Multi-scale Semantic Information Fusion for Object Detection
-
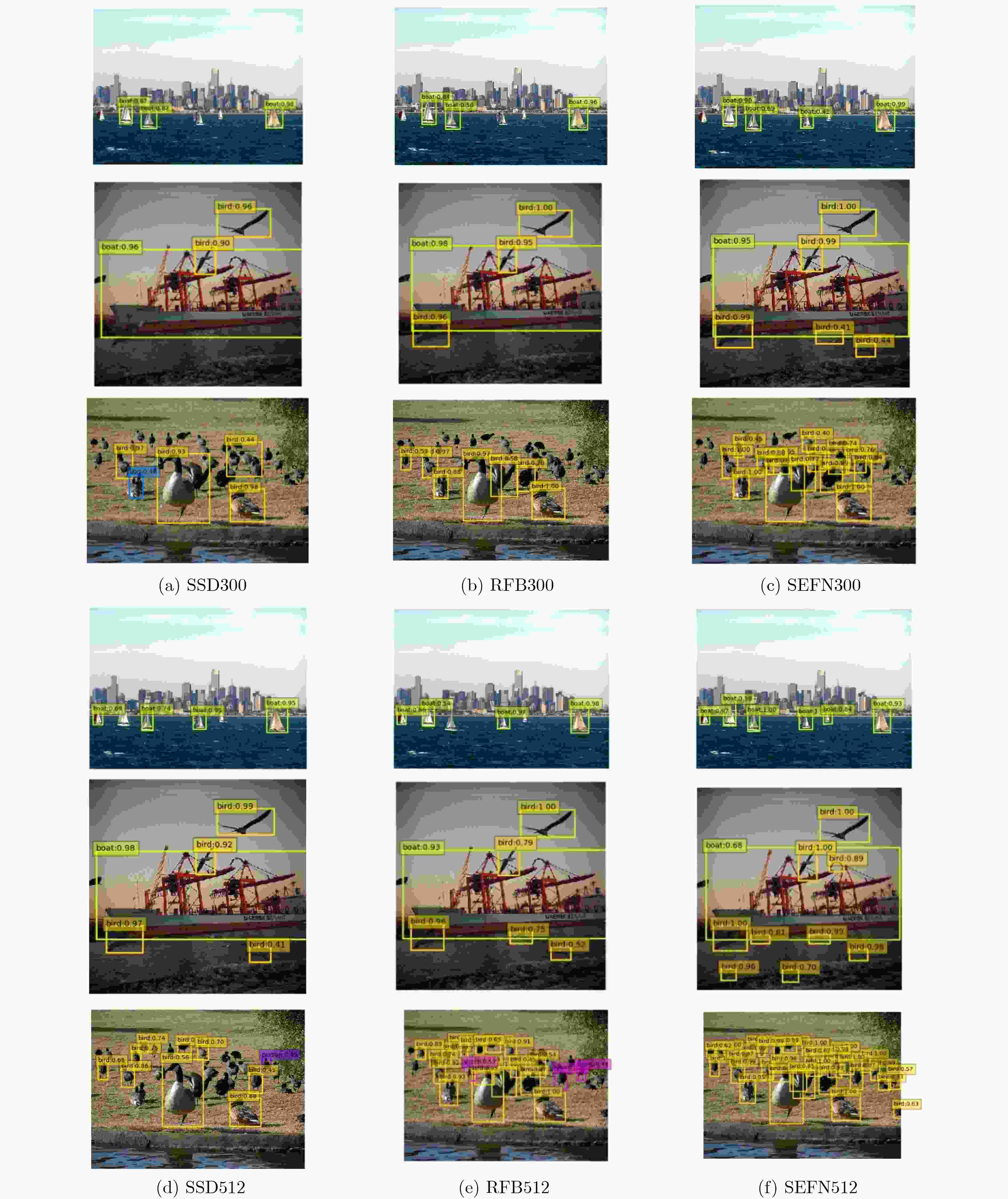
摘要: 针对当前目标检测算法对小目标及密集目标检测效果差的问题,该文在融合多种特征和增强浅层特征表征能力的基础上提出了浅层特征增强网络(SEFN),首先将特征提取网络VGG16中Conv4_3层和Conv5_3层提取的特征进行融合形成基础融合特征;然后将基础融合特征输入到小型的多尺度语义信息融合模块中,得到具有丰富上下文信息和空间细节信息的语义特征,同时把语义特征和基础融合特征经过特征重利用模块获得浅层增强特征;最后基于浅层增强特征进行一系列卷积获取多个不同尺度的特征,并输入各检测分支进行检测,利用非极大值抑制算法实现最终的检测结果。在PASCAL VOC2007和MS COCO2014数据集上进行测试,模型的平均精度均值分别为81.2%和33.7%,相对于经典的单极多盒检测器(SSD)算法,分别提高了2.7%和4.9%;此外,该文方法在检测小目标和密集目标场景上,检测精度和召回率都有显著提升。实验结果表明该文算法采用特征金字塔结构增强了浅层特征的语义信息,并利用特征重利用模块有效保留了浅层的细节信息用于检测,增强了模型对小目标和密集目标的检测效果。Abstract: Current object detection algorithms have poor detection results on small targets and dense targets. To address this challenge, a Shallow Enhanced Feature Network (SEFN) is proposed in this paper, which is based on the fusion of multiple features and enhanced shallow feature characterization capabilities. Firstly, the features extracted from the Conv4_3 layer and Conv5_3 layer are combined to form basic fusion features. Then the basic fusion features are inputted into a small multi-scale semantic information fusion module to obtain semantic features of rich contextual information and spatial detail information. The semantic features are fused into