|
GARDNER W A, NAPOLITANO A, and PAURA L. Cyclostationarity: Half a century of research[J]. Signal Processing, 2006, 86(4): 639–697. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2005.06.016
|
|
GARDNER W A and CHEN C K. Signal-selective time-difference-of-arrival estimation for passive location of man-made signal sources in highly corruptive environments. I. Theory and method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1992, 40(5): 1168–1184. doi: 10.1109/78.134479
|
|
CHEN C K and GARDNER W A. Signal-selective time-difference of arrival estimation for passive location of man-made signal sources in highly corruptive environments. II. Algorithms and performance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1992, 40(5): 1185–1197. doi: 10.1109/78.134480
|
|
马济通, 邱天爽, 李蓉, 等. 脉冲噪声下基于Renyi熵的分数低阶双模盲均衡算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(2): 378–385. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170366MA Jitong, QIU Tianshuang, LI Rong, et al. Dual-mode blind equalization algorithm based on Renyi entropy and fractional lower order statistics under impulsive noise[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(2): 378–385. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170366
|
|
邱天爽, 郭莹. 信号处理与数据分析[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2015: 368–374.QIU Tianshuang and GUO Ying. Signal Processing and Data Analysis[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2015: 368–374.
|
|
MA Xinyu and NIKIAS C L. Joint estimation of time delay and frequency delay in impulsive noise using fractional lower order statistics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1996, 44(11): 2669–2687. doi: 10.1109/78.542175
|
|
GEORGIOU P G, TSAKALIDES P, and KYRIAKAKIS C. Alpha-stable modeling of noise and robust time-delay estimation in the presence of impulsive noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 1999, 1(3): 291–301. doi: 10.1109/6046.784467
|
|
ZENG Wenjun, SO H C, and ZOUBIR A M. An ℓp-norm minimization approach to time delay estimation in impulsive noise[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2013, 23(4): 1247–1254. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2013.03.013
|
|
YU Ling, QIU Tianshuang, and SONG Aimin. A time delay estimation algorithm based on the weighted correntropy spectral density[J]. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 2017, 36(3): 1115–1128. doi: 10.1007/s00034-016-0347-y
|
|
LUAN Shengyang, QIU Tianshuang, ZHU Yongjie, et al. Cyclic correntropy and its spectrum in frequency estimation in the presence of impulsive noise[J]. Signal Processing, 2016, 120: 503–508. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2015.09.023
|
|
邱天爽. 相关熵与循环相关熵信号处理研究进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 105–118. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190646QIU Tianshuang. Development in signal processing based on correntropy and cyclic correntropy[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 105–118. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190646
|
|
FONTES A I R, REGO J B A, DE M. MARTINS A, et al. Cyclostationary correntropy: Definition and applications[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2017, 69: 110–117. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2016.10.029
|
|
LIU Tao, QIU Tianshuang, and LUAN Shengyang. Cyclic correntropy: Foundations and theories[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 34659–34669. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2847346
|
|
MA Jitong and QIU Tianshuang. Automatic modulation classification using cyclic correntropy spectrum in impulsive noise[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2019, 8(2): 440–443. doi: 10.1109/lwc.2018.2875001
|
|
ZHANG Jinfeng, QIU Tianshuang, SONG Aimin, et al. A novel correntropy based DOA estimation algorithm in impulsive noise environments[J]. Signal Processing, 2014, 104: 346–357. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2014.04.033
|
|
LI Sen, LIN Bin, DING Yabo, et al. Signal-selective time difference of arrival estimation based on generalized cyclic correntropy in impulsive noise environments[C]. The 13th International Conference on Wireless Algorithms, Systems, and Applications, Tianjin, China, 2018: 274–283. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-94268-1_23.
|
|
CHEN Xing, QIU Tianshuang, LIU Cheng, et al. TDOA estimation algorithm based on generalized cyclic correntropy in impulsive noise and cochannel interference[J]. IEICE Transactions on Fundamentals of Electronics, Communications and Computer Sciences, 2018, E101(10): 1625–1630. doi: 10.1587/transfun.E101.A.1625
|
|
CHEN Badong, XING Lei, ZHAO Haiquan, et al. Generalized correntropy for robust adaptive filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(13): 3376–3387. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2539127
|
|
栾声扬. 有界非线性协方差与相关熵及在无线定位中的应用[D]. [博士论文], 大连理工大学, 2017.LUAN Shengyang. Bounded nonlinear covariance and correntropy for the application of wireless location[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Dalian University of Technology, 2017.
|
|
罗忠涛, 詹燕梅, 郭人铭, 等. 脉冲噪声中基于指数函数的可变拖尾非线性变换设计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(4): 932–940. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190401LUO Zhongtao, ZHAN Yanmei, GUO Renming, et al. Variable tailing nonlinear transformation design based on exponential function in impulsive noise[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(4): 932–940. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190401
|
|
SHARIFI K and LEON-GARCIA A. Estimation of shape parameter for generalized gaussian distributions in subband decompositions of video[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 1995, 5(1): 52–56. doi: 10.1109/76.350779
|
|
ZHANG Jiacheng, QIU Tianshuang, LUAN Shengyang, et al. Bounded non-linear covariance based ESPRIT method for noncircular signals in presence of impulsive noise[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2019, 87: 104–111. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2019.01.018
|
|
LUAN Shengyang, QIU Tianshuang, YU Ling, et al. BNC-based projection approximation subspace tracking under impulsive noise[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2017, 11(7): 1055–1061. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2016.0267
|
|
LIU Tao, QIU Tianshuang, and LUAN Shengyang. Hyperbolic-tangent-function-based cyclic correlation: Definition and theory[J]. Signal Processing, 2019, 164: 206–216. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2019.06.001
|
|
LIU Yang, QIU Tianshuang, and SHENG Hu. Time-difference-of-arrival estimation algorithms for cyclostationary signals in impulsive noise[J]. Signal Processing, 2012, 92(9): 2238–2247. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2012.02.016
|





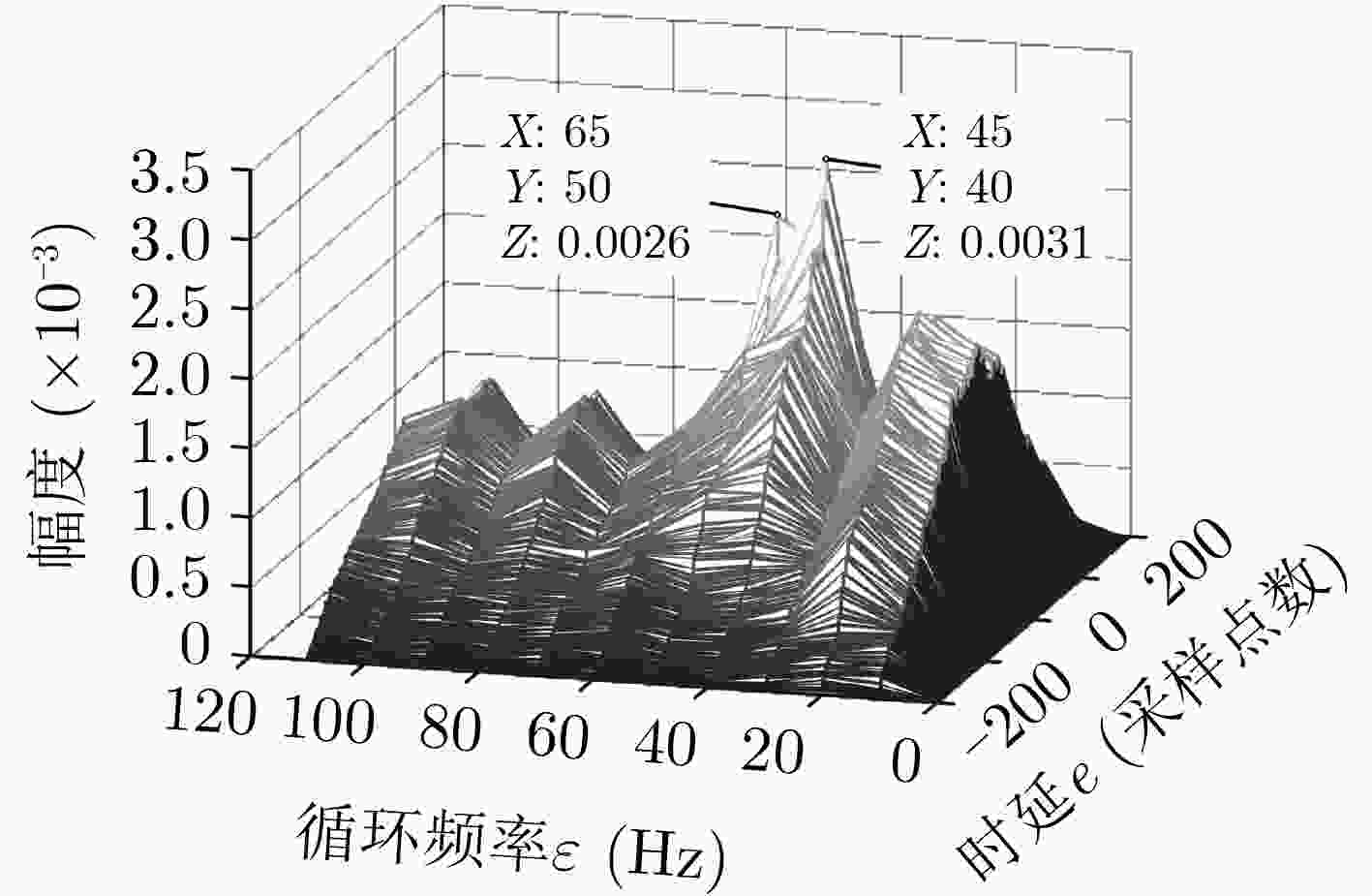
 下载:
下载:
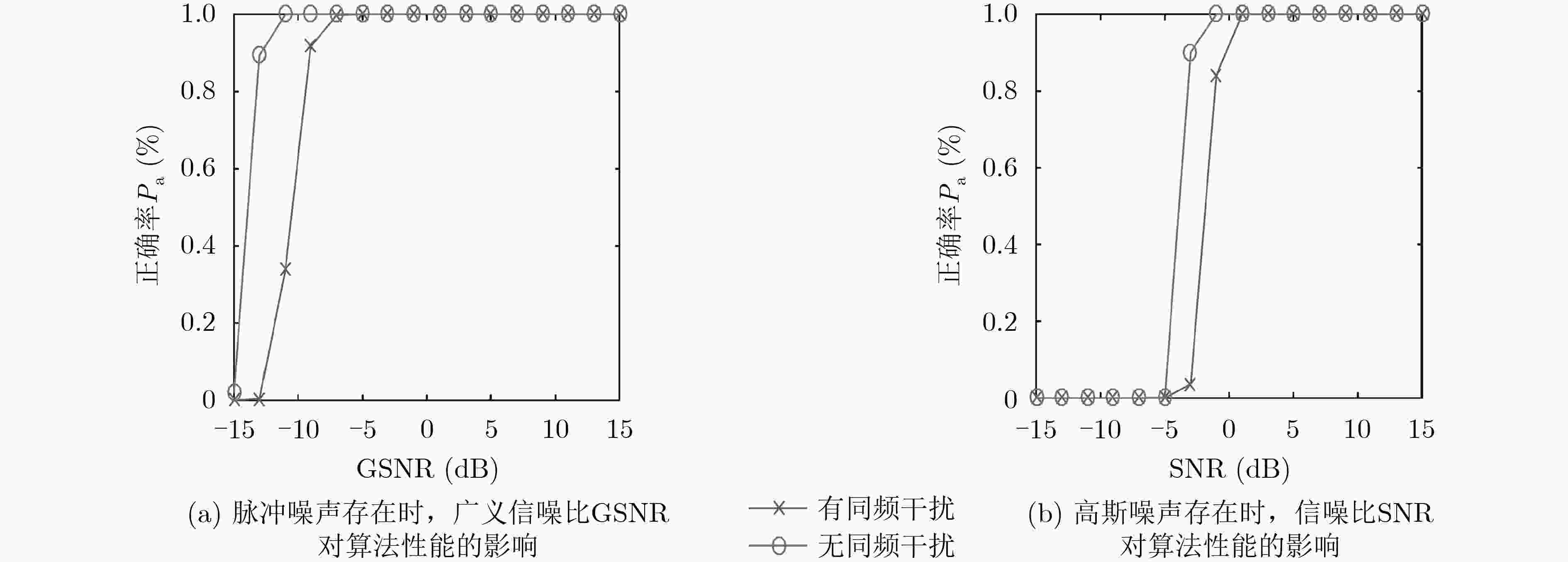
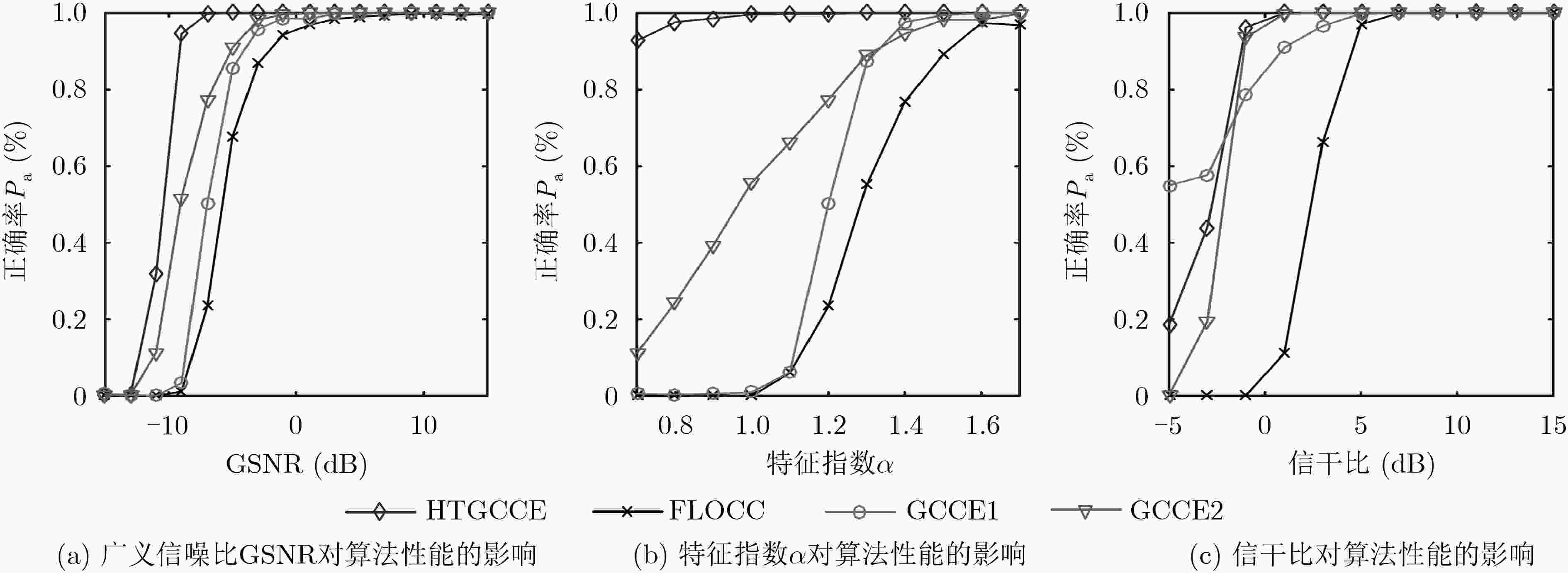
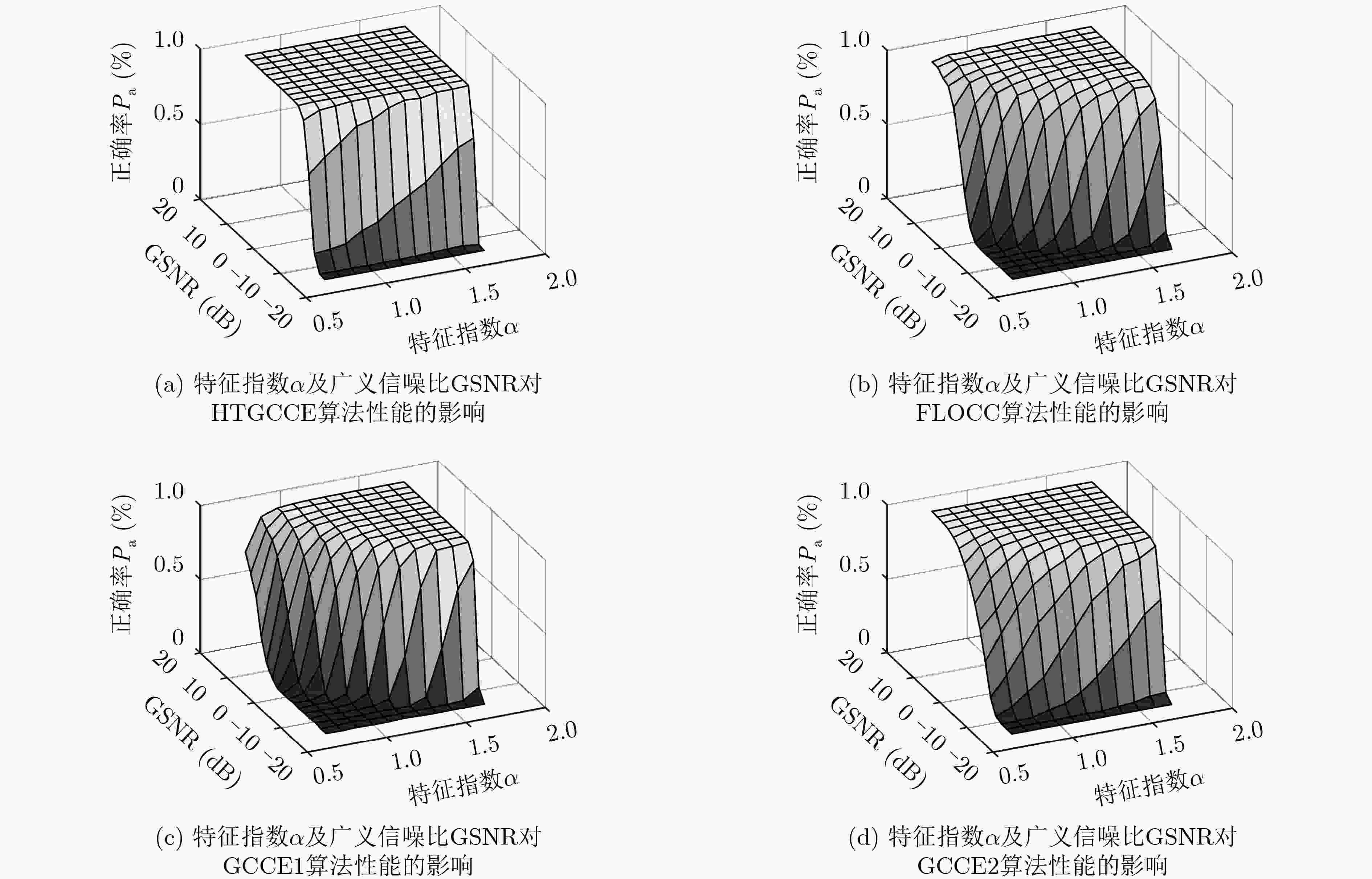


 下载:
下载:
