Storage of The Microwave Window of Space Traveling Wave Tubes
-
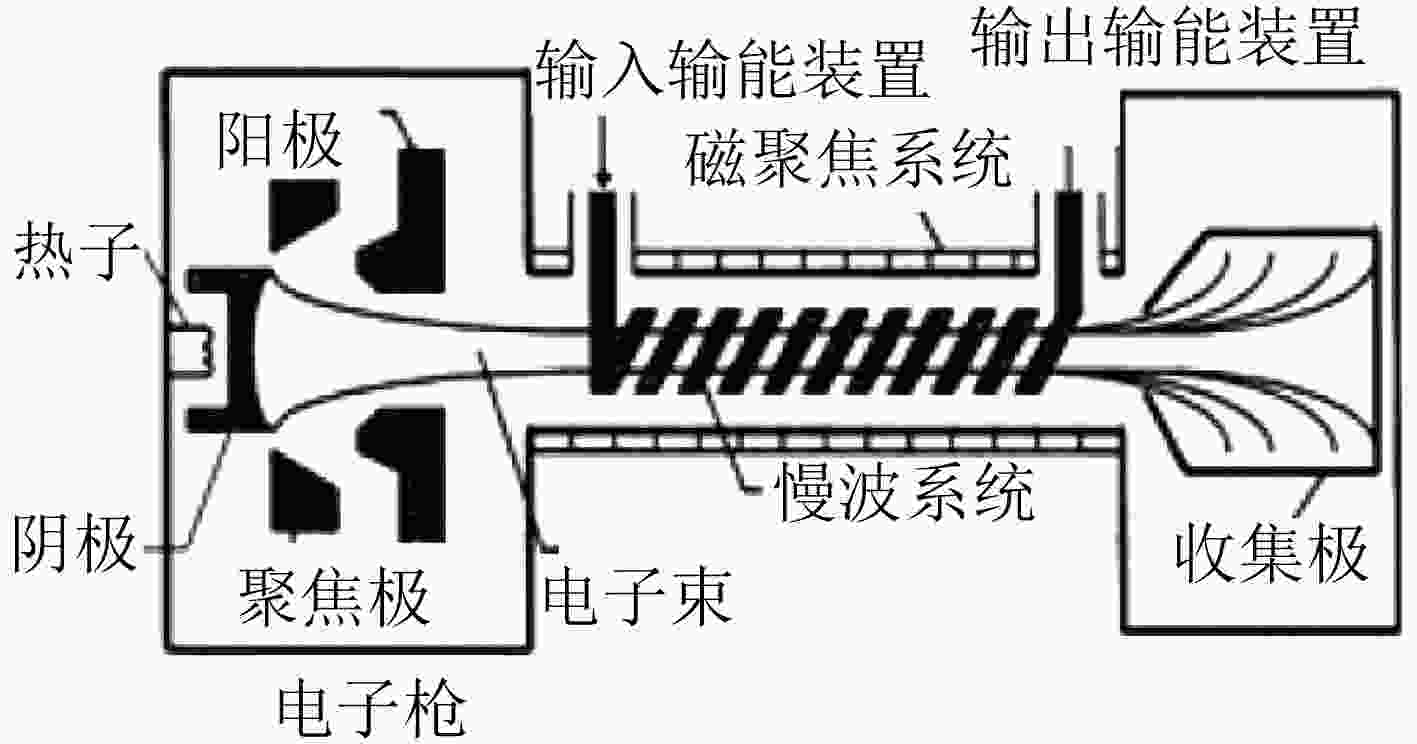
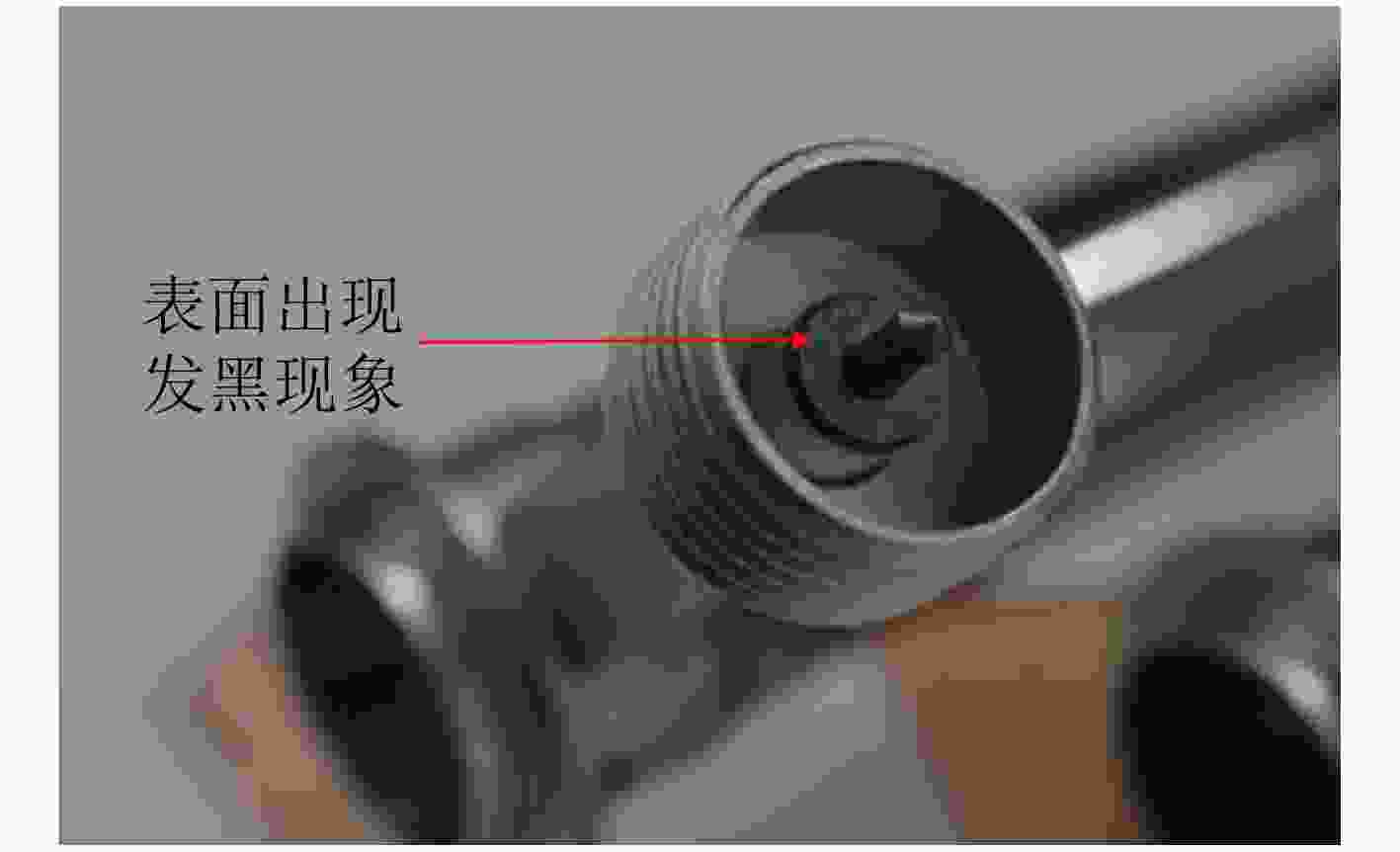
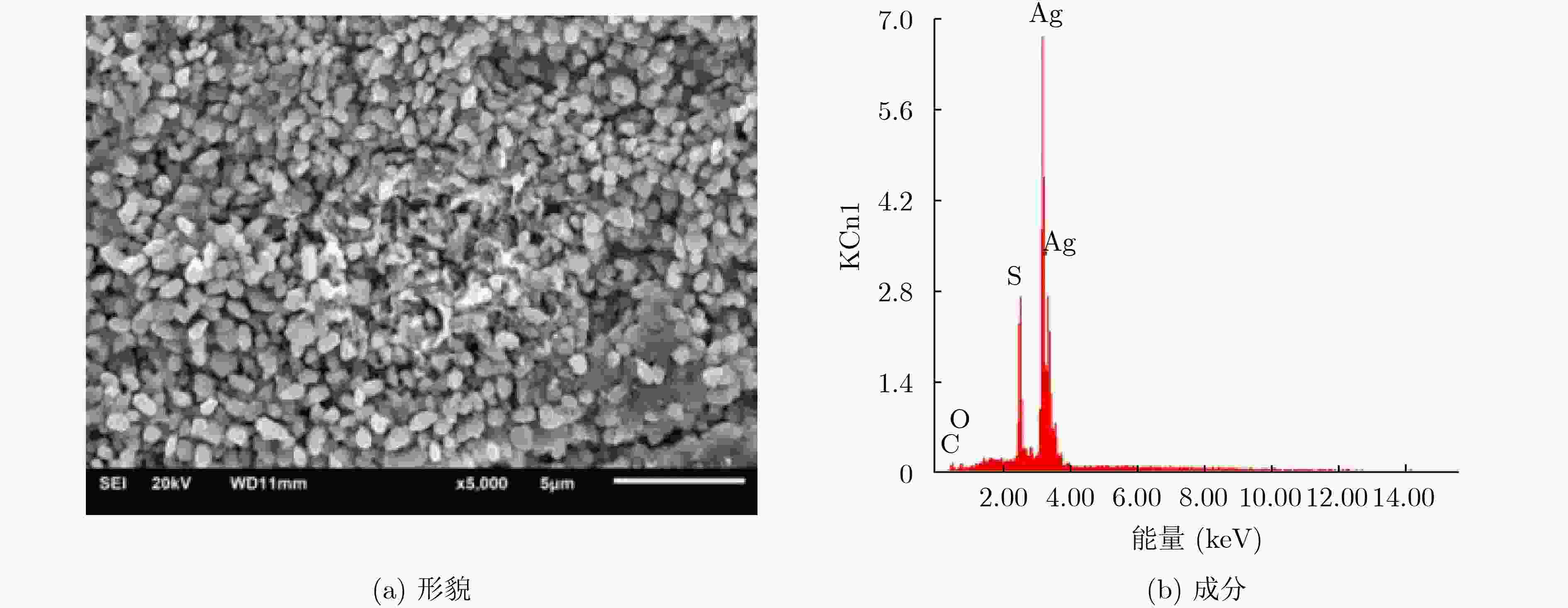
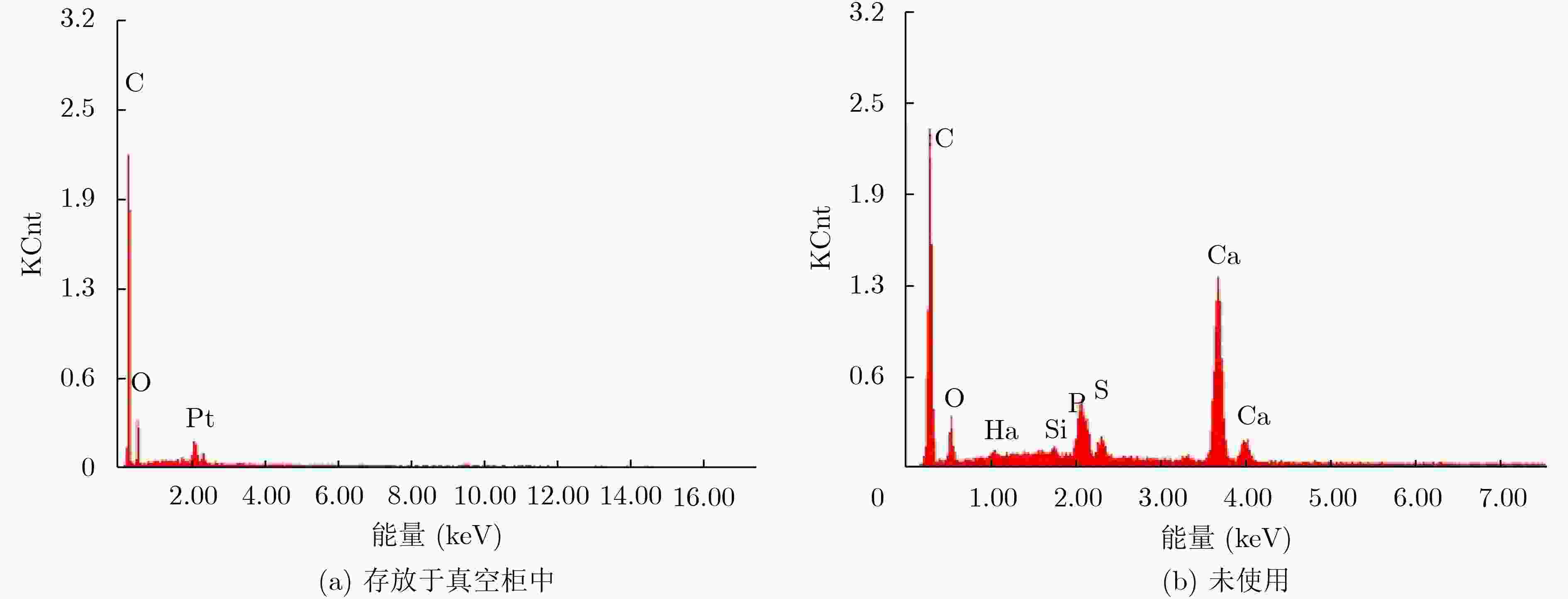
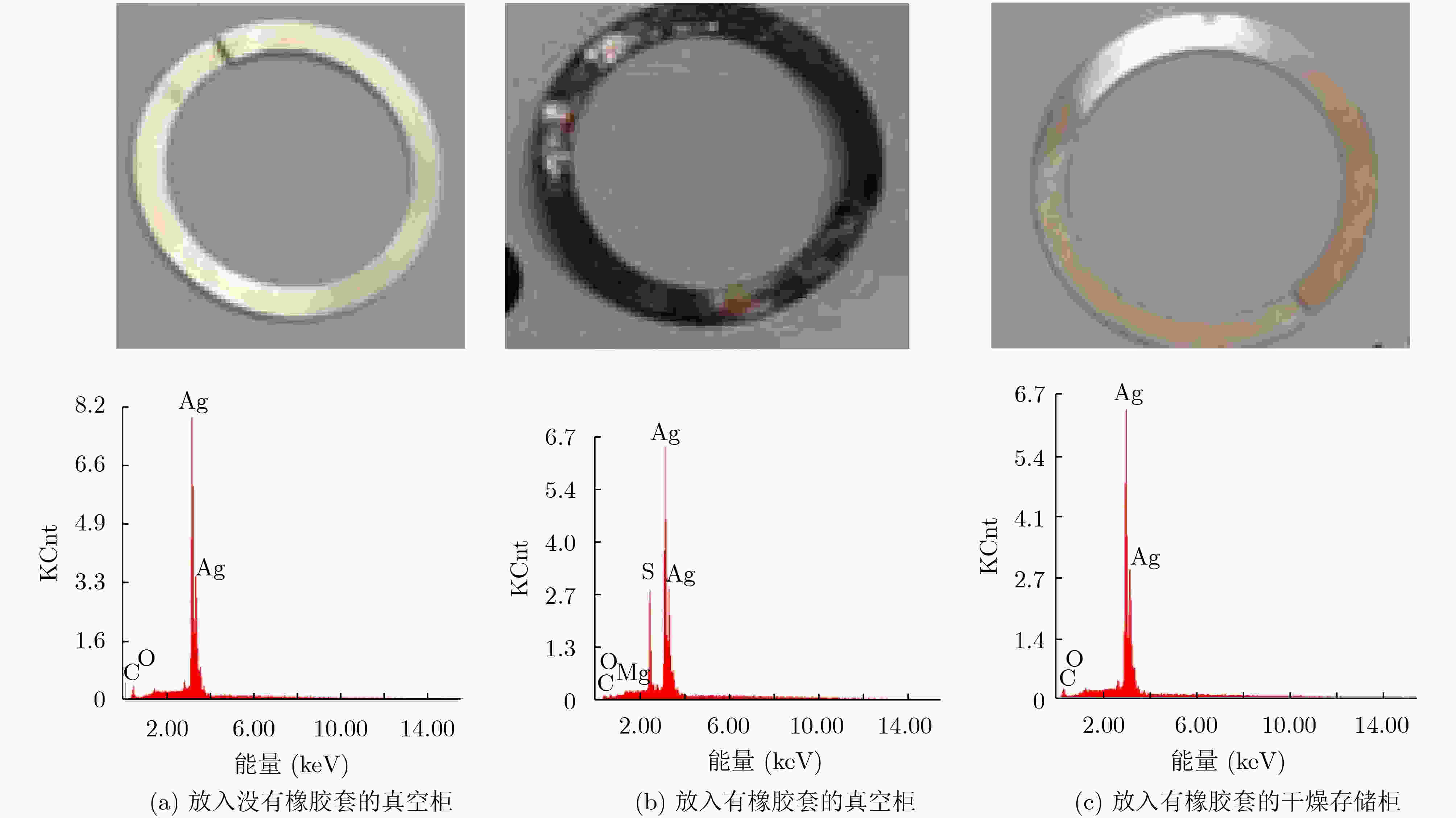
摘要: 高频组件是空间行波管的主要部件,是管内传播高频电磁波的重要传输部件,其中陶瓷封接部位一般采用银焊料进行焊接,它一般存放于真空柜中。存放一段时间后,组件表面出现了发黑现象。分析表明真空柜中放置的橡胶制品导致了高频组件银焊料焊接部位发生硫化,导致贮存失效。结合实验结果和理论分析,在大气状态下,橡胶套中的硫是比较稳定的。然而在真空状态下,硫是比较容易从橡胶套中升华进入真空柜中的,从而会在真空柜中弥漫大量硫蒸气,这些硫蒸气与银焊料发生化学反应形成Ag2S,因此含硫的橡胶套不宜放入真空柜。Abstract: The microwave window is the main component of the space traveling wave tube and an important transmission component for transmitting high-frequency electromagnetic waves in the tube. The microwave window is generally welded with silver solder, and stored in a vacuum cabinet. After storage for some time, the microwave window surface becomes black. The analysis shows that the rubber products placed in the vacuum cabinet cause vulcanization of the silver soldered joints of the high-frequency components, leading to storage failure. Combining experimental results and theoretical analysis, the sulfur in the rubber is relatively stable under atmospheric conditions. However, in a vacuum state, sulfur is relatively easy to sublimate from the rubber into the vacuum cabinet, which will diffuse a large amount of sulfur vapor in the vacuum cabinet. These sulfur vapors react with the silver solder to form Ag2S, so the sulfur-containing rubber should not be placed in a vacuum cabinet.
-
Key words:
- Space traveling wave tubes /
- Microwave window /
- Storage failure
-
表 1 硫的温度与蒸气压的关系
化学元素 熔点 沸点 蒸气压(133 Pa) 10–8 10–7 10–6 10–5 10–4 10–3 10–2 10–1 1 温度(K) S 388 717 263 276 290 310 328 353 382 420 462 -
[1] LIU Yanwen, TIAN Hong, LU Yuxin, et al. Influences of diamond material on heat dissipation capabilities of helical slow wave structures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2019, 66(12): 5321–5326. doi: 10.1109/TED.2019.2945969 [2] 刘燕文, 王小霞, 田宏, 等. 纳米粒子薄膜热电子发射性能[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2015, 45(1): 145–156. doi: 10.1360/N112013-00201LIU Yanwen, WANG Xiaoxia, TIAN Hong, et al. Study on emission properties of the nanopatical films[J]. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2015, 45(1): 145–156. doi: 10.1360/N112013-00201 [3] 康立, 卢晓春, 王雪, 等. GPS L1频点授权信号质量评估[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(4): 905–911. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170440KANG Li, LU Xiaochun, WANG Xue, et al. Authorized signals quality assessment on GPS L1[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(4): 905–911. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170440 [4] LIU Yanwen and TIAN Hong. Temperature variation of a thermionic cathode during electron emission[J]. Science in China Series E: Technological Sciences, 2008, 51(9): 1497–1501. doi: 10.1007/s11431-008-0161-2 [5] 贺成艳, 郭际, 卢晓春, 等. 北斗卫星导航系统B1信号伪距偏差问题研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(11): 2698–2704. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180074HE Chengyan, GUO Ji, LU Xiaochun, et al. Researches on pseudo-range biases of BeiDou navigation satellite system B1 signals[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(11): 2698–2704. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180074 [6] SHIN Y M, BARNETT L R, GAMZINA D, et al. Terahertz vacuum electronic circuits fabricated by UV lithographic molding and deep reactive ion etching[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2009, 95(18): 181505. doi: 10.1063/1.3259823 [7] SIRIGIRI J R, SHAPIRO M A, and TEMKIN R J. High-power 140-GHz quasioptical gyrotron traveling-wave amplifier[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2003, 90(25): 258302. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.90.258302 [8] 刘燕文, 田宏, 韩勇, 等. 支取发射电流过程对热阴极温度影响的研究[J]. 中国科学 E辑: 技术科学, 2008, 38(9): 1515–1520. doi: 10.1360/ze2008-38-9-1515LIU Yanwen, TIAN Hong, HAN Yong, et al. Study on the influence of discharge current on hot cathode temperature[J]. China Science E, 2008, 38(9): 1515–1520. doi: 10.1360/ze2008-38-9-1515 [9] 刘燕文, 田宏, 陆玉新, 等. 用于浸渍阴极的钨海绵基体的净化[J]. 真空科学与技术学报, 2018, 38(2): 144–149. doi: 10.13922/j.cnki.cjovst.2018.02.12LIU Yanwen, TIAN Hong, LU Yuxin, et al. Purificationand cleaning of spongy tungsten disc used as impregnated dispenser-cathode in vacuum[J]. Chinese Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology, 2018, 38(2): 144–149. doi: 10.13922/j.cnki.cjovst.2018.02.12 [10] WANG Xiaoxia, LIAO Xianheng, ZHAO Qinglan, et al. Performance of an oxide cathode prepared from submicrometer carbonates[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2011, 58(9): 3195–3199. doi: 10.1109/TED.2011.2158648 [11] 刘燕文, 田宏, 韩勇, 等. 新型的覆纳米粒子薄膜阴极的研究[J]. 物理学报, 2009, 58(12): 8635–8642. doi: 10.7498/aps.58.8635LIU Yanwen, TIAN Hong, HAN Yong, et al. Emission properties of impregnated cathode with nanoparticle films[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2009, 58(12): 8635–8642. doi: 10.7498/aps.58.8635 [12] LIU Yanwen, TIAN Hong, HAN Yong, et al. Study on the emission properties of the impregnated cathode with nanoparticle films[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2012, 59(12): 3618–3624. doi: 10.1109/TED.2012.2219583 [13] 廖复疆, 吴固基. 真空电子技术-军事电子装备的心脏[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2001: 12.LIAO Fujiang and WU Guji. Vacuum Electronics-the Heart of Military Electronic Equipment[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2001: 12. [14] 李咏今. 丁腈硫化胶烘箱加速老化与室内自然老化相关性的研究[J]. 特种橡胶制品, 2001, 22(4): 51–56, 33. doi: 10.16574/j.cnki.issn1005-4030.2001.04.017LIU Yongjin. Study on the correlation of oven accelerated aging and room temperature auto age for NBR[J]. Special Purpose Rubber Products, 2001, 22(4): 51–56, 33. doi: 10.16574/j.cnki.issn1005-4030.2001.04.017 [15] 刘联保, 莫纯昌. 电子工业生产技术手册(4): 电真空器件卷[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 1990: 317.LIU Lianbao and MO Chunchang. Technical Manual for Electronic Industry(4)[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 1990: 317. [16] 刘燕文, 王小霞, 陆玉新, 等. 用于电真空器件的金属材料蒸发特性[J]. 物理学报, 2016, 65(6): 068502. doi: 10.7498/aps.65.068502LIU Yanwen, WANG Xiaoxia, LU Yuxin, et al. Study on evaporation from alloys used in microwave vacuum electron devices[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2016, 65(6): 068502. doi: 10.7498/aps.65.068502 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