the basics features by the feature reuse module to obtain shallow enhanced features. Finally, a series of convolutions are performed based on the shallow enhanced features to obtain multiple features with different scales. Multiple detection branches are then constructed based on the features of different scales. The non-maximum suppression algorithm is used to achieve the final detection. The average accuracy of the proposed model is 81.2% and 33.7% on the PASCAL VOC2007 and MS COCO2014 datasets respectively, which is 2.7% and 4.9% higher than the classic Single Shot multibox Detector (SSD) algorithm. In addition, on detecting small targets in dense target scenes, the detection accuracy and recall rate of the proposed method are significantly improved. The experimental results show that the feature pyramid structure can enhance the semantic information of shallow features, and the feature reuse module can effectively retain shallow detail information for detection, so the proposed method can get better detection performance on small targets and dense targets.
-
表 1 在PASCAL VOC2007测试集本文方法与其他方法的结果对比
方法 骨干网络 输入尺度 GPU fps(帧/s) mAP(%),IOU=0.5 Faster RCNN[16] VGG16 1000×600 Tian X 7.0 73.2 Faster RCNN[16] ResNet-101 1000×600 K40 2.4 76.4 HyperNet[17] VGG16 1000×600 Tian X 5.0 76.3 OHEM[18] VGG16 1000×600 Tian X 7.0 74.6 ION[19] VGG16 1000×600 Tian X 1.3 76.5 R-FCN[12] ResNet-101 1000×600 K40 5.8 79.5 YOLOv1[14] GoogleNet 448×448 Tian X 45.0 63.4 YOLOv2[15] Darknet-19 352×352 Tian X 81.0 73.7 SSD300[1] VGG16 300×300 Tian X 46.0 77.2 DSSD321[4] ResNet-101 321×321 Tian X 9.5 78.6 RSSD300[13] VGG16 300×300 Tian X 35.0 78.5 FSSD300[6] VGG16 300×300 1080Ti 65.8 78.8 RFB300[7] VGG16 300×300 1080Ti 83.0 80.5 本文SEFN300 VGG16 300×300 Tesla P100 55.0 79.6 YOLOv2[15] Darknet-19 544×544 Tian X 40.0 78.6 SSD512[1] VGG16 512×512 Tian X 19.0 78.5 DSSD513[4] ResNet-101 513×513 Tian X 5.5 81.5 RSSD512[13] VGG16 512×512 Tian X 16.6 80.8 FSSD512[6] VGG16 512×512 1080Ti 35.7 80.9 RFB512[7] VGG16 512×512 1080Ti 38.0 82.2 本文SEFN512 VGG16 512×512 Tesla P100 30.0 81.2 表 2 在MS COCO2014_minival测试集上本文方法与其他方法的结果对比
方法 骨干网络 检测精度mAP(%) mAP(%) 召回率AR(%) IOU=0.5:0.95 IOU=0.5 IOU=0.75 area: S area: M area: L area: S area: M area: L Faster R-CNN[16] VGG16 24.2 45.3 23.5 7.7 26.4 37.1 – – – R-FCN[12] ResNet-101 29.2 51.5 – 10.3 32.4 43.3 – – – YOLOv2[15] Darknet-19 21.6 44.0 19.2 5.0 22.4 35.5 9.8 36.5 54.4 SSD512[1] VGG16 28.8 48.5 30.3 10.9 31.8 43.5 16.5 46.6 60.8 DSSD513[4] ResNet-101 33.2 53.3 35.2 13.0 35.4 51.5 21.8 49.1 66.4 FSSD512[6] VGG16 31.8 52.8 33.5 14.2 35.1 45.0 22.3 49.9 62.0 RFB512[7] VGG16 34.4 55.7 36.4 17.6 37.0 49.7 27.3 52.3 65.4 本文SEFN512 VGG16 33.7 54.7 35.6 19.2 38.0 47.3 29.1 52.5 63.2 -
[1] LIU Wei, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot MultiBox detector[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 21–37. [2] 罗会兰, 卢飞, 孔繁胜. 基于区域与深度残差网络的图像语义分割[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(11): 2777–2786. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190056LUO Huilan, LU Fei, and KONG Fansheng. Image semantic segmentation based on region and deep residual network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(11): 2777–2786. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190056 [3] LIN T Y, DOLLÁR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 936–944. [4] FU Chengyang, LIU Wei, RANGA A, et al. DSSD: Deconvolutional single shot detector[EB/OL]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1701.06659, 2017. [5] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. [6] LI Zuoxin and ZHOU Fuqiang. FSSD: Feature fusion single shot multibox detector[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1712.00960, 2017. [7] LIU Songtao, HUANG Di, and WANG Yunhong. Receptive field block net for accurate and fast object detection[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 404–419. [8] EVERINGHAM M, VAN GOOL L, WILLIAMS C K I, et al. The PASCAL Visual Object Classes (VOC) challenge[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2010, 88(2): 303–338. doi: 10.1007/s11263-009-0275-4 [9] LIN T Y, MAIRE M, BELONGIE S, et al. Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context[C]. 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 740–755. [10] LI Hanchao, XIONG Pengfei, AN Jie, et al. Pyramid attention network for semantic segmentation[C]. British Machine Vision Conference, Newcastle, UK, 2018. [11] 罗会兰, 卢飞, 严源. 跨层融合与多模型投票的动作识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(3): 649–655. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180373LUO Huilan, LU Fei, and YAN Yuan. Action recognition based on multi-model voting with cross layer fusion[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(3): 649–655. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180373 [12] DAI Jifeng, LI Yi, HE Kaiming, et al. R-FCN: Object detection via region-based fully convolutional networks[C]. The 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, SPAIN, 2016: 379–387. [13] JEONG J, PARK H, and KWAK N. Enhancement of SSD by concatenating feature maps for object detection[C]. British Machine Vision Conference, London, UK, 2017. [14] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 779–788. [15] REDMON J and FARHADI A. YOLO9000: Better, faster, stronger[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6517–6525. [16] REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137–1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [17] KONG Tao, YAO Anbang, CHEN Yurong, et al. HyperNet: Towards accurate region proposal generation and joint object detection[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 845–853. [18] SHRIVASTAVA A, GUPTA A, and GIRSHICK R. Training region-based object detectors with online hard example mining[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016. [19] BELL S, ZITNICK C L, BALA K, et al. Inside-outside net: Detecting objects in context with skip pooling and recurrent neural networks[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016, 2874–2883. -





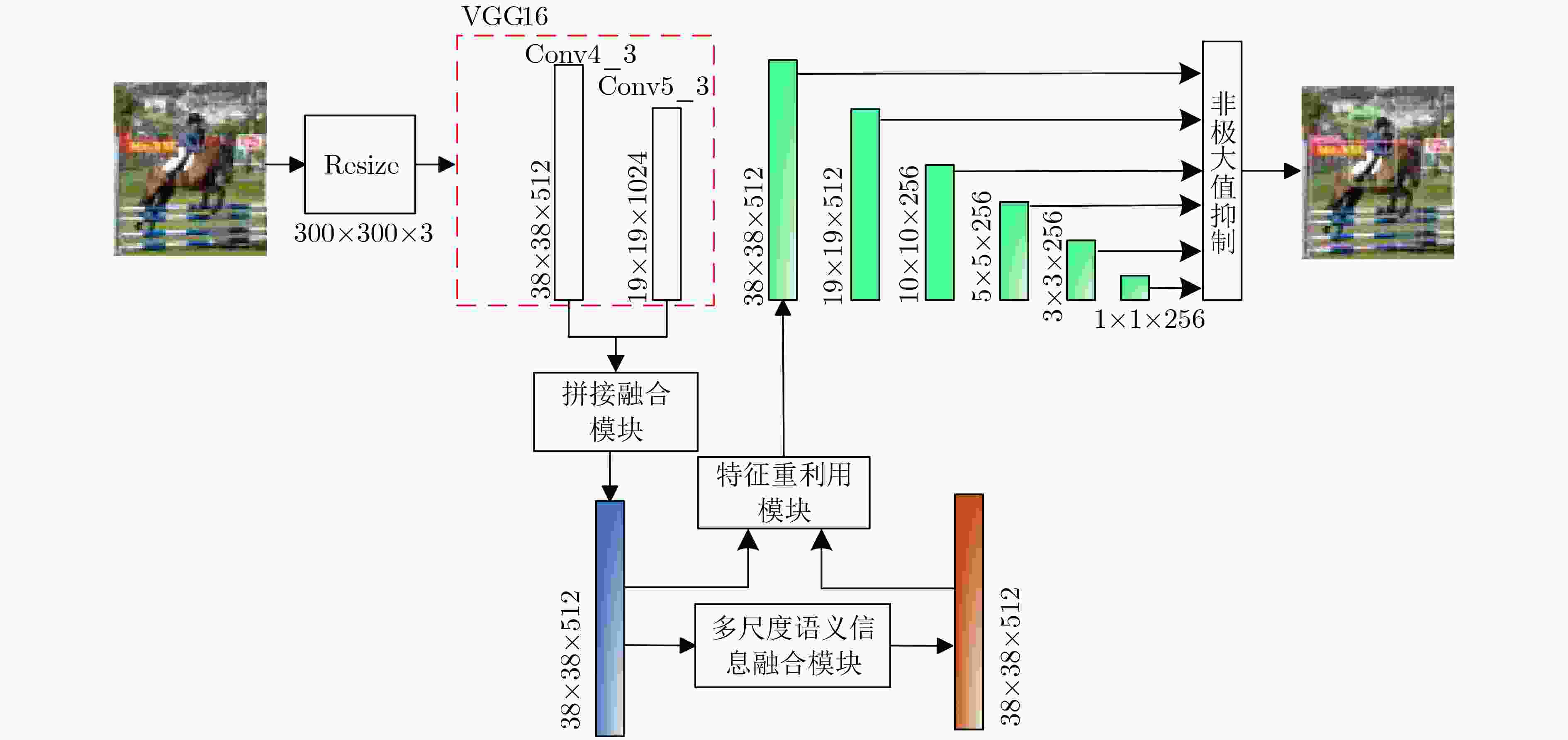
 下载:
下载:
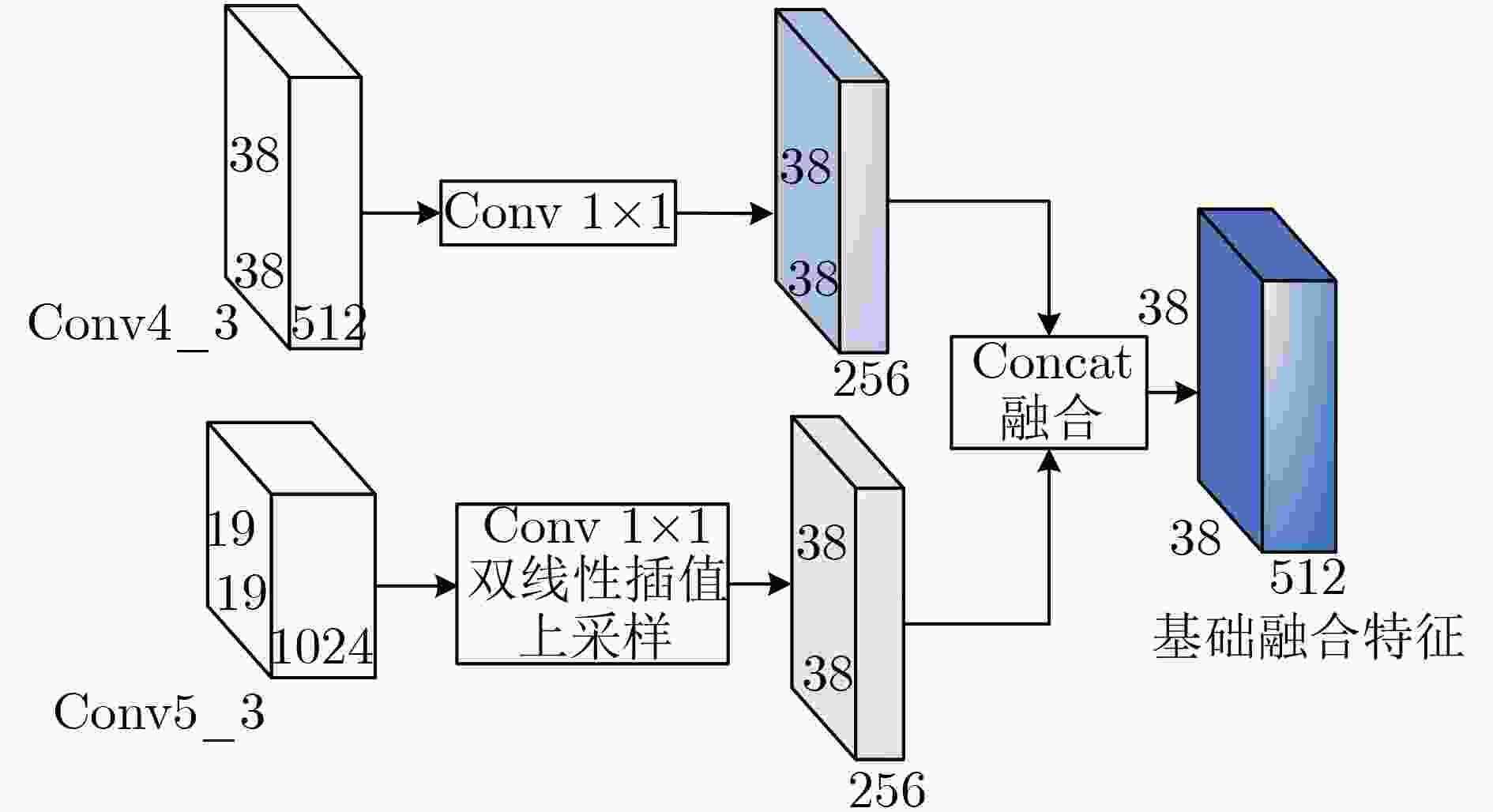
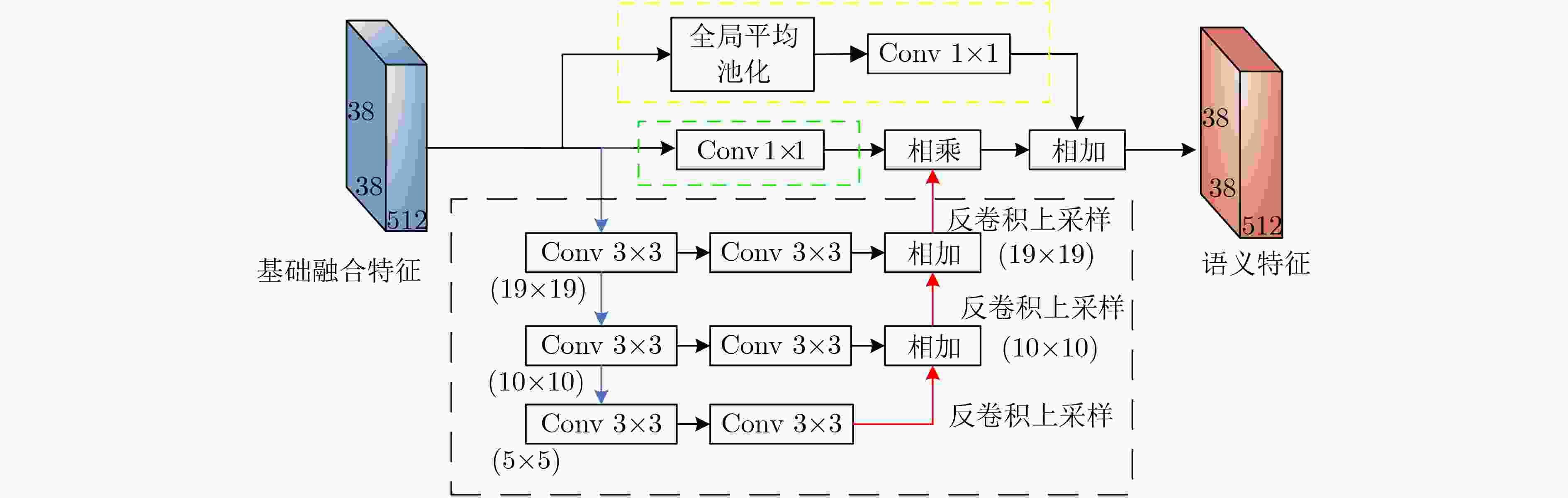
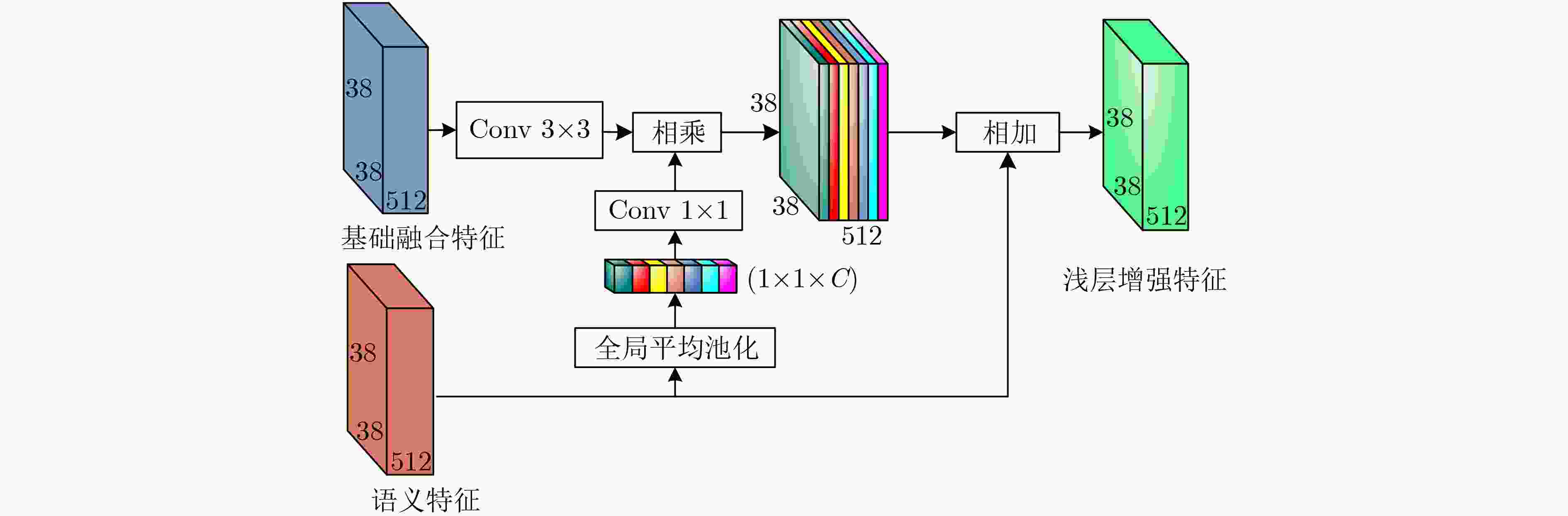


 下载:
下载:
