 12(5): 1182–1194. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2017.2656461 [40] WANG Huaqun, HE Debiao, FU Anmin, et al. Provable data possession with outsourced data transfer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, To be published. doi: 10.1109/TSC.2019.2892095 [41] WANG Huaqun, HE Debiao, YU Jia, et al. Incentive and unconditionally anonymous identity-based public provable data possession[J]. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, 2019, 12(5): 824–835. doi: 10.1109/TSC.2016.2633260 [42] JUELS A and KALISKI B S. Pors: Proofs of retrievability for large files[C]. The 14th ACM conference on Computer and communications security, Alexandria, USA, 2007: 584–597. doi: 10.1145/1315245.1315317. [43] SHACHAM H and WATERS B. Compact proofs of retrievability[J]. Journal of Cryptology, 2013, 26(3): 442–483. doi: 10.1007/s00145-012-9129-2 [44] WANG Cong, WANG Qian, REN Kui, et al. Toward secure and dependable storage services in cloud computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, 2012, 5(2): 220–232. doi: 10.1109/TSC.2011.24 [45] JIANG Tao, CHEN Xiaofeng, and MA Jianfeng. Public integrity auditing for shared dynamic cloud data with group user revocation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2016, 65(8): 2363–2373. doi: 10.1109/TC.2015.2389955 [46] LI Yannan, YU Yong, MIN Geyong, et al. Fuzzy identity-based data integrity auditing for reliable cloud storage systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2019, 16(1): 72–83. doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2017.2662216 [47] DU Minxin, WANG Qian, HE Meiqi, et al. Privacy-preserving indexing and query processing for secure dynamic cloud storage[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2018, 13(9): 2320–2332. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2018.2818651 [48] SUN Jianfei, HU Shengnan, NIE Xuyun, et al. Efficient ranked multi-keyword retrieval with privacy protection for multiple data owners in cloud computing[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2020, 14(2): 1728–1739. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2019.2933346 [49] PINKAS B and REINMAN T. Oblivious RAM revisited[C]. The 30th Annual Cryptology Conference on Advances in Cryptology, Santa Barbara, USA, 2010: 502–519. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-14623-7_27. [50] TANG Jun, CUI Yong, LI Qi, et al. Ensuring security and privacy preservation for cloud data services[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2016, 49(1): 13. doi: 10.1145/2906153 [51] WILLIAMS P, SION R, and CARBUNAR B. Building castles out of mud: Practical access pattern privacy and correctness on untrusted storage[C]. The 15th ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Alexandria, USA, 2008: 139–148. doi: 10.1145/1455770.1455790. [52] UENO Y, MIYAHO N, SUZUKI S, et al. Performance evaluation of a disaster recovery system and practical network system applications[C]. 2010 5th International Conference on Systems and Networks Communications, Nice, France, 2010: 195–200. doi: 10.1109/ICSNC.2010.37. [53] JAVARAIAH V. Backup for cloud and disaster recovery for consumers and SMBs[C]. 2011 5th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Telecommunication Systems and Networks (ANTS), Bangalore, India, 2011: 1–3. doi: 10.1109/ANTS.2011.6163671. [54] UENO Y, MIYAHO N, and SUZUKI S. Disaster recovery mechanism using widely distributed networking and secure metadata handling technology[C]. The 4th Edition of the UPGRADE-CN Workshop on Use of P2P, GRID and Agents for the Development of Content Networks, New York, USA, 2009: 45–48. doi: 10.1145/1552486.1552514. [55] PALKOPOULOU E, SCHUPKE D A, and BAUSCHERT T. Recovery time analysis for the Shared Backup Router Resources (SBRR) architecture[C]. 2011 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Kyoto, Japan, 2011: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/icc.2011.5963411. [56] LU Jintian, YAO Lili, HE Xudong, et al. A security analysis method for security protocol implementations based on message construction[J]. Applied Sciences, 2018, 8(12): 2543. doi: 10.3390/app8122543 [57] ZHAO Chuan, ZHAO Shengnan, ZHAO Minghao, et al. Secure multi-party computation: Theory, practice and applications[J]. Information Sciences, 2019, 476: 357–372. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2018.10.024 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
