A Decoding Algorithm of Polar Codes Based on Perturbation with CNN
-
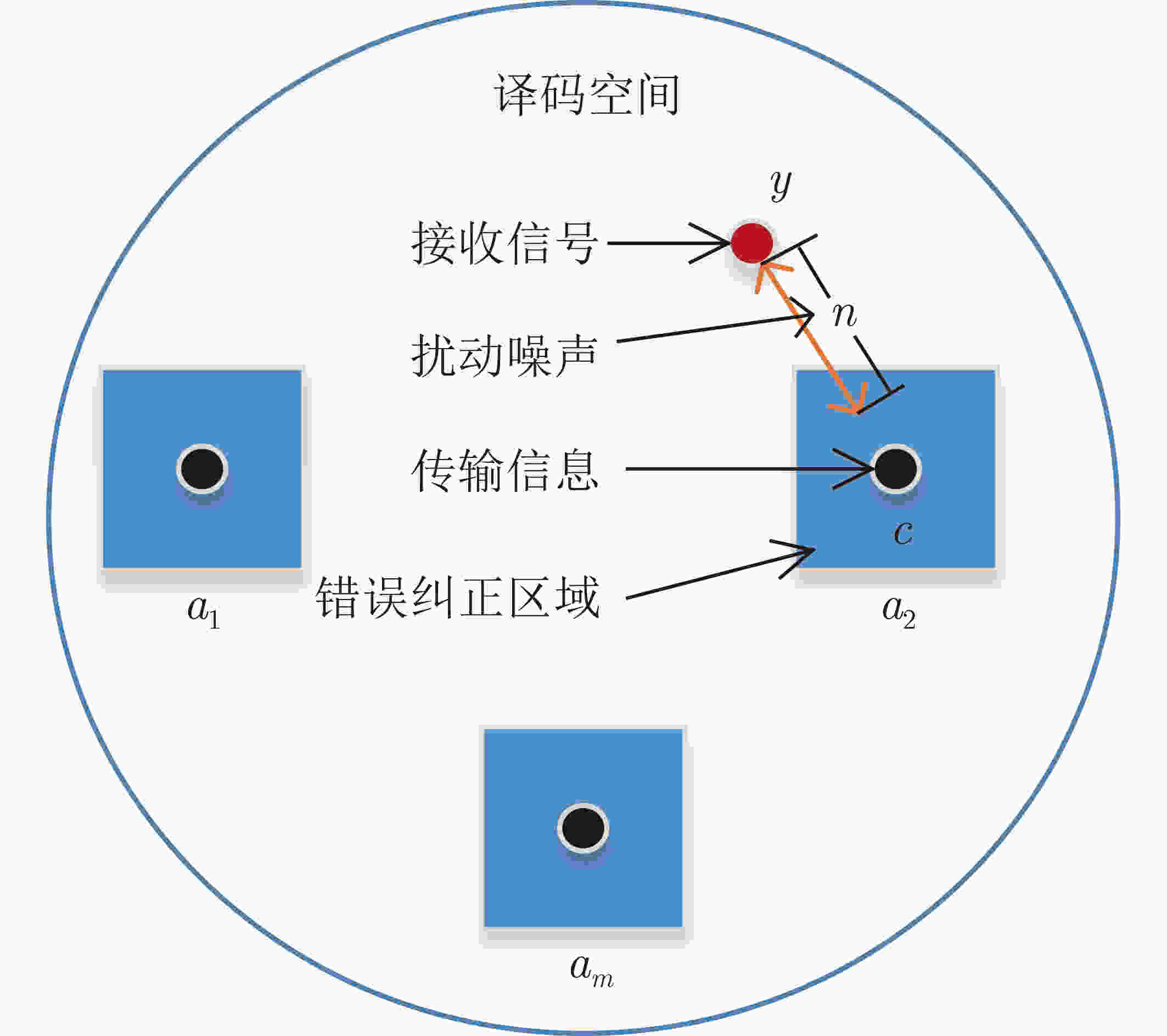
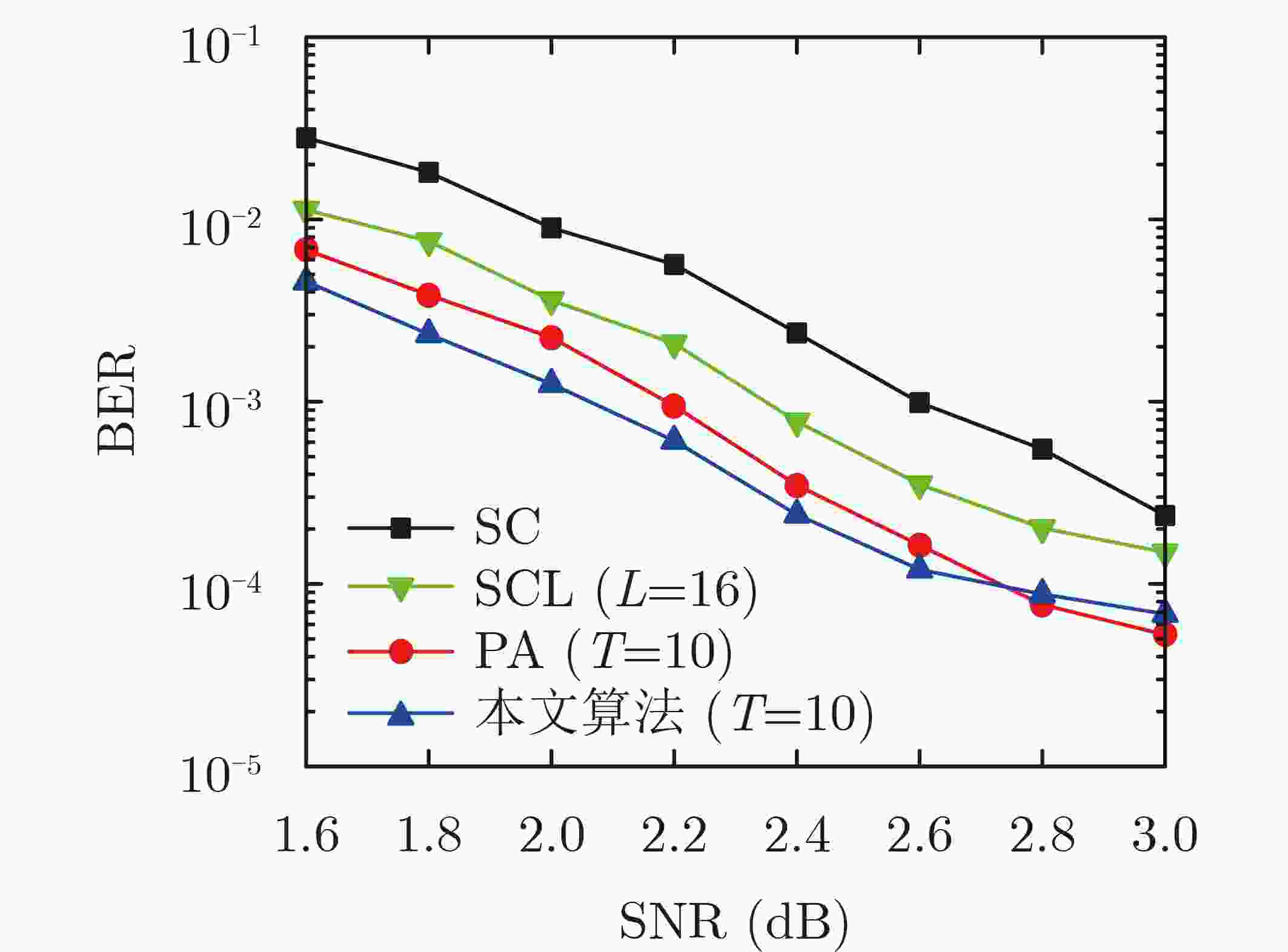
摘要: 针对中短码长下串行抵消(SC)算法性能较差,且串行抵消列表(SCL)算法复杂度较高等问题,根据译码纠错空间理论,该文提出了一种基于卷积神经网络(CNN)扰动的极化码译码算法。对SC译码失败的接收序列,通过CNN产生相应的扰动噪声,并将该扰动噪声添加到接收信号中,然后根据重新计算的似然信息进行译码。仿真结果表明:与SC译码算法相比,所提出的算法约有0.6 dB的增益,与SCL(L=16)译码算法相比,该算法约有0.1 dB的提升,且平均复杂度更低。Abstract: According to the space theory for error correction, a Polar decoding algorithm for medium and short code lengths, based on the perturbation with a Convolution Neural Network (CNN), is presented to overcome the poor performance of the Successive Cancellation (SC) decoding algorithm and the high complexity of the Successive Cancellation List (SCL) decoding algorithm. For any receiving signals that failing to decode, a perturbation noise, generated through the CNN, is added to the receiving signal, and the likelihood information is then recalculated for further decoding. The simulation results show that the proposed algorithm has a gain of about 0.6 dB compared with the SC decoding algorithm, and an improvement of about 0.1 dB and a lower average complexity than that of SCL decoding algorithm when L=16.
-
表 1 基于CNN扰动噪声译码算法
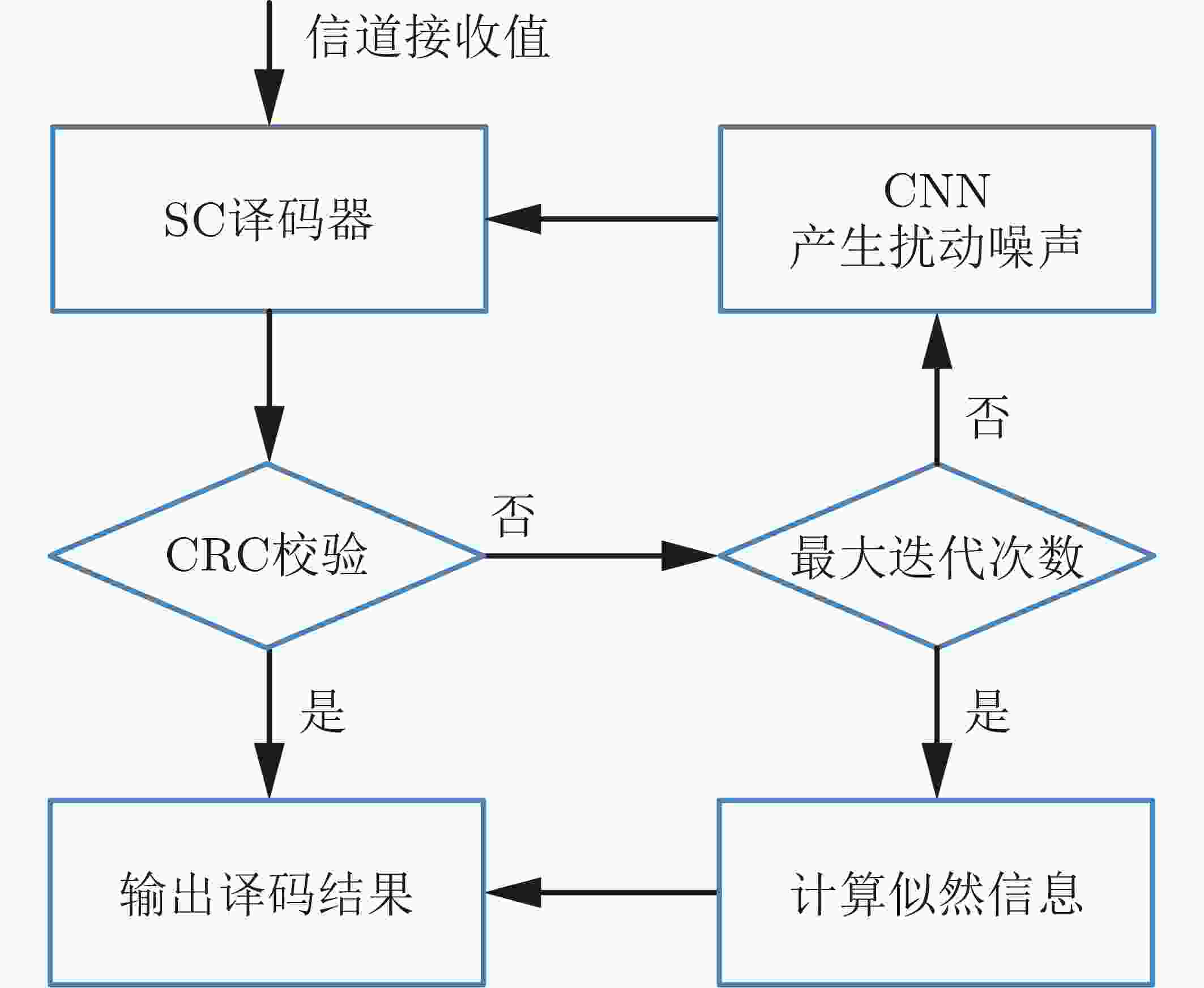
输入:${{y} }_1^N$, A, a, N, ite_max;
输出:$\hat u$(1) d ← SC (y) \\ SC decoding of received signal (2) if CRC (d)$ \in c$ then (3) return d as $\hat u$ (4) else (5) for i = 1 → ite_max do (6) CNN \\ Well trained CNN (7) ${n_i}$ ← CNN (y) \\ Generation of perturbation noise (8) ${y_i}$ ← y +${n_i}$ \\ Addition of perturbation noise (9) ${\rm{L}}{{\rm{R}}_i} \leftarrow {y_i}$ \\ Update LR (10) ${\hat u_i}$ ← SC $ ({\rm{LR}}_{i})$)\\ SC decoding of perturbed signal (11) if CRC (${\hat u_i} \in $) c then (12) return ${\hat u_i}$ as $\hat u$ (13) terminate Algorithm (14) else (15) Store $ {\hat u_i}$ (16) end if (17) end for (18) for i = 1 → ite_max do (19) Calculate $L({\hat u})$ from ${\hat u_i}$ (20) end for (21) max $L({\hat u})$ (22) return ${\hat u}$ as $\hat u$ (23) end if 表 2 CNN训练相关参数
CNN结构 {4; 18, 9, 3, 5; 128, 32, 16, 1} Mini-batch size 500 训练数据量 700000 测试数据量 200000 产生数据的SNR (dB) {0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 3.5, 4.0} 初始化方法 Xavier 优化方法 Adam -
[1] ARIKAN E. Channel polarization: A method for constructing capacity-achieving codes for symmetric binary-input memoryless channels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2009, 55(7): 3051–3073. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2009.2021379 [2] 郭锐, 王美洁, 王杰. 基于缩短极化码的MLC NAND Flash差错控制技术研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(7): 1658–1665. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160864GUO Rui, WANG Meijie, and WANG Jie. Research on the MLC NAND Flash error control technology based on Polar codes[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(7): 1658–1665. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160864 [3] ARIKAN E and TELATAR E. On the rate of channel polarization[C]. 2009 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory, Seoul, South Korea, 2009: 1493–1495. [4] WANG Xianbin, ZHANG Huazi, LI Rong, et al. Learning to flip successive cancellation decoding of Polar codes with LSTM networks[C]. 2019 IEEE 30th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications, Istanbul, Turkey, 2019. [5] 刘建航, 何怡静, 李世宝, 等. 基于预译码的极化码最大似然简化连续消除译码算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(4): 959–966. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180324LIU Jianhang, HE Yijing, LI Shibao, et al. Pre-decoding based maximum-likelihood simplified successive-cancellation decoding of Polar codes[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(4): 959–966. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180324 [6] AFISIADIS O, BALATSOUKAS-STIMMING A, and BURG A. A low-complexity improved successive cancellation decoder for Polar codes[C]. 2014 48th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, USA, 2014: 2116–2120. doi: 10.1109/ACSSC.2014.7094848. [7] TAL I and VARDY A. List decoding of Polar codes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2015, 61(5): 2213–2226. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2015.2410251 [8] HASHEMI S A, CONDO C, and GROSS W J. Simplified successive-cancellation list decoding of polar codes[C]. 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 815–819. [9] HASHEMI S A, CONDO C, and GROSS W J. Fast simplified successive-cancellation list decoding of polar codes[C]. 2017 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference Workshops, San Francisco, USA, 2017: 1–6. [10] NIU Kai and CHEN Kai. CRC-aided decoding of polar codes[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2012, 16(10): 1668–1671. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2012.090312.121501 [11] LI Bin, SHEN Hui, and TSE D. An adaptive successive cancellation list decoder for polar codes with cyclic redundancy check[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2012, 16(12): 2044–2047. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2012.111612.121898 [12] 王琼, 罗亚洁, 李思舫. 基于分段循环冗余校验的极化码自适应连续取消列表译码算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(7): 1572–1578. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180716WANG Qiong, LUO Yajie, and LI Sifang. Polar adaptive successive cancellation list decoding based on segmentation cyclic redundancy check[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(7): 1572–1578. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180716 [13] CAO Miao, ZHAO Shuang, and ZHAO Shengmei. Multiple CRC-aided variable successive cancellation list decoder of polar codes[J]. The Journal of China Universities of Posts and Telecommunications, 2017, 24(2): 83–88. doi: 10.1016/S1005-8885(17)60202-4 [14] TRIFONOV P and MILOSLAVSKAYA V. Polar subcodes[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2016, 34(2): 254–266. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2015.2504269 [15] KAY S. Can detectability be improved by adding noise?[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2000, 7(1): 8–10. doi: 10.1109/97.809511 [16] LIANG Fei, SHEN Cong, and WU Feng. An iterative BP-CNN architecture for channel decoding[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2018, 12(1): 144–159. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2018.2794062 [17] JIN Wenyi and FOSSORIER M P C. Reliability-based soft-decision decoding with multiple biases[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2007, 53(1): 105–120. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.887510 [18] MCDONNELL M D, ABBOTT D and FRISTON K J. What is stochastic resonance? definitions, misconceptions, debates, and its relevance to biology[J]. PLoS Computational Biology, 2009, 5(5): e1000348. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000348 [19] 吴皓威, 武小飞, 邹润秋, 等. 空间耦合LDPC码的分层译码算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(8): 1881–1887. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190626WU Haowei, WU Xiaofei, ZOU Runqiu, et al. A layered decoding algorithm for spatially-coupled LDPC codes[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(8): 1881–1887. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190626 [20] 张顺外, 魏琪. 多信源多中继编码协作系统准循环LDPC码的联合设计与性能分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(10): 2325–2333. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190069ZHANG Shunwai and WEI Qi. Joint design of quasi-cyclic low density parity check codes and performance analysis of multi-source multi-relay coded cooperative system[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(10): 2325–2333. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190069 -





 下载:
下载:
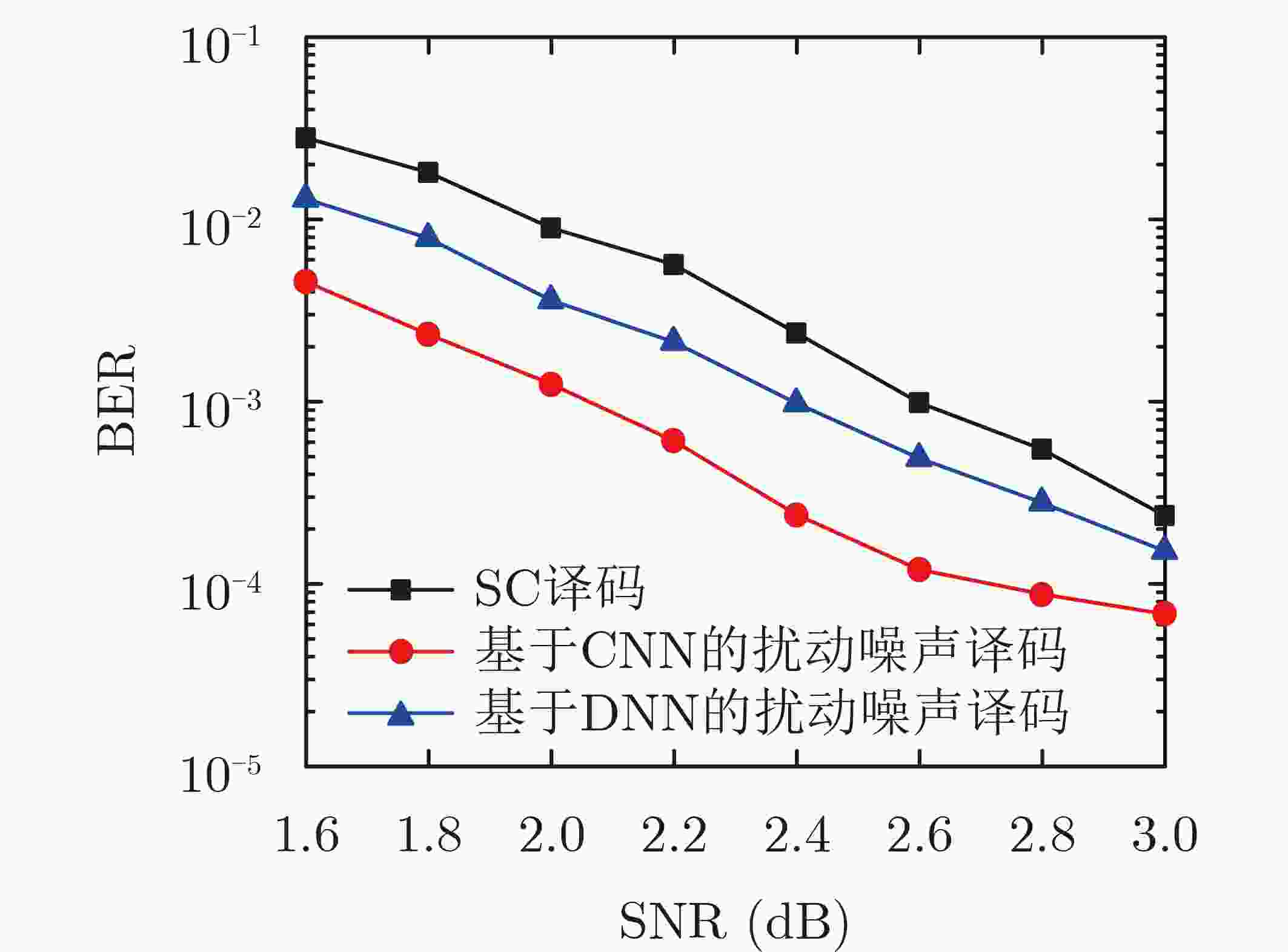
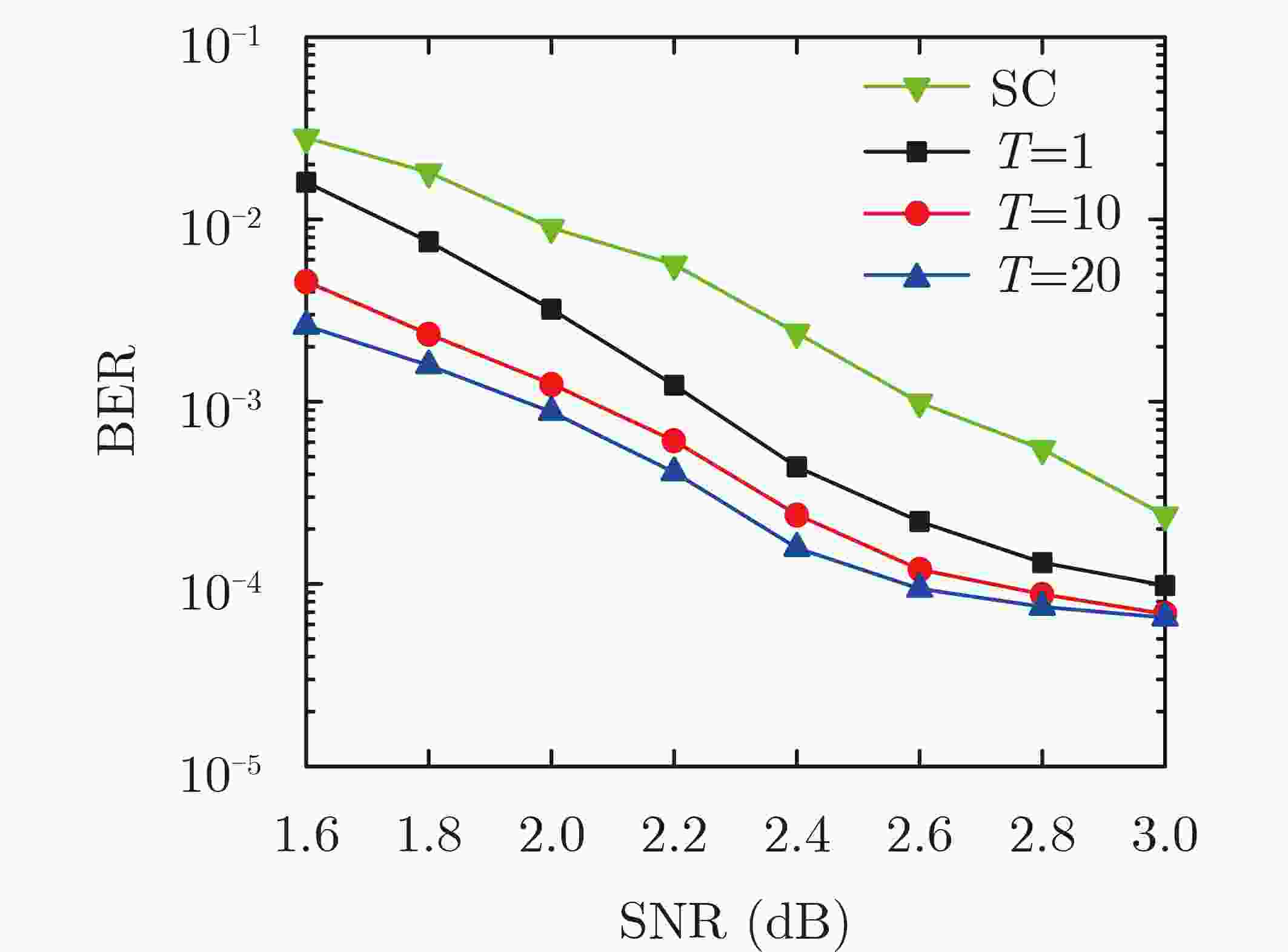
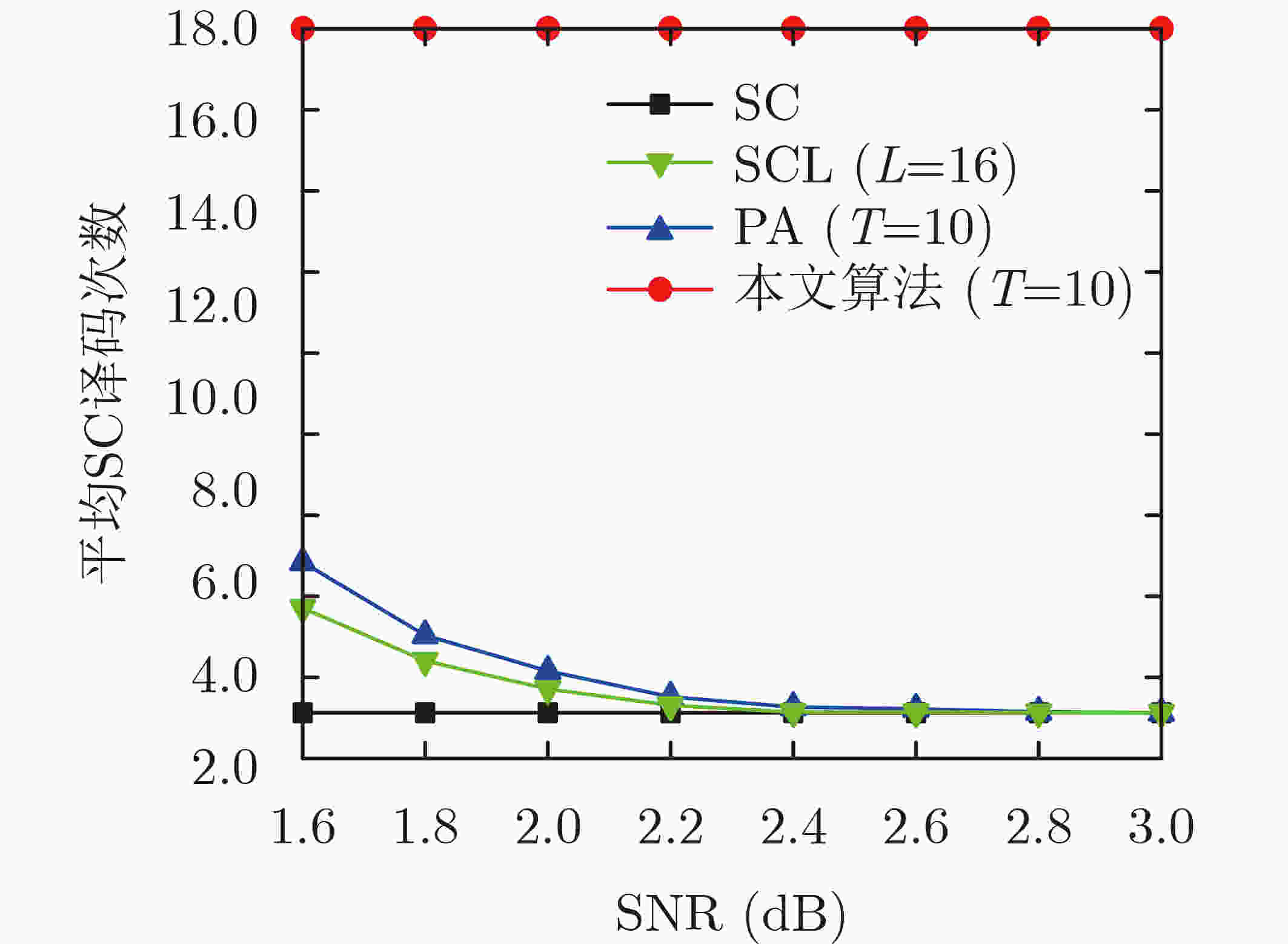


 下载:
下载:
